SWOT Analysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Although the SWOT analysis was originally designed for business and industries, it has been used in non-governmental organisations as a tool for identifying external and internal support to combat internal and external opposition for successful implementation of
Although the SWOT analysis was originally designed for business and industries, it has been used in non-governmental organisations as a tool for identifying external and internal support to combat internal and external opposition for successful implementation of
strategic planning
Strategic planning is the activity undertaken by an organization through which it seeks to define its future direction and makes decisions such as resource allocation aimed at achieving its intended goals. "Strategy" has many definitions, but it ...
and strategic management
In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of Resource management, resources ...
, SWOT analysis (also known as the SWOT matrix, TOWS, WOTS, , and situational analysis) is a decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
technique that identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of an organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
or project.
SWOT analysis evaluates the strategic position of organizations and is often used in the preliminary stages of decision-making processes to identify internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieving goals. Users of a SWOT analysis ask questions to generate answers for each category and identify competitive advantage
In business, a competitive advantage is an attribute that allows an organization to outperform its competitors.
A competitive advantage may include access to natural resources, such as high-grade ores or a low-cost power source, highly skille ...
s.
SWOT has been described as a "tried-and-true" tool of strategic analysis, but has also been criticized for limitations such as the static nature of the analysis, the influence of personal biases in identifying key factors, and the overemphasis on external factors, leading to reactive strategies. Consequently, alternative approaches to SWOT have been developed over the years.
Overview
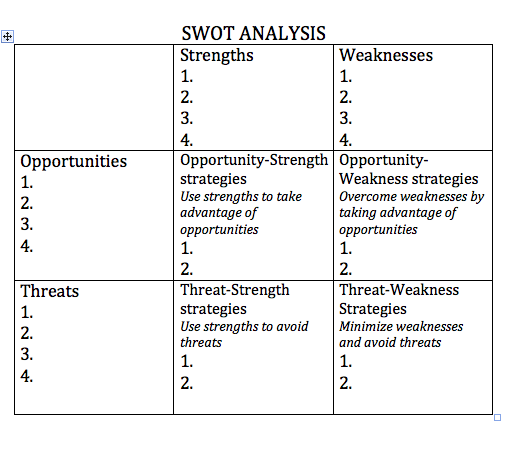
The name is an acronym for four components: * : characteristics of the business or project that give it an advantage over others * : characteristics that place the business or project at a disadvantage relative to others * : elements in the environment that the business or project could exploit to its advantage * : elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business or project Results of the assessment are often presented in the form of amatrix
Matrix (: matrices or matrixes) or MATRIX may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Matrix (mathematics), a rectangular array of numbers, symbols or expressions
* Matrix (logic), part of a formula in prenex normal form
* Matrix (biology), the m ...
.
Internal and external factors
Strengths and weaknesses are usually considered internal, while opportunities and threats are usually considered external. See also . The degree to which an organization's internal strengths matches with its external opportunities is known as its strategic fit. Internal factors may include: * Human resources—staff, volunteers, board members, stakeholders * Physical resources—location, building, equipment, plant * Financial—revenue, grants, investments, other sources of income * Activities and processes—projects, programs, systems * Past experiences—reputation, knowledge External factors may include: * Future trends in the organization's field or society at large (e.g.macroeconomic
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output/ GDP ...
s, technological change
Technological change (TC) or technological development is the overall process of invention, innovation and diffusion of innovations, diffusion of technology or business process, processes.From ''The New Palgrave Dictionary otechnical change by S. ...
)
* The economy—local, national, or international
* Funding sources—investors, foundations, donors, legislatures
* Demographics—changes in the age, race, gender, culture of those in the organization serviceable area
* Physical environment—growth of location in which organisation is situated, access to location
* Legislation
Legislation is the process or result of enrolling, enacting, or promulgating laws by a legislature, parliament, or analogous governing body. Before an item of legislation becomes law it may be known as a bill, and may be broadly referred ...
