Samandarine Family on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Samandarin or Samandarine is the main
 Samandarin belongs to a family of toxic compounds called samandarines. Samandarines are biologically active, lipid-soluble steroidal alkaloids. They all contain a similar 7-6-6-5 fused ring system. Nine structures in this family have been characterized.
Samandarines are exclusively produced and secreted by the fire salamander through their
Samandarin belongs to a family of toxic compounds called samandarines. Samandarines are biologically active, lipid-soluble steroidal alkaloids. They all contain a similar 7-6-6-5 fused ring system. Nine structures in this family have been characterized.
Samandarines are exclusively produced and secreted by the fire salamander through their

 The carbon chain on the D ring of cholesterol is degraded by functionalizations with carboxyl groups and sequential decarboxylation reactions. A hydroxyl group is also installed on the adjacent carbon to yield samandarin. These steps are performed by
The carbon chain on the D ring of cholesterol is degraded by functionalizations with carboxyl groups and sequential decarboxylation reactions. A hydroxyl group is also installed on the adjacent carbon to yield samandarin. These steps are performed by

steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
al alkaloid
Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids.
Alkaloids are produced by a large varie ...
secreted by the fire salamander
The fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra'') is a common species of salamander found in Europe.
It is black with yellow spots or stripes to a varying degree; some specimens can be nearly completely black while on others the yellow is dominant ...
(''Salamandra salamandra''). The compound is extremely toxic ( LD50 = 70 μg/kg in mice). Poisoning can cause convulsions
A convulsion is a medical condition where the body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term ''convulsion'' is often used as a synony ...
, respiratory paralysis
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a ris ...
, and eventual death. Samandarin is also believed to be the active ingredient in Salamander brandy
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
, a Slovenian traditional medicinal alcoholic drink
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
with purported hallucinogenic
Hallucinogens, also known as psychedelics, entheogens, or historically as psychotomimetics, are a large and diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, moo ...
and aphrodisiac
An aphrodisiac is a substance that increases libido, sexual desire, sexual attraction, sexual pleasure, or sexual behavior. These substances range from a variety of plants, spices, and foods to synthetic chemicals. Natural aphrodisiacs, such as ...
effects.
Samandarine family

 Samandarin belongs to a family of toxic compounds called samandarines. Samandarines are biologically active, lipid-soluble steroidal alkaloids. They all contain a similar 7-6-6-5 fused ring system. Nine structures in this family have been characterized.
Samandarines are exclusively produced and secreted by the fire salamander through their
Samandarin belongs to a family of toxic compounds called samandarines. Samandarines are biologically active, lipid-soluble steroidal alkaloids. They all contain a similar 7-6-6-5 fused ring system. Nine structures in this family have been characterized.
Samandarines are exclusively produced and secreted by the fire salamander through their parotoid gland
The parotoid gland (alternatively, paratoid gland) is an external skin gland on the back, neck, and shoulder of some frogs (especially toads), and salamanders. It can secrete a number of milky alkaloid substances (depending on the species) known ...
s (20 mg/gland). Samandarin is the main component of these glandular secretions, although the precise ratio of the alkaloids can vary from species to species and individual to individual.
Fire salamanders are indigenous to central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
and reside in deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
forests. Salamander secretions have been shown to be toxic and distasteful to mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s, fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
es, and even other amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s. It has also been suggested that this alkaloid helps to prevent the salamander from contracting bacterial
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
and fungal infections
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is Infection, a disease caused by pathogenic fungi, fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected: superficial, subcutaneous tissue, subcutaneous, and system ...
.
History
Discovery
Early descriptions of salamander poisonings were found in the writings of many physicians and philosophers inClassical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
and the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. Little was known about the toxic compounds, but the recorded symptoms from poisonings were consistent with what is known today. The ancient healers also had some interesting theories about how one contracted poison from the salamander. They believed that the mere sighting of the black and yellow spotted animal or ingestion of salamander ashes would lead to sickness and death.
It was not until 1768 when Laurentius, a physician, discovered that the secretions
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mech ...
from the skin glands of the salamander were the source of the poison. In 1866, Zalesky performed more studies on the toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating ex ...
of samandarines. He was able to isolate the family of alkaloids (believing they were one compound) and tested their toxicity on a variety of animals. He also found that the salamander could be poisoned by its own venom if it entered the salamander's bloodstream.
