SIEM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a field within
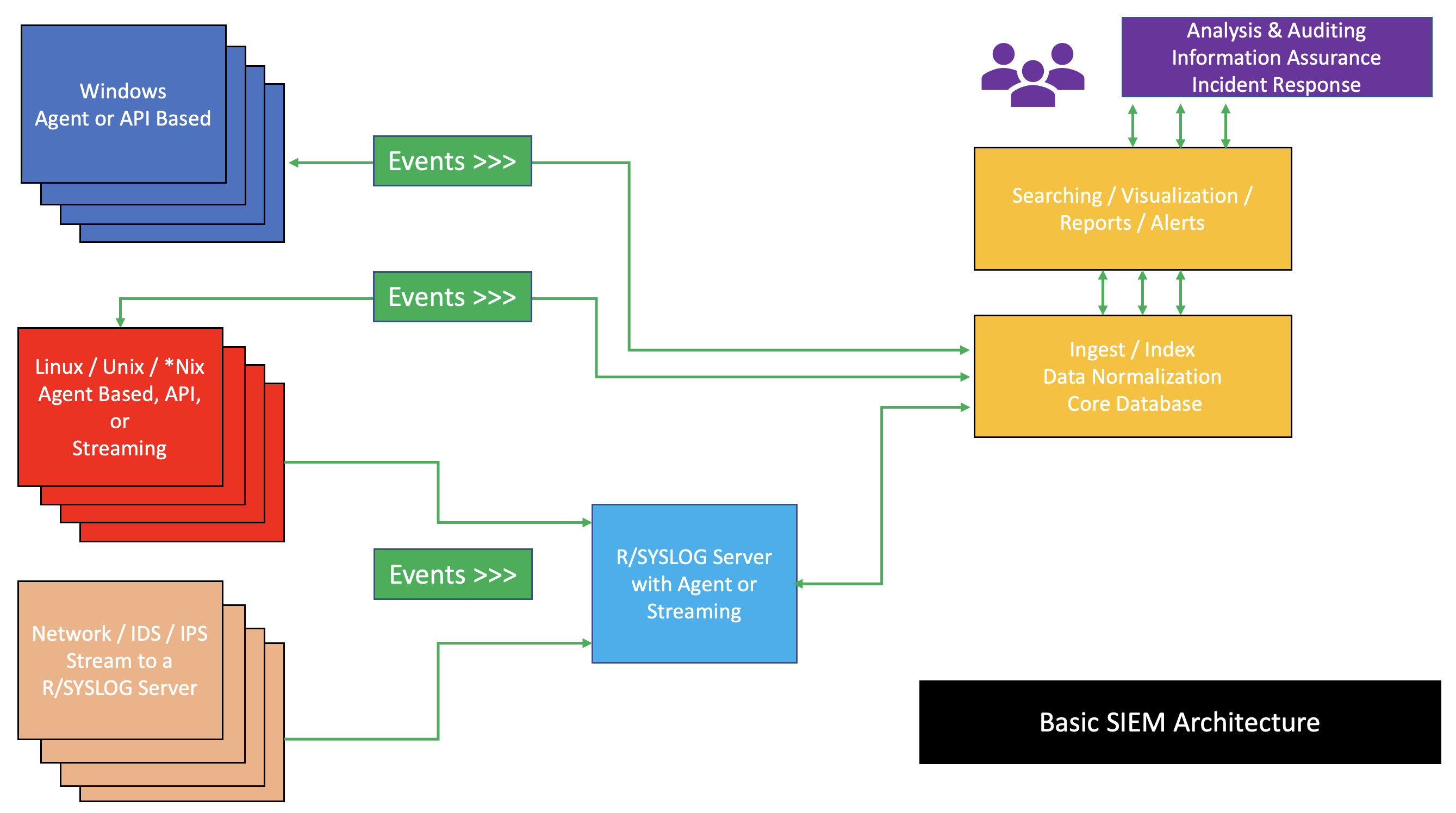 SIEM architectures may vary by vendor; however, generally, essential components comprise the SIEM engine. The essential components of a SIEM are as follows:
* A data collector forwards selected audit logs from a host (agent based or host based log streaming into index and aggregation point)
* An ingest and indexing point aggregation point for parsing, correlation, and
SIEM architectures may vary by vendor; however, generally, essential components comprise the SIEM engine. The essential components of a SIEM are as follows:
* A data collector forwards selected audit logs from a host (agent based or host based log streaming into index and aggregation point)
* An ingest and indexing point aggregation point for parsing, correlation, and
Essential SIEM Correlation Rules for Compliance
{{DEFAULTSORT:Security information And event management Data security
computer security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, n ...
that combines security information management
Security information management (SIM) is an information security industry term for the collection of data such as log files into a central repository for trend analysis.
