Rubroboletus Satanas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Rubroboletus satanas'', commonly known as Satan's bolete or the Devil's bolete, is a
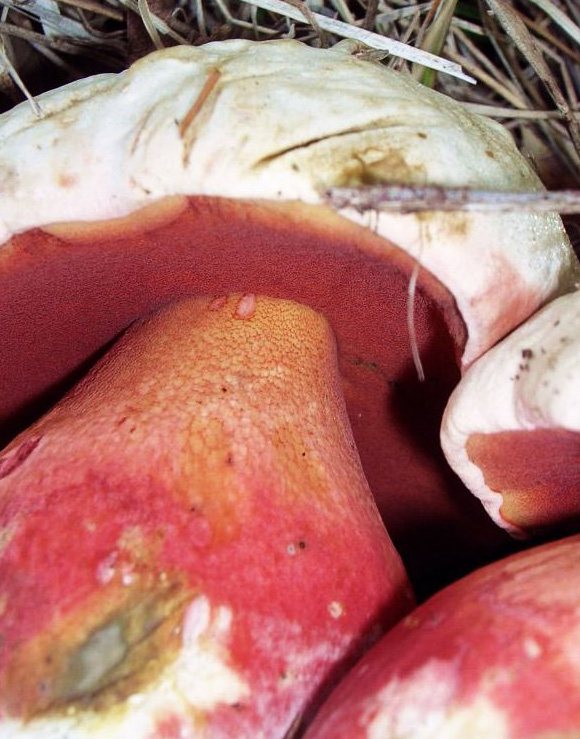 The free to slightly adnate tubes are up to long, pale yellow or greenish yellow and bluing when cut. The pores (tube mouths) are rounded, yellow to orange at first, but soon turning red from the point of their attachment to the stem outwards, eventually becoming entirely purplish red or carmine-red at full maturity and instantly bluing when touched or bruised. The stipe is , extraordinarily , very rarely long, distinctly bulbous (, extraordinarily , very rarely ), and often wider than its length, becoming more ventricose as the fungus expands but remaining bulbous at the base. Its colour is golden-yellow to orange at the apex, becoming increasingly pinkish-red to reddish-orange further down and deep carmine-red to purple-red towards the base. It is decorated in a fine, yellowish to reddish hexagonal net, sometimes confined to the upper half of the stipe. The flesh is thick, spongy and whitish, but may be yellow to straw-coloured in immature specimens and is sometimes reddish at the stem base. It slowly turns a faded blue colour when cut, bluing more intensely around the apex and above the tubes. The smell is weak and pleasantly musky in young fruit bodies, but becomes increasingly putrid in older specimens, reminiscent of carrion. Young specimens have a reportedly pleasant, nutty taste. The
The free to slightly adnate tubes are up to long, pale yellow or greenish yellow and bluing when cut. The pores (tube mouths) are rounded, yellow to orange at first, but soon turning red from the point of their attachment to the stem outwards, eventually becoming entirely purplish red or carmine-red at full maturity and instantly bluing when touched or bruised. The stipe is , extraordinarily , very rarely long, distinctly bulbous (, extraordinarily , very rarely ), and often wider than its length, becoming more ventricose as the fungus expands but remaining bulbous at the base. Its colour is golden-yellow to orange at the apex, becoming increasingly pinkish-red to reddish-orange further down and deep carmine-red to purple-red towards the base. It is decorated in a fine, yellowish to reddish hexagonal net, sometimes confined to the upper half of the stipe. The flesh is thick, spongy and whitish, but may be yellow to straw-coloured in immature specimens and is sometimes reddish at the stem base. It slowly turns a faded blue colour when cut, bluing more intensely around the apex and above the tubes. The smell is weak and pleasantly musky in young fruit bodies, but becomes increasingly putrid in older specimens, reminiscent of carrion. Young specimens have a reportedly pleasant, nutty taste. The
basidiomycete
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basid ...
fungus of the bolete family (Boletaceae
The Boletaceae are a Family (biology), family of mushroom-forming fungi, primarily characterised by small pores on the spore-bearing hymenium, hymenial surface (at the underside of the mushroom), instead of Lamella (mycology), gills as are found ...
) and one of its most infamous members. It was known as ''Boletus satanas'' before its transfer to the new genus '' Rubroboletus'' in 2014, based on molecular phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
data.
These squat, brightly coloured fruiting bodies are often massive and imposing, with a beige-coloured velvet-textured cap up to across, yellow to orange-red pores and a bulbous red stem. The flesh turns blue when cut or bruised and the fruit bodies often emit an unpleasant rotten odor.