Samandarin was the first in the family of compounds to be isolated. In 1899, Faust purified samandarin as a crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
by killing the salamanders with chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and po ...
, mincing their corpses, and performing a number of acid-base extractions. In 1926, the pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
of samandarin was further examined by Gessner who administered the poison to animals and dissected their corpses. He determined that the poison primarily affected the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
.
Most studies on samandarin and other samandarine alkaloids were performed in the mid-1900s by German scientists Schöpf and Habermehl. They were able to elucidate the structures of nine samandarines and found that samandarin was the main alkaloid in the salamander's secretions. The structure and stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, studies the spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which are defined ...
of samandarin was confirmed in 1961 using X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
. In 1968, Habermehl and Haaf also investigated biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
of samandarines with ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' and ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, an ...
'' experiments, finding that the compounds originate from a cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
precursor.
Use in Salamander Brandy
It is believed that the samandarine family of compounds is the active ingredient in an indigenousSlovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
n drink called Salamander brandy. Salamander brandy was first brought to attention in 1995 by an article published in the Slovenian magazine ''Mladina
''Mladina'' (English: Youth) is a Slovenian weekly political and current affairs magazine. Since the 1920s, when it was first published, it has become a voice of protest against those in power. Today, ''Mladinas weekly issues are distributed ...
'', describing the hallucinogenic and intensely aphrodisiac effects of the drink.
Ogorevc, the author of the article, writes about his first-hand experience of obtaining and experimenting with Salamander brandy. In the excerpt below, Ogorevc describes his intoxication with Salamander brandy:
Ogorevc also reported on a few methods he observed for making Salamander brandy. One is by adding live black and yellow spotted salamanders to a barrel of fermenting
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduced ...
fruit (one salamander for every ten liters). The mixture is then left for a couple of months while the salamander secretes its toxins (supposedly samandarines) to avoid ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
absorption until its eventual death. Another method he describes is to hang a salamander by its hind legs under a stream of brandy
Brandy is a liquor produced by distilling wine. Brandy generally contains 35–60% alcohol by volume (70–120 US proof) and is typically consumed as an after-dinner digestif. Some brandies are aged in wooden casks. Others are coloured ...
during the distillation
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixt ...
process. The salamander will excrete its poisons to defend itself while the brandy continues to wash away its secretions. A third technique is to kill and dry the salamanders and hang them above the pot of cooking fruit. The steam that rises will extract the poisonous compounds from the salamander and will then be distilled and collected in a vessel.
The publication of Ogorevc's account brought much public attention and curiosity to this enigmatic drink. Yet, the credibility of the existence of Salamander brandy as described by Ogorevc has been brought into question. Anthropologist
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
Miha Kozorog from University of Ljubljana
The University of Ljubljana (, , ), abbreviated UL, is the oldest and largest university in Slovenia. It has approximately 38,000 enrolled students. The university has 23 faculties and three art academies with approximately 4,000 teaching and re ...
decided to investigate Ogorevc's claims in 2003. Although he and his colleagues traveled to the region where Ogorevc supposedly bought Salamander brandy, Kozorog was unable to obtain any samples.
However, from many discussions with the locals in that region, he learned that Salamander brandy was not a psychedelic
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary mental states (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips") and a perceived "expansion of consciousness". Also referred to as classic halluci ...
drink as exclaimed by Ogorevc and the media but was rather a derogatory term for bad or fake brandy. The locals explain that brandy distillers who make Salamander brandy are swindlers. Those who do consume Salamander brandy, only do so accidentally and as a result, will experience paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
in the legs (which is one of the symptoms of samandarin poisoning). Kozorog quotes “there are fair and good brandy distillers who cook pure and good brandy; there are also those who swindle with brandy and whose brandy is a fake one (and sometimes poisoned)…”
Kozorog also learned of a folktale
Oral literature, orature, or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung in contrast to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used va ...
surrounding Salamander brandy. The story tells a tale of a woman who lived on a farm and often cooked a special brandy to which she added a live salamander. Those who drank her brandy were driven mad from the poison. Whenever the devil
A devil is the mythical personification of evil as it is conceived in various cultures and religious traditions. It is seen as the objectification of a hostile and destructive force. Jeffrey Burton Russell states that the different conce ...
came by for a drink, the locals could hear terrible rumbling throughout their village as the devil ran around intoxicated from her concoction.
