Samarium(II) Iodide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Samarium(II) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula SmI2. When employed as a solution for organic synthesis, it is known as Henri B. Kagan, Kagan's reagent. SmI2 is a green solid and forms a dark blue solution in Tetrahydrofuran, THF. It is a strong one-electron reducing agent that is used in organic synthesis.
 In the Markó-Lam deoxygenation, an alcohol could be almost instantaneously deoxygenated by reducing their toluate ester in presence of SmI2.
:
In the Markó-Lam deoxygenation, an alcohol could be almost instantaneously deoxygenated by reducing their toluate ester in presence of SmI2.
: SmI2 can also be used in the transannulation of Bicyclic molecule, bicyclic molecules. An example is the SmI2 induced ketone - alkene cyclization of 5-methylenecyclooctanone which proceeds through a ketyl intermediate:
:
SmI2 can also be used in the transannulation of Bicyclic molecule, bicyclic molecules. An example is the SmI2 induced ketone - alkene cyclization of 5-methylenecyclooctanone which proceeds through a ketyl intermediate:
: :
The applications of SmI2 have been reviewed. The book ''Organic Synthesis Using Samarium Diiodide'', published in 2009, gives a detailed overview of reactions mediated by SmI2.
:
The applications of SmI2 have been reviewed. The book ''Organic Synthesis Using Samarium Diiodide'', published in 2009, gives a detailed overview of reactions mediated by SmI2.
Structure
In solid samarium(II) iodide, the metal centers are seven-coordinate with a face-capped Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry. In its ether complex, ether adducts, samarium remains heptacoordinate with five ether and two terminal iodide ligands.Preparation
Samarium iodide is easily prepared in nearly quantitative yields from samarium metal and either diiodomethane or 1,2-Diiodoethane, 1,2-diiodoethane. When prepared in this way, its solutions is most often used without purification of the inorganic reagent. Solid, solvent-free SmI2 forms by high temperature chemical decomposition, decomposition of samarium(III) iodide (SmI3).G. Jantsch, N. Skalla: "Zur Kenntnis der Halogenide der seltenen Erden. IV. – Über Samarium(II)jodid und den thermischen Abbau des Samarium(III)jodids", ''Zeitschrift für Allgemeine und Anorganische Chemie'', 1930, ''193'', 391–405; .''Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie'', System Nr. 39, Band C 6, p. 192–194.Reactions
Samarium(II) iodide is a powerful reducing agent – for example it rapidly reduces water to hydrogen. It is available commercially as a dark blue 0.1 Concentration, M solution in THF. Although used typically in superstoichiometric amounts, catalytic applications have been described.Organic chemistry
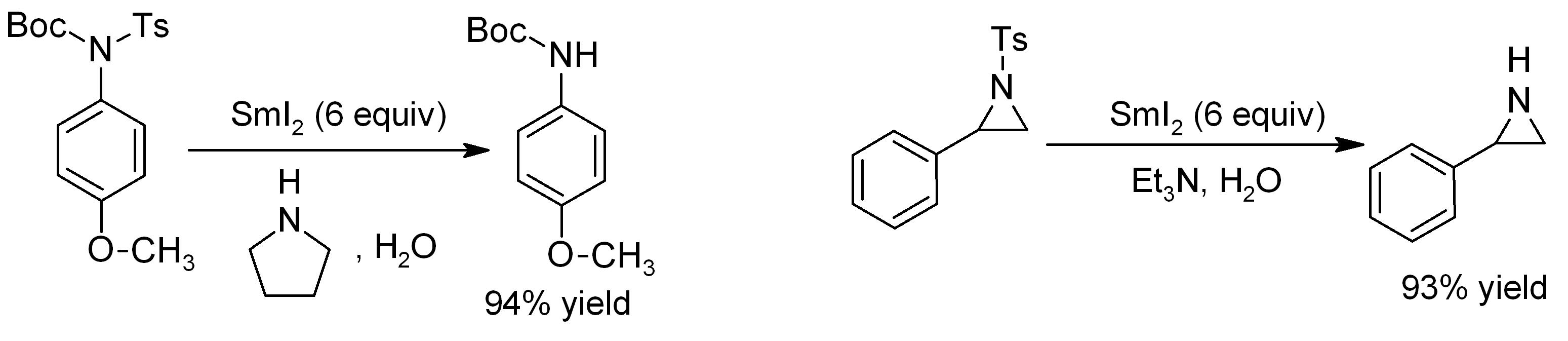
Samarium(II) iodide is a reagent for carbon-carbon bond formation, for example in a Barbier reaction (similar to the Grignard reaction) between a ketone and an alkyl iodide to form a tertiary alcohol: :R1I + R2COR3 → R1R2C(OH)R3 Typical reaction conditions use SmI2 in THF in the presence of catalytic NiI2. Esters react similarly (adding two R groups), but aldehydes give by-products. The reaction is convenient in that it is often very rapid (5 minutes or less in the cold). Although samarium(II) iodide is considered a powerful single-electron reducing agent, it does display remarkable chemoselectivity among functional groups. For example, sulfones and sulfoxides can be reduced to the corresponding sulfide in the presence of a variety of carbonyl-containing functionalities (such as esters, ketones, amides, aldehydes, etc.). This is presumably due to the considerably slower reaction with carbonyls as compared to sulfones and sulfoxides. Furthermore, hydrodehalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbons to the corresponding hydrocarbon compound can be achieved using samarium(II) iodide. Also, it can be monitored by the color change that occurs as the dark blue color of SmI2 in THF discharges to a light yellow once the reaction has occurred. The picture shows the dark colour disappearing immediately upon contact with the Barbier reaction mixture. Work-up is with dilute hydrochloric acid, and the samarium is removed as aqueous Sm3+. Carbonyl compounds can also be coupled with simple alkenes to form five, six or eight membered rings. Tosyl groups can be removed from ''N''-tosylamides almost instantaneously, using SmI2 in conjunction with distilled water and an amine base. The reaction is even effective for deprotection of sensitive substrates such as aziridines: : In the Markó-Lam deoxygenation, an alcohol could be almost instantaneously deoxygenated by reducing their toluate ester in presence of SmI2.
:
In the Markó-Lam deoxygenation, an alcohol could be almost instantaneously deoxygenated by reducing their toluate ester in presence of SmI2.
: :
The applications of SmI2 have been reviewed. The book ''Organic Synthesis Using Samarium Diiodide'', published in 2009, gives a detailed overview of reactions mediated by SmI2.
:
The applications of SmI2 have been reviewed. The book ''Organic Synthesis Using Samarium Diiodide'', published in 2009, gives a detailed overview of reactions mediated by SmI2.
References
{{Lanthanide halides Iodides Samarium(II) compounds Lanthanide halides One-electron reducing agents Reagents for organic chemistry