Found in broad-leaved
A broad-leaved, broad-leaf, or broadleaf tree is any tree within the diverse botanical group of angiosperms that has flat leaves and produces seeds inside of fruits. It is one of two general types of trees, the other being a conifer, a tree with ne ...
and mixed woodland in the warmer regions of Europe, it is classified as a poisonous mushroom
Mushroom poisoning is poisoning resulting from the ingestion of mushrooms that contain toxic substances. Symptoms can vary from slight gastrointestinal discomfort to death in about 10 days. Mushroom toxins are secondary metabolites produced by th ...
, known to cause violent gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
. However, reports of poisoning are rare, due to the striking coloration and unpleasant odor of the fruiting bodies, which discourage experimentation.
Taxonomy
Originally known as ''Boletus satanas'', Satan's bolete was described by German mycologist Harald Othmar Lenz in 1831. Lenz was aware of several reports of adverse reactions from people who had consumed this fungus and apparently felt himself ill from its "emanations" while describing it, hence giving it its sinister epithet. TheGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word (''satanas'', or Satan
Satan, also known as the Devil, is a devilish entity in Abrahamic religions who seduces humans into sin (or falsehood). In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the '' yetzer hara'', or ' ...
) is derived from Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
''śāṭān'' (שטן). The American mycologist Harry D. Thiers
Harry Delbert Thiers (January 22, 1919, in Fort McKavett, Texas – August 8, 2000, in Ohio) was an American mycologist who studied and named many fungi native to North America, particularly California. Thiers taught mycology at San Francisco ...
concluded that material from North America matches the species description; however, genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
has since confirmed that western North American collections represent '' Rubroboletus eastwoodiae'', a different species.
Genetic analysis published in 2013 revealed that ''B. satanas'' and several other red-pored boletes are part of the "dupainii" clade (named after '' B. dupainii'') and are distantly nested from the core group of ''Boletus
''Boletus'' is a genus of mushroom-producing fungi, comprising over 100 species. The genus ''Boletus'' was originally broadly defined and described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753, essentially containing all fungi with hymenial pores instead of gills. ...
'' (including '' B. edulis'' and relatives) within the Boletineae
The Boletineae are a suborder of the fungal order Boletales. Families in the Boletineae include the Boletaceae and the Paxillaceae.
Taxa
*Paxillaceae
**'' Alpova''
**'' Austrogaster''
**'' Gyrodon''
**'' Hydnomerulius''
**'' Meiorganum''
**''Me ...
. This indicated that ''B. satanas'' and its relatives belonged to a distinct genus. The species was hence transferred to the new genus '' Rubroboletus'' in 2014, along with several allied red-pored, blue-staining bolete species. Genetic testing on several species of the genus revealed that ''R. satanas'' is most closely related to '' R. pulchrotinctus'', a morphologically similar but much rarer species occurring in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
regions.
Common names
Both ''Rubroboletus satanas'' and '' Suillellus luridus'' are known as ''ayimantari'' ('bear mushroom') in eastern Turkey.Description
The compactcap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
can reach an impressive , exceptionally , and very rarely in diameter. It is arguably the largest bolete found in Europe. At first it is hemispherical with an inrolled margin, but becomes convex at maturity as the fruit body expands, while in older specimens the margin might be slightly undulating. When young, the pileus is greyish white to silvery-white or buff, but older specimens tend to develop olivaceous, ochraceous or brownish tinges. The surface of the cap is finely tomentose
Trichomes (; ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a plant ...
, becoming smooth at maturity and is often slightly viscid in wet weather. The cuticle is tightly attached to the flesh and does not peel.