Overview
SIM products generally are software agents running on the computer ...
(SIM) and security event management Security event management (SEM), and the related SIM and SIEM, are computer security disciplines that use data inspection tools to centralize the storage and interpretation of logs or events generated by other software running on a network.
Overvi ...
(SEM) to enable real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. SIEM systems are central to security operations centers (SOCs), where they are employed to detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents. SIEM technology collects and aggregates data from various systems, allowing organizations to meet compliance requirements while safeguarding against threats
A threat is a communication of intent to inflict harm or loss on another person. Intimidation is a tactic used between conflicting parties to make the other timid or psychologically insecure for coercion or control. The act of intimidation fo ...
. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) definition for SIEM tool is application that provides the ability to gather security data from information system components and present that data as actionable information via a single interface.
SIEM tools can be implemented as software, hardware, or managed services. SIEM systems log security events and generating reports to meet regulatory frameworks such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Ted Kennedy, Kennedy–Nancy Kassebaum, Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President ...
(HIPAA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is an information security standard used to handle credit cards from major card brands. The standard is administered by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council, and its us ...
(PCI DSS). The integration of SIM and SEM within SIEM provides organizations with a centralized approach for monitoring security events and responding to threats in real-time.
First introduced by Gartner
Gartner, Inc. is an American research and advisory firm focusing on business and technology topics. Gartner provides its products and services through research reports, conferences, and consulting. Its clients include large corporations, gover ...
analysts Mark Nicolett and Amrit Williams in 2005, the term SIEM has evolved to incorporate advanced features such as threat intelligence and behavioral analytics, which allow SIEM solutions to manage complex cybersecurity threats, including zero-day vulnerabilities and polymorphic malware
In computing, polymorphic code is code that uses a polymorphic engine to mutate while keeping the original algorithm intact - that is, the ''code'' changes itself every time it runs, but the ''function'' of the code (its semantics) stays the sam ...
.
In recent years, SIEM has become increasingly incorporated into national cybersecurity initiatives. For instance, Executive Order 14028 signed in 2021 by U.S. President Joseph Biden mandates the use of SIEM technologies to improve incident detection and reporting in federal systems. Compliance with these mandates is further reinforced by frameworks such as NIST SP 800-92, which outlines best practices for managing computer security logs.
Modern SIEM platforms are aggregating and normalizing data not only from various Information Technology (IT)
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
sources, but from production and manufacturing Operational Technology (OT) environments as well.
History
Initially, system logging was primarily used for troubleshooting and debugging. However, as operating systems and networks have grown more complex, so has the generation of system logs. The monitoring of system logs has also become increasingly common due to the rise of sophisticatedcyberattacks
A cyberattack (or cyber attack) occurs when there is an unauthorized action against computer infrastructure that compromises the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of its content.
The rising dependence on increasingly complex and inte ...
and the need for compliance with regulatory frameworks, which mandate logging security controls
Security controls or security measures are safeguards or countermeasures to avoid, detect, counteract, or minimize security risks to physical property, information, computer systems, or other assets. In the field of information security, such co ...
within risk management frameworks (RMF).
Starting in the late 1970s, working groups began establishing criteria for managing auditing and monitoring programs, laying the groundwork for modern cybersecurity practices, such as insider threat detection and incident response. A key publication during this period was NIST’s Special Publication 500-19.
In 2005, the term "SIEM" (Security Information and Event Management) was introduced by Gartner analysts Mark Nicolett and Amrit Williams. SIEM systems provide a single interface for gathering security data from information systems and presenting it as actionable intelligence. The National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of p ...
provides the following definition of SIEM: "Application that provides the ability to gather security data from information system components and present that data as actionable information via a single interface." In addition, NIST has designed and implemented a federally mandated RMF.
