ruminants on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are
Medicine and Surgery of Camelids
, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biology and Evolution addresses the fact that camelids (including camels and llamas) are not ruminants, pseudo-ruminants, or modified ruminants. It has also been suggested that notoungulates also relied on rumination, as opposed to other atlantogenates that rely on the more typical
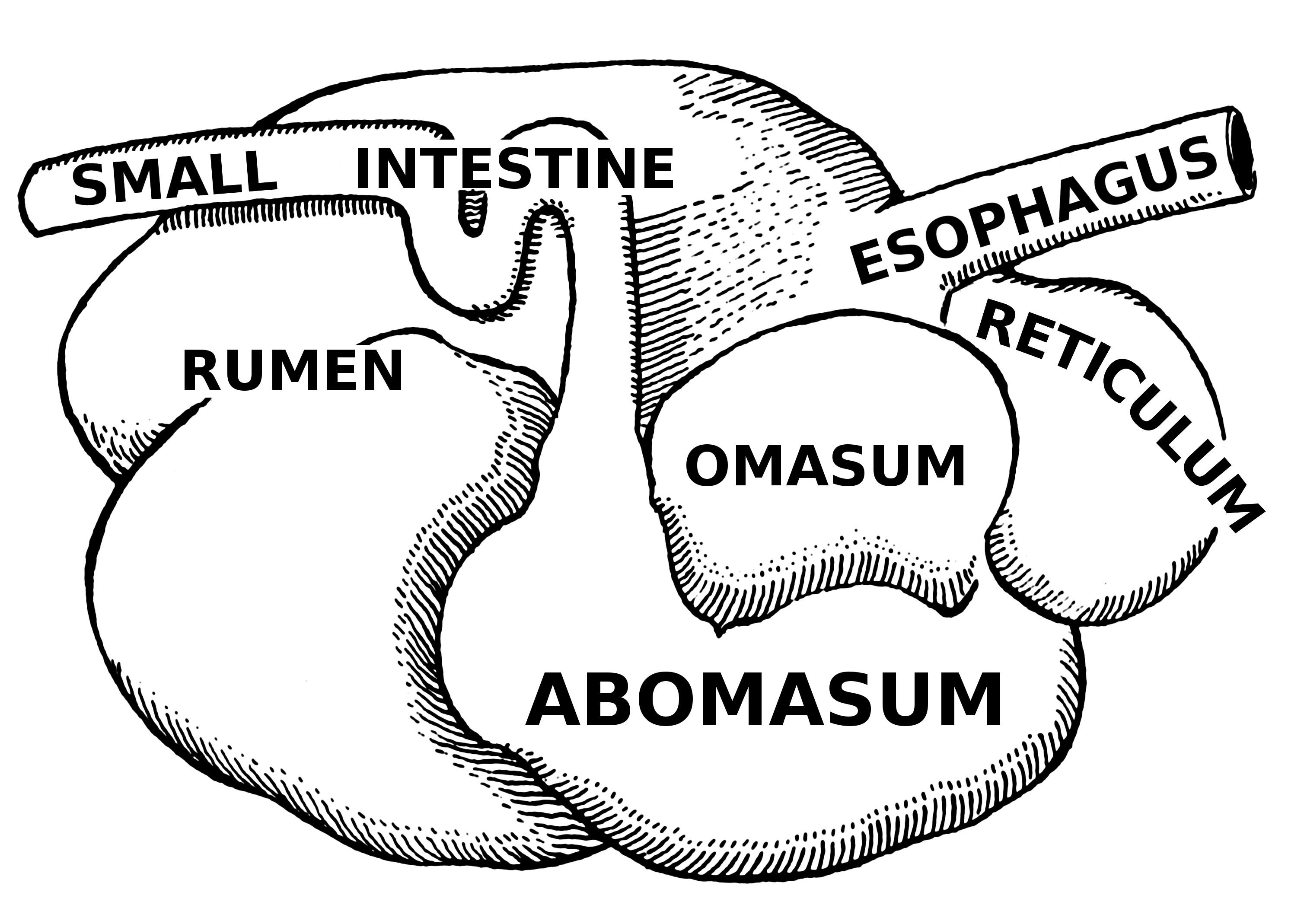
 The primary difference between ruminants and nonruminants is that ruminants' stomachs have four compartments:
#
The primary difference between ruminants and nonruminants is that ruminants' stomachs have four compartments:
#
"Ruminant ecology and evolution: Perspectives useful to livestock research and production"
''Journal of Dairy Science'', 93:1320–1334 and are native to all continents except Antarctica and Australia. Nearly 90% of all species are found in Eurasia and Africa. Species inhabit a wide range of climates (from tropic to arctic) and habitats (from open plains to forests). The population of domestic ruminants is greater than 3.5 billion, with cattle, sheep, and goats accounting for about 95% of the total population. Goats were domesticated in the Near East ''circa'' 8000 BC. Most other species were domesticated by 2500 BC., either in the Near East or southern Asia.
