Rome Summit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rome (

 After the foundation by Romulus according to a legend, Rome was ruled for a period of 244 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of
After the foundation by Romulus according to a legend, Rome was ruled for a period of 244 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of
 In 27 BC, Octavian was named ''
In 27 BC, Octavian was named '' After the end of the
After the end of the  Rome, which had lost its central role in the administration of the empire, was sacked in 410 by the
Rome, which had lost its central role in the administration of the empire, was sacked in 410 by the
 After the
After the
 The rule of the Popes was interrupted by the short-lived Roman Republic (18th century), Roman Republic (1798–1800), which was established under the influence of the French Revolution. The
The rule of the Popes was interrupted by the short-lived Roman Republic (18th century), Roman Republic (1798–1800), which was established under the influence of the French Revolution. The  Soon after World War I in late 1922 Rome witnessed the rise of Italian Fascism led by Benito Mussolini, who led a March on Rome, march on the city. He did away with democracy by 1926, eventually declaring a new Imperial Italy (fascist), Italian Empire and allying Italy with Nazi Germany in 1938. Mussolini demolished fairly large parts of the city centre in order to build wide avenues and squares which were supposed to celebrate the fascist regime and the resurgence and glorification of classical Rome. The interwar period saw a rapid growth in the city's population which surpassed one million inhabitants soon after 1930. During World War II, due to the art treasuries and the presence of the Vatican, Rome largely escaped the tragic destiny of other European cities. However, on 19 July 1943, the Quartiere San Lorenzo, San Lorenzo district was Bombing of Rome in World War II, subject to Allied bombing raids, resulting in about 3,000 fatalities and 11,000 injuries, of whom another 1,500 died. Mussolini Fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, was arrested on 25 July 1943. On the date of the Armistice of Cassibile, Italian Armistice 8 September 1943 the city was occupied by the Germans. Allied bombing raids continued throughout 1943 and extended into 1944. Rome was liberated on 4 June 1944.
Rome developed greatly after the war as part of the "Italian economic miracle" of post-war reconstruction and modernisation in the 1950s and early 1960s. During this period, the years of ''la dolce vita'' ("the sweet life"), Rome became a fashionable city, with popular classic films such as ''Ben-Hur (1959 film), Ben Hur'', ''Quo Vadis (1951 film), Quo Vadis'', ''Roman Holiday'' and ''La Dolce Vita'' filmed in the city's iconic
Soon after World War I in late 1922 Rome witnessed the rise of Italian Fascism led by Benito Mussolini, who led a March on Rome, march on the city. He did away with democracy by 1926, eventually declaring a new Imperial Italy (fascist), Italian Empire and allying Italy with Nazi Germany in 1938. Mussolini demolished fairly large parts of the city centre in order to build wide avenues and squares which were supposed to celebrate the fascist regime and the resurgence and glorification of classical Rome. The interwar period saw a rapid growth in the city's population which surpassed one million inhabitants soon after 1930. During World War II, due to the art treasuries and the presence of the Vatican, Rome largely escaped the tragic destiny of other European cities. However, on 19 July 1943, the Quartiere San Lorenzo, San Lorenzo district was Bombing of Rome in World War II, subject to Allied bombing raids, resulting in about 3,000 fatalities and 11,000 injuries, of whom another 1,500 died. Mussolini Fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, was arrested on 25 July 1943. On the date of the Armistice of Cassibile, Italian Armistice 8 September 1943 the city was occupied by the Germans. Allied bombing raids continued throughout 1943 and extended into 1944. Rome was liberated on 4 June 1944.
Rome developed greatly after the war as part of the "Italian economic miracle" of post-war reconstruction and modernisation in the 1950s and early 1960s. During this period, the years of ''la dolce vita'' ("the sweet life"), Rome became a fashionable city, with popular classic films such as ''Ben-Hur (1959 film), Ben Hur'', ''Quo Vadis (1951 film), Quo Vadis'', ''Roman Holiday'' and ''La Dolce Vita'' filmed in the city's iconic
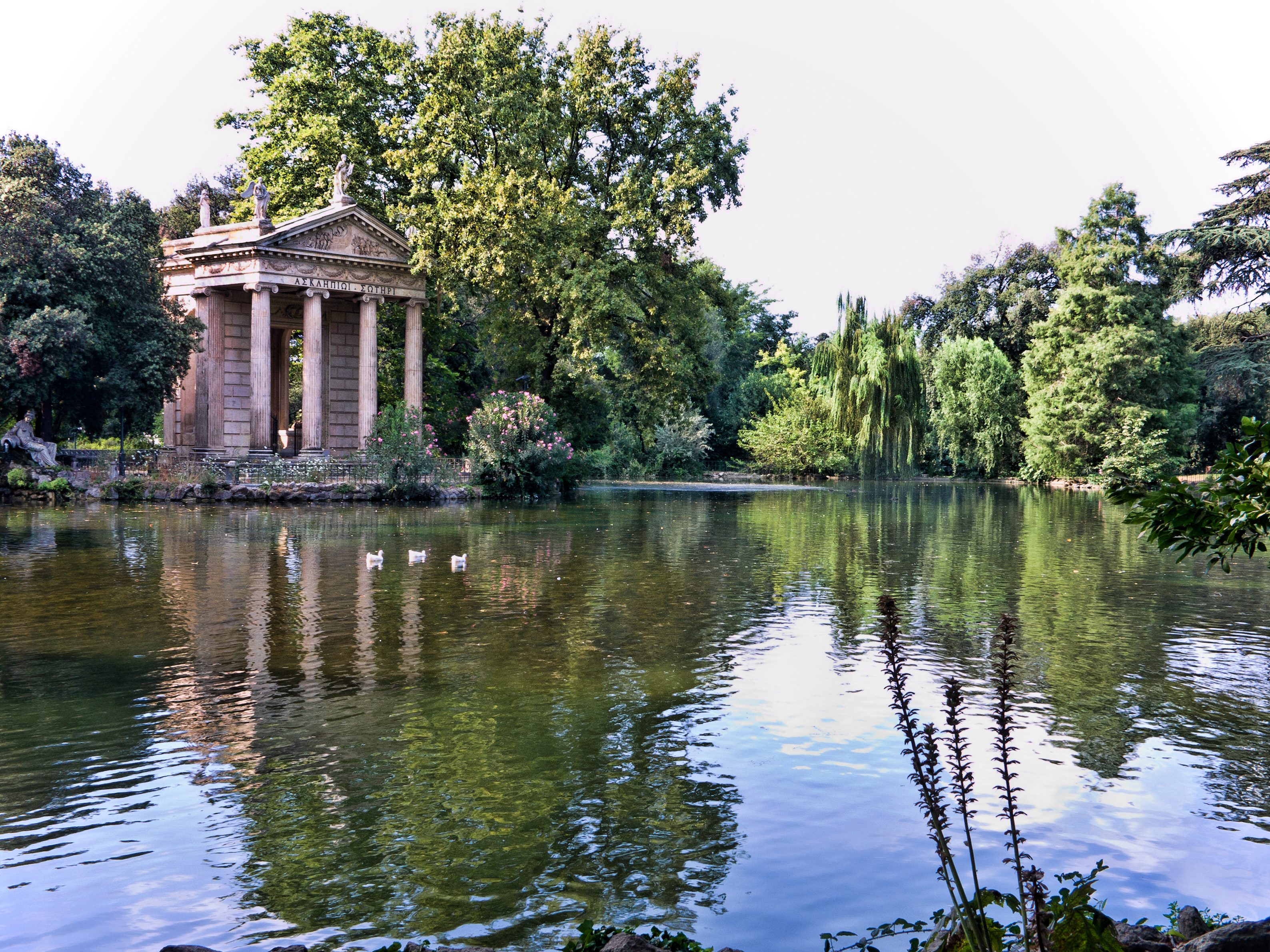 Public parks and nature reserves cover a large area in Rome, and the city has one of the largest areas of green space among European capitals. The most notable part of this green space is represented by the large number of villas and landscaped gardens created by the Italian aristocracy. While most of the parks surrounding the villas were destroyed during the building boom of the late 19th century, some of them remain. The most notable of these are the Villa Borghese gardens, Villa Borghese, Villa Ada, and Villa Doria Pamphili. Villa Doria Pamphili is west of the Gianicolo hill, comprising some . The Villa Sciarra (Rome), Villa Sciarra is on the hill, with playgrounds for children and shaded walking areas. In the nearby area of Trastevere, the Orto Botanico dell'Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Orto Botanico (Botanical Garden) is a cool and shady green space. The old Roman hippodrome (Circus Maximus) is another large green space: it has few trees but is overlooked by the Palatine and the Rose Garden ('roseto comunale'). Nearby is the lush Villa Celimontana, close to the gardens surrounding the Baths of Caracalla. The Villa Borghese garden is the best known large green space in Rome, with famous art galleries among its shaded walks. Overlooking Piazza del Popolo and the Spanish Steps are the gardens of Pincio and Villa Medici. There is also a notable pine wood at Castelfusano, near Ostia. Rome also has a number of regional parks of much more recent origin, including the Pineto Regional Park and the Appian Way Regional Park. There are also nature reserves at Marcigliana and at Tenuta di Castelporziano.
Public parks and nature reserves cover a large area in Rome, and the city has one of the largest areas of green space among European capitals. The most notable part of this green space is represented by the large number of villas and landscaped gardens created by the Italian aristocracy. While most of the parks surrounding the villas were destroyed during the building boom of the late 19th century, some of them remain. The most notable of these are the Villa Borghese gardens, Villa Borghese, Villa Ada, and Villa Doria Pamphili. Villa Doria Pamphili is west of the Gianicolo hill, comprising some . The Villa Sciarra (Rome), Villa Sciarra is on the hill, with playgrounds for children and shaded walking areas. In the nearby area of Trastevere, the Orto Botanico dell'Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Orto Botanico (Botanical Garden) is a cool and shady green space. The old Roman hippodrome (Circus Maximus) is another large green space: it has few trees but is overlooked by the Palatine and the Rose Garden ('roseto comunale'). Nearby is the lush Villa Celimontana, close to the gardens surrounding the Baths of Caracalla. The Villa Borghese garden is the best known large green space in Rome, with famous art galleries among its shaded walks. Overlooking Piazza del Popolo and the Spanish Steps are the gardens of Pincio and Villa Medici. There is also a notable pine wood at Castelfusano, near Ostia. Rome also has a number of regional parks of much more recent origin, including the Pineto Regional Park and the Appian Way Regional Park. There are also nature reserves at Marcigliana and at Tenuta di Castelporziano.