With the implementation of RMFs globally, auditing and monitoring have become central to information assurance
Information assurance (IA) is the practice of assuring information and managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and data transmission, transmission of information. Information assurance includes protection of the data integrity, inte ...
and security. Cybersecurity professionals now rely on logging data to perform real-time security functions, driven by governance models that incorporate these processes into analytical tasks. As information assurance matured in the late 1990s and into the 2000s, the need to centralize system logs became apparent. Centralized log management allows for easier oversight and coordination across networked systems.
On May 17, 2021, U.S. President Joseph Biden signed Executive Order 14028, "Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity," which established further logging requirements, including audit logging and endpoint protection, to enhance incident response capabilities. This order was a response to an increase in ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that Encryption, encrypts the victim's personal data until a ransom is paid. Difficult-to-trace Digital currency, digital currencies such as paysafecard or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency, cryptocurrencies are com ...
attacks targeting critical infrastructure. By reinforcing information assurance controls within RMFs, the order aimed to drive compliance and secure funding for cybersecurity initiatives.
Information assurance
Published in September 2006, the NIST SP 800-92 Guide to Computer Security Log Management serves as a key document within the NIST Risk Management Framework to guide what should be auditable. As indicated by the absence of the term "SIEM", the document was released before the widespread adoption of SIEM technologies. Although the guide is not exhaustive due to rapid changes in technology since its publication, it remains relevant by anticipating industry growth. NIST is not the only source of guidance on regulatory mechanisms for auditing and monitoring, and many organizations are encouraged to adopt SIEM solutions rather than relying solely on host-based checks. Several regulations and standards reference NIST’s logging guidance, including the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) of 2002, Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and ISO 27001. Public and private organizations frequently reference NIST documents in their security policies. NIST SP 800-53 AU-2 Event Monitoring is a key security control that supports system auditing and ensures continuous monitoring for information assurance and cybersecurity operations. SIEM solutions are typically employed as central tools for these efforts. Federal systems categorized based on their impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) have five specific logging requirements (AU-2 a-e) that must be met. While logging every action is possible, it is generally not recommended due to the volume of logs and the need for actionable security data. AU-2 provides a foundation for organizations to build a logging strategy that aligns with other controls. NIST SP 800-53 SI-4 System Monitoring outlines the requirements for monitoring systems, including detecting unauthorized access and tracking anomalies, malware, and potential attacks. This security control specifies both the hardware and software requirements for detecting suspicious activities. Similarly, NIST SP 800-53 RA-10 Threat Hunting, added in Revision 5, emphasizes proactive network defense by identifying threats that evade traditional controls. SIEM solutions play a critical role in aggregating security information for threat hunting teams. Together, AU-2, SI-4, and RA-10 demonstrate how NIST controls integrate into a comprehensive security strategy. These controls, supported by SIEM solutions, help ensure continuous monitoring, risk assessments, and in-depth defense mechanisms across federal and private networks.Terminology
The acronyms ''SEM'', ''SIM'' and ''SIEM'' have sometimes been used interchangeably, but generally refer to the different primary focus of products: * ''Log management
Log management is the process for generating, transmitting, storing, accessing, and disposing of log data. A log data (or ''logs'') is composed of entries (records), and each entry contains information related to a specific event that occur within ...
'': Focus on simple collection and storage of log messages and audit trail
An audit trail (also called audit log) is a security-relevant chronological record, set of records, and/or destination and source of records that provide documentary evidence of the sequence of activities that have affected at any time a specific ...
s.
* ''Security information management'' ( SIM): Long-term storage as well as analysis and reporting of log data.
* ''Security event manager'' ( SEM): Real-time monitoring, correlation of events, notifications and console views.
* ''Security information and event management'' (SIEM): Combines SIM and SEM and provides real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications.
*''Managed Security Service:'' ( MSS) or ''Managed Security Service Provider:'' (MSSP): The most common managed services appear to evolve around connectivity and bandwidth, network monitoring, security, virtualization
In computing, virtualization (abbreviated v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers.
Virtualization began in the 1960s wit ...
, and disaster recovery.
