Salsette on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Salsette Island (, , Sashti) is an
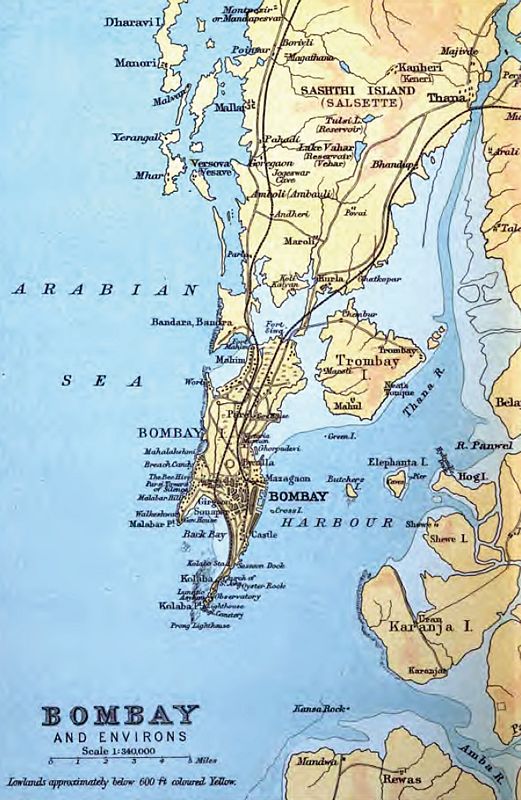
 Salsette is dominated by a central mass of hills surrounded by tidal flats. A number of much smaller islands lay on its western flank. These included
Salsette is dominated by a central mass of hills surrounded by tidal flats. A number of much smaller islands lay on its western flank. These included
island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
in Konkan division
Konkan division is one of the six administrative divisions of Maharashtra state in India. It comprises the central portions of the Konkani region, excluding Goa and Damaon, which were absorbed into Maharashtra owing to the States Reorganisat ...
of the state of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, along India's west coast. Administratively known as the Mumbai Suburban district
Mumbai Suburban district (Marathi language, Marathi: ''Mumbai Upanagar Jilhā'') is the second most populous Districts of Maharashtra, district of Maharashtra in the Konkan Division. With its administrative headquarters in Bandra, the district co ...
, Mira Bhayander and a portion of Thana (Thane) lie on it; making it very populous and one of the most densely populated islands in the world. It has a population of more than 20 million inhabitants living on an area of about .
Location
Salsette is bounded on the north by Vasai Creek, on the northeast by the Ulhas River, on the east byThane Creek
Thane Creek, previously Thana Creek, is an estuary of the Arabian Sea and one of the two main distributaries of the Ulhas River, in Konkan division of Maharashtra, India. The Ulhas splits at the northeast corner of Salsette island into its ...
and Mumbai Harbour
Mumbai Harbour (also English; Bombay Harbour or Front Bay, Marathi ''Mumba'ī bandar''), is a natural deep-water harbour in the southern portion of the Ulhas River estuary. The narrower, northern part of the estuary is called Thana Creek. Th ...
, and on the south and west by the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
. The original seven islands of Mumbai, which were merged by land reclamation
Land reclamation, often known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new Terrestrial ecoregion, land from oceans, list of seas, seas, Stream bed, riverbeds or lake ...
during the 19th and early 20th centuries to form the city of Mumbai, are now practically a southward protruding peninsula of the much larger Salsette Island.
The island of Trombay that was to the southeast of Salsette is today part of Salsette as much of the intervening swamps have been reclaimed. It contains Sanjay Gandhi National Park
Sanjay Gandhi National Park is a national park in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It was established in 1969 with its headquarters situated at Borivali.
The 2400-year-old Kanheri caves, sculpted by monks out of the rocky basaltic cliffs, lie within the ...
, also known as Borivali National Park. The city of Thane
Thane (; previously known as Thana, List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city located on the northwestern side of the list of Indian states, state of Maharashtra in India and on ...
is at the northeastern corner, on Thane Creek
Thane Creek, previously Thana Creek, is an estuary of the Arabian Sea and one of the two main distributaries of the Ulhas River, in Konkan division of Maharashtra, India. The Ulhas splits at the northeast corner of Salsette island into its ...