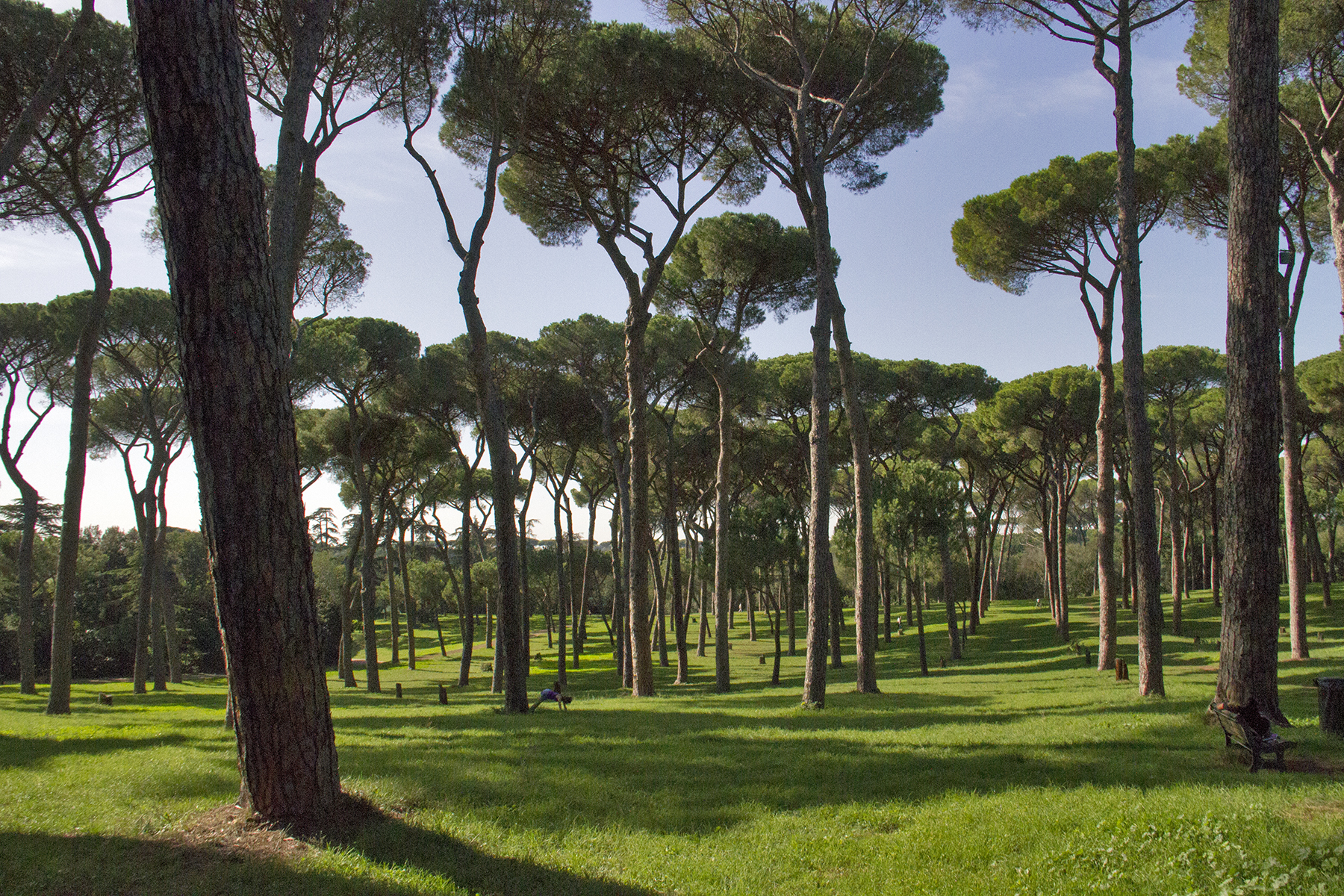 Rome has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with hot, dry summers and mild, humid winters.
Its average annual temperature is above during the day and at night. In the coldest month, January, the average temperature is during the day and at night. In the warmest month, August, the average temperature is during the day and at night.
December, January and February are the coldest months, with a daily mean temperature of approximately . Temperatures during these months generally vary between during the day and between at night, with colder or warmer spells occurring frequently. Snowfall is rare but not unheard of, with light snow or flurries occurring on some winters, generally without accumulation, and major snowfalls on a very rare occurrence (the most recent ones were in 2018, 2012 and 1986).
The average relative humidity is 75%, varying from 72% in July to 77% in November. Sea temperatures vary from a low of in February to a high of in August.Monthly Tor San Lorenzo water temperature chart
Rome has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with hot, dry summers and mild, humid winters.
Its average annual temperature is above during the day and at night. In the coldest month, January, the average temperature is during the day and at night. In the warmest month, August, the average temperature is during the day and at night.
December, January and February are the coldest months, with a daily mean temperature of approximately . Temperatures during these months generally vary between during the day and between at night, with colder or warmer spells occurring frequently. Snowfall is rare but not unheard of, with light snow or flurries occurring on some winters, generally without accumulation, and major snowfalls on a very rare occurrence (the most recent ones were in 2018, 2012 and 1986).
The average relative humidity is 75%, varying from 72% in July to 77% in November. Sea temperatures vary from a low of in February to a high of in August.Monthly Tor San Lorenzo water temperature chart
, seatemperature.org. The highest temperature ever recorded in Rome was on 18 July 2023.
 According to the 2011 statistics conducted by ISTAT, approximately 9.5% of the population consists of non-Italians. About half of the immigrant population consists of those of various other European origins (chiefly Romanian, Polish, Ukrainian, and Albanian) numbering a combined total of 131,118 or 4.7% of the population. The remaining 4.8% are those with non-European origins, chiefly Filipinos (26,933), Bangladeshis (12,154), and Chinese (10,283).
The Esquilino (rione of Rome), Esquilino ''Rioni of Rome, rione'', off Termini Station (Rome), Termini Railway Station, has evolved into a largely immigrant neighbourhood. It is perceived as Rome's Chinatown. Immigrants from more than a hundred different countries reside there. A commercial district, Esquilino contains restaurants featuring many kinds of international cuisine. There are wholesale clothes shops. Of the 1,300 or so commercial premises operating in the district 800 are Chinese-owned; around 300 are run by immigrants from other countries around the world; 200 are owned by Italians.
Summary table
According to the 2011 statistics conducted by ISTAT, approximately 9.5% of the population consists of non-Italians. About half of the immigrant population consists of those of various other European origins (chiefly Romanian, Polish, Ukrainian, and Albanian) numbering a combined total of 131,118 or 4.7% of the population. The remaining 4.8% are those with non-European origins, chiefly Filipinos (26,933), Bangladeshis (12,154), and Chinese (10,283).
The Esquilino (rione of Rome), Esquilino ''Rioni of Rome, rione'', off Termini Station (Rome), Termini Railway Station, has evolved into a largely immigrant neighbourhood. It is perceived as Rome's Chinatown. Immigrants from more than a hundred different countries reside there. A commercial district, Esquilino contains restaurants featuring many kinds of international cuisine. There are wholesale clothes shops. Of the 1,300 or so commercial premises operating in the district 800 are Chinese-owned; around 300 are run by immigrants from other countries around the world; 200 are owned by Italians.
Summary table
 Much like the rest of Italy, Rome is predominantly Christianity, Christian, and the city has been an important centre of religion and Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage for centuries, the base of the ancient Roman religion with the Pontifex Maximus, pontifex maximus and later the seat of the Holy See, Vatican and the pope. Before the arrival of the Christians in Rome, the Religion in ancient Rome, Religio Romana (literally, the "Roman Religion") was the major religion of the city in classical antiquity. The first gods held sacred by the Romans were Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter, the Most High, and Mars (mythology), Mars, the god of war, and father of Rome's twin founders,
Much like the rest of Italy, Rome is predominantly Christianity, Christian, and the city has been an important centre of religion and Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage for centuries, the base of the ancient Roman religion with the Pontifex Maximus, pontifex maximus and later the seat of the Holy See, Vatican and the pope. Before the arrival of the Christians in Rome, the Religion in ancient Rome, Religio Romana (literally, the "Roman Religion") was the major religion of the city in classical antiquity. The first gods held sacred by the Romans were Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter, the Most High, and Mars (mythology), Mars, the god of war, and father of Rome's twin founders,
12.2
(from LacusCurtius) According to
 Rome constitutes a comune ''comune, speciale'', named ''"Roma Capitale"'', and is the largest both in terms of land area and population among the 8,101 ''comuni'' of Italy. It is governed by a mayor and a city council. The seat of the ''comune'' is the ''Palazzo Senatorio'' on the Capitoline Hill, the historic seat of the city government. The local administration in Rome is commonly referred to as ''"Campidoglio"'', the Italian name of the hill. ''Palazzo Senatorio'', seat of the municipality of Rome, has been a town hall since AD 1144, making it the oldest town hall in the world.
Since 1972, the city has been divided into administrative areas, called ''municipi'' (sing. ''municipio'') (until 2001 named ''circoscrizioni''). They were created for administrative reasons to increase decentralisation in the city. Each ''municipio'' is governed by a president and a council of twenty-five members who are elected by its residents every five years. The ''municipi'' frequently cross the boundaries of the traditional, non-administrative divisions of the city. The municipi were originally 20, then 19, and in 2013, their number was reduced to 15.
Rome is also divided into differing types of non-administrative units. The historic centre is divided into 22 ''Rioni of Rome, rioni'', all of which are located within the Aurelian Walls except Prati and Borgo (rione of Rome), Borgo. These originate from the 14 regions of Augustan Rome, which evolved in the Middle Ages into the 14 regions of Medieval Rome, medieval rioni. In the
Rome constitutes a comune ''comune, speciale'', named ''"Roma Capitale"'', and is the largest both in terms of land area and population among the 8,101 ''comuni'' of Italy. It is governed by a mayor and a city council. The seat of the ''comune'' is the ''Palazzo Senatorio'' on the Capitoline Hill, the historic seat of the city government. The local administration in Rome is commonly referred to as ''"Campidoglio"'', the Italian name of the hill. ''Palazzo Senatorio'', seat of the municipality of Rome, has been a town hall since AD 1144, making it the oldest town hall in the world.
Since 1972, the city has been divided into administrative areas, called ''municipi'' (sing. ''municipio'') (until 2001 named ''circoscrizioni''). They were created for administrative reasons to increase decentralisation in the city. Each ''municipio'' is governed by a president and a council of twenty-five members who are elected by its residents every five years. The ''municipi'' frequently cross the boundaries of the traditional, non-administrative divisions of the city. The municipi were originally 20, then 19, and in 2013, their number was reduced to 15.