*''Security as a service (SECaaS
Security as a service (SECaaS) is a business model in which a service provider integrates their security services into a corporate infrastructure on a subscription basis more cost-effectively than most individuals or corporations can provide on th ...
)'': These security services often include authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ...
, anti-virus
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware.
Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name ...
, anti-malware
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware.
Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name ...
/spyware, intrusion detection
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a device or software application that monitors a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations. Any intrusion activity or violation is typically either reported to an administrator or collec ...
, penetration testing and security event management, among others.
In practice many products in this area will have a mix of these functions, so there will often be some overlap – and many commercial vendors also promote their own terminology. Oftentimes commercial vendors provide different combinations of these functionalities which tend to improve SIEM overall. Log management alone doesn't provide real-time insights on network security, SEM on its own won't provide complete data for deep threat analysis. When SEM and log management are combined, more information is available for SIEM to monitor.
A key focus is to monitor and help manage user and service privileges, directory services
In computing, a directory service or name service maps the names of network resources to their respective network addresses. It is a shared information infrastructure for locating, managing, administering and organizing everyday items and network ...
and other system-configuration changes; as well as providing log auditing and review and incident response.
Capabilities
* Data aggregation:Log management
Log management is the process for generating, transmitting, storing, accessing, and disposing of log data. A log data (or ''logs'') is composed of entries (records), and each entry contains information related to a specific event that occur within ...
aggregates data from many sources, including networks, security, servers, databases, applications, providing the ability to consolidate monitored data to help avoid missing crucial events.
* Correlation: Looks for common attributes and links events together into meaningful bundles. This technology provides the ability to perform a variety of correlation techniques to integrate different sources, in order to turn data into useful information. Correlation is typically a function of the Security Event Management portion of a full SIEM solution.
* Alerting: The automated analysis of correlated events.
* Dashboards: Tools can take event data and turn it into informational charts to assist in seeing patterns, or identifying activity that is not forming a standard pattern.
* Compliance: Applications can be employed to automate the gathering of compliance data, producing reports that adapt to existing security, governance and auditing processes.
* Retention: Employing long-term storage of historical data to facilitate correlation of data over time, and to provide the retention necessary for compliance requirements. The Long term log data retention
Data retention defines the policies of persistent data and records management for meeting legal and business data archival requirements. Although sometimes interchangeable, it is not to be confused with the Data Protection Act 1998.
The differe ...
is critical in forensic investigations as it is unlikely that the discovery of a network breach will be at the time of the breach occurring.
* Forensic analysis: The ability to search across logs on different nodes and time periods based on specific criteria. This mitigates having to aggregate log information in your head or having to search through thousands and thousands of logs.
Components
 SIEM architectures may vary by vendor; however, generally, essential components comprise the SIEM engine. The essential components of a SIEM are as follows:
* A data collector forwards selected audit logs from a host (agent based or host based log streaming into index and aggregation point)
* An ingest and indexing point aggregation point for parsing, correlation, and
SIEM architectures may vary by vendor; however, generally, essential components comprise the SIEM engine. The essential components of a SIEM are as follows:
* A data collector forwards selected audit logs from a host (agent based or host based log streaming into index and aggregation point)
* An ingest and indexing point aggregation point for parsing, correlation, and data normalization
In mathematics and computer science, a canonical, normal, or standard form of a mathematical object is a standard way of presenting that object as a mathematical expression. Often, it is one which provides the simplest representation of an obje ...
* A search node that is used for visualization, queries, reports, and alerts (analysis take place on a search node)
A basic SIEM infrastructure is depicted in the image to the right.
Use cases
Computer security researcher Chris Kubecka identified the following SIEM use cases, presented at the hacking conference 28C3 (Chaos Communication Congress
The Chaos Communication Congress is an annual hacker conference organized by the Chaos Computer Club. The congress features a variety of lectures and workshops on technical and political issues related to security, cryptography, privacy and ...
).
* SIEM visibility and anomaly detection could help detect zero-days
A zero-day (also known as a 0-day) is a Vulnerability (computer security), vulnerability or security hole in a computer system unknown to its developers or anyone capable of mitigation, mitigating it. Until the vulnerability is remedied, threat act ...
or polymorphic code
In computing, polymorphic code is code that uses a polymorphic engine to mutate while keeping the original algorithm intact - that is, the ''code'' changes itself every time it runs, but the ''function'' of the code (its semantics) stays the sam ...
