S-adenosylmethionine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in
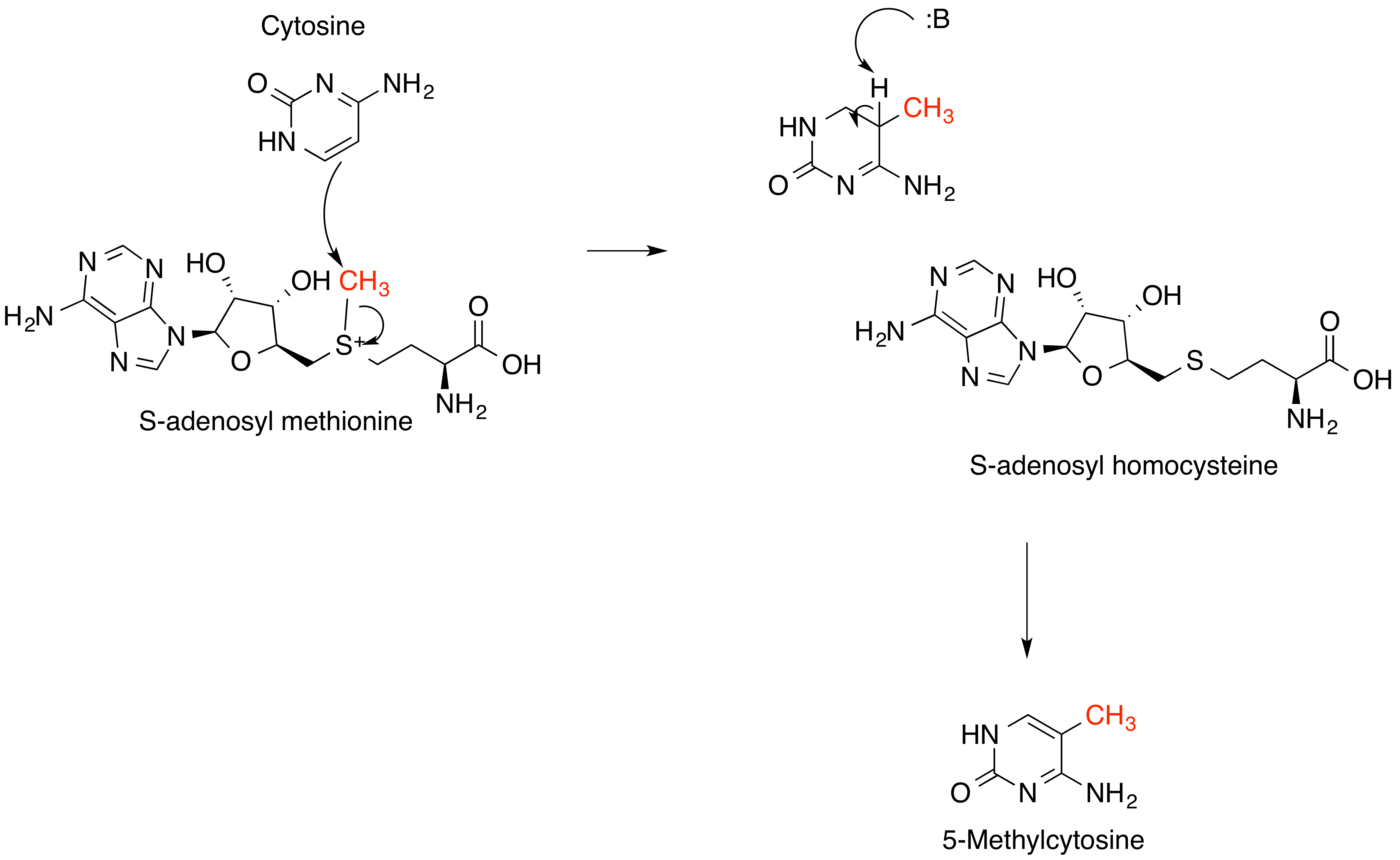 The reactions that produce, consume, and regenerate SAM are called the SAM cycle. In the first step of this cycle, the SAM-dependent
The reactions that produce, consume, and regenerate SAM are called the SAM cycle. In the first step of this cycle, the SAM-dependent
and the homocysteine recycled back to
EC 2.1.1.13
or cobalamin-independent
EC 2.1.1.14
). This methionine can then be converted back to SAM, completing the cycle. In the rate-limiting step of the SAM cycle, MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) irreversibly reduces 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
EC 4.1.1.50
to form ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine. This compound then donates its ''n''-propylamine group in the biosynthesis of polyamines such as
methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...
transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catab ...
reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s and secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites, also called ''specialised metabolites'', ''secondary products'', or ''natural products'', are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved ...
s. It is made from adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP) and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952.
In bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s involved in methionine or cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
biosynthesis. In eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, tRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the gene ...
, and rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replac ...
; immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
, an important plant hormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anat ...
and signaling molecule.
SAMe has been studied for depression, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, and liver diseases
Hepato-biliary diseases include liver diseases and biliary diseases. Their study is known as hepatology.
Liver diseases
Viral hepatitis
* Acute hepatitis A
* Acute hepatitis B
* Acute hepatitis C
* Acute hepatitis D – this is a superinfecti ...
with inconclusive results, and while generally considered safe short-term, its long-term safety, use during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, and risks for people with bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
or compromised immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
s remain unclear.
Structure
''S''-Adenosyl methionine consists of the adenosyl group attached to the sulfur of methionine, providing it with a positive charge. It is synthesized from ATP and methionine by ''S''-Adenosylmethionine synthetase enzyme through the following reaction: : ATP + L-methionine + H2Ophosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
+ diphosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate () and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (), among others. Often pyrophosphate ...
+ ''S''-adenosyl-L-methionine
The sulfonium
In organic chemistry, a sulfonium ion, also known as sulphonium ion or sulfanium ion, is a positively-charged ion (a "cation") featuring three organic Substitution (chemistry), substituents attached to sulfur. These organosulfur compounds have t ...
functional group present in ''S''-adenosyl methionine is the center of its peculiar reactivity. Depending on the enzyme, ''S''-adenosyl methionine can be converted into one of three products:
*adenosyl radical, which converts to deoxyadenosine (AdO): classic rSAM reaction, also cogenerates methionine
* ''S''-adenosyl homocysteine, releasing methyl radical
* methylthioadenosine (SMT), homoalanine radical
Biochemistry
SAM cycle
 The reactions that produce, consume, and regenerate SAM are called the SAM cycle. In the first step of this cycle, the SAM-dependent
The reactions that produce, consume, and regenerate SAM are called the SAM cycle. In the first step of this cycle, the SAM-dependent methylase
Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which contain a Ro ...
s (EC 2.1.1) that use SAM as a substrate produce ''S''-adenosyl homocysteine as a product. ''S''-Adenosyl homocysteine is a strong negative regulator of nearly all SAM-dependent methylases despite their biological diversity. This is hydrolysed to homocysteine and adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside build ...
by ''S''-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolasebr>EC 3.3.1.1and the homocysteine recycled back to
methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
through transfer of a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, by one of the two classes of methionine synthases (i.e. cobalamin
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
-dependentEC 2.1.1.13
or cobalamin-independent
EC 2.1.1.14
). This methionine can then be converted back to SAM, completing the cycle. In the rate-limiting step of the SAM cycle, MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) irreversibly reduces 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
Radical SAM enzymes
A large number of enzymes cleave SAM reductively to produce radicals: 5′-deoxyadenosyl 5′-radical, methyl radical, and others. These enzymes are calledradical SAM
Radical SAM enzymes belong to a superfamily of enzymes that use an iron-sulfur cluster (4Fe-4S) to reductively cleave S-Adenosyl methionine, ''S''-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to generate a radical (chemistry), radical, usually a 5′-deoxyadenosyl ...
s. They all feature iron-sulfur cluster at their active sites. Most enzymes with this capability share a region of sequence homology that includes the motif CxxxCxxC or a close variant. This sequence provides three cysteinyl thiolate ligands that bind to three of the four metals in the 4Fe-4S cluster. The fourth Fe binds the SAM.
The radical intermediates generated by these enzymes perform a wide variety of unusual chemical reactions. Examples of radical SAM enzymes include spore photoproduct lyase, activases of pyruvate formate lyase and anaerobic sulfatases, lysine 2,3-aminomutase
Lysine 2,3-aminomutase (KAM or LAM) () is a radical SAM enzyme that facilitates the conversion of the Amino Acid, amino acid lysine to beta-lysine. It accomplishes this interconversion using three Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors and a 5'-deoxyad ...