In his research, Kozorog was unable to find any hard evidence of the hallucinogenic properties Ogorevc described in Salamander brandy. Considering the methods that have been described for preparing Salamander brandy, it is likely that samandarine toxins do play a role in the effects of the drink. However, the brandy is rather stigmatized among locals as adulterated
An adulterant is a substance secretly added to another that may compromise the safety or effectiveness. Typical substances that are adulterated include food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals or fuels.
Definition
Adulteration is the practice of secre ...
brandy. Kozorog claims that the excitement surrounding the psychedelic properties of Salamander brandy was engendered mainly by Ogorevc's humorous writing style and grandiose media coverage.
Biological effects
Samandarin is extremely toxic (LD50 = 70 μg/kg in mice, LD50 = 700-900 μg/kg in dogs) but little is known about its precisemechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical Drug interaction, interaction through which a Medication, drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention o ...
. Samandarin mainly affects the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, specifically neurons in the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
. No treatment or antidote
An antidote is a substance that can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek term φάρμακον ἀντίδοτον ''(pharmakon antidoton)'', "(medicine) given as a remedy". An older term in English which is ...
is known for the poison. Although samandarin is thought to have some local anesthetic effects, there are currently no therapeutic uses for samandarin.
Samandarin poisoning can occur through transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointm ...
exposure or oral ingestion. In the early stages of samandarin poisoning, there is over-excitation of the muscles
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
– restlessness, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, rapid breathing, dilated pupils
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs. It may also b ...
, and increased mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
and saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
. In the later stages, samandarin can cause convulsion
A convulsion is a medical condition where the body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term ''convulsion'' is often used as a synony ...
s, dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
, and paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
. Death eventually occurs by respiratory paralysis after a few hours. Animals poisoned with samandarin show hemorrhaging
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
in the internal organs.
The hallucinogen
Hallucinogens, also known as psychedelics, entheogens, or historically as psychotomimetics, are a large and diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mo ...
ic and aphrodisiac
An aphrodisiac is a substance that increases libido, sexual desire, sexual attraction, sexual pleasure, or sexual behavior. These substances range from a variety of plants, spices, and foods to synthetic chemicals. Natural aphrodisiacs, such as ...