. Primarily due to low rates of anti-virus
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware.
Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name ...
detection against this type of rapidly changing malware.
* Parsing, log normalization and categorization can occur automatically, regardless of the type of computer or network device, as long as it can send a log.
* Visualization with a SIEM using security events and log failures can aid in pattern detection.
* Protocol anomalies that can indicate a misconfiguration or a security issue can be identified with a SIEM using pattern detection, alerting, baseline and dashboards.
* SIEMS can detect covert, malicious communications and encrypted channels.
* Cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyberattack, cyber attacks against an enemy State (polity), state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems. Some intended outcomes could be espionage, sabotage, propaganda, ...
can be detected by SIEMs with accuracy, discovering both attackers and victims.
Modern SIEM platforms support not only detection, but response too. The response can be manual or automated including AI based response.
Correlation rules examples
SIEM systems can have hundreds and thousands of correlation rules. Some of these are simple, and some are more complex. Once a correlation rule is triggered the system can take appropriate steps to mitigate a cyber attack. Usually, this includes sending a notification to a user and then possibly limiting or even shutting down the system.Brute Force Detection
Brute force detection is relatively straightforward. Brute forcing relates to continually trying to guess a variable. It most commonly refers to someone trying to constantly guess your password - either manually or with a tool. However, it can refer to trying to guess URLs or important file locations on your system. An automated brute force is easy to detect as someone trying to enter their password 60 times in a minute is impossible.Impossible Travel
When a user logs in to a system, generally speaking, it creates a timestamp of the event. Alongside the time, the system may often record other useful information such as the device used, physical location, IP address, incorrect login attempts, etc. The more data is collected the more use can be gathered from it. For impossible travel, the system looks at the current and last login date/time and the difference between the recorded distances. If it deems it's not possible for this to happen, for example traveling hundreds of miles within a minute, then it will set off a warning. Many employees and users are now using VPN services which may obscure physical location. This should be taken into consideration when setting up such a rule.Excessive File Copying
The average user does not typically copy or move files on the system repeatedly. Thus, any excessive file copying on a system could be attributed to an attacker wanting to cause harm to an organization. Unfortunately, it's not as simple as stating someone has gained access to your network illegally and wants to steal confidential information. It could also be an employee looking to sell company information, or they could just want to take home some files for the weekend.Network Anomaly Detection
Monitoring network traffic against unusual patterns that includes any threats or attacks ranging from DDOS to network scans. Note SIEM can monitor data flow in the network and to detect and prevent potential data exfiltration efforts. In general dedicated Data loss prevention (DLP) take care about data loss prevention.DDoS Attack
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attack could cause significant damage to a company or organization. A DDoS attack can not only take a website offline, it can also make a system weaker. With suitable correlation rules in place, a SIEM should trigger an alert at the start of the attack so that the company can take the necessary precautionary measures to protect vital systems.File Integrity Change
File Integrity and Change Monitoring (FIM) is the process of monitoring the files on your system. Unexpected changes in your system files will trigger an alert as it's a likely indication of a cyber attack.Alerting examples
Some examples of customized rules to alert on event conditions involve user authentication rules, attacks detected and infections detected.See also
*Computer security incident management
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', whi ...
* Gordon–Loeb model
The Gordon–Loeb model is an economic model that analyzes the optimal level of investment in information security.
The benefits of investing in cybersecurity stem from reducing the costs associated with cyber breaches. The Gordon-Loeb model pro ...
for cyber security investments
* IT risk
It or IT may refer to:
* It (pronoun), in English
* Information technology
Arts and media Film and television
* ''It'' (1927 film), a film starring Clara Bow
* '' It! The Terror from Beyond Space'', a 1958 science fiction film
* ''It!'' (1967 ...
* Log management
Log management is the process for generating, transmitting, storing, accessing, and disposing of log data. A log data (or ''logs'') is composed of entries (records), and each entry contains information related to a specific event that occur within ...
* Extended detection and response (XDR)
* Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
* Network detection and response (NDR)
* Security orchestration, automation and response
References
External links
Essential SIEM Correlation Rules for Compliance
{{DEFAULTSORT:Security information And event management Data security