, while the western suburbs of Mumbai which stretches from Bhayandar in the northwest corner to Bandra
Bandra ( æːɳɖɾa is a coastal suburb located in Mumbai, the largest city of the Konkan division in Maharashtra, India. The area is located to the immediate north of the River Mithi, which separates Bandra from the Mumbai City district. It ...
which lies just before the Mumbai City district lies on its western side while the eastern suburbs of Mumbai that stretches from Thane
Thane (; previously known as Thana, List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city located on the northwestern side of the list of Indian states, state of Maharashtra in India and on ...
to Kurla
Kurla (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, uɾlaː is a suburb of East Mumbai, India. It is the headquarters of the Kurla taluka of Mumbai Suburban district. The neighbourhood is named after the eponymous Bombay East Indians, East Indian vill ...
lies on the eastern half of the island. Both suburbs are separated by the Borivali National Park till the neighbourhood of Powai
Powai (Pronunciation: əʋəiː is a residential suburb located in central Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It is situated on the banks of Powai Lake, and is bound by the hills of Vikhroli Parksite to the south-east, Chandivali to the south-west ...
in Andheri. Politically, the Mumbai City district
Mumbai City district is a Districts of Maharashtra, district of Maharashtra in Konkan Division, India. As a city district, it has no headquarters or subdivisions. It, along with the Mumbai Suburban District, makes up the metropolis of Mumbai. Thi ...
covers the peninsula south of Mahim and Sion while most of the original island constitutes the Mumbai Suburban district
Mumbai Suburban district (Marathi language, Marathi: ''Mumbai Upanagar Jilhā'') is the second most populous Districts of Maharashtra, district of Maharashtra in the Konkan Division. With its administrative headquarters in Bandra, the district co ...
. The northern portion lies within Thane district
Thane district (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, �ʰaːɳe previously named Taana or Thana) is a districts of Maharashtra, district in the Konkan Division of Maharashtra, India. At the 2011 Census it was the most populated district in the c ...
, which extends across Thane creeks onto the mainland.
History
The word ''Sasashti'' (also shortened to ''Sashti'') is Maharashtri Konkani term for "sixty-six", referring to the original "sixty-six villages" on the island. It was inhabited by (Aagri, Kunbi) farmers, agriculturists, (Bhandaris) toddy tappers, (Sutar, Malis) artisans and (Kolis) fisherfolk who trace their conversion to Christianity back to 55 AD with the arrival of Christ's disciple,Bartholomew the Apostle
Bartholomew was one of the twelve apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Most scholars today identify Bartholomew as Nathanael, who appears in the Gospel of John (1:45–51; cf. 21:2).
New Testament references
The name ''Bartholomew ...
, in north Konkan region. They were later converted to the Latin Church in India
The Catholic Church in India is part of the worldwide Catholic Church under the leadership of the Pope. There are over 23 million Catholics in India,religious orders
A religious order is a subgroup within a larger confessional community with a distinctive high-religiosity lifestyle and clear membership. Religious orders often trace their lineage from revered teachers, venerate their founders, and have a d ...
—the Dominicans, Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
s, Augustinians & Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
s— who arrived in the 15th century with the Portuguese. These original inhabitants of Salsette are the Bombay East Indian Catholics
The Bombay East Indians, also called East Indian Catholics or simply East Indians, are an ethno-religious Indian Christian community native to the Seven Islands of Bombay, the Mumbai Metropolitan Area and the northern Konkan region; along the ...
, the Aagris & Kolis
The Koli is an Indian caste that is predominantly found in India, but also in Pakistan and Nepal. Koli is an agriculturist caste of Gujarat but in coastal areas they also work as fishermen along with agriculture.
In the beginning of 20th ce ...
.
109 Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
caves, including those at Kanheri, can be found on the island, and date from the end of the 2nd century. Salsette was ruled by a succession of Hindu kingdoms, the last of which were the Silharas and later the Maratha
The Marathi people (; Marathi: , ''Marāṭhī lōk'') or Marathis (Marathi: मराठी, ''Marāṭhī'') are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are native to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-A ...
s. In 1343, the islands were annexed by the Sultan of Guzerat.