The effect of condensed tannins on the nutrition and health of ruminants fed fresh temperate forages: a review
Animal Feed Science and Technology 106(1):3–19 Tannins can be toxic to ruminants, in that they precipitate proteins, making them unavailable for digestion, and they inhibit the absorption of nutrients by reducing the populations of proteolytic rumen bacteria. Very high levels of tannin intake can produce
hoofed
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the r ...
herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In foo ...
it in a specialized stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again".
The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ...
, all domesticated and wild bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship be ...
s, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of ...
s, sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sh ...
, giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, '' Giraffa cameloparda ...
s, deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the ...
, gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, ''Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third ...
s, and antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
s.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids
, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biology and Evolution addresses the fact that camelids (including camels and llamas) are not ruminants, pseudo-ruminants, or modified ruminants. It has also been suggested that notoungulates also relied on rumination, as opposed to other atlantogenates that rely on the more typical
hindgut fermentation
Hindgut fermentation is a digestive process seen in monogastric herbivores, animals with a simple, single-chambered stomach. Cellulose is digested with the aid of symbiotic bacteria.Ruminantia
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. Th ...
is a lineage of herbivorous artiodactyls that includes the most advanced and widespread of the world's ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraff ...
s. The suborder Ruminantia includes six different families: Tragulidae, Giraffidae
The Giraffidae are a family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a common ancestor with deer and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe (one ...
, Antilocapridae, Moschidae
Moschidae is a family of pecoran even-toed ungulates, containing the musk deer (''Moschus'') and its extinct relatives. They are characterized by long 'saber teeth' instead of horns, antlers or ossicones, modest size (''Moschus'' only reaches ...
, Cervidae
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the rei ...
, and Bovidae
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species ...
.
Taxonomy and evolution
Hofmann and Stewart divided ruminants into three major categories based on their feed type and feeding habits: concentrate selectors, intermediate types, and grass/roughage eaters, with the assumption that feeding habits in ruminants cause morphological differences in their digestive systems, including salivary glands, rumen size, and rumen papillae. However, Woodall found that there is little correlation between the fiber content of a ruminant's diet and morphological characteristics, meaning that the categorical divisions of ruminants by Hofmann and Stewart warrant further research. Also, some mammals are pseudoruminants, which have a three-compartment stomach instead of four like ruminants. The Hippopotamidae (comprising hippopotami) are well-known examples. Pseudoruminants, like traditional ruminants, are foregut fermentors and most ruminate or chew cud. However, their anatomy and method of digestion differs significantly from that of a four-chambered ruminant. Monogastricherbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthp ...
s, such as rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family (biology), family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member ...
es, horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million ...
s, and rabbits
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit spe ...
, are not ruminants, as they have a simple single-chambered stomach. These hindgut fermenters digest cellulose in an enlarged cecum. In smaller hindgut fermenters of the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
Lagomorpha
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae (hares and rabbits) and the Ochotonidae ( pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek ''lagos'' (λαγ ...