, and various enzymes of cofactor biosynthesis, peptide modification, metalloprotein
Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins (out of ~20,000) contain zinc-binding protein domains al ...
cluster formation, tRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the gene ...
modification, lipid metabolism, etc. Some radical SAM enzymes use a second SAM as a methyl donor. Radical SAM enzymes are much more abundant in anaerobic bacteria than in aerobic organisms. They can be found in all domains of life and are largely unexplored. A recent bioinformatics study concluded that this family of enzymes includes at least 114,000 sequences including 65 unique reactions.
Deficiencies in radical SAM enzymes have been associated with a variety of diseases including congenital heart disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital he ...
, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
, and increased viral susceptibility.
Polyamine biosynthesis
Another major role of SAM is inpolyamine
A polyamine is an organic compound having two or more amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally, but some are synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. ...
biosynthesis. Here, SAM is decarboxylated by adenosylmethionine decarboxylaseEC 4.1.1.50
to form ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine. This compound then donates its ''n''-propylamine group in the biosynthesis of polyamines such as
spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine compound () found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms.
Function
Spermidine is an Aliphatic compound, aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS) catalyzes its form ...
and spermine
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some bacteria as well. It is found as a p ...
from putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of Putrefaction, putref ...
.
SAM is required for cellular growth and repair. It is also involved in the biosynthesis of several hormones and neurotransmitters that affect mood, such as epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
. Methyltransferases are also responsible for the addition of methyl groups to the 2′ hydroxyls of the first and second nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s next to the 5′ cap in messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
.
Therapeutic uses
SAMe has been studied for depression,osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, and liver diseases
Hepato-biliary diseases include liver diseases and biliary diseases. Their study is known as hepatology.
Liver diseases
Viral hepatitis
* Acute hepatitis A
* Acute hepatitis B
* Acute hepatitis C
* Acute hepatitis D – this is a superinfecti ...
with inconclusive results, and while generally considered safe short-term, its long-term safety, use during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, and risks for people with bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
or compromised immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
s remain unclear.
Osteoarthrtitis pain
As of 2012, the evidence was inconclusive as to whether SAM can mitigate the pain ofosteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
; clinical trials that had been conducted were too small from which to generalize.
Liver disease
The SAM cycle has been closely tied to the liver since 1947 because people with alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver would accumulate large amounts of methionine in their blood. While multiple lines of evidence from laboratory tests on cells andanimal models
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Mod ...
suggest that SAM might be useful to treat various liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Liver diseases
File:Ground gla ...
s, as of 2012 SAM had not been studied in any large randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials that would allow an assessment of its efficacy and safety.
Depression
A 2016 Cochrane review concluded that formajor depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
, "Given the absence of high quality evidence and the inability to draw firm conclusions based on that evidence, the use of SAMe for the treatment of depression in adults should be investigated further."
A 2020 systematic review found that it performed significantly better than placebo, and had similar outcomes to other commonly used antidepressants (imipramine
Imipramine, sold under the brand name Tofranil, among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) mainly used in the treatment of depression. It is also effective in treating anxiety and panic disorder. Imipramine is taken by mouth.
Common s ...
and escitalopram
Escitalopram ( ), sold under the brand names Lexapro and Cipralex, among others, is an antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is mainly used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized ...
).
Anti-cancer treatment
SAM has recently been shown to play a role inepigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
regulation. DNA methylation is a key regulator in epigenetic modification during mammalian cell development and differentiation. In mouse models, excess levels of SAM have been implicated in erroneous methylation patterns associated with diabetic neuropathy. SAM serves as the methyl donor in cytosine methylation, which is a key epigenetic regulatory process. Because of this impact on epigenetic regulation, SAM has been tested as an anti-cancer treatment. In many cancers, proliferation is dependent on having low levels of DNA methylation. In vitro addition in such cancers has been shown to remethylate oncogene promoter sequences and decrease the production of proto-oncogenes. In cancers such as colorectal cancer, aberrant global hypermethylation can inhibit promoter regions of tumor-suppressing genes. Contrary to the former information, colorectal cancers (CRCs) are characterized by global hypomethylation and promoter-specific DNA methylation.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral SAM achieves peak plasma concentrations three to five hours after ingestion of an enteric-coated tablet (400–1000 mg). The half-life is about 100 minutes.Availability in different countries
In Canada, the UK, and the United States, SAM is sold as adietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill (pharmacy), pill, capsule (pharmacy), capsule, tablet (pharmacy), tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients eithe ...