In 1534, the Portuguese empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
seized the islands from Sultan Bahadur Shah. Sashti became part of the northern province of Portuguese India
The State of India, also known as the Portuguese State of India or Portuguese India, was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded seven years after the discovery of the sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the ...
, which was governed from Vasai (Bassein) on the north shore of Bassein Creek. It was leased to the explorer Diogo Rodrigues from 25 October, 1535 to 1548. In 1554, the islands were handed over to Garcia de Orta
Garcia de Orta (or Garcia d'Orta; 1501–1568) was a Portuguese physician, herbalist, and naturalist, who worked primarily in Goa and Bombay in Portuguese India.
A pioneer of tropical medicine, pharmacognosy, and ethnobotany, Garcia used an e ...
, a renowned physician and botanist and the author of ''Colloquies on the Simples Drugs and Medical Matter of India'', a seminal work on Indian Eastern medicine of its time.
Nine churches were built on Salsette island by the Portuguese; Nirmal (1557), Nossa Senhora dos Remédios (1557), Sandor (1566), Agashi (1568), Nandakal (1573), Papdy (1574), Pale (1595), Manickpur (1606), and Nossa Senhora das Mercês (1606). The St Andrews Church and the Mount St Mary's Church in Bandra, the Cross at Cross Maidan, Gloria Church
Gloria Church or Our Lady of Glory Church ( Portuguese: ''Nossa Senhora de Gloria'') was built in 1911-13 on one of the oldest Roman Catholic church sites in Mumbai; its predecessor was built by the Portuguese Franciscans in 1632. The church is ...
(1632) in Mazagaon and the remnants of a church in Santa Cruz are the sole places of worship that have survived to the 21st century.
In 1661, the seven Bombay (Mumbai) islets were ceded to Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
as part of the dowry
A dowry is a payment such as land, property, money, livestock, or a commercial asset that is paid by the bride's (woman's) family to the groom (man) or his family at the time of marriage.
Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price ...
of Catherine de Braganza to Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651 and King of England, Scotland, and King of Ireland, Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest su ...
; while Salsette remained in Portuguese hands. Charles II in turn, leased the Bombay islets to the English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast A ...
in 1668 for £10 per year. The company found the deep harbour at Mumbai (Bombay)
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12.5 ...
eminently apposite, and the population rose from 10,000 in 1661 to 60,000 by 1675. In 1687, the East India Company transferred their headquarters there from Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
. In 1737, the island was captured by Mahratta violence, all of the Portuguese northern province in India, except Damaon, Diu & Silvassa, as it was frequently invaded by the Mahratta forces until 1739. Marquis de Pombal formally ceded what would become Greater Bombay, to Peshwa
The Peshwa was the second highest office in the Maratha Empire, next in rank and prestige only to that of the Chhatrapati. Initially serving as the appointed prime minister in the Maratha Kingdom, the office became hereditary when Shahu gave t ...
Balaji Bajirao of the Mahratta Confederacy in the 1750s.
The British occupied Salsette in 1774, and it was formally ceded to the East India Company in the 1782 Treaty of Salbai. In 1782, William Hornby, then Governor of Bombay Province, initiated the project of connecting the islets of Bombay. By 1845, the seven southern islands had been connected to form South Bombay, with an area of 435 km². Railway viaducts and causeways were built in the 19th century to connect Bombay Island to the mainland via Salsette. The channels separating Mumbai from Salsette and Trombay were bridged by the Sion Causeway in 1803. Accessibility considerably increased after construction of this causeway. Mahim and Bandra were connected by the Mahim Causeway
The Mahim Causeway is a vital link road connecting Mumbai City district/South Mumbai (Churchgate to Mahim) with its Northern and Western Mumbai Suburban district, Suburbs (Bandra to Dahisar). The causeway links the neighbourhoods of Mahim to the ...
in 1845.
These railway lines and roads encouraged wealthier merchants to build villas on Salsette. By 1901, the population of Salsette had increased to 146,993 and the area began to be referred to as Greater Bombay.
