Rose Handler's Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sporotrichosis, also known as rose handler's disease, is a
 * ''Cutaneous or skin sporotrichosis''
:This is the most common form of this disease. Symptoms of this form include nodular
* ''Cutaneous or skin sporotrichosis''
:This is the most common form of this disease. Symptoms of this form include nodular
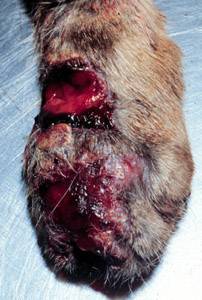 Sporotrichosis can be diagnosed in domestic and wild mammals. In veterinary medicine it is most frequently seen in cats and horses. Cats have a particularly severe form of cutaneous sporotrichosis. Infected cats may exhibit abscesses, cellulitis, or draining wounds that fail to respond to antibiotic treatment.
Sporotrichosis can spread from nonhuman animals to humans (
Sporotrichosis can be diagnosed in domestic and wild mammals. In veterinary medicine it is most frequently seen in cats and horses. Cats have a particularly severe form of cutaneous sporotrichosis. Infected cats may exhibit abscesses, cellulitis, or draining wounds that fail to respond to antibiotic treatment.
Sporotrichosis can spread from nonhuman animals to humans (
fungal infection
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected: superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common ...
that may be localised to skin, lungs, bone and joint, or become systemic. It presents with firm painless nodules
Nodule may refer to:
*Nodule (geology), a small rock or mineral cluster
*Manganese nodule, a metallic concretion found on the seafloor
*Nodule (medicine), a small aggregation of cells
*Root nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, p ...
that later ulcerate
Ulcerate is a New Zealand-based extreme metal band formed by guitarist Michael Hoggard and drummer Jamie Saint Merat in 2000. The band have released seven studio albums to date. The band have been featured in numerous articles as one of New Ze ...
. Following initial exposure to ''Sporothrix schenckii
''Sporothrix schenckii'', a fungus that can be found worldwide in the environment, is named for medical student Benjamin Schenck, who in 1896 was the first to isolate it from a human specimen. The species is present in soil as well as in and on l ...
'', the disease typically progresses over a period of a week to several months. Serious complications may develop in people who have a weakened immune system
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affec ...
.
Sporotrichosis is caused by fungi of the ''S. schenckii'' species complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each oth ...
. Because ''S. schenckii'' is naturally found in soil, hay
Hay is grass, legumes, or other herbaceous plants that have been cut and dried to be stored for use as animal fodder, either for large grazing animals raised as livestock, such as cattle, horses, goats, and sheep, or for smaller domesticate ...
, sphagnum moss
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since ...
, and plants, it most often affects farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer ...
s, gardeners, and agricultural workers. It enters through small cuts in the skin to cause a fungal infection. In cases of sporotrichosis affecting the lungs, the fungal spores enter by inhalation
Inhalation (or inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
. Sporotrichosis can be acquired by handling cats with the disease; it is an occupational hazard for veterinarians.
Treatment depends on the site and extent of infection. Topical antifungal
Topical antifungal drugs are used to treat fungal infections on the skin, scalp, nails, vagina or inside the mouth. These medications come as creams, gels, lotions, ointments, powders, shampoos, tinctures and sprays. Most antifungal drugs induce fu ...
s may be applied to skin lesions. Deep infection in the lungs may require surgery. Systemic medications used include Itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given ...
, posaconazole
Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication.
It was approved for medical use in the European Union in October 2005, and in the United States in September 2006. It is available as a generic ...
and amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococ ...
. With treatment, most people will recover, but an immunocompromised status and systemic infection carry a worse prognosis.
''S. schenkii'', the causal fungus, is found worldwide. The species was named for Benjamin Schenck, a medical student who, in 1896, was the first to isolate it from a human specimen.
Sporotrichosis has been reported in cats, mules, dogs, mice and rats.
Signs and symptoms
 * ''Cutaneous or skin sporotrichosis''
:This is the most common form of this disease. Symptoms of this form include nodular
* ''Cutaneous or skin sporotrichosis''
:This is the most common form of this disease. Symptoms of this form include nodular lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
s or bumps in the skin, at the point of entry and also along lymph
Lymph () is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the ori ...
nodes and vessels. The lesion starts off small and painless, and ranges in color from pink to purple. Left untreated, the lesion becomes larger and look similar to a boil
A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, which is an infection of the hair follicle. It is most commonly caused by infection by the bacterium ''Staphylococcus aureus'', resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by ...
and more lesions will appear, until a chronic ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughin ...
develops.