Rome is also divided into differing types of non-administrative units. The historic centre is divided into 22 ''Rioni of Rome, rioni'', all of which are located within the Aurelian Walls except Prati and Borgo (rione of Rome), Borgo. These originate from the 14 regions of Augustan Rome, which evolved in the Middle Ages into the 14 regions of Medieval Rome, medieval rioni. In the
 Rome is a nationwide and major international centre for higher education, containing numerous academies, colleges and universities. It boasts a large variety of academies and colleges, and has always been a major worldwide intellectual and educational centre, especially during Ancient Rome and the
Rome is a nationwide and major international centre for higher education, containing numerous academies, colleges and universities. It boasts a large variety of academies and colleges, and has always been a major worldwide intellectual and educational centre, especially during Ancient Rome and the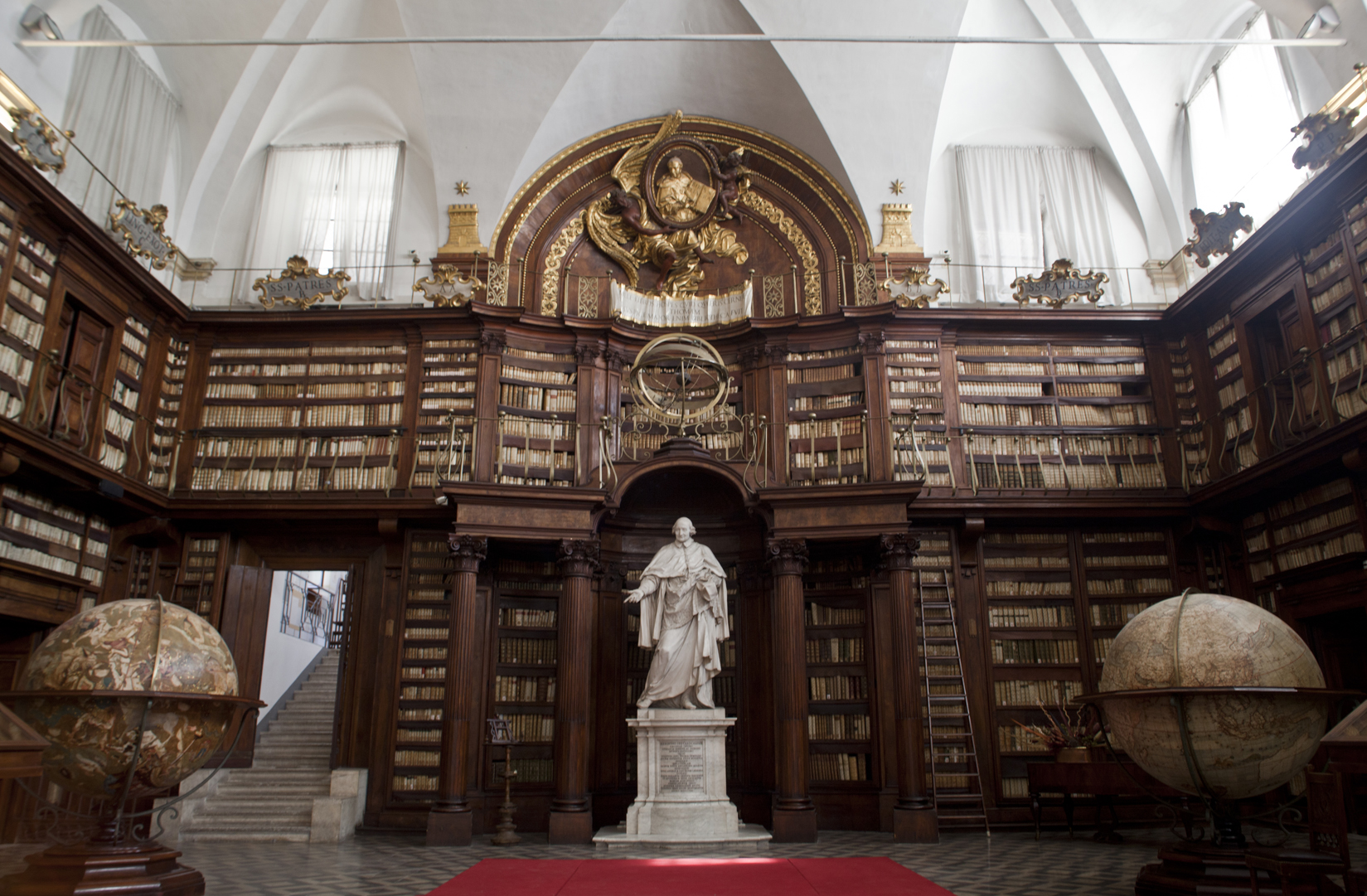  Rome contains many pontifical university, pontifical universities and other institutes, including the British School at Rome, the French Academy in Rome, French School in Rome, the Pontifical Gregorian University (the oldest Society of Jesus, Jesuit university in the world, founded in 1551), Istituto Europeo di Design, the Lorenzo de' Medici School, Scuola Lorenzo de' Medici, the Link Link Campus, Campus of Malta, and the Università Campus Bio-Medico. Rome is also the location of two American Universities; The American University of Rome and John Cabot University as well as St. John's University (Italy), St. John's University branch campus, John Felice Rome Center, a campus of Loyola University Chicago and Temple University Rome, a campus of Temple University. The Roman Colleges are several seminary, seminaries for students from foreign countries studying for the Catholic priesthood, priesthood at the Pontifical Universities. Examples include the Venerable English College, the Pontifical North American College, the Scots College (Rome), Scots College, and the Pontifical Croatian College of St. Jerome. Rome's major libraries include: the , opened in 1604, making it Italy's first public library; the Biblioteca Vallicelliana, established in 1565; the Biblioteca Casanatense, opened in 1701; the National Central Library (Rome), National Central Library, one of the two national libraries in Italy, which contains 4,126,002 volumes; The Biblioteca del Ministero degli Affari Esteri, specialised in diplomacy, foreign affairs and modern history; the Biblioteca dell'Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana; the Biblioteca Don Bosco, one of the largest and most modern of all Salesian libraries; the Biblioteca e Museo teatrale del Burcardo, a museum-library specialised in history of drama and theatre; the Biblioteca della Società Geografica Italiana, which is based in the Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana and is the most important geographical library in Italy, and one of Europe's most important; and the Vatican Library, one of the oldest and most important libraries in the world, which was formally established in 1475, though in fact much older and has 75,000 codex, codices, as well as 1.1 million printed books, which include some 8,500 Incunabulum, incunabula. There are also many specialist libraries attached to various foreign cultural institutes in Rome, among them that of the American Academy in Rome, the French Academy in Rome and the Bibliotheca Hertziana – Max Planck Institute of Art History, a German library, often noted for excellence in the arts and sciences.
Rome contains many pontifical university, pontifical universities and other institutes, including the British School at Rome, the French Academy in Rome, French School in Rome, the Pontifical Gregorian University (the oldest Society of Jesus, Jesuit university in the world, founded in 1551), Istituto Europeo di Design, the Lorenzo de' Medici School, Scuola Lorenzo de' Medici, the Link Link Campus, Campus of Malta, and the Università Campus Bio-Medico. Rome is also the location of two American Universities; The American University of Rome and John Cabot University as well as St. John's University (Italy), St. John's University branch campus, John Felice Rome Center, a campus of Loyola University Chicago and Temple University Rome, a campus of Temple University. The Roman Colleges are several seminary, seminaries for students from foreign countries studying for the Catholic priesthood, priesthood at the Pontifical Universities. Examples include the Venerable English College, the Pontifical North American College, the Scots College (Rome), Scots College, and the Pontifical Croatian College of St. Jerome. Rome's major libraries include: the , opened in 1604, making it Italy's first public library; the Biblioteca Vallicelliana, established in 1565; the Biblioteca Casanatense, opened in 1701; the National Central Library (Rome), National Central Library, one of the two national libraries in Italy, which contains 4,126,002 volumes; The Biblioteca del Ministero degli Affari Esteri, specialised in diplomacy, foreign affairs and modern history; the Biblioteca dell'Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana; the Biblioteca Don Bosco, one of the largest and most modern of all Salesian libraries; the Biblioteca e Museo teatrale del Burcardo, a museum-library specialised in history of drama and theatre; the Biblioteca della Società Geografica Italiana, which is based in the Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana and is the most important geographical library in Italy, and one of Europe's most important; and the Vatican Library, one of the oldest and most important libraries in the world, which was formally established in 1475, though in fact much older and has 75,000 codex, codices, as well as 1.1 million printed books, which include some 8,500 Incunabulum, incunabula. There are also many specialist libraries attached to various foreign cultural institutes in Rome, among them that of the American Academy in Rome, the French Academy in Rome and the Bibliotheca Hertziana – Max Planck Institute of Art History, a German library, often noted for excellence in the arts and sciences.
 The city hosts eight ancient Egyptian and five ancient Rome, ancient Roman obelisks, together with a number of more modern obelisks; there was also formerly (until 2005) an Aksumite Empire, ancient Ethiopian obelisk in Rome. The city contains some of obelisks in piazzas, such as in Piazza Navona, Saint Peter's Square, St Peter's Square, Piazza di Monte Citorio, Piazza Montecitorio, and Piazza del Popolo, and others in villas, thermae parks and gardens, such as in Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana, the Baths of Diocletian, and the Pincian Hill. Moreover, the centre of Rome hosts also Trajan's column, Trajan's and Column of Marcus Aurelius, Antonine Column, two ancient Roman columns with spiral relief. The Column of Marcus Aurelius is located in Piazza Colonna and it was built around 180 AD by
The city hosts eight ancient Egyptian and five ancient Rome, ancient Roman obelisks, together with a number of more modern obelisks; there was also formerly (until 2005) an Aksumite Empire, ancient Ethiopian obelisk in Rome. The city contains some of obelisks in piazzas, such as in Piazza Navona, Saint Peter's Square, St Peter's Square, Piazza di Monte Citorio, Piazza Montecitorio, and Piazza del Popolo, and others in villas, thermae parks and gardens, such as in Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana, the Baths of Diocletian, and the Pincian Hill. Moreover, the centre of Rome hosts also Trajan's column, Trajan's and Column of Marcus Aurelius, Antonine Column, two ancient Roman columns with spiral relief. The Column of Marcus Aurelius is located in Piazza Colonna and it was built around 180 AD by
 The city of Rome contains numerous famous bridges which cross the
The city of Rome contains numerous famous bridges which cross the
 Rome has an extensive amount of ancient catacombs, or underground burial places under or near the city, of which there are at least forty, some discovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, they include Religion in ancient Rome, pagan and Jewish burials, either in separate catacombs or mixed together. The first large-scale catacombs were excavated from the 2nd century onwards. Originally they were carved through tuff, a soft volcanic rock, outside the boundaries of the city, because Roman law forbade burial places within city limits. Currently, maintenance of the catacombs is in the hands of the Pope, Papacy which has invested in the Salesians of Don Bosco the supervision of the Catacombs of St. Callixtus on the outskirts of Rome.
Rome has an extensive amount of ancient catacombs, or underground burial places under or near the city, of which there are at least forty, some discovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, they include Religion in ancient Rome, pagan and Jewish burials, either in separate catacombs or mixed together. The first large-scale catacombs were excavated from the 2nd century onwards. Originally they were carved through tuff, a soft volcanic rock, outside the boundaries of the city, because Roman law forbade burial places within city limits. Currently, maintenance of the catacombs is in the hands of the Pope, Papacy which has invested in the Salesians of Don Bosco the supervision of the Catacombs of St. Callixtus on the outskirts of Rome.
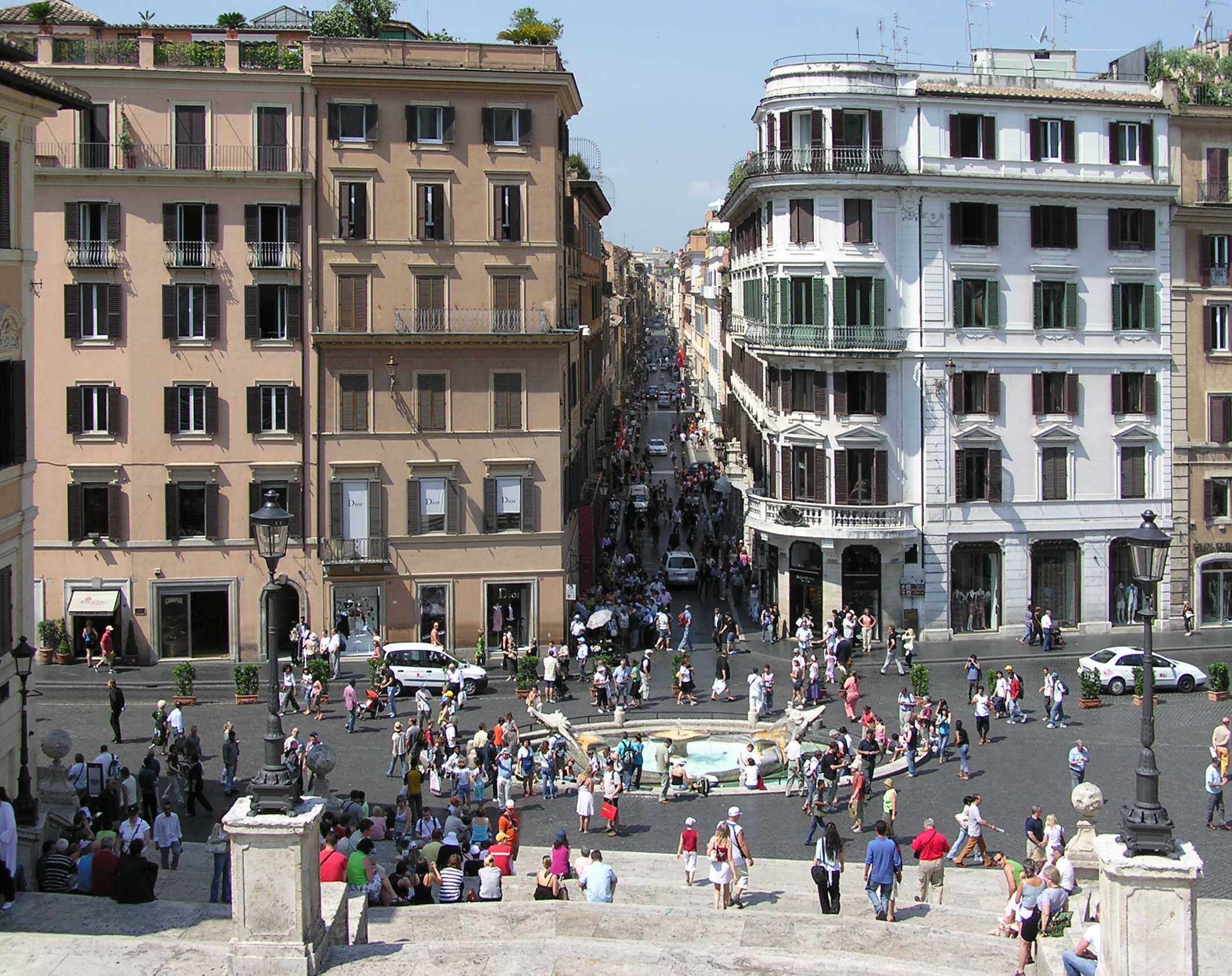 Rome is also widely recognised as a world fashion capital. Although not as important as Milan, Rome is the fourth most important centre for fashion in the world, according to the 2009 Global Language Monitor after
Rome is also widely recognised as a world fashion capital. Although not as important as Milan, Rome is the fourth most important centre for fashion in the world, according to the 2009 Global Language Monitor after

 Rome's cuisine has evolved through centuries and periods of social, cultural, and political changes. Rome became a major gastronomical centre during the Ancient Rome, ancient age. Ancient Roman cuisine was highly influenced by Ancient Greek culture, and after, the empire's enormous expansion exposed Romans to many new, provincial culinary habits and cooking techniques.