* Local, national, or international events
A number of authors advocate assessing external factors before internal factors.
Use
SWOT analysis has been used at different levels of analysis, includingbusiness
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
es, non-profit organizations
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or so ...
, governmental units, and individuals. It is often used alongside other frameworks, such as PEST, as a basis for the analysis of internal and environmental factors. SWOT analysis may also be used in pre-crisis planning, preventive crisis management
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and envi ...
, and viability study recommendation construction.
Strategic planning
SWOT analysis can be used to build organizational or personal strategy. Steps necessary to execute strategy-oriented analysis involve identifying internal and external factors, selecting and evaluating the most important factors, and identifying relationships between internal and external features. For instance, strong relations between strengths and opportunities can suggest good conditions in the company and allow using an strategy. On the other hand, strong interactions between weaknesses and threats could be analyzed as a warning to use a strategy. One form of SWOT analysis combines each of the four components with another to examine four distinct strategies: * WT strategy (mini–mini): Faced with external threats and internal weaknesses, how to minimize both weaknesses and threats? * WO strategy (mini–maxi): Faced with external opportunities and internal weaknesses, how to minimize weaknesses and maximize opportunities? * ST strategy (maxi–mini): Faced with internal strengths and external threats, how to maximize strengths and minimize threats? * SO strategy (maxi–maxi): Faced with external opportunities and internal strengths, how to maximize both opportunities and strengths?Matching and converting
A SWOT analysis can be used to generate matching and converting strategies. Matching refers to seekingcompetitive advantage
In business, a competitive advantage is an attribute that allows an organization to outperform its competitors.
A competitive advantage may include access to natural resources, such as high-grade ores or a low-cost power source, highly skille ...
by matching strengths to opportunities. This strategy ensures that an organization leverages its core competencies, resources, and capabilities to capitalize on favorable market conditions, emerging trends, or unmet customer needs. Conversion refers to converting weaknesses or threats into strengths or opportunities. An example of a conversion strategy is to buy off a threat through collaboration or merger.
Marketing
Incompetitor analysis
Competitive analysis in marketing and strategic management is an assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of current and potential competitors. This analysis provides both an offensive and defensive strategic context to identify opportunities a ...
, marketers can use SWOT analysis to detail and profile the competitive strengths and weaknesses of each competitor in the market. This process may involve analysing competitors' cost structures, sources of profits, resources and competencies, competitive positioning, product differentiation, degree of vertical integration
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration, also referred to as vertical consolidation, is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each ...
, historical responses to industry developments, among other factors. Relevant marketing research
Marketing research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of qualitative data, qualitative and quantitative data, quantitative data about issues relating to marketing products and services. The goal is to identify and assess how chan ...
methods may include:
* Qualitative marketing research such as focus groups
* Quantitative marketing research such as statistical surveys
* Experimental techniques such as test markets
* Observational techniques such as ethnographic (on-site) observation
Marketing managers may also design and oversee various environmental scanning and competitive intelligence
Competitive intelligence (CI) is the process and forward-looking practices used in producing knowledge about the competitive environment to improve organizational performance. Competitive intelligence involves systematically collecting and anal ...
processes to help identify trends and inform the company's marketing analysis.
In community organizations

 Although the SWOT analysis was originally designed for business and industries, it has been used in non-governmental organisations as a tool for identifying external and internal support to combat internal and external opposition for successful implementation of
Although the SWOT analysis was originally designed for business and industries, it has been used in non-governmental organisations as a tool for identifying external and internal support to combat internal and external opposition for successful implementation of social services
Social services are a range of public services intended to provide support and assistance towards particular groups, which commonly include the disadvantaged. Also available amachine-converted HTML They may be provided by individuals, private and i ...
and social change
Social change is the alteration of the social order of a society which may include changes in social institutions, social behaviours or social relations. Sustained at a larger scale, it may lead to social transformation or societal transformat ...
efforts. Understanding particular communities can come from public forums, listening campaigns, and informational interviews and other data collection. SWOT analysis provides direction to the next stages of the change process. It has been used by community organizers and community members to further social justice in the context of social work practice, and can be applied directly to communities served by a specific nonprofit or community organization.
