Rosemary Bamforth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rosemary Bamforth (19 October 1924 – 17 April 2018) was a Scottish
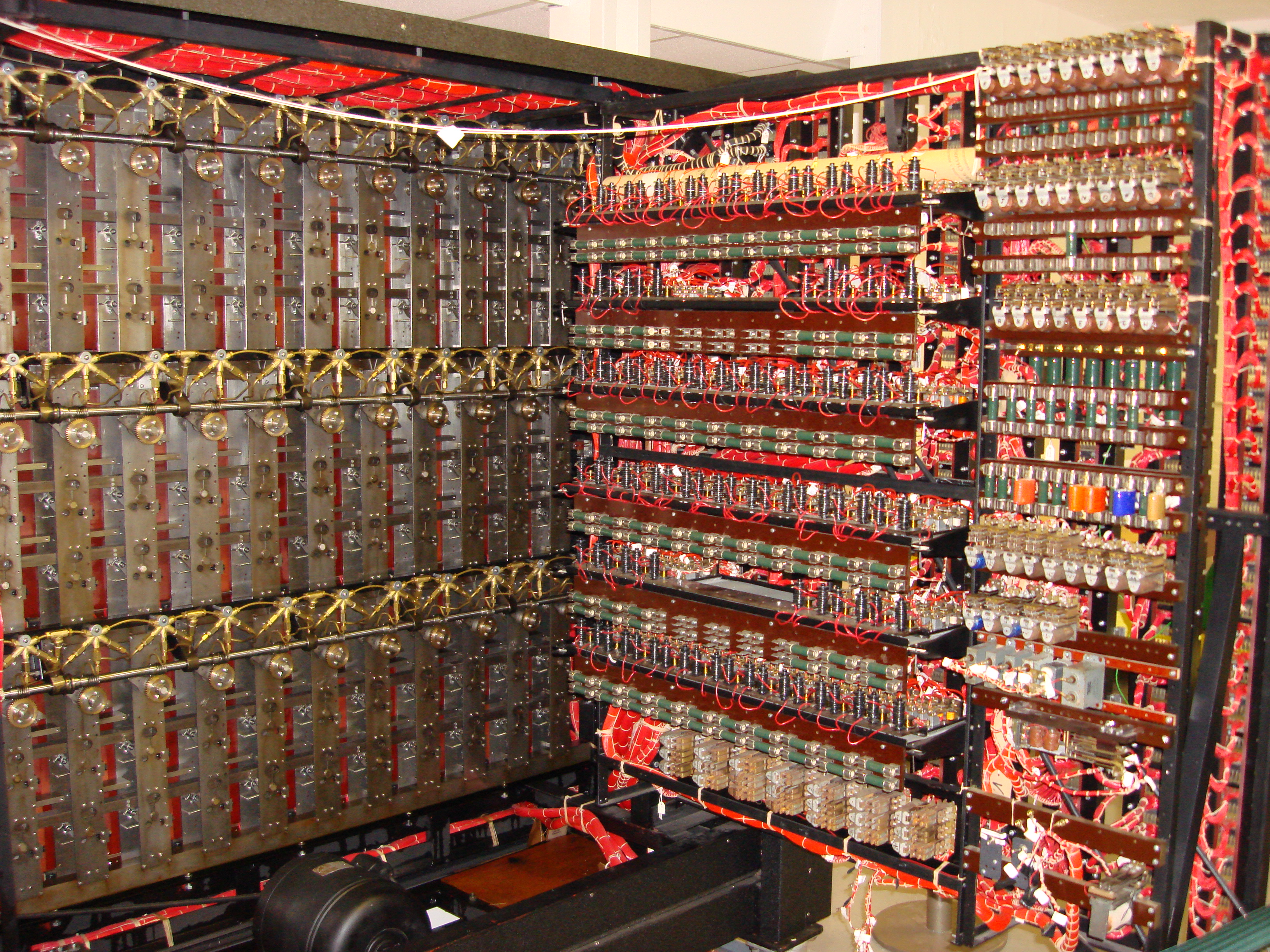 Bamforth completed her initial WRNS at Balloch by
Bamforth completed her initial WRNS at Balloch by
pathologist
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
who worked at Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the S ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Working as a consultant at Southampton Hospital, she made an early link in her research between ship workers dying of mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lini ...
and asbestos
Asbestos ( ) is a group of naturally occurring, Toxicity, toxic, carcinogenic and fibrous silicate minerals. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous Crystal habit, crystals, each fibre (particulate with length su ...
exposure on ships, before the cause of this illness had been fully determined.