(rabbits, hares, and pikas), cecotropes formed in the cecum are passed through the large intestine and subsequently reingested to allow another opportunity to absorb nutrients.
Phylogeny
Ruminantia is a crown group of ruminants within theorder
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poste ...
, cladistically defined by Spaulding et al. as "the least inclusive clade that includes '' Bos taurus'' (cow) and '' Tragulus napu'' (mouse deer)". Ruminantiamorpha is a higher-level clade of artiodactyls, cladistically defined by Spaulding et al. as "Ruminantia plus all extinct taxa more closely related to extant members of Ruminantia than to any other living species." This is a stem-based definition for Ruminantiamorpha, and is more inclusive than the crown group Ruminantia. As a crown group, Ruminantia only includes the last common ancestor
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are descended. The ...
of all extant (living) ruminants and their descendants (living or extinct), whereas Ruminantiamorpha, as a stem group, also includes more basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
extinct ruminant ancestors that are more closely related to living ruminants than to other members of Artiodactyla. When considering only living taxa (neontology
Neontology is a part of biology that, in contrast to paleontology, deals with living (or, more generally, ''recent'') organisms. It is the study of extant taxa (singular: extant taxon): taxa (such as species, genera and families) with members st ...
), this makes Ruminantiamorpha and Ruminantia synonymous, and only Ruminantia is used. Thus, Ruminantiamorpha is only used in the context of paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fos ...
. Accordingly, Spaulding grouped some genera of the extinct family Anthracotheriidae within Ruminantiamorpha (but not in Ruminantia), but placed others within Ruminantiamorpha's sister clade, Cetancodontamorpha.
Ruminantia's placement within Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poste ...
can be represented in the following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
:(see e.g. Fig S10)
Within Ruminantia, the Tragulidae (mouse deer) are considered the most basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
family, with the remaining ruminants classified as belonging to the infraorder Pecora. Until the beginning of the 21st century it was understood that the family Moschidae
Moschidae is a family of pecoran even-toed ungulates, containing the musk deer (''Moschus'') and its extinct relatives. They are characterized by long 'saber teeth' instead of horns, antlers or ossicones, modest size (''Moschus'' only reaches ...
(musk deer) was sister to Cervidae
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the rei ...
. However, a 2003 phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
study by Alexandre Hassanin (of National Museum of Natural History, France) and colleagues, based on mitochondrial and nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
analyses, revealed that Moschidae
Moschidae is a family of pecoran even-toed ungulates, containing the musk deer (''Moschus'') and its extinct relatives. They are characterized by long 'saber teeth' instead of horns, antlers or ossicones, modest size (''Moschus'' only reaches ...
and Bovidae
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species ...
form a clade sister to Cervidae
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the rei ...
. According to the study, Cervidae diverged from the Bovidae-Moschidae clade 27 to 28 million years ago. The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
is based on a large-scale genome ruminant genome sequence study from 2019:
Classification
* ORDERARTIODACTYLA
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poste ...
** Suborder Tylopoda
Tylopoda (meaning "calloused foot") is a suborder of terrestrial herbivorous even-toed ungulates belonging to the order Artiodactyla. They are found in the wild in their native ranges of South America and Asia, while Australian feral camels are ...
: camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. ...
s and llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with others as a herd. Their wool is so ...
s, 7 living species in 3 genera
** Suborder Suina
Suina (also known as Suiformes) is a suborder of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the domestic pig and peccaries. A member of this clade is known as a suine. Suina includes the family Suidae, termed suids, known in ...
: pigs and peccaries
A peccary (also javelina or skunk pig) is a medium-sized, pig-like hoofed mammal of the family Tayassuidae (New World pigs). They are found throughout Central and South America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and in the southwestern area of No ...