Limitations and alternatives
SWOT analysis is intended as a starting point for discussion and not to, in itself, show managers how to achieve a competitive advantage. In a highly-cited 1997 critique, "SWOT Analysis: It's Time for a Product Recall", Terry Hill and Roy Westbrook observed that one among many problems of SWOT analysis as often practiced is that "no-one subsequently used the outputs f SWOT analysiswithin the later stages of the strategy". Hill and Westbrook, among others, also criticized hastily designed SWOT lists. Other limitations of SWOT practice include: preoccupation with a single strength, such as cost control, leading to a neglect of weaknesses, such as product quality; and domination by one or two team members doing the SWOT analysis and devaluing possibly important contributions of other team members. Many other limitations have been identified. Business professors have suggested various ways to remedy the common problems and limitations of SWOT analysis while retaining the SWOT framework.Some examples of publications that suggest remedies for common problems and limitations of SWOT analysis: * * * * * *Porter's five forces
Michael Porter
Michael Eugene Porter (born May 23, 1947) is an American businessman and professor at Harvard Business School. He was one of the founders of the consulting firm The Monitor Group (now part of Deloitte) and FSG, a social impact consultancy. ...
developed the five forces framework as an alternative to SWOT analyses, which he found lacking in rigor and over-dependent on individual company circumstances.
SOAR
SOAR (strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results) is an alternative technique inspired by appreciative inquiry. SOAR has been criticized as having similar limitations as SWOT, such as "the inability to identify the necessary data".SVOR
In project management, the alternative to SWOT known by the acronym SVOR (Strengths, Vulnerabilities, Opportunities, and Risks) compares the project elements along two axes: internal and external, and positive and negative. It takes into account the mathematical link that exists between these various elements, considering also the role of infrastructures. The SVOR table provides an intricate understanding of the elements hypothesized to be at play in a given project: Constraints consist of: calendar of tasks and activities, costs, and norms of quality. The "''k''" constant varies with each project (for example, it may be valued at 1.3).History
In 1965, three colleagues at the Long Range Planning Service (LRPS) ofStanford Research Institute
SRI International (SRI) is a nonprofit organization, nonprofit scientific research, scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California, United States. It was established in 1946 by trustees of Stanford Univer ...
—Robert F. Stewart, Otis J. Benepe, and Arnold Mitchell—wrote a technical report titled ''Formal Planning: The Staff Planner's Role at Start-Up''. The report described how a person in the role of a company's staff planner would gather information from managers assessing operational issues grouped into four components represented by the acronym SOFT: the "satisfactory" in present operations, "opportunities" in future operations, "faults" in present operations, and "threats" to future operations. Stewart et al. focused on internal operational assessment and divided the four components into (satisfactory and fault) and (opportunity and threat), and not, as would later become common in SWOT analysis, into (strengths and weaknesses) and (opportunities and threats).
Also in 1965, four colleagues at the Harvard Graduate School of Business Administration
Harvard Business School (HBS) is the graduate school, graduate business school of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university. Located in Allston, Massachusetts, HBS owns Harvard Business Publishing, which p ...
(later the Harvard Business School)—Edmund P. Learned, C. Roland Christensen, Kenneth R. Andrews, and William D. Guth—published the first of many editions of the textbook ''Business Policy: Text and Cases''. (See also .) Many publications cite this textbook as an early statement of the ideas behind SWOT, although it contains neither a 2 × 2 matrix nor any detailed procedure for doing a SWOT assessment; for example, Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton called this textbook "one of the early SWOT references", in: ( was a term then current for what has come to be called strategic management.) The first chapter of the textbook stated, without using the acronym, the four components of SWOT and their division into internal and external appraisal:
Looking back from three decades later, in the book ''Strategy Safari'' (1998), management scholar Henry Mintzberg
Henry Mintzberg is a Canadian academic and author on business and management. He is currently the Cleghorn Professor of Management Studies at the Desautels Faculty of Management of McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, where he has been ...