Later, during the
Rome's cuisine has evolved through centuries and periods of social, cultural, and political changes. Rome became a major gastronomical centre during the Ancient Rome, ancient age. Ancient Roman cuisine was highly influenced by Ancient Greek culture, and after, the empire's enormous expansion exposed Romans to many new, provincial culinary habits and cooking techniques.
Later, during the
 Rome hosts the
Rome hosts the
 Rome hosted the
Rome hosted the
 Rome is at the centre of the radial network of roads that roughly follow the lines of the ancient Roman roads which began at the Capitoline Hill and connected Rome with its empire. Today Rome is circled, at a distance of about from the Capitol, by the ring-road (the Grande Raccordo Anulare or GRA).
Due to its location in the centre of the Italian peninsula, Rome is the principal railway node for central Italy. Rome's main railway station, Roma Termini railway station, Termini, is one of the largest railway stations in Europe and the most heavily used in Italy, with around 400 thousand travellers passing through every day. The second-largest station in the city, Roma Tiburtina railway station, Roma Tiburtina, has been redeveloped as a High-speed rail in Italy, high-speed rail terminus. As well as frequent high-speed day trains to all major Italian cities, Rome is linked nightly by 'boat train' sleeper services to Sicily, and internationally by overnight sleeper services to Munich and Vienna.
Rome is served by three airports. The intercontinental Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport, Leonardo da Vinci International Airport, Italy's chief airport is located in the nearby Fiumicino, south-west of Rome. The older Ciampino–G. B. Pastine International Airport, Rome Ciampino Airport is a joint civilian and military airport. It is commonly referred to as "Ciampino Airport", as it is located beside Ciampino, south-east of Rome. A third airport, the Rome Urbe Airport, is a small, low-traffic airport located about north of the city centre, which handles most helicopter and private flights. The main city airport of Fiumicino, with over 49 million passengers transported in 2024, is the busiest airport in Italy.
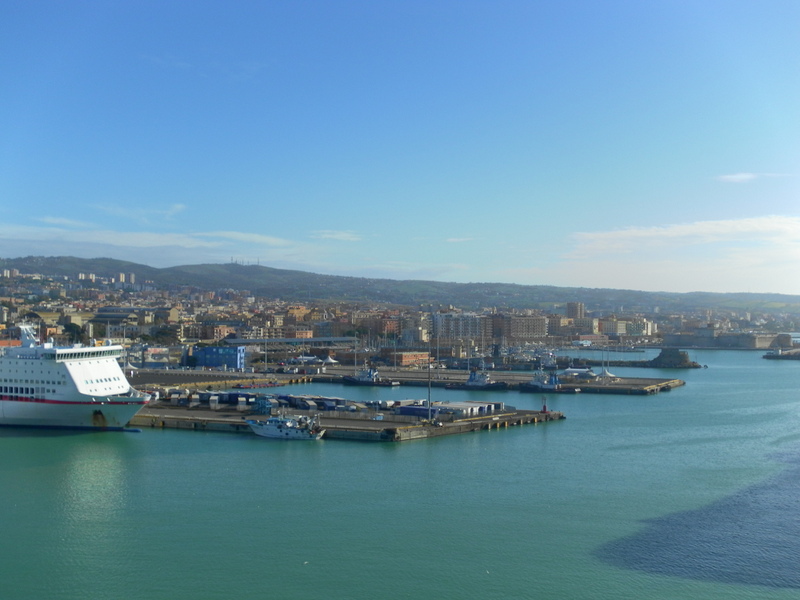
Although the city has its own quarter on the Mediterranean Sea (Ostia (Rome), Lido di Ostia), this has only a marina and a small channel-harbour for fishing boats. The main harbour which serves Rome is Port of Civitavecchia, located about northwest of the city.
The city suffers from traffic problems largely due to this radial street pattern, making it difficult for Romans to move easily from the vicinity of one of the radial roads to another without going into the historic centre or using the ring-road. These problems are not helped by the limited size of Rome's metro system when compared to other cities of similar size. Rome has only 21 taxis for every 10,000 inhabitants, far below other major European cities. Chronic congestion caused by cars during the 1970s and 1980s led to restrictions being placed on vehicle access to the inner city-centre during daylight hours. Areas, where these restrictions apply, are known as Limited Traffic Zones (''Zona a Traffico Limitato'' (ZTL)). More recently, heavy night-time traffic in Trastevere, Testaccio and San Lorenzo (Rome), San Lorenzo has led to the creation of night-time ZTLs in those districts.
Rome is at the centre of the radial network of roads that roughly follow the lines of the ancient Roman roads which began at the Capitoline Hill and connected Rome with its empire. Today Rome is circled, at a distance of about from the Capitol, by the ring-road (the Grande Raccordo Anulare or GRA).
Due to its location in the centre of the Italian peninsula, Rome is the principal railway node for central Italy. Rome's main railway station, Roma Termini railway station, Termini, is one of the largest railway stations in Europe and the most heavily used in Italy, with around 400 thousand travellers passing through every day. The second-largest station in the city, Roma Tiburtina railway station, Roma Tiburtina, has been redeveloped as a High-speed rail in Italy, high-speed rail terminus. As well as frequent high-speed day trains to all major Italian cities, Rome is linked nightly by 'boat train' sleeper services to Sicily, and internationally by overnight sleeper services to Munich and Vienna.
Rome is served by three airports. The intercontinental Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport, Leonardo da Vinci International Airport, Italy's chief airport is located in the nearby Fiumicino, south-west of Rome. The older Ciampino–G. B. Pastine International Airport, Rome Ciampino Airport is a joint civilian and military airport. It is commonly referred to as "Ciampino Airport", as it is located beside Ciampino, south-east of Rome. A third airport, the Rome Urbe Airport, is a small, low-traffic airport located about north of the city centre, which handles most helicopter and private flights. The main city airport of Fiumicino, with over 49 million passengers transported in 2024, is the busiest airport in Italy.
Although the city has its own quarter on the Mediterranean Sea (Ostia (Rome), Lido di Ostia), this has only a marina and a small channel-harbour for fishing boats. The main harbour which serves Rome is Port of Civitavecchia, located about northwest of the city.
The city suffers from traffic problems largely due to this radial street pattern, making it difficult for Romans to move easily from the vicinity of one of the radial roads to another without going into the historic centre or using the ring-road. These problems are not helped by the limited size of Rome's metro system when compared to other cities of similar size. Rome has only 21 taxis for every 10,000 inhabitants, far below other major European cities. Chronic congestion caused by cars during the 1970s and 1980s led to restrictions being placed on vehicle access to the inner city-centre during daylight hours. Areas, where these restrictions apply, are known as Limited Traffic Zones (''Zona a Traffico Limitato'' (ZTL)). More recently, heavy night-time traffic in Trastevere, Testaccio and San Lorenzo (Rome), San Lorenzo has led to the creation of night-time ZTLs in those districts.
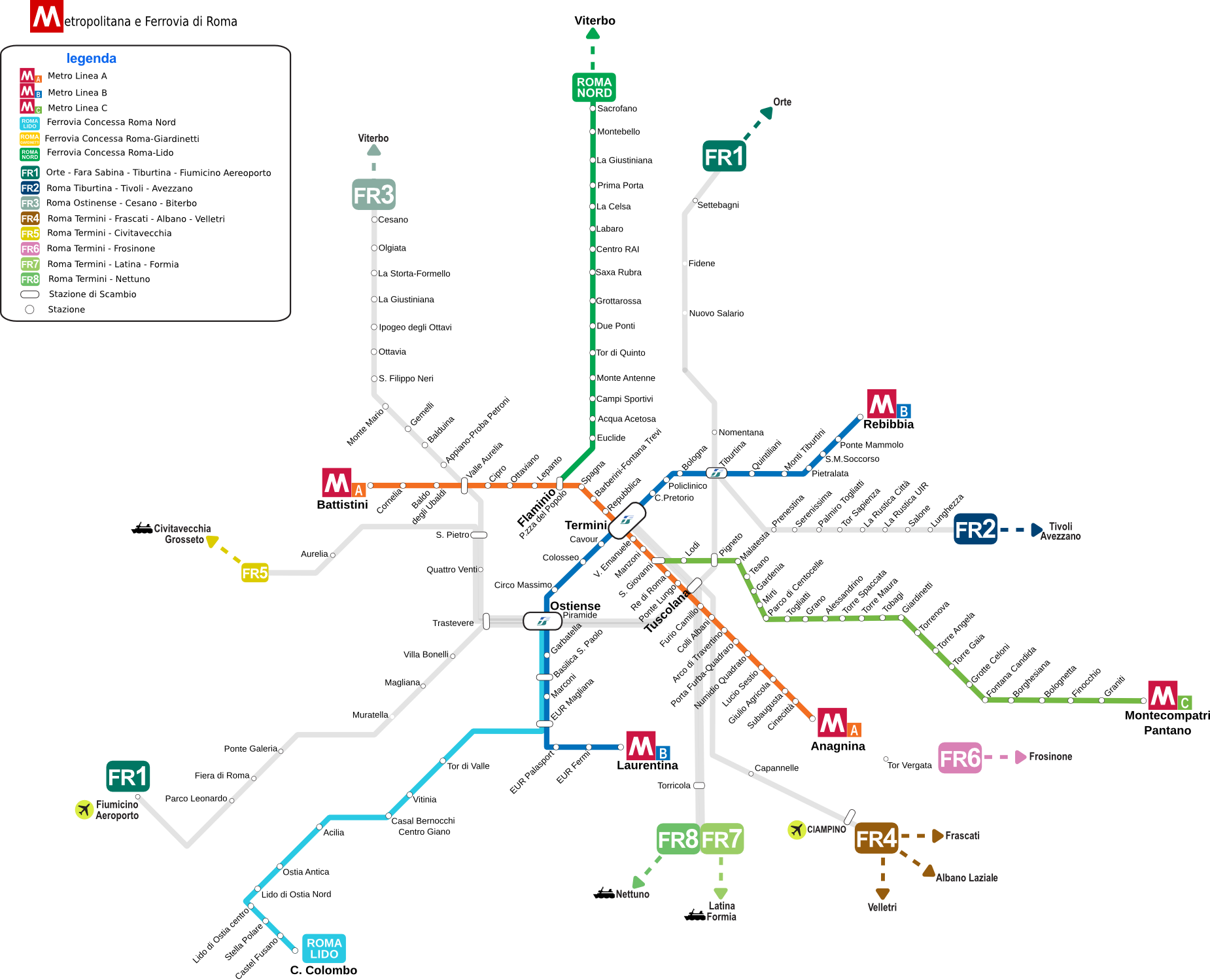
 A three-line metro system called the ''Rome Metro, Metropolitana'' operates in Rome. Construction on the first branch started in the 1930s. The line had been planned to quickly connect the Roma Termini railway station, main railway station with the newly planned E42 area in the southern suburbs, where 1942 the List of world expositions, World Fair was supposed to be held. The event never took place because of war, but the area was later partly redesigned and renamed EUR, Rome, Esposizione Universale Roma in the 1950s to serve as a modern business district. The line was finally opened in 1955, and it is now the south part of the B Line.