:Usually, cutaneous sporotrichosis lesions occur in the finger, hand, and arm.
* ''Pulmonary sporotrichosis''
:This rare form of the disease occurs when ''S. schenckii'' spores are inhaled. Symptoms of pulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
sporotrichosis include productive cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing, nodules and cavitations of the lungs, fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
, and swollen hilar lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s. Patients with this form of sporotrichosis are susceptible to developing tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
* ''Disseminated sporotrichosis''
:When the infection spreads from the initial site to secondary sites in the body, the disease develops into an uncommon and potentially life-threatening form, called disseminated
To disseminate (from lat. ''disseminare'' "scattering seeds"), in the field of communication, is to broadcast a message to the public without direct feedback from the audience.
Meaning
Dissemination takes on the theory of the traditional view ...
sporotrichosis. The infection can spread to joints and bones (called ''osteoarticular sporotrichosis'') as well as the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
and the brain (called ''sporotrichosis meningitis'').
:Some symptoms of disseminated sporotrichosis include weight loss, anorexia
Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by Calorie restriction, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin.
Individuals wit ...
, and bone lesions.
Complications
Open sporotrichosis lesions on the skin will on occasion become superinfected with bacteria.Cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
may also occur.
Diagnosis
Sporotrichosis is an acute infection with slow progression and often subtle symptoms. It is often difficult to diagnose, as many other diseases share similar symptoms and therefore must be ruled out. Patients with sporotrichosis will haveantibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
against the fungus ''S. schenckii''; however, due to variability in sensitivity and specificity, antibody detection may not be a reliable diagnostic test for this disease. The confirming diagnosis remains culturing the fungus from the skin, sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked-eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections, and Cytopathology, cytological ...
, synovial fluid
Synovial fluid, also called synovia, elp 1/sup> is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articul ...
, and cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
. Smears should be taken from any draining fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
s or ulcers.
Cats with sporotrichosis are unique in that the exudate
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation.
''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin language, Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat').
Medi ...
from their lesions may contain numerous infectious organisms. This makes cytological evaluation of exudate a valuable diagnostic tool in this species. Exudate is pyogranulomatous, and phagocytic cells
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ...
may be packed with yeast forms. These yeast cells are variable in size; many are cigar-shaped.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnoses includes:leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' an ...
, nocardiosis
Nocardiosis is an infectious disease affecting either the lungs (''pulmonary nocardiosis'') or the whole body (''systemic nocardiosis''). It is due to infection by a bacterium of the genus ''Nocardia'', most commonly ''Nocardia asteroides'' or ''N ...
, mycobacterium marinum
''Mycobacterium marinum'' is a slow growing fresh and saltwater mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus ''Mycobacterium'' and the phylum Actinobacteria. It was formerly known as ''Mycobacterium balnei''. The strain marinum was first identified ...
, cat-scratch disease
Cat-scratch disease (CSD) is an infectious disease that most often results from a scratch or bite of a cat. Symptoms typically include a non-painful bump or blister at the site of injury and painful and swollen lymph nodes. People may feel tire ...
, leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respir ...
, syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
, sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph n ...
and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
.
Prevention
The majority of sporotrichosis cases occur when the fungus is introduced through a cut or puncture in the skin while handling vegetation containing the fungal spores. Prevention of this disease includes wearing long sleeves and gloves while working with soil, hay bales, rose bushes, pine seedlings, and sphagnum moss. The risk of sporotrichosis in cats is increased in male cats that roam outdoors. Accordingly, the risk may be reduced by keeping cats indoors or neutering them. Isolating infected animals can also be a preventive measure. The risk of spread from infected cats to humans can be reduced by appropriate biosafety measures, including wearingpersonal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
when handling a cat with suspected sporotrichosis and by washing hands, arms and clothing after handling the cat.
Treatment
Treatment of sporotrichosis depends on the severity and location of the disease. The following are treatment options for this condition: * Oralpotassium iodide
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound, medication, and dietary supplement. It is a medication used for treating hyperthyroidism, in radiation emergencies, and for protecting the thyroid gland when certain types of radiopharmaceuticals are u ...