** Suborder Cetruminantia: ruminants, whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s and hippos
*** unranked Ruminantia
**** Infraorder Tragulina (paraphyletic)
***** Family † Prodremotheriidae
***** Family † Hypertragulidae
***** Family † Praetragulidae
***** Family † Protoceratidae
***** Family Tragulidae: chevrotain
Chevrotains, or mouse-deer, are small even-toed ungulates that make up the family Tragulidae, the only extant members of the infraorder Tragulina. The 10 extant species are placed in three genera, but several species also are known on ...
s, 6 living species in 4 genera
***** Family † Archaeomerycidae
***** Family † Lophiomerycidae
**** Infraorder Pecora
***** Family Cervidae
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the rei ...
: deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the ...
and moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
, 49 living species in 16 genera
***** Family † Gelocidae
***** Family † Palaeomerycidae
***** Family † Hoplitomerycidae
***** Family † Climacoceratidae
***** Family Giraffidae
The Giraffidae are a family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a common ancestor with deer and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe (one ...
: giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, '' Giraffa cameloparda ...
and okapi
The okapi (; ''Okapia johnstoni''), also known as the forest giraffe, Congolese giraffe, or zebra giraffe, is an artiodactyl mammal that is endemic to the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo in central Africa. It is the only species ...
, 2 living species in 2 genera
***** Family Antilocapridae: pronghorn, one living species in one genus
***** Family † Leptomerycidae
***** Family Moschidae
Moschidae is a family of pecoran even-toed ungulates, containing the musk deer (''Moschus'') and its extinct relatives. They are characterized by long 'saber teeth' instead of horns, antlers or ossicones, modest size (''Moschus'' only reaches ...
: musk deer
Musk deer can refer to any one, or all seven, of the species that make up ''Moschus'', the only extant genus of the family Moschidae. Despite being commonly called deer, they are not true deer belonging to the family Cervidae, but rather their f ...
, 4 living species in one genus
***** Family Bovidae
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species ...
: cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ...
, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of ...
s, sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sh ...
, and antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
, 143 living species in 53 genera
Digestive system of ruminants

 The primary difference between ruminants and nonruminants is that ruminants' stomachs have four compartments:
#
The primary difference between ruminants and nonruminants is that ruminants' stomachs have four compartments:
#rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allow ...
—primary site of microbial fermentation
# reticulum
# omasum—receives chewed cud, and absorbs volatile fatty acids
#abomasum
The abomasum, also known as the maw,The Cham ...
—true stomach
The first two chambers are the rumen and the reticulum. These two compartments make up the fermentation vat and are the major site of microbial activity. Fermentation is crucial to digestion because it breaks down complex carbohydrates, such as cellulose, and enables the animal to use them. Microbes function best in a warm, moist, anaerobic environment with a temperature range of 37.7 to 42.2 °C (100 to 108 °F) and a pH between 6.0 and 6.4. Without the help of microbes, ruminants would not be able to use nutrients from forages. The food is mixed with saliva and separates into layers of solid and liquid material. Solids clump together to form the cud or bolus
Bolus may refer to:
Geography
* Bolus, Iran, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran
* Bolus, or Baulus, an Anatolian village on the site of ancient Berissa
Medicine
* Bolus (digestion), a ball-shaped mass moving through the digestive tract
* Bolus ...
.
The cud is then regurgitated and chewed to completely mix it with saliva and to break down the particle size. Smaller particle size allows for increased nutrient absorption. Fiber, especially cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
and hemicellulose, is primarily broken down in these chambers by microbes (mostly bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, as well as some protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histor ...
, fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
, and yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to consti ...
) into the three volatile fatty acids (VFAs): acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
, propionic acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a li ...
, and butyric acid
Butyric acid (; from grc, βούτῡρον, meaning "butter"), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CO2H. It is an oily, colorless liquid with an unpl ...
. Protein and nonstructural carbohydrate (pectin
Pectin ( grc, πηκτικός ': "congealed" and "curdled") is a heteropolysaccharide, a structural acid contained in the primary lamella, in the middle lamella, and in the cell walls of terrestrial plants. The principal, chemical component o ...
