SN 2010jl on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
SN 2010jl was a luminous
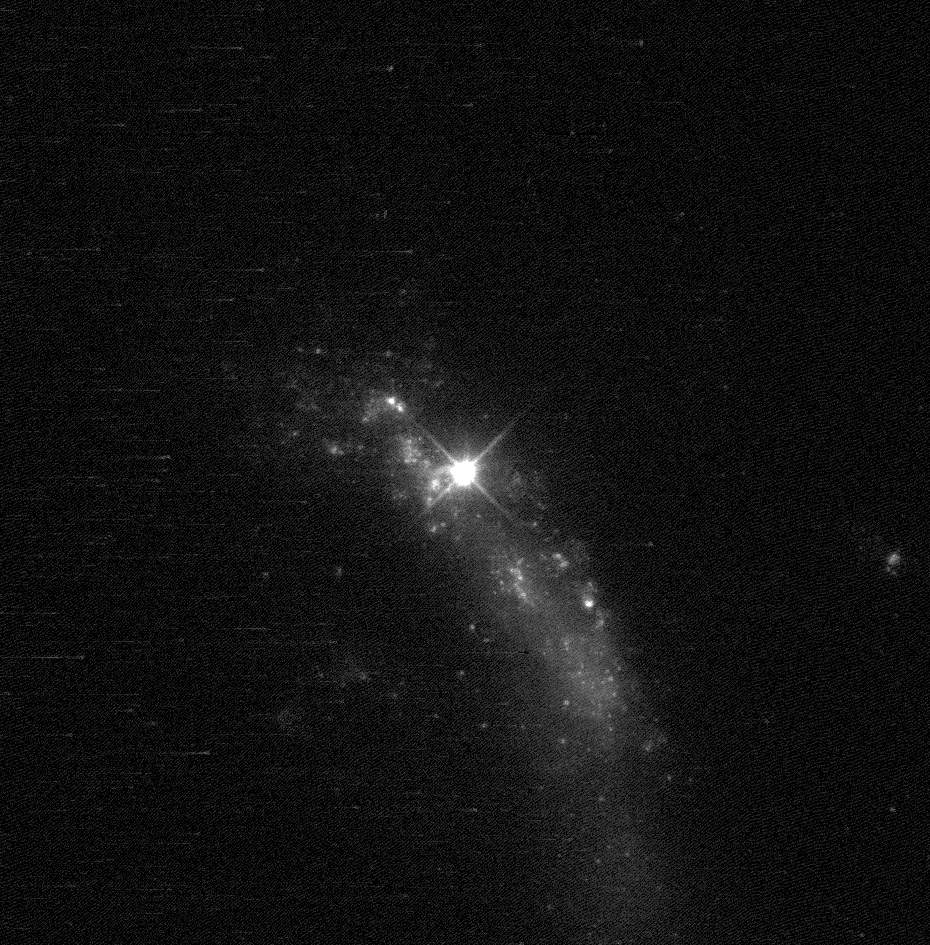
 Following the discovery of 2010jl, several other type IIn supernovae with long-lasting infrared excess were discovered. Their H- and K-band and mid-infrared light curve is dominated by two increases of the brightness. The first increase appears during the discovery and is attributed to the CSM interaction and the light echo. The second increase is attributed to the formation of new dust. After the second increase the infrared light curve shows a fading.
The following 2010jl-like supernovae are known: SN 2014ab, SN 2015da and SN 2017hcc. The supernova ASASSN-15ua is also mentioned to be similar to 2010jl. Additionally there are type II supernovae with mid-infrared light curves that are similar to 2010jl.{{Cite journal , last=Thévenot , first=Melina , date=2020-12-01 , title=Mid-Infrared Detections of SNe II with NEOWISE , journal=Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society , volume=4 , issue=12 , pages=243 , doi=10.3847/2515-5172/abd415 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2020RNAAS...4..243T , issn=2515-5172
Following the discovery of 2010jl, several other type IIn supernovae with long-lasting infrared excess were discovered. Their H- and K-band and mid-infrared light curve is dominated by two increases of the brightness. The first increase appears during the discovery and is attributed to the CSM interaction and the light echo. The second increase is attributed to the formation of new dust. After the second increase the infrared light curve shows a fading.
The following 2010jl-like supernovae are known: SN 2014ab, SN 2015da and SN 2017hcc. The supernova ASASSN-15ua is also mentioned to be similar to 2010jl. Additionally there are type II supernovae with mid-infrared light curves that are similar to 2010jl.{{Cite journal , last=Thévenot , first=Melina , date=2020-12-01 , title=Mid-Infrared Detections of SNe II with NEOWISE , journal=Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society , volume=4 , issue=12 , pages=243 , doi=10.3847/2515-5172/abd415 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2020RNAAS...4..243T , issn=2515-5172
type IIn supernova
A Type II supernova or SNII (plural: ''supernovae'') results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun () to undergo this type ...
that was discovered on November 3, 2010, in the irregular galaxy UGC 5189A
UGC may refer to:
Organisations
* Canadian Geophysical Union, official abbreviation in French (Union géophysique canadienne)
* UGC (cinema operator), a European cinema chain, formerly Union Générale Cinématographique
* UGC Fox Distribution, a ...