The A line opened in 1980 from Ottaviano to Anagnina stations, later extended in stages (1999–2000) to Battistini. In the 1990s, an extension of the B line was opened from Termini to Rebibbia. The A and B lines intersect at Roma Termini station. A new branch of the B line (B1) opened on 13 June 2012 after an estimated building cost of €500 million. B1 connects to line B at Piazza Bologna and has four stations over a distance of .
A third line, the C line, is under construction with an estimated cost of €3 billion and will have 30 stations over a distance of . It will partly replace the existing Roma Termini railway station, Termini-Pantano rail line. It will feature full automated, driverless trains. The first section with 15 stations connecting Pantano with the quarter of Centocelle in the eastern part of the city, opened on 9 November 2014. The end of the work was scheduled in 2015, but archaeological findings often delay underground construction work.
A fourth line, D line, is also planned. It will have 22 stations over a distance of . The first section was projected to open in 2015 and the final sections before 2035, but due to the city's financial crisis, the project has been put on hold.
Above-ground public transport in Rome is made up of a bus, tram and urban train network (FR lines). The bus network has in excess of 350 bus lines and over eight thousand bus stops, whereas the more-limited tram system has of track and 192 stops. There are also trolleybuses.
A three-line metro system called the ''Rome Metro, Metropolitana'' operates in Rome. Construction on the first branch started in the 1930s. The line had been planned to quickly connect the Roma Termini railway station, main railway station with the newly planned E42 area in the southern suburbs, where 1942 the List of world expositions, World Fair was supposed to be held. The event never took place because of war, but the area was later partly redesigned and renamed EUR, Rome, Esposizione Universale Roma in the 1950s to serve as a modern business district. The line was finally opened in 1955, and it is now the south part of the B Line.
The A line opened in 1980 from Ottaviano to Anagnina stations, later extended in stages (1999–2000) to Battistini. In the 1990s, an extension of the B line was opened from Termini to Rebibbia. The A and B lines intersect at Roma Termini station. A new branch of the B line (B1) opened on 13 June 2012 after an estimated building cost of €500 million. B1 connects to line B at Piazza Bologna and has four stations over a distance of .
A third line, the C line, is under construction with an estimated cost of €3 billion and will have 30 stations over a distance of . It will partly replace the existing Roma Termini railway station, Termini-Pantano rail line. It will feature full automated, driverless trains. The first section with 15 stations connecting Pantano with the quarter of Centocelle in the eastern part of the city, opened on 9 November 2014. The end of the work was scheduled in 2015, but archaeological findings often delay underground construction work.
A fourth line, D line, is also planned. It will have 22 stations over a distance of . The first section was projected to open in 2015 and the final sections before 2035, but due to the city's financial crisis, the project has been put on hold.
Above-ground public transport in Rome is made up of a bus, tram and urban train network (FR lines). The bus network has in excess of 350 bus lines and over eight thousand bus stops, whereas the more-limited tram system has of track and 192 stops. There are also trolleybuses.
Comune of Rome
APT (official Tourist Office) of the City of Rome
Rome Museums – official site
.
Capitoline Museums
* {{Authority control Rome, Ancient city of Rome, Capitals in Europe Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, Catholic pilgrimage sites Holy cities Places in the deuterocanonical books New Testament cities Populated places established in the 8th century BC 8th-century BC establishments in Italy World Heritage Sites in Italy
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
and , ) is the capital city
A capital city, or just capital, is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state (polity), state, province, department (administrative division), department, or other administrative division, subnational division, usually as its ...
and most populated (municipality) of Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. It is also the administrative centre
An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located.
In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgi ...
of the Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
and of the Metropolitan City of Rome
Metropolitan City of Rome Capital () is an area of local government at the level of metropolitan city in the Lazio region of Italy. It comprises the territory of the city of Rome and 120 other ''comuni'' (: ''comune'') in the hinterland of the c ...
. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the third most populous city in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital
Metropolitan City of Rome Capital () is an area of local government at the level of metropolitan city in the Lazio region of Italy. It comprises the territory of the city of Rome and 120 other ''comuni'' (: ''comune'') in the hinterland of the c ...
, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan city in Italy. Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
), along the shores of the Tiber Valley
The Tiber Valley (Italian: ''Valle del Tevere'') is the largest geographical part of the of the Tiber river included in the Emilia-Romagna, Tuscany, Umbria, and the Lazio regions; it is characterized by river terraces and floodplain areas that e ...
. Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
(the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
under the governance of the Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop ...
) is an independent country inside the city boundaries of Rome, the only existing example of a country within a city. Rome is often referred to as the City of Seven Hills due to its geography, and also as the "Eternal City". Rome is generally considered to be one of the cradles of Western civilization
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social no ...
and Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
Christian culture
Christian culture generally includes all the cultural practices which have developed around the religion of Christianity. There are variations in the application of Christian beliefs in different cultures and traditions.
Christian culture has i ...
, and the centre of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.
Rome's history spans 28 centuries. While Roman mythology
Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans, and is a form of Roman folklore. "Roman mythology" may also refer to the modern study of these representations, and to th ...
dates the founding of Rome
The founding of Rome was a prehistoric event or process later greatly embellished by Roman historians and poets. Archaeological evidence indicates that Rome developed from the gradual union of several hillfort, hilltop villages during the Prehi ...
at around 753 BC, the site has been inhabited for much longer, making it a major human settlement for over three millennia and one of the oldest continuously occupied cities in Europe.Heiken, G., Funiciello, R. and De Rita, D. (2005), ''The Seven Hills of Rome: A Geological Tour of the Eternal City''. Princeton University Press. The city's early population originated from a mix of Latins
The term Latins has been used throughout history to refer to various peoples, ethnicities and religious groups using Latin or the Latin-derived Romance languages, as part of the legacy of the Roman Empire. In the Ancient World, it referred to th ...
, Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. Af ...
, and Sabines
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
. Eventually, the city successively became the capital of the Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom, also known as the Roman monarchy and the regal period of ancient Rome, was the earliest period of Ancient Rome, Roman history when the city and its territory were King of Rome, ruled by kings. According to tradition, the Roma ...
, the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, and is regarded by many as the first-ever Imperial city and metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural area for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big city b ...
. It was first called ''The Eternal City'' (; ) by the Roman poet Tibullus
Albius Tibullus ( BC BC) was a Latin poet and writer of elegies. His first and second books of poetry are extant; many other texts attributed to him are of questionable origins.
Little is known about the life of Tibullus. There are only a few r ...
in the 1st century BC, and the expression was also taken up by Ovid
Publius Ovidius Naso (; 20 March 43 BC – AD 17/18), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a younger contemporary of Virgil and Horace, with whom he i ...
, Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
, and Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
. Rome is also called (Capital of the World).
After the fall of the Empire in the west, which marked the beginning of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, Rome slowly fell under the political control of the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, and in the 8th century, it became the capital of the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, which lasted until 1870. Beginning with the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, almost all popes since Nicholas V
Pope Nicholas V (; ; 15 November 1397 – 24 March 1455), born Tommaso Parentucelli, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 6 March 1447 until his death in March 1455. Pope Eugene IV made him a cardinal in 1446 afte ...
(1447–1455) pursued a coherent architectural and urban programme over four hundred years, aimed at making the city the artistic and cultural centre of the world. In this way, Rome first became one of the major centres of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
and then became the birthplace of both the Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
style and Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism, also spelled Neo-classicism, emerged as a Western cultural movement in the decorative arts, decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiq ...
. Famous artists, painters, sculptors, and architects made Rome the centre of their activity, creating masterpieces throughout the city. In 1871, Rome became the capital of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
, which, in 1946, became the Italian Republic.
In 2019, Rome was the 14th most visited city in the world, with 8.6 million tourists, the third most visited city in the European Union, and the most popular tourist destination in Italy. Its historic centre is listed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
as a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. The host city for the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad () and commonly known as Rome 1960 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 25 August to 11 September 1960 in Rome, Italy. Rome had previously been awar ...
, Rome is also the seat of several specialised agencies of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
, World Food Programme
The World Food Programme (WFP) is an international organization within the United Nations that provides food assistance worldwide. It is the world's largest humanitarian organization and the leading provider of school meals. Founded in 1961 ...
, International Fund for Agricultural Development
The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) is an international financial institution and a specialised agency of the United Nations that works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries. It is the on ...
and UN System Network on Rural Development and Food Security. The city also hosts the European Union (EU) Delegation to the United Nations (UN), Secretariat of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Union for the Mediterranean
The Union for the Mediterranean (UfM; , ''Al-Ittiḥād min ajl al-Mutawasseṭ'') is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 Member state of the European Union, EU member states (i ...
, headquarters of the World Farmers' Organisation
The World Farmers' Organization (WFO) is an international organisation of farmers with a focus on agroecology, farming typologies, food chains, indigenous peoples, and mountain farming.
History
A former organisation, the International Federation ...
, multi-country office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, l ...
, Human Resources Office for International Cooperation of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, headquarters of the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the firs ...
Office for Italy, headquarters of the WORLD BANK GROUP
The World Bank Group (WBG) is a family of five international organizations that make leveraged loans to developing countries. It is the largest and best-known development bank in the world and an observer at the United Nations Development Group ...
for Italy, Office for Technology Promotion and Investment in Italy under the United Nations Industrial Development Organization
The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) (French: Organisation des Nations unies pour le développement industriel; French/Spanish acronym: ONUDI) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that assists countries in e ...
, Rome office of the United Nations Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute
The United Nations Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute (UNICRI) is one of the five United Nations Research and Training Institutes. The institute was founded in 1968 to assist the international community in formulating and imple ...
, and support office of the United Nations Humanitarian Response Depot, as well as the headquarters of several Italian multinational companies such as Eni
Eni is an Italian oil and gas corporation.
Eni or ENI may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* Escuela Nacional de Inteligencia, the Argentine intelligence academy
* Groupe des écoles nationales d’ingénieurs (Groupe ENI), a French engi ...
, Enel
Enel S.p.A. is an Italian multinational manufacturer and distributor of electricity and gas. Enel was first established as a public body at the end of 1962, and then transformed into a limited company in 1992. In 1999, following the liberali ...
, TIM, Leonardo, and banks such as BNL. Numerous companies are based within Rome's EUR
The euro (symbol: €; currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the euro area or, more commonly, the eurozone. The euro is divided into 10 ...
business district, such as the luxury fashion house Fendi
Fendi Srl () is an Culture of Italy, Italian luxury goods, luxury fashion house producing fur, ready-to-wear, leather goods, shoes, fragrances, eyewear, timepieces and accessories. Founded in Rome in 1925 by fashion designers Edoardo Fendi and ...
located in the Palazzo della Civiltà Italiana
The Palazzo della Civiltà Italiana, also known as the Palazzo della Civiltà del Lavoro, or in everyday speech as the ("Square Colosseum"), is a building in the EUR district in Rome. It was designed in 1938 by three Italian architects: Giovanni ...
. The presence of renowned international brands in the city has made Rome an important centre of fashion and design, and the Cinecittà Studios
Cinecittà Studios (; Italian for Cinema City) is a large film studio in Rome, Italy. With an area of 400,000 square metres (99 acres), it is the largest film studio in Europe, and is considered the hub of Italian cinema. The studios were constru ...
have been the set of many Academy Award
The Academy Awards, commonly known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit in film. They are presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) in the United States in recognition of excellence ...
–winning movies.
Name and symbol
Etymology
According to the Ancient Romans'founding myth
An origin myth is a type of myth that explains the beginnings of a natural or social aspect of the world. Creation myths are a type of origin myth narrating the formation of the universe. However, numerous cultures have stories that take place a ...