 The free to slightly adnate tubes are up to long, pale yellow or greenish yellow and bluing when cut. The pores (tube mouths) are rounded, yellow to orange at first, but soon turning red from the point of their attachment to the stem outwards, eventually becoming entirely purplish red or carmine-red at full maturity and instantly bluing when touched or bruised. The stipe is , extraordinarily , very rarely long, distinctly bulbous (, extraordinarily , very rarely ), and often wider than its length, becoming more ventricose as the fungus expands but remaining bulbous at the base. Its colour is golden-yellow to orange at the apex, becoming increasingly pinkish-red to reddish-orange further down and deep carmine-red to purple-red towards the base. It is decorated in a fine, yellowish to reddish hexagonal net, sometimes confined to the upper half of the stipe. The flesh is thick, spongy and whitish, but may be yellow to straw-coloured in immature specimens and is sometimes reddish at the stem base. It slowly turns a faded blue colour when cut, bluing more intensely around the apex and above the tubes. The smell is weak and pleasantly musky in young fruit bodies, but becomes increasingly putrid in older specimens, reminiscent of carrion. Young specimens have a reportedly pleasant, nutty taste. The
The free to slightly adnate tubes are up to long, pale yellow or greenish yellow and bluing when cut. The pores (tube mouths) are rounded, yellow to orange at first, but soon turning red from the point of their attachment to the stem outwards, eventually becoming entirely purplish red or carmine-red at full maturity and instantly bluing when touched or bruised. The stipe is , extraordinarily , very rarely long, distinctly bulbous (, extraordinarily , very rarely ), and often wider than its length, becoming more ventricose as the fungus expands but remaining bulbous at the base. Its colour is golden-yellow to orange at the apex, becoming increasingly pinkish-red to reddish-orange further down and deep carmine-red to purple-red towards the base. It is decorated in a fine, yellowish to reddish hexagonal net, sometimes confined to the upper half of the stipe. The flesh is thick, spongy and whitish, but may be yellow to straw-coloured in immature specimens and is sometimes reddish at the stem base. It slowly turns a faded blue colour when cut, bluing more intensely around the apex and above the tubes. The smell is weak and pleasantly musky in young fruit bodies, but becomes increasingly putrid in older specimens, reminiscent of carrion. Young specimens have a reportedly pleasant, nutty taste. The spore print
300px, Making a spore print of the mushroom ''Volvariella volvacea'' shown in composite: (photo lower half) mushroom cap laid on white and dark paper; (photo upper half) cap removed after 24 hours showing warm orange ("tussock") color spore print. ...
is olivaceous green.
The spores are fusiform (spindle-shaped) when viewed under a microscope and measure 10–16 × 4.5–7.5 μm
The micrometre (Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a unit of length in the International System ...
. The cap cuticle is composed of interwoven septate hyphae, which are often finely incrusted.
Similar species
Satan's bolete can be confused with a number of other species: *'' Rubroboletus rhodoxanthus'' is found predominantly onacidic soil
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a soil. Soil pH is a key characteristic that can be used to make informative analysis both qualitative and quantitatively regarding soil characteristics. pH is defined as the nega ...
, develops pinkish tinges of the cap, has a more or less cylindrical or clavate stipe with a very dense, well-developed net and lemon-yellow flesh that distinctly stains blue only in the cap when longitudinally sliced.
*''Rubroboletus legaliae
''Rubroboletus legaliae'', previously known as ''Boletus splendidus'', ''B. satanoides'', and ''B. legaliae'' is a basidiomycete fungus of the family Boletaceae. It is Mushroom poisoning, poisonous, with predominantly gastrointestinal s ...
'' is also acidophilous, has pinkish tinges on the cap, flesh that stains more extensively blue when cut and narrower spores, measuring 9–15 × 4–6 μm.
*'' Rubroboletus pulchrotinctus'' has a variable cap colour often featuring a pinkish band at the margin; has a dull-coloured stipe without deep red tinges, pores that remain yellow or orange even in mature fruit bodies, and somewhat narrower spores, measuring 12–15 × 4.5–6 μm.
*'' Rubroboletus rubrosanguineus'' is associated with spruce (''Picea
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' is the sole genus ...
'') or fir (''Abies
Firs are evergreen coniferous trees belonging to the genus ''Abies'' () in the family Pinaceae. There are approximately 48–65 extant species, found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Eurasia, and North Africa. The genu ...
''), has pinkish tinges on the cap and smaller spores, measuring 10–14.5 × 4–6 μm.
*''Caloboletus calopus
''Caloboletus calopus'', commonly known as the bitter bolete, bitter beech bolete or scarlet-stemmed bolete, is a species of fungus in the bolete family. Christiaan Persoon first described ''Boletus calopus'' in 1801. Modern molecular phylo ...
'' is usually associated with coniferous trees, has pores that remain persistently yellow even in overripe fruit bodies, has a more slender, cylindrical or clavate stipe and narrower spores, measuring 11–16 × 4–5.5 μm.