:Potassium iodide is an anti-fungal drug that is widely used as a treatment for cutaneous sporotrichosis. Despite its wide use, there is no high-quality evidence for or against this practice. Further studies are needed to assess the efficacy and safety of oral potassium iodide in the treatment of sporotrichosis.
* Itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given ...
(Sporanox) and fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. These include candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and tinea versicolor. It is also used to pr ...
:These are antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as ...
drugs. Itraconazole is currently the drug of choice and is significantly more effective than fluconazole. Fluconazole should be reserved for patients who cannot tolerate itraconazole.
* Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococ ...
:This antifungal medication is delivered intravenously. Many patients, however, cannot tolerate Amphotericin B due to its potential side effects of fever, nausea, and vomiting.
:Lipid formulations of amphotericin B are usually recommended instead of amphotericin B deoxycholate because of a better adverse-effect profile. Amphotericin B can be used for severe infection during pregnancy. For children with disseminated or severe disease, amphotericin B deoxycholate can be used initially, followed by itraconazole.
:In case of sporotrichosis meningitis, the patient may be given a combination of Amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine/Flucytosine
Flucytosine, also known as 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), is an antifungal medication. It is specifically used, together with amphotericin B, for serious ''Candida'' infections and cryptococcosis. It may be used by itself or with other antifungals for ...
.
* Terbinafine
Terbinafine, sold under the brand name Lamisil among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat pityriasis versicolor, onychomycosis, fungal nail infections, and ringworm including jock itch and athlete's foot. It is either oral adminis ...
:500mg and 1000mg daily dosages of terbinafine for twelve to 24 weeks has been used to treat cutaneous sporotrichosis.
* Newer triazole
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial Isomer, isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms w ...
s
:Several studies have shown that posaconazole
Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication.
It was approved for medical use in the European Union in October 2005, and in the United States in September 2006. It is available as a generic ...
has in vitro activity similar to that of amphotericin B and itraconazole; therefore, it shows promise as an alternative therapy. However, voriconazole
Voriconazole, sold under the brand name Vfend among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, penicilliosis, and infections b ...
susceptibility varies. Because the correlation between in vitro data and clinical response has not been demonstrated, there is insufficient evidence to recommend either posaconazole or voriconazole for treatment of sporotrichosis at this time.
* Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
:In cases of bone infection and cavitary nodules in the lungs, surgery may be necessary.
* Heat therapy
Heat therapy, also called thermotherapy, is the use of heat in therapy, such as for pain relief and health. It can take the form of a hot cloth, hot water bottle, ultrasound, heating pad, hydrocollator packs, whirlpool baths, cordless FIR heat ...
:Heat creates higher tissue temperatures, which may inhibit fungus growth while the immune system counteracts the infection. The "pocket warmer" used for this purpose has the advantage of being able to maintain a constant temperature of 44 degrees-45 degrees C on the skin surface for several hours, while permitting unrestricted freedom of movement. The duration of treatment depends on the type of lesion, location, depth, and size. Generally, local application for 1-2 h per day, or in sleep time, for 5-6 weeks seems to be sufficient.
Other animals
 Sporotrichosis can be diagnosed in domestic and wild mammals. In veterinary medicine it is most frequently seen in cats and horses. Cats have a particularly severe form of cutaneous sporotrichosis. Infected cats may exhibit abscesses, cellulitis, or draining wounds that fail to respond to antibiotic treatment.
Sporotrichosis can spread from nonhuman animals to humans (
Sporotrichosis can be diagnosed in domestic and wild mammals. In veterinary medicine it is most frequently seen in cats and horses. Cats have a particularly severe form of cutaneous sporotrichosis. Infected cats may exhibit abscesses, cellulitis, or draining wounds that fail to respond to antibiotic treatment.
Sporotrichosis can spread from nonhuman animals to humans (zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When ...
). Infected cats in particular exude large quantities of ''Sporothrix'' organisms from their skin leasions and can spread the infection to people who handle them. Although cats are the most common animal source, the infection has also been known to spread to humans from dogs, rats, squirrels, and armadillos.
See also
*Mucormycosis
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a severe fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the ...
* List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function o ...
References
External links
{{Mycoses Animal fungal diseases Bird diseases Bovine diseases Cat diseases Horse diseases Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions Rodent diseases Sheep and goat diseases Swine diseases Zoonoses Fungal diseases