, the name ''Roma'' came from the city's founder and first king
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
, Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
.
However, it is possible that the name Romulus was actually derived from Rome itself. As early as the 4th century, there have been alternative theories proposed on the origin of the name ''Roma''. Several hypotheses have been advanced focusing on its linguistic roots which however remain uncertain:
* From ''Rumon'' or ''Rumen'', archaic name of the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
, which in turn is supposedly related to the Greek verb () 'to flow, stream' and the Latin verb 'to hurry, rush';
* From the Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*Etruscan civilization (1st millennium BC) and related things:
**Etruscan language
** Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
**Etruscan coins
**Etruscan history
**Etruscan myt ...
word (), whose root is ''*rum-'' "teat", with possible reference either to the totem wolf that adopted and suckled the cognately named twins Romulus and Remus
In Roman mythology, Romulus and (, ) are twins in mythology, twin brothers whose story tells of the events that led to the Founding of Rome, founding of the History of Rome, city of Rome and the Roman Kingdom by Romulus, following his frat ...
, or to the shape of the Palatine
A palatine or palatinus (Latin; : ''palatini''; cf. derivative spellings below) is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman Empire, Roman times.
and Aventine Hill
The Aventine Hill (; ; ) is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth ''rione'', or ward, of Rome.
Location and boundaries
The Aventine Hill is the southernmost of Rome's seven hills. I ...
s;
* From the Greek word (), which means ''strength''.
Other names and symbols
Rome has also been called in ancient times simply "Urbs" (central city), from ''urbs roma'', or identified with its ancient Romaninitialism
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial letter of each word in all caps wi ...
of SPQR
SPQR or S.P.Q.R., an initialism for (; ), is an emblematic phrase referring to the government of the Roman Republic. It appears on documents made public by an inscription in stone or metal, in dedications of monuments and public works, and on ...
, the symbol of Rome's constituted republican government. In 192, emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Commodus
Commodus (; ; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was Roman emperor from 177 to 192, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father Marcus Aurelius and then ruling alone from 180. Commodus's sole reign is commonly thought to mark the end o ...
renamed the city ''Colonia Lucia Annia Commodiana'' after himself. The name was reverted to Rome after his assassination at the end of the year. Furthermore, Rome has been called Urbs Aeterna (The Eternal City), Caput Mundi (The Capital of the world), Throne of St. Peter and Roma Capitale.
History
Earliest history
While there have been discoveries of archaeological evidence of human occupation of the Rome area from approximately 14,000 years ago, the dense layer of much younger debris obscuresPalaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
and Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
sites. Evidence of stone tools, pottery, and stone weapons attest to about 10,000 years of human presence. Several excavations support the view that Rome grew from pastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
settlements on the Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the ...
built above the area of the future Roman Forum
A forum (Latin: ''forum'', "public place outdoors", : ''fora''; English : either ''fora'' or ''forums'') was a public square in a municipium, or any civitas, of Ancient Rome reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, alon ...
. Between the end of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
and the beginning of the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
, each hill between the sea and the Capitoline Hill was topped by a village (on the Capitoline, a village is attested since the end of the 14th century BC).Coarelli (1984) p. 9 However, none of them yet had an urban quality. Nowadays, there is a wide consensus that the city developed gradually through the aggregation ("synoecism
Synoecism or synecism ( ; , ''sunoikismos'', ), also spelled synoikism ( ), was originally the amalgamation of villages in Ancient Greece into ''poleis'', or city-states. Etymologically, the word means "dwelling together (''syn'') in the same h ...
") of several villages around the largest one, placed above the Palatine. This aggregation was facilitated by the increase of agricultural productivity above the subsistence level
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing and shelter) rather than to the market.
Definition
"Subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself and family at a minimum level. Basic subsiste ...
, which also allowed the establishment of secondary and tertiary activities. These, in turn, boosted the development of trade with the Greek colonies of southern Italy (mainly Ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from the city of Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Although inhabited since the Bronze Age, as a Ancient G ...
and Cumae
Cumae ( or or ; ) was the first ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia on the mainland of Italy and was founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BCE. It became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of ...
). These developments, which according to archaeological evidence took place during the mid-eighth century BC, can be considered as the "birth" of the city. Despite recent excavations at the Palatine hill, the view that Rome was founded deliberately in the middle of the eighth century BC, as the legend of Romulus suggests, remains a fringe hypothesis.
Legend of the founding of Rome
Traditional stories handed down by theancient Romans
The Roman people was the ethnicity and the body of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens
(; ) during the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic, and the Roman Empire. This concept underwent considerable changes throughout the long history of the Roman ...
themselves explain the earliest history of their city in terms of legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess certain qualities that give the ...
and myth
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
. The most familiar of these myths, and perhaps the most famous of all Roman myths, is the story of Romulus and Remus
In Roman mythology, Romulus and (, ) are twins in mythology, twin brothers whose story tells of the events that led to the Founding of Rome, founding of the History of Rome, city of Rome and the Roman Kingdom by Romulus, following his frat ...
, the twins who were suckled by a she-wolf. They decided to build a city, but after an argument, Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
killed his brother and the city took his name. According to the Roman annalist
Annalists (from Latin ''annus'', year; hence ''annales'', sc. ''libri'', annual records), were a class of writers on Roman history, the period of whose literary activity lasted from the time of the Second Punic War to that of Sulla. They wrote t ...
s, this happened on 21 April 753 BC. This legend had to be reconciled with a dual tradition, set earlier in time, that had the Trojan refugee Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas ( , ; from ) was a Troy, Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus (mythology), Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy ...
escape to Italy and found the line of Romans through his son Iulus
Ascanius (; Ancient Greek: Ἀσκάνιος) was a legendary king of Alba Longa (traditional reign: 1176 BC to 1138 BC) and the son of the Trojan hero Aeneas and of Creusa, daughter of Priam. He is a significant figure in Roman mythology b ...
, the namesake of the Julio-Claudian dynasty
The Julio-Claudian dynasty comprised the first five Roman emperors: Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero.
This line of emperors ruled the Roman Empire, from its formation (under Augustus, in 27 BC) until the last of the line, Emper ...
. This was accomplished by the Roman poet Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
in the first century BC. In addition, Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
mentions an older story, that the city was an Arcadian colony founded by Evander
Evander is a masculine given name. It is an anglicization of the Greek name Εὔανδρος (lit. "good man", Latinized ''Evandrus''). It has also been adopted as an anglicization of the Gaelic name Ìomhar (the Gaelic variant of the name Ivor) ...
. Strabo also writes that Lucius Coelius Antipater Lucius Coelius Antipater was a Roman jurist and historian. He is not to be confused with Coelius Sabinus, the Coelius of the Digest. He was a contemporary of Gaius Gracchus, C. Gracchus (b. c. 123); Lucius Licinius Crassus, L. Crassus, the orator, w ...
believed that Rome was founded by Greeks.
Monarchy and republic

 After the foundation by Romulus according to a legend, Rome was ruled for a period of 244 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of
After the foundation by Romulus according to a legend, Rome was ruled for a period of 244 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and Sabine
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
origin, later by Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*Etruscan civilization (1st millennium BC) and related things:
**Etruscan language
** Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
**Etruscan coins
**Etruscan history
**Etruscan myt ...
kings. The tradition handed down seven kings: Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
, Numa Pompilius
Numa Pompilius (; 753–672 BC; reigned 715–672 BC) was the Roman mythology, legendary second king of Rome, succeeding Romulus after a one-year interregnum. He was of Sabine origin, and many of Rome's most important religious and political ins ...
, Tullus Hostilius
Tullus Hostilius (; r. 672–640 BC) was the legendary third king of Rome. He succeeded Numa Pompilius and was succeeded by Ancus Marcius. Unlike his predecessor, Tullus was known as a warlike king who, according to the Roman historian Livy, b ...
, Ancus Marcius
Ancus Marcius () was the Roman mythology, legendary fourth king of Rome, who traditionally reigned 24 years. Upon the death of the previous king, Tullus Hostilius, the Roman Senate appointed an interrex, who in turn called a session of the Roman a ...
, Tarquinius Priscus
Lucius Tarquinius Priscus (), or Tarquin the Elder, was the legendary fifth king of Rome and first of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned for thirty-eight years.Livy, '' ab urbe condita libri'', I Tarquinius expanded Roman power through military ...
, Servius Tullius
Servius Tullius was the legendary sixth king of Rome, and the second of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned from 578 to 535 BC. Roman and Greek sources describe his servile origins and later marriage to a daughter of Lucius Tarquinius Pri ...
and Lucius Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', wikisource:From_the_ ...
.
In 509 BC, the Romans expelled the last king from their city and established an oligarchic
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or throug ...
republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
led by two annually-elected consuls
A consul is an official representative of a government who resides in a foreign country to assist and protect citizens of the consul's country, and to promote and facilitate commercial and diplomatic relations between the two countries.
A consu ...
. Rome then began a period characterised by internal struggles between patricians
The patricians (from ) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 B ...
(aristocrats) and plebeians
In ancient Rome, the plebeians or plebs were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not Patrician (ancient Rome), patricians, as determined by the Capite censi, census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary.
Et ...
(small landowners), and by constant warfare against the populations of central Italy: Etruscans, Latins, Volsci
The Volsci (, , ) were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the ...
, Aequi
300px, Location of the Aequi (Equi) in central Italy, 5th century BC.
The Aequi were an Italic tribe on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains to the east of Latium in central Italy who appear in the early history of ancient Rome. After a long stru ...
, and Marsi
The Marsi were an Italic people of ancient Italy, whose chief centre was Marruvium, on the eastern shore of Lake Fucinus (which was drained in the time of Claudius). The area in which they lived is now called Marsica. They originally spoke a l ...
. After becoming master of Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
, Rome led several wars (against the Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
, Osci
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the langua ...
-Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic peoples, Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan language, Oscan-speaking Osci, people, who originated as an offsh ...
and the Greek colony of Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
, allied with Pyrrhus, king of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
) whose result was the conquest of the Italian peninsula, from the central area up to Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
.
The 3rd and 4th century BC saw the establishment of Roman hegemony over the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
through the three Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
(264–146 BC) fought against Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
and the three Macedonian Wars
The Macedonian Wars (214–148 BC) were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Ancient ...
(212–168 BC) against Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
. The first Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
s were established at this time: Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, Sardinia and Corsica
The Province of Sardinia and Corsica () was an ancient Roman province including the islands of Sardinia and Corsica.
Pre-Roman times
The Nuragic civilization flourished in Sardinia from 1800 to 500 BC. The ancient Sardinians, also known as ...
, Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divide ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
, Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwest ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
.
From the beginning of the 2nd century BC, power was contested between two groups of aristocrats: the optimates
''Optimates'' (, ; Latin for "best ones"; ) and ''populares'' (; Latin for "supporters of the people"; ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated ...
, representing the conservative part of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, and the populares
''Optimates'' (, ; Latin for "best ones"; ) and ''populares'' (; Latin for "supporters of the people"; ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated ...
, which relied on the help of the plebs
In ancient Rome, the plebeians or plebs were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary.
Etymology
The precise origins of the gro ...
(urban lower class) to gain power. In the same period, the bankruptcy of the small farmers and the establishment of large slave estates caused large-scale migration to the city. The continuous warfare led to the establishment of a professional army, which turned out to be more loyal to its generals than to the republic. Because of this, in the late 2nd and early 1st century BC there were several conflicts both abroad and internally: after the failed attempt of social reform of the populares Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
and Gaius Gracchus
Gaius Sempronius Gracchus ( – 121 BC) was a reformist Roman politician and soldier who lived during the 2nd century BC. He is most famous for his tribunate for the years 123 and 122 BC, in which he proposed a wide set of laws, i ...
, and the war against Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia, the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Micipsa's two sons, Hiempsal and Adherbal ...
, there was a civil war from which the general Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (, ; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman of the late Roman Republic. A great commander and ruthless politician, Sulla used violence to advance his career and his co ...
emerged victorious. A major slave revolt under Spartacus
Spartacus (; ) was a Thracians, Thracian gladiator (Thraex) who was one of the Slavery in ancient Rome, escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major Slave rebellion, slave uprising against the Roman Republic.