Distribution and habitat
''Rubroboletus satanas'' is widely distributed throughout the temperate zone, but is rare in most of its reported localities. In Europe, it mostly occurs in the southern regions and is rare or absent in northern countries. It fruits in the summer and early autumn in warm,broad-leaved
A broad-leaved, broad-leaf, or broadleaf tree is any tree within the diverse botanical group of angiosperms that has flat leaves and produces seeds inside of fruits. It is one of two general types of trees, the other being a conifer, a tree with ne ...
and mixed forests, forming ectomycorrhizal
An ectomycorrhiza (from Greek ἐκτός ', "outside", μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; ectomycorrhizas or ectomycorrhizae, abbreviated EcM) is a form of symbiotic relationship that occurs between a fungal symbiont, or mycobion ...
associations with oak (''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
'') and sweet chestnut (''Castanea
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Description
C ...
''), with a preference for calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime (mineral), lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of Science, scientific disciplines.
In zoology
''Calcare ...
(chalky) soils. Other frequently reported hosts are hornbeam (''Carpinus
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the family Betulaceae. Its species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Common names
The common English name ''hornbeam'' derives from the hard ...
''), beech (''Fagus
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of Mesophyte, mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted ...
'') and lime and linden trees (''Tilia
''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperateness, temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Great Bri ...
'').
In the United Kingdom, this striking bolete is found only in the south of England. It is rare in Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
, occurring primarily on a few islands in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
where conditions are favourable, with highly calcareous soil. In the eastern Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
region, it has been reported from the Bar'am Forest in the Upper Galilee
The Upper Galilee (, ''HaGalil Ha'Elyon''; , ''Al Jaleel Al A'alaa'') is a geographical region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Part of the larger Galilee region, it is characterized by its higher elevations and mountainous terra ...
region of northern Israel, as well as the island of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, where it is found in association with the narrow-endemic golden oak (''Quercus alnifolia
''Quercus alnifolia'', commonly known as the golden oak, is an evergreen oak species of Cyprus. Its common English name refers to the golden coloured lower surface of its leaves. ''Quercus alnifolia'' belongs to the endemic flora of the island a ...
''). It has further been documented in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
and eastern Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
regions of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, as well as Crimea and Ukraine, with its distribution possibly extending as far south as Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.
In the past, ''R. satanas'' had been reported from the United States, but these sightings are instead of the closely related species '' Rubroboletus eastwoodiae''.
Toxicity
This mushroom is moderatelypoisonous
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
, especially if eaten raw. The symptoms, which are predominantly gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
in nature, include nausea, abdominal pain, and violent vomiting with bloody diarrhea that can last up to six hours.
The toxic enzyme bolesatine has been isolated from fruiting bodies of ''R. satanas'' and is implicated in the poisonings. Bolesatine is a protein synthesis inhibitor
A protein synthesis inhibitor is a compound that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins.
While a broad interpretation of this definition could be used t ...
and, when given to mice, causes massive thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
. At lower concentrations, bolesatine is a mitogen
A mitogen is a small bioactive protein or peptide that induces a cell to begin cell division, or enhances the rate of division (mitosis). Mitogenesis is the induction (triggering) of mitosis, typically via a mitogen.
The cell cycle
Mitogens a ...
, inducing cell division in human T lymphocyte
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s. Muscarine
Muscarine, L-(+)-muscarine, or muscarin is a Secondary metabolite, natural product found in certain mushrooms, particularly in ''Inocybe'' and ''Clitocybe'' species, such as the deadly ''Clitocybe dealbata, C. dealbata''. Mushrooms in the g ...
has also been isolated from this fungus, but the quantities are believed to be far too small to cause toxic effects in humans. More recent studies have associated the poisoning caused by ''R. satanas'' with hyperprocalcitonemia, and classified it as a distinct syndrome among fungal poisonings.White J, Weinstein SA, De Haro L, Bédry R, Schaper A, Rumack BH, Zilker T. (2018). Mushroom poisoning: a proposed new clinical classification. Toxicon. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.11.007
Controversially, English mycologist John Ramsbottom reported in 1953 that ''R. satanas'' is consumed in certain parts of Italy and the former Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
. In those regions, the fungus is reportedly eaten following prolonged boiling that may neutralise the toxins, though this has never been proven scientifically. Similar reports exist from the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a List of regions of California, region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay, and anchored by the cities of Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose, California, S ...
of the United States, but probably involve a different fungus misidentified as ''R. satanas''. Ramsbottom speculated that there may be a regional variation in its toxicity, and conceded that the fungus may not be as poisonous as widely reported. Nevertheless, ''R. satanas'' is rarely sampled casually, not least because of the foul smell, which in addition to their bright red colour and blue staining, make this fungus unappealing for human consumption.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q26203731, from2=Q274407 Poisonous fungi satanas Fungi of Europe Fungi described in 1831 Fungus species