, sugars
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, and starches
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
) are also fermented. Saliva is very important because it provides liquid for the microbial population, recirculates nitrogen and minerals, and acts as a buffer for the rumen pH. The type of feed the animal consumes affects the amount of saliva that is produced.
Though the rumen and reticulum have different names, they have very similar tissue layers and textures, making it difficult to visually separate them. They also perform similar tasks. Together, these chambers are called the reticulorumen. The degraded digesta, which is now in the lower liquid part of the reticulorumen, then passes into the next chamber, the omasum. This chamber controls what is able to pass into the abomasum. It keeps the particle size as small as possible in order to pass into the abomasum. The omasum also absorbs volatile fatty acids and ammonia.
After this, the digesta is moved to the true stomach, the abomasum. This is the gastric compartment of the ruminant stomach. The abomasum is the direct equivalent of the monogastric stomach, and digesta is digested here in much the same way. This compartment releases acids and enzymes that further digest the material passing through. This is also where the ruminant digests the microbes produced in the rumen. Digesta is finally moved into the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through t ...
, where the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs. The small intestine is the main site of nutrient absorption. The surface area of the digesta is greatly increased here because of the villi that are in the small intestine. This increased surface area allows for greater nutrient absorption. Microbes produced in the reticulorumen are also digested in the small intestine. After the small intestine is the large intestine. The major roles here are breaking down mainly fiber by fermentation with microbes, absorption of water (ions and minerals) and other fermented products, and also expelling waste. Fermentation continues in the large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being r ...
in the same way as in the reticulorumen.
Only small amounts of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, usi ...
are absorbed from dietary carbohydrates. Most dietary carbohydrates are fermented into VFAs in the rumen. The glucose needed as energy for the brain and for lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ...
and milk fat in milk production, as well as other uses, comes from nonsugar sources, such as the VFA propionate, glycerol, lactate, and protein. The VFA propionate is used for around 70% of the glucose and glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
produced and protein for another 20% (50% under starvation conditions).
Abundance, distribution, and domestication
Wild ruminants number at least 75 millionHackmann. T. J., and Spain, J. N. 201"Ruminant ecology and evolution: Perspectives useful to livestock research and production"
''Journal of Dairy Science'', 93:1320–1334 and are native to all continents except Antarctica and Australia. Nearly 90% of all species are found in Eurasia and Africa. Species inhabit a wide range of climates (from tropic to arctic) and habitats (from open plains to forests). The population of domestic ruminants is greater than 3.5 billion, with cattle, sheep, and goats accounting for about 95% of the total population. Goats were domesticated in the Near East ''circa'' 8000 BC. Most other species were domesticated by 2500 BC., either in the Near East or southern Asia.
Ruminant physiology
Ruminating animals have various physiological features that enable them to survive in nature. One feature of ruminants is their continuously growing teeth. During grazing, the silica content inforage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also us ...
causes abrasion of the teeth. This is compensated for by continuous tooth growth throughout the ruminant's life, as opposed to humans or other nonruminants, whose teeth stop growing after a particular age. Most ruminants do not have upper incisors; instead, they have a thick dental pad
The dental pad or browsing pad is a feature of ruminant dental anatomy that results from a lack of upper incisors and helps them gather large quantities of grass and other plant matter. This feature can be found in ruminants such as cattle and she ...
to thoroughly chew plant-based food. Another feature of ruminants is the large ruminal storage capacity that gives them the ability to consume feed rapidly and complete the chewing process later. This is known as rumination, which consists of the regurgitation of feed, rechewing, resalivation, and reswallowing. Rumination reduces particle size, which enhances microbial function and allows the digesta to pass more easily through the digestive tract.
Rumen microbiology
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s lack the ability to hydrolyse the beta –4glycosidic bond of plant cellulose due to the lack of the enzyme cellulase. Thus, ruminants completely depend on the microbial flora, present in the rumen or hindgut, to digest cellulose. Digestion of food in the rumen is primarily carried out by the rumen microflora, which contains dense populations of several species of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histor ...