. It is 48.9 ± 3.4 Mpc MPC, Mpc or mpc may refer to:
Astronomy
* Megaparsec (Mpc), unit of length used in astronomy
* Minor Planet Center, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
** ''Minor Planet Circulars'' (MPC, M.P.C. or MPCs), astronomical publication from the Minor ...
distant from the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. It showed an infrared excess
An infrared excess is a measurement of an astronomical source, typically a star, that in their spectral energy distribution has a greater measured infrared flux than expected by assuming the star is a blackbody radiator. Infrared excesses are of ...
which lasted for over 1400 days.
Discovery
2010jl was discovered during thePuckett Observatory
Puckett Observatory is a private astronomical observatory located in the state of Georgia. It is owned and operated by Tim Puckett. Its primary observation goals are the study of comets and the discovery of supernovae. To facilitate the latter ...
Supernova Search, by Newton & Puckett with a 0.40-m reflector
Reflector may refer to:
Science
* Reflector, a device that causes reflection (for example, a mirror or a retroreflector)
* Reflector (photography), used to control lighting contrast
* Reflecting telescope
* Reflector (antenna), the part of an ant ...
at Portal
Portal may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Gaming
* ''Portal'' (series), a series of video games developed by Valve
** ''Portal'' (video game), a 2007 video game, the first in the series
** '' Portal 2'', the 2011 sequel
** '' Portal Stori ...
, Arizona. The discovery was made on Nov. 3.52 UT and was confirmed on Nov. 4.50. Follow-up spectroscopy showed broad emission and narrow-line emission from hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
leading to a classification of type IIn.
Infrared excess

CSM interaction
The classification as type IIn showed that the supernova was interacting with the circumstellar medium (CSM). The supernova itself produces the broad emission, the flash-ionized circumstellar medium produces on the other hand the type IIn typical narrow-line emission features. Observations withChandra
Chandra (), also known as Soma (), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) and Dikpala (guardians of the directions).
Etymology and other ...
-ACIS
The 3D ACIS Modeler (ACIS) is a geometric modeling kernel developed by Spatial Corporation (formerly Spatial Technology), part of Dassault Systèmes. ACIS is used by software developers in industries such as computer-aided design, computer-ai ...
X-ray showed absorption features caused by circumstellar matter. At the time of the observation it was one of the most luminous supernovae observed in X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s.
Infrared echo
Observations with Hubble detected near-infrared excess that lasted for 400 days. While the early near-infrared detection is dominated by the supernova, the later near-infrared detection becomes more dominated by the infrared echo. The echo is caused by pre-existing circumstellar dust that does not interact with the supernova, but that scatters the light of the supernova.New dust
A later study withGemini
Gemini most often refers to:
* Gemini (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Gemini (astrology), an astrological sign
Gemini may also refer to:
Science and technology Space
* Gemini in Chinese astronomy, the Gemini constellat ...
and Spitzer
Spitzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Andre Spitzer (1945–1972), Israeli fencing coach and victim of the Munich massacre
* Bernard Spitzer (1924–2014), American real estate developer and philanthropist, father of E ...
showed that infrared excess persisted until the end of the observations on day 1367 after the discovery. This very late detection of infrared excess cannot be explained with an infrared echo alone. Between days 260 and 464 the near-infrared jumps in brightness and then slowly fades until day 1000. The jump in near-infrared brightness is explained with the formation of new dust.
The formation of new dust can be shown by several other features. 2010jl showed on the one hand infrared excess caused by thermal radiation of the newly formed dust. It also showed blueshift of the emission-lines, which is caused by the dust blocking the material that is further away from our line of sight. A third line of evidence is increased fading in the optical, which could not be shown due to lacking observations in a specific timespan. It was determined that the supernova produced about 0.005-0.01 (about 5-10 Jupiter masses) of predominantly carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
dust grains by the day 1400.
2010jl-like supernovae
 Following the discovery of 2010jl, several other type IIn supernovae with long-lasting infrared excess were discovered. Their H- and K-band and mid-infrared light curve is dominated by two increases of the brightness. The first increase appears during the discovery and is attributed to the CSM interaction and the light echo. The second increase is attributed to the formation of new dust. After the second increase the infrared light curve shows a fading.
The following 2010jl-like supernovae are known: SN 2014ab, SN 2015da and SN 2017hcc. The supernova ASASSN-15ua is also mentioned to be similar to 2010jl. Additionally there are type II supernovae with mid-infrared light curves that are similar to 2010jl.{{Cite journal , last=Thévenot , first=Melina , date=2020-12-01 , title=Mid-Infrared Detections of SNe II with NEOWISE , journal=Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society , volume=4 , issue=12 , pages=243 , doi=10.3847/2515-5172/abd415 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2020RNAAS...4..243T , issn=2515-5172
Following the discovery of 2010jl, several other type IIn supernovae with long-lasting infrared excess were discovered. Their H- and K-band and mid-infrared light curve is dominated by two increases of the brightness. The first increase appears during the discovery and is attributed to the CSM interaction and the light echo. The second increase is attributed to the formation of new dust. After the second increase the infrared light curve shows a fading.
The following 2010jl-like supernovae are known: SN 2014ab, SN 2015da and SN 2017hcc. The supernova ASASSN-15ua is also mentioned to be similar to 2010jl. Additionally there are type II supernovae with mid-infrared light curves that are similar to 2010jl.{{Cite journal , last=Thévenot , first=Melina , date=2020-12-01 , title=Mid-Infrared Detections of SNe II with NEOWISE , journal=Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society , volume=4 , issue=12 , pages=243 , doi=10.3847/2515-5172/abd415 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2020RNAAS...4..243T , issn=2515-5172
References