effects of this molecule class have been mentioned in folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
and reported by media but are largely unfounded.
Synthesis

By the salamander
Habermehl and Haaf have investigated thebiosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
of samandarin with ''in vivo'' and ''in vitro'' experiments. Samandarin is synthesized from cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
, or ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
. They found that the enlargement of ring A occurs by nitrogen insertion from a glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
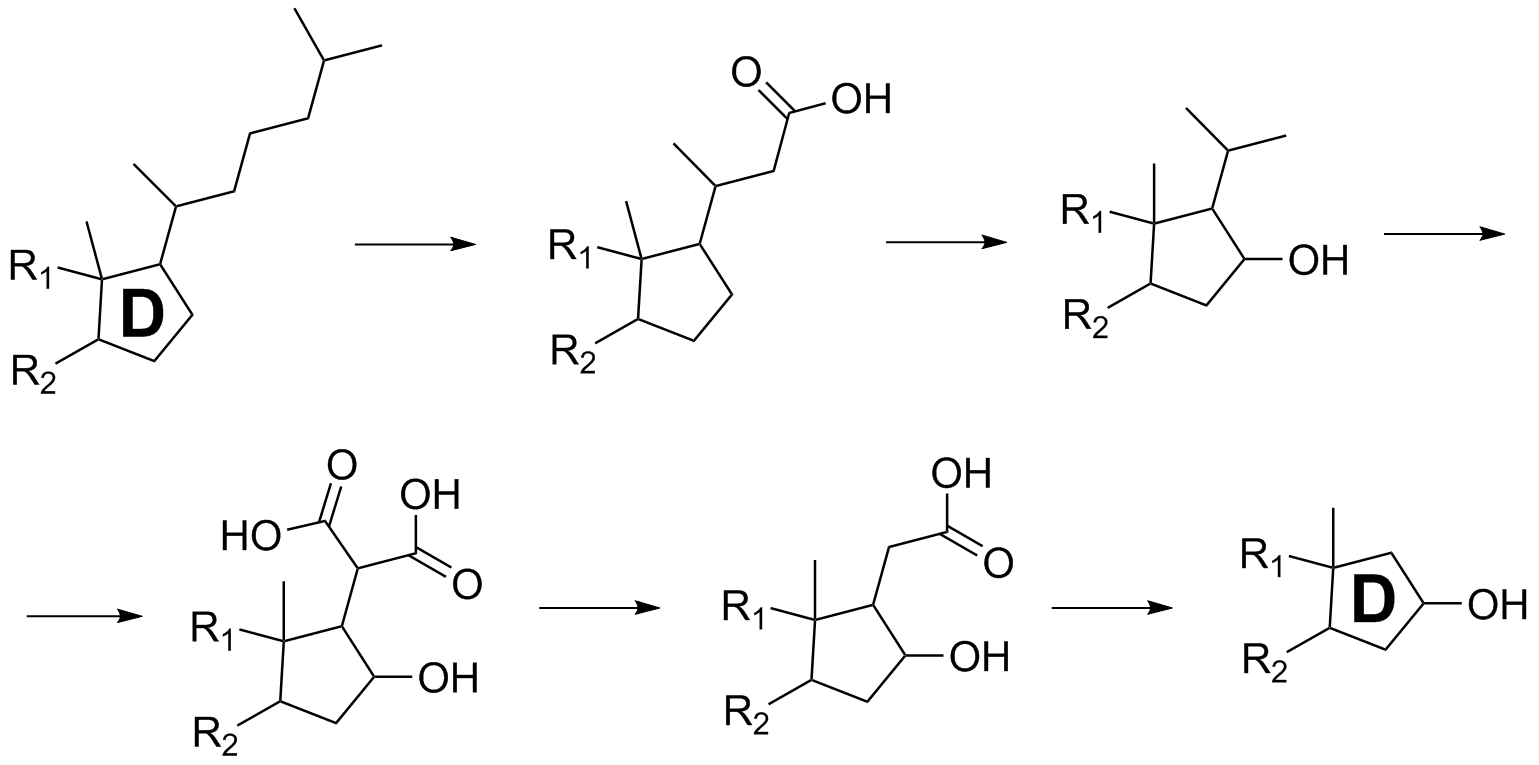
residue. The degradation of the carbon chain and hydroxylation of ring D is shown through the intermediates in the scheme below.
 The carbon chain on the D ring of cholesterol is degraded by functionalizations with carboxyl groups and sequential decarboxylation reactions. A hydroxyl group is also installed on the adjacent carbon to yield samandarin. These steps are performed by
The carbon chain on the D ring of cholesterol is degraded by functionalizations with carboxyl groups and sequential decarboxylation reactions. A hydroxyl group is also installed on the adjacent carbon to yield samandarin. These steps are performed by enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s in the salamander. The details of the biosynthesis have not been elucidated completely.
In the lab
Thechemical synthesis
Chemical synthesis (chemical combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses ...
of samandarin was of interest by a few groups in the 1960s and 1970s but has not been pursued in recent years. The construction of ring A was of greatest synthetic interest. Shimizu in 1976 was able to successfully construct the bridged oxazolidone system with correct stereoselectivity
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non- stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation ...
. The steps proceeded with low to moderate yields.
The last few steps of the synthesis is shown below. Using m-chloroperobenzoic acid, an epoxide is created onto the alkene. The addition of sodium azide
Sodium azide is an inorganic compound with the formula . This colorless salt is the gas-forming component in some car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is highly soluble in water and is acutely poisonou ...
will facilitate the anti-Markovnikov opening of the epoxide. Reduction with sodium borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula (sometimes written as ). It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodi ...
completes the azaheterocycle and bridged oxazolidone through either a cyclic amidine intermediate or imino ester intermediate.

See also
*Samandaridine
Samandaridine is an extremely toxic alkaloid produced by the skin glands of various salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs pro ...
References
{{Toxins Cyclopentanes Neurotoxins Secondary alcohols Steroidal alkaloids Amphibian toxins Salamanders Slovenian distilled drinks