Historical accounts o ...
followed, and then the establishment of the first Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, Marcus Licinius Crassus, and Gaius Julius Caesar. The republican constitution had many veto points. ...
with Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war. He ...
, Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
and Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome". Wallechinsky, David & Walla ...
.
The conquest of Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
made Caesar immensely powerful and popular, which led to a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
against the Senate and Pompey. After his victory, Caesar established himself as dictator for life. His assassination in 44 BC led to a second Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created at the end of the Roman republic for Mark Antony, Lepidus, and Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November ...
among Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
(Caesar's grandnephew and heir), Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
and Lepidus
Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (; 89 BC – late 13 or early 12 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who formed the Second Triumvirate alongside Octavian and Mark Antony during the final years of the Roman Republic. Lepidus had previously been ...
, and to a final civil war between Octavian and Antony.
Empire
 In 27 BC, Octavian was named ''
In 27 BC, Octavian was named ''Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
'' and ''princeps
''Princeps'' (plural: ''Principes'') is a Latin word meaning "first in time or order; the first, foremost, chief, the most eminent, distinguished, or noble; the first person". As a title, ''Princeps'' originated in the Roman Republic wherein the ...
'', founding the principate
The Principate was the form of imperial government of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the Dominate. The principate was ch ...
, a diarchy
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally spelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate. is a form of government charac ...
between the ''princeps'' and the senate. Over time, the new monarch came to be known as the ''imperator
The title of ''imperator'' ( ) originally meant the rough equivalent of ''commander'' under the Roman Republic. Later, it became a part of the titulature of the Roman Emperors as their praenomen. The Roman emperors generally based their autho ...
'' (hence emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
), meaning "commander". During the reign of Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
, two thirds of the city was ruined after the Great Fire of Rome
The Great Fire of Rome () began on 19 July 64 AD. The fire started in the merchant shops around Rome's chariot stadium, Circus Maximus. After six days, the fire was brought under control, but before the damage could be assessed, the fire reignit ...
, and the persecution of Christians
The persecution of Christians can be historically traced from the first century of the Christian era to the present day. Christian missionaries and converts to Christianity have both been targeted for persecution, sometimes to the point ...
commenced. Rome's empire reached its greatest expansion in the second century under the Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
. Rome was known as the caput Mundi
is a Latin phrase which literally means "Head of the world" whereas ''Roma Caput Mundi'' means "Rome capital of the world" and is one of the many nicknames given to the city of Rome throughout its history.
The phrase is related to the endurin ...
, i.e. the capital of the known world, an expression which had already been used in the Republican period. During its first two centuries, the empire was ruled by emperors of the Julio-Claudian
The Julio-Claudian dynasty comprised the first five Roman emperors: Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero.
This line of emperors ruled the Roman Empire, from its formation (under Augustus, in 27 BC) until the last of the line, Emper ...
, Flavian (who built an eponymous amphitheatre known as the Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; , ultimately from Ancient Greek word "kolossos" meaning a large statue or giant) is an Ellipse, elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphi ...
), and Antonine dynasties. This time was also characterised by the spread of the Christian religion, preached by Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
in Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
in the first half of the first century (under Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
) and popularised by his apostle
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary. The word is derived from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", itself derived from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to se ...
s through the empire and beyond. The Antonine age is considered the zenith of the Empire, whose territory ranged from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
and from Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
to Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
.
 After the end of the
After the end of the Severan dynasty
The Severan dynasty, sometimes called the Septimian dynasty, ruled the Roman Empire between 193 and 235.
It was founded by the emperor Septimius Severus () and Julia Domna, his wife, when Septimius emerged victorious from civil war of 193 - 197, ...
in AD 235, the Empire entered into a 50-year period known as the Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis, was a period in History of Rome, Roman history during which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressure of repeated Barbarian invasions ...
, during which numerous generals fought for power and the central authority in Rome weakened dramatically. Around the same time, the Plague of Cyprian
The Plague of Cyprian was a pandemic which afflicted the Roman Empire from about AD 249 to 262, or 251/2 to 270. The plague is thought to have caused widespread manpower shortages for food production and the Roman army, severely weakening the em ...
( 250–270) afflicted the Mediterranean. Instability caused economic deterioration, and there was a rapid rise in inflation as the government debased the currency in order to meet expenses. The Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
along the Rhine and north of the Balkans made serious uncoordinated incursions that were more like giant raiding parties rather than attempts to settle. The Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
invaded from the east several times during the 230s to 260s but were eventually defeated. The civil wars ended in 285 with the final victory of Diocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
, who undertook the restoration of the State. He ended the Principate
The Principate was the form of imperial government of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the Dominate. The principate was ch ...
and introduced a new authoritarian model known as the Dominate
The Dominate is a periodisation of the Roman Empire during late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was p ...
, derived from his title of ''dominus'' ("lord"). His most marked feature was the unprecedented intervention of the State down to the city level: whereas the State had submitted a tax demand to a city and allowed it to allocate the charges, from his reign the State did this down to the village level. In a vain attempt to control inflation, he imposed price controls
Price controls are restrictions set in place and enforced by governments, on the prices that can be charged for goods and services in a market. The intent behind implementing such controls can stem from the desire to maintain affordability of go ...
which did not last.
Diocletian divided the empire in 286, ruling over the eastern half from Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; , ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocletian who rul ...
, while his co-emperor Maximian
Maximian (; ), nicknamed Herculius, was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was ''Caesar (title), Caesar'' from 285 to 286, then ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his co-emperor and superior, Diocleti ...
ruled the western half from Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubres, Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Ancient Rome, Roman city in Northern Italy.
The city was settled by a Celts, Celtic tribe belonging to the Ins ...
(when not on the move). The empire was further divided in 293, when Diocletian named two caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war. He ...
, one for each augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
(emperor). Diocletian tried to turn into a system of non-dynastic succession, similar to the Antonine dynasty. Upon abdication in 305, both caesars succeeded and they, in turn, appointed two colleagues for themselves. However, a series of civil wars between rival claimants to power resulted in the unification of the empire under Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
in 324. Hereditary succession was restored, but the east–west division was maintained. Constantine undertook a major reform of the bureaucracy, not by changing the structure but by rationalising the competencies of the several ministries. The so-called Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan (; , ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. (1965). ''The Early Church''. SPCK, p. 137. Western Roman Emperor Constantine I and ...
of 313, actually a fragment of a letter from his co-emperor Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Λικίνιος; c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign, he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan that ...
to the governors of the eastern provinces, granted freedom of worship to everyone, including Christians, and ordered the restoration of confiscated church properties upon petition to the newly created vicars of dioceses. He funded the building of several churches and allowed clergy to act as arbitrators in civil suits (a measure that did not outlast him but which was restored in part much later). In 330, he transformed Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
into Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, which became his new capital. However, it was not officially anything more than an imperial residence like Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
, Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a v ...
or Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; , ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocletian who rul ...
until given a city prefect in 359 by Constantius II
Constantius II (; ; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic peoples, while internally the Roman Empire went through repeated civ ...
.
Constantine, following Diocletian's reforms, regionalised the administration, which fundamentally changed the way it was governed by creating regional dioceses. The existence of regional fiscal units from 286 served as the model for this unprecedented innovation. The emperor quickened the process of removing military command from governors. Henceforth, civilian administration and military command would be separate. He gave governors more fiscal duties and placed them in charge of the army logistical support system as an attempt to control it by removing the support system from its control.
Christianity in the form of the Nicene Creed became the official religion of the empire in 380, via the Edict of Thessalonica
An edict is a decree or announcement of a law, often associated with monarchies, but it can be under any official authority. Synonyms include "dictum" and "pronouncement". ''Edict'' derives from the Latin wikt:edictum#Latin, edictum.
Notable ed ...
issued in the name of three emperors – Gratian, Valentinian II, and Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also known as Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. He won two civil wars and was instrumental in establishing the Nicene Creed as the orthodox doctrine for Nicene C ...
– with Theodosius clearly the driving force behind it. He was the last emperor of a unified empire: after his death in 395, his young children, Honorius
Honorius (; 9 September 384 – 15 August 423) was Roman emperor from 393 to 423. He was the younger son of emperor Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla. After the death of Theodosius in 395, Honorius, under the regency of Stilicho ...
and Arcadius
Arcadius ( ; 377 – 1 May 408) was Roman emperor from 383 to his death in 408. He was the eldest son of the ''Augustus'' Theodosius I () and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla, and the brother of Honorius (). Arcadius ruled the eastern half of ...
, inherited the western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and eastern
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:
Transportation
Airlines
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 192 ...
empires respectively. The seat of government in the Western Roman Empire was transferred to Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
in 408, but from 450 the emperors mostly resided in Rome.
 Rome, which had lost its central role in the administration of the empire, was sacked in 410 by the
Rome, which had lost its central role in the administration of the empire, was sacked in 410 by the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group unite ...
led by Alaric I
Alaric I (; , 'ruler of all'; ; – 411 AD) was the first Germanic kingship, king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades earlier by a combine ...
, but very little physical damage was done, most of which was repaired. What could not be so easily replaced were portable items such as artwork in precious metals and items for domestic use (loot). The popes embellished the city with large basilicas, such as Santa Maria Maggiore
Santa Maria Maggiore (), also known as the Basilica of Saint Mary Major or the Basilica of Saint Mary the Great, is one of the four Basilicas in the Catholic Church#Major and papal basilicas, major papal basilicas and one of the Seven Pilgrim C ...
(with the collaboration of the emperors). The population of the city had fallen from 800,000 to 450–500,000 by the time the city was sacked in 455 by Genseric
Gaiseric ( – 25 January 477), also known as Geiseric or Genseric (; reconstructed Vandalic: ) was king of the Vandals and Alans from 428 to 477. He ruled over a kingdom and played a key role in the decline of the Western Roman Empire during ...
, king of the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
. The weak emperors of the fifth century could not stop the decay, leading to the deposition of Romulus Augustus
Romulus Augustus (after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne while still a minor by his father Orestes, the , for whom he served as littl ...
, who resided on Ravenna, on 4 September 476. This marked the end of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
and, for many historians, the beginning of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
.
The decline of the city's population was caused by the loss of grain shipments from North Africa, from 440 onward, and the unwillingness of the senatorial class to maintain donations to support a population that was too large for the resources available. Even so, strenuous efforts were made to maintain the monumental centre, the palatine, and the largest baths, which continued to function until the Gothic siege of 537. The large baths of Constantine on the Quirinale were even repaired in 443, and the extent of the damage exaggerated and dramatised.
However, the city gave an appearance overall of shabbiness and decay because of the large abandoned areas due to population decline. The population declined to 500,000 by 452 and 100,000 by 500 AD (perhaps larger, though no certain figure can be known). After the Gothic siege of 537, the population dropped to 30,000 but had risen to 90,000 by the papacy of Gregory the Great
Pope Gregory I (; ; – 12 March 604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great (; ), was the 64th Bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 until his death on 12 March 604. He is known for instituting the first recorded large-scale mission from Rom ...
. The population decline coincided with the general collapse of urban life in the West in the fifth and sixth centuries, with few exceptions. Subsidized state grain distributions to the poorer members of society continued right through the sixth century and probably prevented the population from falling further. The figure of 450,000–500,000 is based on the amount of pork, 3,629,000 lbs. distributed to poorer Romans during five winter months at the rate of five Roman lbs per person per month, enough for 145,000 persons or 1/4 or 1/3 of the total population. Grain distribution to 80,000 ticket holders at the same time suggests 400,000 (Augustus set the number at 200,000 or one-fifth of the population).
Middle Ages
 After the
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast ...
in AD 476, Rome was first under the control of Odoacer
Odoacer ( – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube who deposed the Western Roman child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became the ruler of Italy (476–493). Odoacer' ...
and then became part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), was a barbarian kingdom established by the Germanic Ostrogoths that controlled Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas between 493 and 553. Led by Theodoric the Great, the Ost ...
before returning to East Roman control after the Gothic War, which devastated the city in 546 and 550
__NOTOC__
Year 550 ( DL) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 550 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe ...
