ST Depression on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
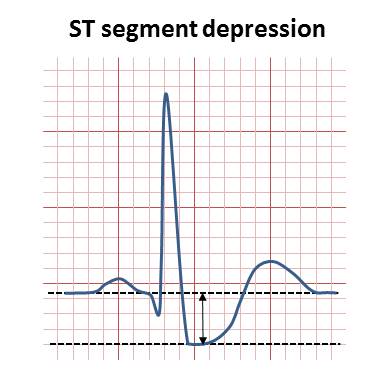 ST depression refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram, wherein the trace in the
ST depression refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram, wherein the trace in the
Frank G. Yanowitz, MD. University of Utah School of Medicine * Physiologic J-junctional depression with sinus tachycardia * Hyperventilation Other, non-ischemic, causes include:
* Side effect of
Other, non-ischemic, causes include:
* Side effect of
Retrieved September 2010-3 millimeters from the
 ST depression refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram, wherein the trace in the
ST depression refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram, wherein the trace in the ST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.005 to 0.150 sec (5 to 150 ms).
It starts at the J point (junction between the QRS complex and ST segment) and ends at the beginning of the T ...
is abnormally low below the baseline.
Causes
It is often a sign of myocardialischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
, of which coronary insufficiency is a major cause. Other ischemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the ...
s causing ST depression include:
* Subendocardial ischemia or even infarction. Subendocardial means non full thickness ischemia. In contrast, ST elevation is transmural (or full thickness) ischemia
* Non Q-wave myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
* Reciprocal changes in acute Q-wave myocardial infarction (e.g., ST depression in leads I & aVL with acute inferior myocardial infarction)
* ST segment depression and T-wave changes may be seen in patients with unstable angina
Depressed but ''upsloping'' ST segment generally rules out ischemia as a cause.
Also, it can be a normal variant or artifacts, such as:
* Pseudo-ST-depression, which is a wandering baseline due to poor skin contact of the electrodeX. ST Segment AbnormalitiesFrank G. Yanowitz, MD. University of Utah School of Medicine * Physiologic J-junctional depression with sinus tachycardia * Hyperventilation
 Other, non-ischemic, causes include:
* Side effect of
Other, non-ischemic, causes include:
* Side effect of digoxin
Digoxin (better known as digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart disease, heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. ...
* Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an a ...
* Right or left ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both vent ...
* Intraventricular conduction abnormalities (e.g., right
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
or left
Left may refer to:
Music
* ''Left'' (Hope of the States album), 2006
* ''Left'' (Monkey House album), 2016
* ''Left'' (Helmet album), 2023
* "Left", a song by Nickelback from the album ''Curb'', 1996
Direction
* Left (direction), the relativ ...
bundle branch block
A bundle branch block is a partial or complete interruption in the flow of electrical impulses in either of the bundle branches of the heart's electrical system.
Anatomy and physiology
The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatri ...
, WPW, etc.)
* Hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
* Tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
* Reciprocal ST elevation
* Mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the atria of the heart, left atrium during Systole (medicine), systole. It is the primary form of myxom ...
* Central nervous system disease
Central nervous system diseases or central nervous system disorders are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). These disorders ...
, such as stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
Mnemonic
Amnemonic
A mnemonic device ( ), memory trick or memory device is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval in the human memory, often by associating the information with something that is easier to remember.
It makes use of e ...
can be used for some causes of ST depression, namely ''DEPRESSED ST'':
D - Drooping valve (mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the atria of the heart, left atrium during Systole (medicine), systole. It is the primary form of myxom ...
) E - Enlargement of the left ventricle P - Potassium loss R - Reciprocal ST depression (e.g. inferior wall MI) E - Encephalon hemorrhage S - Subendocardial infarct S - Subendocardial ischemia E - Embolism (pulmonary) D - Dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. C ...
S - Shock T - Toxicity (digitalis
''Digitalis'' ( or ) is a genus of about 20 species of herbaceous perennial plants, shrubs, and Biennial plant, biennials, commonly called foxgloves.
''Digitalis'' is native to Europe, Western Asia, and northwestern Africa. The flowers are ...
/quinidine
Quinidine is a class I antiarrhythmic agent, class IA antiarrhythmic agent used to treat heart rhythm disturbances. It is a diastereomer of Antimalarial medication, antimalarial agent quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tre ...
)
Physiology
For non-transmural ischemia (subendocardial ischemia) injured cells are closer to the inside of heart wall, resulting in a systolic injury current. A systolic injury current results from a greater depolarization in healthier cells. Because the subepicardial region is more depolarized (more positive) compared to the endomyocardial cells, the current in the left ventricle flows toward the endomyocardial cells. The current flows from the more positive subepicardium to the less positive subendocardium during phase 2 of the fast fiber type depolarization, which on ECG occurs during ST segment. The positive electrodes on the anterior chest wall detect the movement of positive charge away from the electrode and record it as a downward deflection on the ECG paper.Measurement
ST segment depression may be determined by measuring the vertical distance between the patient's trace and the isoelectric line at a location 2madscientist software > MicroEKG ManualRetrieved September 2010-3 millimeters from the
QRS complex
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the ri ...
.
It is significant if it is more than 1 mm in V5-V6, or 1.5 mm in AVF or III.
In a cardiac stress test
A cardiac stress test is a cardiological examination that evaluates the cardiovascular system's response to external stress within a controlled clinical setting. This stress response can be induced through physical exercise (usually a treadmill) o ...
, an ST depression of at least 1 mm after adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside build ...
administration indicates a reversible ischaemia, while an exercise stress test requires an ST depression of at least 2 mm to significantly indicate reversible ischaemia.
See also
*ST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.005 to 0.150 sec (5 to 150 ms).
It starts at the J point (junction between the QRS complex and ST segment) and ends at the beginning of the T ...
* ST elevation
References
{{Heart diseases Cardiac arrhythmia Medical mnemonics