under the marketing name SAM-e (also spelled SAME or SAMe). It was introduced in the US in 1999, after the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act was passed in 1994.
It was introduced as a prescription drug
A prescription drug (also prescription medication, prescription medicine or prescription-only medication) is a pharmaceutical drug that is permitted to be dispensed only to those with a medical prescription. In contrast, over-the-counter drugs c ...
in Italy in 1979, in Spain in 1985, and in Germany in 1989. As of 2012, it was sold as a prescription drug in Russia, India, China, Italy, Germany, Vietnam, and Mexico.
Adverse effects
Gastrointestinal disorder,dyspepsia
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia or upset stomach, is a condition of impaired digestion. Symptoms may include upper abdominal fullness, heartburn, nausea, belching, or upper abdominal pain. People may also experience feeling full earlier ...
and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
can occur with SAM consumption. Long-term effects are unknown. SAM is a weak DNA- alkylating agent.
Another reported side effect of SAM is insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low ene ...
; therefore, the supplement is often taken in the morning. Other reports of mild side effects include lack of appetite, constipation, nausea, dry mouth, sweating, and anxiety/nervousness, but in placebo-controlled studies, these side effects occur at about the same incidence in the placebo groups.
Interactions and contraindications
Taking SAM at the same time as some drugs may increase the risk ofserotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a group of symptoms that may occur with the use of certain Serotonin, serotonergic medications or Recreational drug use, drugs. The symptoms can range from mild to severe, and are potentially fatal. Symptoms in mild c ...
, a potentially dangerous condition caused by having too much serotonin. These drugs include, but are certainly not limited to, dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan, sold under the brand name Robitussin among others, is a cough suppressant used in many cough and Common cold, cold medicines. In 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the combination dextromethorphan/bupropi ...
(Robitussin), meperidine (Demerol), pentazocine (Talwin), and tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Tramal among others, is an opioid analgesic, pain medication and a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) used to treat moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release form ...
(Ultram).
SAM can also interact with many antidepressant medications — including tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
and the herbal medicine ''Hypericum perforatum
''Hypericum perforatum'', commonly known as St. John's wort (sometimes perforate St. John's wort or common St. John's wort), is a flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae. It is a hairless, Perennial, perennial herb with woody Root, roots, y ...
'' (St. John's wort) — increasing the potential for serotonin syndrome or other side effects, and may reduce the effectiveness of levodopa
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA and sold under many brand names, is a dopaminergic medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) and certain other conditions like dopamine-responsive dystonia and restless legs syndrome. ...
for Parkinson's disease. SAM can increase the risk of manic episodes in people who have bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
.
Toxicity
A 2022 study concluded that SAMe could be toxic. Jean-Michel Fustin ofManchester University
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is c ...
said that the researchers found that excess SAMe breaks down into adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
and methylthioadenosine in the body, both producing the paradoxical effect of inhibiting methylation. This was found in laboratory mice
The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory animal sources for these mice are usually of the species ''Mus musculus''. They a ...
, causing harm to health, and in ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' tests on human cells.
See also
*DNA methyltransferase
In biochemistry, the DNA methyltransferase (DNA MTase, DNMT) family of enzymes catalyze the transfer of a methyl group to DNA. DNA methylation serves a wide variety of biological functions. All the known DNA methyltransferases use S-adenosyl ...
* SAM-I riboswitch
* SAM-II riboswitch
* SAM-III riboswitch
* SAM-IV riboswitch
* SAM-V riboswitch
* SAM-VI riboswitch
* List of investigational antidepressants
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Adenosyl Methionine, S- Alpha-Amino acids Coenzymes Dietary supplements Biology of bipolar disorder Psychopharmacology Sulfonium compounds