Rotane on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
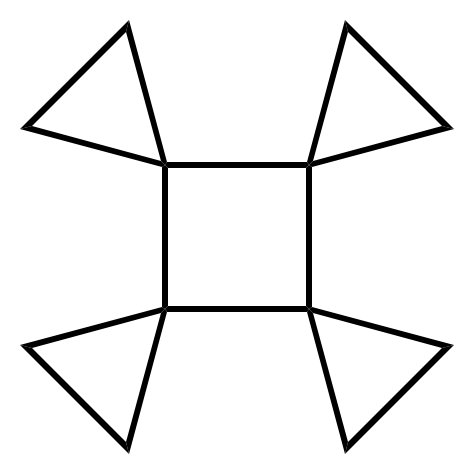 A rotane is a hydrocarbon consisting of a central
A rotane is a hydrocarbon consisting of a central
 A rotane is a hydrocarbon consisting of a central
A rotane is a hydrocarbon consisting of a central cycloalkane
In organic chemistry, the cycloalkanes (also called naphthenes, but distinct from naphthalene) are the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, a cycloalkane consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a structure containing ...
ring with cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself ...
units spiro-linked to each corner. The systematic naming pattern for these molecules is " 'n''otane", where ''n'' is the number of atoms in the central ring.
The simplest such chemical, otane, consists solely of a branched array of spiro-cyclopropane units, and is thus a branched triangulane
A triangulane is a hydrocarbon consisting exclusively of a series of spiro-linked cyclopropane rings.
Triangulanes are named according to the rules of systematic nomenclature for spiro compounds. The pattern of their common names is " 'n''riangu ...
.
References
* Hydrocarbons Cyclopropanes Spiro compounds {{Hydrocarbon-stub