and colleagues said that ''Business Policy: Text and Cases'' "quickly became the most popular classroom book in the field", widely diffusing its authors' ideas, which Mintzberg et al. called the "design school" model (in contrast to nine other schools that they identified) of strategic management, "with its famous notion of SWOT" emphasizing assessment of a company's internal and external situations.An analysis of the "design school" model was also in Mintzberg's earlier publications such as: However, the textbook contains neither a 2 × 2 SWOT matrix nor any detailed procedure for doing a SWOT assessment. ''Strategy Safari'' and other books identified Kenneth R. Andrews as the co-author of ''Business Policy: Text and Cases'' who was responsible for writing the theoretical part of the book containing the SWOT components. More generally, Mintzberg et al. attributed some conceptual influences on what they called the "design school" (of which they were strongly critical) to earlier books by Philip Selznick (''Leadership in Administration'', 1957) and Alfred D. Chandler Jr. (''Strategy and Structure'', 1962), with other possible influences going back to the McKinsey consulting firm in the 1930s.
However, a 2023 history of SWOT by Richard W. Puyt and colleagues criticized Mintzberg's "vilification of SWOT" and Mintzberg's apparently poor knowledge of the LRPS at Stanford. Puyt et al. considered the LRPS to be the originator of SWOT (via SOFT) and said that the claim of Mintzberg and others that SWOT was invented at, or disseminated by, Harvard Business School is an "academic urban legend".
By the end of the 1960s, the four components of SWOT (without using the acronym) had appeared in other publications on strategic planning by various authors, and by 1972 the acronym had appeared in the title of a journal article by Norman Stait, a management consultant
Management consulting is the practice of providing consulting services to organizations to improve their performance or in any way to assist in achieving organizational objectives. Organizations may draw upon the services of management consultant ...
at the British firm Urwick, Orr and Partners. By 1973, the acronym was well-known enough that accountant William W. Fea, in a published lecture, mentioned "the mnemonic, familiar to students, of S.W.O.T., namely strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats". Early examples of a 2 × 2 SWOT matrix are found in John Argenti's book ''Systematic Corporate Planning'' (1974) and in a 1980 article by management professor Igor Ansoff (but Ansoff used the acronym T/O/S/W instead of SWOT). In the 1960s Ansoff had worked with the LRPS, where the SOFT approach originated.
In popular culture
* Television: In the 2015 ''Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that is a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical area of the Santa Clara Valley ...
'' episode "Homicide" (Season 2, Episode 6), Jared Dunn ( Zach Woods) introduces the Pied Piper team to SWOT analysis. Later in that episode Dinesh ( Kumail Nanjiani) and Gilfoyle ( Martin Starr) employ the method when deciding whether or not to inform a stunt driver that the calculations for his upcoming jump were performed incorrectly.
See also
*Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other companies. Dimensions typically measured are Project management triangle, quality, time and cost.
Benchmarking is ...
* Enterprise planning systems
* Problem structuring methods
Problem structuring methods (PSMs) are a group of techniques used to model or to map the nature or structure of a situation or state of affairs that some people want to change. PSMs are usually used by a group of people in collaboration (rather ...
* Program evaluation and review technique (PERT)
* Semiotic square (Greimas square)
* Situation analysis
* Six forces model
* SWOQe
* VRIO (Value, Rarity, Imitability, Organization)
References
Further reading
SWOT analysis is described in very many publications. A few examples of books that describe SWOT analysis and are widely held byWorldCat
WorldCat is a union catalog that itemizes the collections of tens of thousands of institutions (mostly libraries), in many countries, that are current or past members of the OCLC global cooperative. It is operated by OCLC, Inc. Many of the O ...
member libraries and available in the Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including web ...
are:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
* {{authority control Business intelligence terms Strategic management Management theory