, sometimes yeasts
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ...
and other fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
– 1 ml of rumen is estimated to contain 10–50 billion bacteria and 1 million protozoa, as well as several yeasts and fungi.
Since the environment inside a rumen is anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
*Adhesive#Anaerobic, Anaerobic ad ...
, most of these microbial species are obligate or facultative anaerobes that can decompose complex plant material, such as cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, hemicellulose, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
, and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s. The hydrolysis of cellulose results in sugars, which are further fermented to acetate, lactate, propionate, butyrate, carbon dioxide, and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
.
As bacteria conduct fermentation in the rumen, they consume about 10% of the carbon, 60% of the phosphorus, and 80% of the nitrogen that the ruminant ingests. To reclaim these nutrients, the ruminant then digests the bacteria in the abomasum
The abomasum, also known as the maw,The Cham ...
. The enzyme lysozyme
Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycosid ...
has adapted to facilitate digestion of bacteria in the ruminant abomasum. Pancreatic ribonuclease also degrades bacterial RNA in the ruminant small intestine as a source of nitrogen.
During grazing, ruminants produce large amounts of saliva – estimates range from 100 to 150 litres of saliva per day for a cow. The role of saliva is to provide ample fluid for rumen fermentation and to act as a buffering agent. Rumen fermentation produces large amounts of organic acids, thus maintaining the appropriate pH of rumen fluids is a critical factor in rumen fermentation. After digesta passes through the rumen, the omasum absorbs excess fluid so that digestive enzymes and acid in the abomasum are not diluted.
Tannin toxicity in ruminant animals
Tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner ...
s are phenolic compounds
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are c ...
that are commonly found in plants. Found in the leaf, bud, seed, root, and stem tissues, tannins are widely distributed in many different species of plants. Tannins are separated into two classes: hydrolysable tannins and condensed tannins. Depending on their concentration and nature, either class can have adverse or beneficial effects. Tannins can be beneficial, having been shown to increase milk production, wool growth, ovulation rate, and lambing percentage, as well as reducing bloat risk and reducing internal parasite burdens.B.R Min, et al (2003The effect of condensed tannins on the nutrition and health of ruminants fed fresh temperate forages: a review
Animal Feed Science and Technology 106(1):3–19 Tannins can be toxic to ruminants, in that they precipitate proteins, making them unavailable for digestion, and they inhibit the absorption of nutrients by reducing the populations of proteolytic rumen bacteria. Very high levels of tannin intake can produce
toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
that can even cause death. Animals that normally consume tannin-rich plants can develop defensive mechanisms against tannins, such as the strategic deployment of lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids incl ...
s and extracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with ...
s that have a high affinity to binding to tannins. Some ruminants (goats, deer, elk, moose) are able to consume food high in tannins (leaves, twigs, bark) due to the presence in their saliva of tannin-binding proteins.
Religious importance
TheLaw of Moses
The Law of Moses ( he, תֹּורַת מֹשֶׁה ), also called the Mosaic Law, primarily refers to the Torah or the first five books of the Hebrew Bible. The law revealed to Moses by God.
Terminology
The Law of Moses or Torah of Moses (Hebrew ...
in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts o ...
allowed the eating of some mammals that had cloven hooves (i.e. members of the order Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poste ...
) and "that chew the cud", a stipulation preserved to this day in Jewish dietary laws.
Other uses
The verb 'to ruminate' has been extendedmetaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wit ...
ically to mean to ponder thoughtfully or to meditate
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
on some topic. Similarly, ideas may be 'chewed on' or 'digested'. 'Chew the (one's) cud' is to reflect or meditate. In psychology, "rumination" refers to a pattern of thinking, and is unrelated to digestive physiology.
Ruminants and climate change
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
is produced by a type of archaea, called methanogens, as described above within the rumen, and this methane is released to the atmosphere. The rumen is the major site of methane production in ruminants. Methane is a strong greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), met ...
with a