Geography

 Salsette is dominated by a central mass of hills surrounded by tidal flats. A number of much smaller islands lay on its western flank. These included
Salsette is dominated by a central mass of hills surrounded by tidal flats. A number of much smaller islands lay on its western flank. These included Bandra
Bandra ( æːɳɖɾa is a coastal suburb located in Mumbai, the largest city of the Konkan division in Maharashtra, India. The area is located to the immediate north of the River Mithi, which separates Bandra from the Mumbai City district. It ...
, Khar Danda, Juhu
Juhu (Pronunciation: ͡ʒuɦuː is a suburb of Mumbai. It is known for the sprawling Juhu Beach. It is surrounded by the Arabian Sea to the west, Versova to the north, Vile Parle to the east and Santacruz to the south. Juhu is among the most ...
(an old linear sand bar rising above sea level by just a metre or two), Versova, Marve Island, Dharavi Island and Rai Murdhe, all with a knoll
In geography, knoll is another term for a knowe or hillock, a small, low, round natural hill or mound.
Knoll may also refer to:
Places
* Knoll Camp, site of an Iron Age hill fort Hampshire, England, United Kingdom
* Knoll Lake, Leonard Canyon, ...
core and fringing wave-cut platforms and sandy beaches. These islands seem to have remained separate until as late as 1808.
At the time of writing of the old Gazetteer of Thana in 1882, these islands could be reached during low tides by walking across the tidal inlets in between, except for the island of Dharavi in present-day Gorai (not to be confused with the slum near Mahim), which had to be reached by a boat. These are no longer separate, being joined to Salsette via reclamation. The highest point is the conical peak of Kanheri (467 metres) in Borivali National Park on the northern reaches of the island. This national park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
is the world's biggest within city limits.
Geology
The island is at the confluence of a number of fault lines. This makes the areaearthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
-prone, up to a magnitude of 6. The island is mostly composed of black basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
rock. Since it is along the sea coast, it has a sandy belt on its western coast. The southern region of Old Mumbai is mostly at sea level. However, the parts which were erstwhile shallows are below sea level. Many parts of the city are hilly.
Other natural formations
Lakes
There are three major lakes on the island:Powai Lake
Powai Lake (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, əʋəiː is an artificial lake, situated in Mumbai, in the Powai valley, where a Powai village with a cluster of huts existed. The city suburb called Powai shares its name with the lake.
Indian ...
, Tulsi Lake
Tulsi Lake is a fresh water lake in northern Mumbai. It is stated to be the second largest lake in Mumbai and supplies part of the city's potable water. This is one of the three lakes located in the Salsette Island; the other two being Powai ...
and Vihar Lake
Vihar Lake (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, �iɦaːɾ is located near Vihar village on the Mithi River within the precincts of the Borivali National Park, also called the Sanjay Gandhi National Park, in North Mumbai. When built in 1860 (co ...
. The latter two supply part of Mumbai's water requirements. Numerous other smaller ponds and lakes are present.
Rivers
The Mithi River (Mahim), Poisar River, Oshiwara River and Dahisar River originate in the national park and empty into the Arabian Sea. The Mithi River originates at Vihar Lake. Vasai and Thane creeks areestuarine
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
distributaries
A distributary, or a distributary channel is a stream channel that branches off and flows a main stream channel. It is the opposite of a ''tributary'', a stream that flows another stream or river. Distributaries are a result of river bifurca ...
of the Ulhas River.
Creeks
A number of saline orbrackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
creeks extend inland from the coastline. Mahim Creek separates the city from the suburbs in the west. Further north on the western coast, the Oshiwara river empties into Malad (or Marvé) Creek and the Dahisar River into Gorai Creek. The eastern waterfront also has many small creeks.
Wetlands
The small southern part of the eastern waterfront of Salsette forms Mumbai Harbour. North of this region lie vast amounts of protectedwetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s at Sewree, home to migratory birds. The northern and northwestern part of the island and parts of Mahim River have government-protected marshlands. These swampy regions form massive, dense mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
forests.
See also
*Navi Mumbai
Navi Mumbai (; also known as New Bombay, its official name until 1995) is a large city next to Mumbai, located in the Konkan division of the western Indian state of Maharashtra, on the mainland of India. Navi Mumbai is situated in Thane distr ...
(New Mumbai)
References
{{Authority control Geography of Mumbai Former Portuguese colonies Islands of Mumbai Geography of Thane district Islands of India Populated places in India