S2W on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The S2W (Submarine platform Second generation core Westinghouse) reactor was a naval reactor built by Westinghouse used by the
 This
This
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
to provide electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transm ...
and propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
on warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as b ...
s.
History
The S2W reactor was a naval nuclear reactor developed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation for use in the United States Navy's nuclear-powered submarines. The reactor's designation, S2W, stands for "Submarine platform," "second-generation core design," and "Westinghouse," the contractor responsible for its development. It was a pressurized water reactor (PWR) initially installed aboard the USS ''Seawolf'' (SSN-575), the second nuclear-powered submarine launched by the U.S. Navy in 1955. The S2W reactor was originally designed as a sodium-cooled system, but operational difficulties with this cooling method led to its later conversion to a conventional pressurized water reactor. This design provided substantial improvements in submerged endurance and speed over conventional diesel-electric submarines, marking a pivotal advancement in naval propulsion. The S2W reactor, though eventually phased out, was significant in the early stages of nuclear submarine technology and helped shape the U.S. Navy's future reactor designs, which ultimately favored the reliability and operational ease of pressurized water reactors. This
This nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
is the shipboard equivalent of the prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
S1W reactor
The S1W reactor was the first prototype naval reactor used by the United States Navy to prove that the technology could be used for electricity generation and propulsion on submarines.
The designation of "S1W" stands for
* S = Submarine platfor ...
, with minor design changes, that was installed on . As installed in ''Nautilus'' it generated . It was originally designated STR.
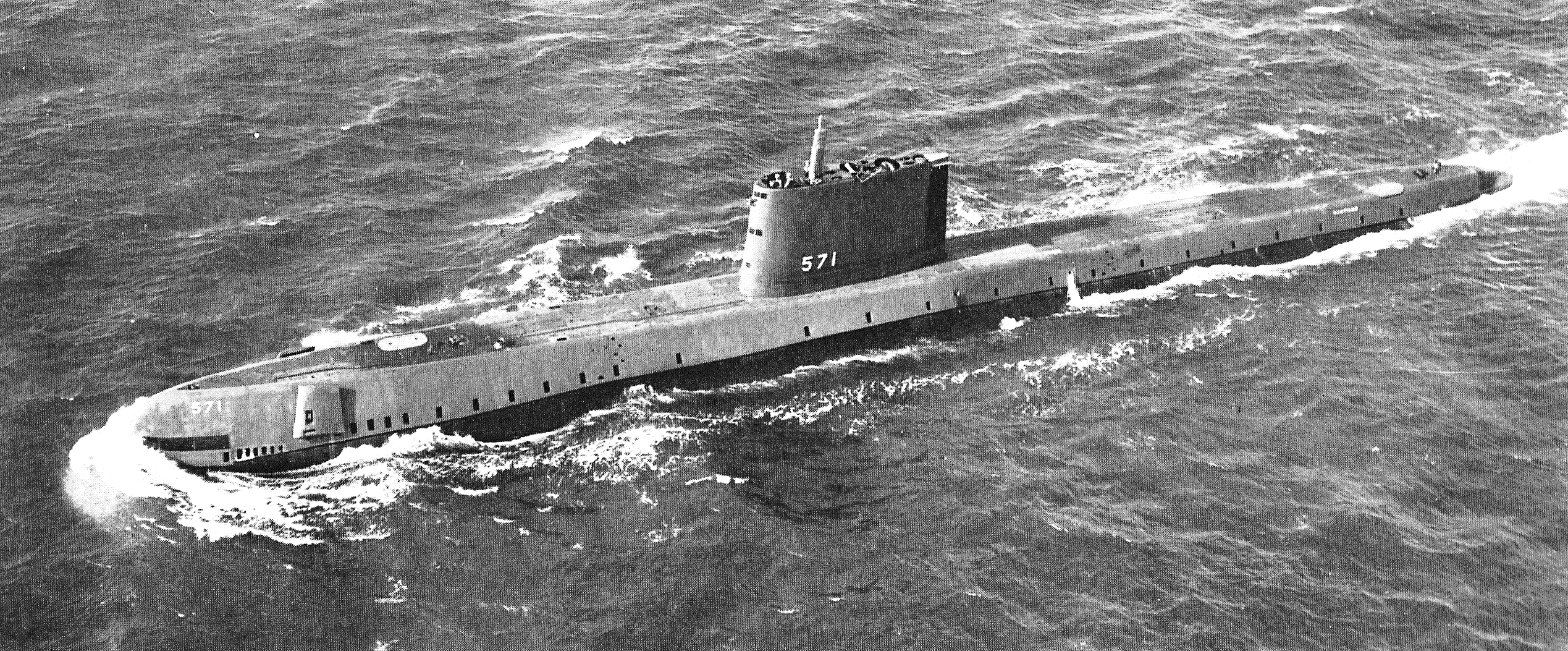
USS ''Nautilus (SSN-571)''
USS Nautilus (SSN-571)
USS ''Nautilus'' (SSN-571) was the world's first operational nuclear-powered submarine and on 3 August 1958 became the first submarine to complete a submerged transit of the North Pole. Her initial commanding officer was Eugene "Dennis" Wilki ...
was powered by the Submarine Thermal Reactor (STR), later redesignated the S2W reactor, a pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada).
In a PWR, water is used both as ...
produced for the US Navy by Westinghouse Electric Corporation
The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse and headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was ...
. Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory
Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory is a U.S. Government-owned research and development facility in the Pittsburgh suburb of West Mifflin, Pennsylvania, that works exclusively on the design and development of nuclear power for the U.S. Navy. It was one ...
, operated by Westinghouse, developed the basic reactor plant design used in ''Nautilus'' after being given the assignment on 31 December 1947 to design a nuclear power plant for a submarine.
After ''Nautilus'' was decommissioned, the reactor equipment was removed. The submarine is now moored and displayed as a museum ship
A museum ship, also called a memorial ship, is a ship that has been preserved and converted into a museum open to the public for educational or memorial purposes. Some are also used for training and recruitment purposes, mostly for the small numb ...
at the Naval Submarine Base New London
Naval Submarine Base New London is the primary United States Navy East Coast submarine base, also known as the "Home of the Submarine Force." It is located in Groton, Connecticut directly across the Thames River from its namesake city of New L ...
in Groton, Connecticut
Groton ( ) is a town in New London County, Connecticut, United States, located on the Thames River (Connecticut), Thames River. It is the home of General Dynamics Electric Boat, which is the major contractor for submarine work for the United St ...
.
Variant
After the predictable problems arose with the S2G's use of 347 stainless steel caused by thesodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
in the liquid sodium reactor in its superheater the had her S2G liquid metal cooled reactor
A liquid metal cooled nuclear reactor (LMR) is a type of nuclear reactor where the primary coolant is a liquid metal. Liquid metal cooled reactors were first adapted for breeder reactor power generation. They have also been used to power nuclear ...
replaced using the spare S2W built for USS ''Nautilus''. During the conversion, the steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
s in the powerplant were also re-bladed to use saturated, rather than superheated, steam. This reactor was designated S2Wa.
References
Notes
{{DEFAULTSORT:S2w Reactor United States naval reactors