Personal life
Born Rosemary Ince, Bamforth, was born inGlasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
on 19 October 1924. Her parents were Isobel and Douglas Ince, a director of an engineering company. She was one of two children and her brother David Ince, was a Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
pilot during World War II. Bamforth met John Bamforth while they were both working as doctors at Southampton General Hospital
Southampton General Hospital (SGH) is a large teaching hospital in Southampton, Hampshire, England run by University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust.
History
The hospital was founded in 1900 as the Southampton Union Infirmary in S ...
. They married in 1960 and together had two daughters and a son.
Bamforth died on the 17 April 2018 at the age of 93.
Education
Bamforth attendedLaurel Bank School
Laurel may refer to:
Plants
* Lauraceae, the laurel family
* Laurel (plant), including a list of trees and plants known as laurel
People
* Laurel (given name), people with the given name
* Laurel (surname), people with the surname
* Laurel (mu ...
in Glasgow followed by Beacon School in Bridge of Allan
Bridge of Allan (, ), also known colloquially as ''Bofa'', is a former spa town in the Stirling (council area), Stirling council area in Scotland, just north of the city of Stirling.
Overlooked by the National Wallace Monument, it lies on th ...
, she then went on to attend Cheltenham Ladies College
Cheltenham Ladies' College (CLC) is a private boarding and day school for girls aged 11 or older in Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, England. The school was established in 1853 to provide "a sound academic education for girls". It is also a member ...
.
She planned to study medicine at the University of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow (abbreviated as ''Glas.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals; ) is a Public university, public research university in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded by papal bull in , it is the List of oldest universities in continuous ...
and applied at the age of 16. She was politely rejected and asked to apply again once she was 17. In 1941, she joined instead the Women's Royal Naval Service
The Women's Royal Naval Service (WRNS; popularly and officially known as the Wrens) was the women's branch of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. First formed in 1917 for the World War I, First World War, it was disbanded in 1919, then revived in ...
(WRNS). Bamforth returned to studying medicine after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and matriculated in 1946 at the University of Glasgow. She graduated with a Bachelor of Medicine
A Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (; MBBS, also abbreviated as BM BS, MB ChB, MB BCh, or MB BChir) is a medical degree granted by medical schools or universities in countries that adhere to the United Kingdom's higher education tradi ...
in 1951 having received a Further Education and Training Grant.
Military service
 Bamforth completed her initial WRNS at Balloch by
Bamforth completed her initial WRNS at Balloch by Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond (; ) is a freshwater Scottish loch which crosses the Highland Boundary Fault (HBF), often considered the boundary between the lowlands of Central Scotland and the Highlands.Tom Weir. ''The Scottish Lochs''. pp. 33-43. Published by ...
. She was then posted to Outstation Eastcote in Hillingdon
Hillingdon is an area of Uxbridge within the London Borough of Hillingdon, centred 14.2 miles (22.8 km) west of Charing Cross. It was an ancient parish in Middlesex that included the market town of Uxbridge. During the 1920s the civil pari ...
, one of the outstations of Bletchley Park, where she was taught teleprinting. She moved from there to the Bletchley outstation at Stanmore, before eventually joining the team of Hut 11 in Bletchley Park, working on the Turing-Welchman Bombe machines. Bamforth had to keep these details of her military service secret until the mid-1970s when the history of Bletchley Park was declassified.
Career
After graduating, Bamforth built her medical experience at hospitals in North America (McGill University
McGill University (French: Université McGill) is an English-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 by royal charter,Frost, Stanley Brice. ''McGill University, Vol. I. For the Advancement of Learning, ...
and Meadowbrook Hospital, Long Island) and the UK, where she practised at hospitals in London, Southampton and Portsmouth. Bamforth specialised as a pathologist and during her time in the United States, she became a recognised specialist in the analysis and diagnosis of cancer from the study of tissue samples.
While working at Southampton Hospital as a senior registrar, Bamforth made the link between a number of ship workers dying of mesothelioma and asbestos exposure on ships. She delivered a paper on her findings to Southampton doctors. Her conclusions raised controversy in the profession at the time, but were later backed up by subsequent research into asbestosis
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis, scarring of the human lung, lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest pain, chest tightness. Complications may include lung canc ...
.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bamforth, Rosemary 1924 births 2018 deaths People educated at Laurel Bank School Scottish pathologists Bletchley Park women 20th-century Scottish women scientists Scientists from Glasgow 20th-century Scottish scientists Alumni of the University of Glasgow People educated at Cheltenham Ladies' College Bletchley Park people Women's Royal Naval Service personnel of World War II