. Its population declined from more than a million in AD 210 to 500,000 in AD 273 to 35,000 after the Gothic War (535–554), reducing the sprawling city to groups of inhabited buildings interspersed among large areas of ruins, vegetation, vineyards and market gardens. It is generally thought the population of the city until AD 300 was 1 million (estimates range from 2 million to 750,000) declining to 750–800,000 in AD 400, then 450–500,000 in AD 450 and down to 80–100,000 in AD 500 (though it may have been twice this).
The Bishop of Rome, called the Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, was important since the early days of Christianity because of the martyrdom of both the apostles Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a su ...
and Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
there. The Bishops of Rome were also seen (and still are seen by Catholics) as the successors of Peter, who is considered the first Bishop of Rome. The city thus became of increasing importance as the centre of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.
After the Lombard invasion of Italy
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) t ...
(569–572), the city remained nominally Byzantine, but in reality, the popes pursued a policy of equilibrium between the Byzantines, the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
, and the Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
. In 729, the Lombard king Liutprand donated the north Latium town of Sutri
Sutri (Latin ''Sutrium'') is an Ancient town, modern ''comune'' and former bishopric (now a Latin titular see) in the province of Viterbo, about from Rome and about south of Viterbo. It is picturesquely situated on a narrow tuff hill, surrounded ...
to the Church, starting its temporal power. In 756, Pepin the Short
the Short (; ; ; – 24 September 768), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian to become king.
Pepin was the son of the Frankish prince Charles Martel and his wife Rotrude of H ...
, after having defeated the Lombards, gave the Pope temporal jurisdiction over the Roman Duchy and the Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna (; ), also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was an administrative district of the Byzantine Empire comprising, between the 6th and 8th centuries, the territories under the jurisdiction of the exarch of Italy (''exarchus ...
, thus creating the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
. Since this period, three powers tried to rule the city: the pope, the nobility (together with the chiefs of militias, the judges, the Senate and the populace), and the Frankish king, as king of the Lombards, patricius, and Emperor. These three parties (theocratic, republican, and imperial) were a characteristic of Roman life during the entire Middle Ages. On Christmas night of 800, Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
was crowned in Rome as Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
by Pope Leo III
Pope Leo III (; died 12 June 816) was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 26 December 795 to his death on 12 June 816. Protected by Charlemagne from the supporters of his predecessor, Adrian I, Leo subsequently strengthened Charlem ...
: on that occasion, the city hosted for the first time the two powers whose struggle for control was to be a constant of the Middle Ages. This event marks the beginning of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
, the first phase of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
.
In 846, Muslim Arabs unsuccessfully stormed the city's walls, but managed to loot St. Peter's and St. Paul's basilica, both outside the city wall. After the decay of Carolingian power, Rome fell prey to feudal chaos: several noble families fought against the pope, the emperor, and each other. These were the times of Theodora and her daughter Marozia
Marozia, born Maria and also known as Mariuccia or Mariozza ( 890 – 937), was a Roman noblewoman who was the alleged mistress of Pope Sergius III and was given the unprecedented titles ''senatrix'' ("senatoress") and ''patricia'' of Rome by Po ...
, concubines and mothers of several popes, and of Crescentius Crescentius may refer to:
* The mediaeval writer on agriculture, Petrus de Crescentius, or Pietro de' Crescenzi
* Crescentius of Jesi or Crescentius Grizi of Jesi (died 1263), Italian Franciscan
* Crescentius Richard Duerr, President of De La Sall ...
, a powerful feudal lord, who fought against the Emperors Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy.
Otto II was ...
and Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was the Holy Roman emperor and King of Italy from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was c ...
. The scandals of this period forced the papacy to reform itself: the election of the pope was reserved to the cardinals, and reform of the clergy was attempted. The driving force behind this renewal was the monk Ildebrando da Soana, who once elected pope under the name of Gregory VII became involved into the Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest (, , ) was a conflict between church and state in medieval Europe, the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture), abbots of monasteri ...
against Emperor Henry IV. Subsequently, Rome was sacked and burned by the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
under Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard ( , ; – 17 July 1085), also referred to as Robert de Hauteville, was a Normans, Norman adventurer remembered for his Norman conquest of southern Italy, conquest of southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Robert was born ...
who had entered the city in support of the Pope, then besieged in Castel Sant'Angelo
Castel Sant'Angelo ( ), also known as Mausoleum of Hadrian (), is a towering rotunda (cylindrical building) in Parco Adriano, Rome, Italy. It was initially commissioned by the Roman Emperor Hadrian as a mausoleum for himself and his family. ...
.
During this period, the city was autonomously ruled by a ''senatore'' or ''patrizio''. In the 12th century, this administration, like other European cities, evolved into the commune, a new form of social organisation controlled by the new wealthy classes. Pope Lucius II
Pope Lucius II (died 15 February 1145), born Gherardo Caccianemici dal Orso, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 March 1144 to his death in 1145. His pontificate was notable for the unrest in Rome associated with ...
fought against the Roman commune, and the struggle was continued by his successor Pope Eugenius III
Pope Eugene III (; c. 1080 – 8 July 1153), born Bernardo Pignatelli, or possibly Paganelli, called Bernardo da Pisa, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 15 February 1145 to his death in 1153. He was the first Cist ...
: by this stage, the commune, allied with the aristocracy, was supported by Arnaldo da Brescia, a monk who was a religious and social reformer. After the pope's death, Arnaldo was taken prisoner by Adrianus IV, which marked the end of the commune's autonomy. Under Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
, whose reign marked the apogee of the papacy, the commune liquidated the senate, and replaced it with a ''Senatore'', who was subject to the pope.
In this period, the papacy played a role of secular importance in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
, often acting as arbitrators between Christian monarch
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest ...
s and exercising additional political powers.Faus, José Ignacio Gonzáles. "''Autoridade da Verdade – Momentos Obscuros do Magistério Eclesiástico''". Capítulo VIII: Os papas repartem terras – Pág.: 64–65 e Capítulo VI: O papa tem poder temporal absoluto – Pág.: 49–55. Edições Loyola. . Embora Faus critique profundamente o poder temporal dos papas ("''Mais uma vez isso salienta um dos maiores inconvenientes do status político dos sucessores de Pedro''" – pág.: 64), ele também admite um papel secular positivo por parte dos papas ("''Não podemos negar que intervenções papais desse gênero evitaram mais de uma guerra na Europa''" – pág.: 65).
In 1266, Charles of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou or Charles d'Anjou, was King of Sicily from 1266 to 1285. He was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the House of Anjou-Sicily. Between 1246 a ...
, who was heading south to fight the Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
on behalf of the pope, was appointed Senator. Charles founded the Sapienza
The Sapienza University of Rome (), formally the Università degli Studi di Roma "La Sapienza", abbreviated simply as Sapienza ('Wisdom'), is a public research university located in Rome, Italy. It was founded in 1303 and is as such one of the ...
, the university of Rome. In that period the pope died, and the cardinals, summoned in Viterbo
Viterbo (; Central Italian, Viterbese: ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in the Lazio region of Italy, the Capital city, capital of the province of Viterbo.
It conquered and absorbed the neighboring town of Ferento (see Ferentium) in ...
, could not agree on his successor. This angered the people of the city, who then unroofed the building where they met and imprisoned them until they had nominated the new pope; this marked the birth of the conclave
A conclave is a gathering of the College of Cardinals convened to appoint the pope of the Catholic Church. Catholics consider the pope to be the apostolic successor of Saint Peter and the earthly head of the Catholic Church.
Concerns around ...
. In this period the city was also shattered by continuous fights between the aristocratic families: Annibaldi, Caetani
The House of Caetani, or Gaetani, is the name of an Italian noble family, originally from the city of Gaeta, connected by some to the lineage of the lords of the Duchy of Gaeta, as well as to the patrician Gaetani of the Republic of Pisa. It pla ...
, Colonna, Orsini Orsini is a surname of Italian origin, originally derived from Latin ''ursinus'' ("bearlike") and originating as an epithet or sobriquet describing the name-bearer's purported strength. Notable people with the surname include the following:
* Aaro ...
, Conti, nested in their fortresses built above ancient Roman edifices, fought each other to control the papacy.
Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII (; born Benedetto Caetani; – 11 October 1303) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 until his death in 1303. The Caetani, Caetani family was of baronial origin with connections t ...
, born Caetani, was the last pope to fight for the church's universal domain
Universal is the adjective for universe.
Universal may also refer to:
Companies
* NBCUniversal, a media and entertainment company that is a subsidiary of Comcast
** Universal Animation Studios, an American Animation studio, and a subsidiary of ...
; he proclaimed a crusade against the Colonna family
The House of Colonna is an Italian noble family, forming part of the papal nobility. It played a pivotal role in Middle Ages, medieval and Roman Renaissance, Renaissance Rome, supplying one pope (Pope Martin V, Martin V), 23 cardinals and many ot ...
and, in 1300, called for the first Jubilee of Christianity, which brought millions of pilgrims to Rome. However, his hopes were crushed by the French king Philip the Fair
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre and Count of Champagne as Philip I from ...
, who took him prisoner and held him hostage for three days at Anagni
Anagni () is an ancient town and ''comune'' in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, in the hills east-southeast of Rome. It is a historical and artistic centre of the Latin Valley.
Geography Overview
Anagni still maintains the appearance of a s ...
. The Pope was able to return to Rome, but died a month later, it was said of shock and grief. Afterwards, a new pope faithful to the French was elected, and the papacy was briefly relocated to Avignon
Avignon (, , ; or , ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the Communes of France, commune had a ...
(1309–1377). During this period Rome was neglected, until a plebeian man, Cola di Rienzo
Nicola di Lorenzo Gabrini (1313 8 October 1354), commonly known as Cola di Rienzo () or Rienzi, was an Italian politician and leader, who styled himself as the "tribune of the Roman people".
During his lifetime, he advocated for the unificatio ...
, came to power. An idealist and a lover of ancient Rome, Cola dreamed about a rebirth of the Roman Empire: after assuming power with the title of '' Tribuno'', his reforms were rejected by the populace. Forced to flee, Cola returned as part of the entourage of Cardinal Gil Álvarez Carrillo de Albornoz, Albornoz, who was charged with restoring the Church's power in Italy. Back in power for a short time, Cola was soon lynched by the populace, and Albornoz took possession of the city. In 1377, Rome became the seat of the papacy again under Gregory XI. The return of the pope to Rome in that year unleashed the Western Schism (1377–1418), and for the next forty years, the city was affected by the divisions which rocked the Church.
Early modern history
In 1418, the Council of Constance settled the Western Schism, and a Roman pope, Martin V, was elected. This brought to Rome a century of internal peace, which marked the beginning of theRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
. The ruling popes until the first half of the 16th century, from Nicholas V, founder of the Vatican Library, to Pius II, humanist and literate, from Sixtus IV, a warrior pope, to Alexander VI, immoral and Nepotism, nepotist, from Julius II, soldier and patron, to Leo X, who gave his name to this period ("the century of Leo X"), all devoted their energy to the greatness and the beauty of the Eternal City and to the patronage of the arts.
During those years, the centre of the Italian Renaissance moved to Rome from Florence. Majestic works, as the new St. Peter's Basilica, Saint Peter's Basilica, the Sistine Chapel and ''Ponte Sisto'' (the first bridge to be built across the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
since antiquity, although on Roman foundations) were created. To accomplish that, the Popes engaged the best artists of the time, including Michelangelo, Pietro Perugino, Perugino, Raphael, Domenico Ghirlandaio, Ghirlandaio, Luca Signorelli, Sandro Botticelli, Botticelli, and Cosimo Rosselli.
The period was also infamous for papal corruption, with many Popes fathering children, and engaging in nepotism and simony. The corruption of the Popes and the huge expenses for their building projects led, in part, to the Protestant Reformation, Reformation and, in turn, the Counter-Reformation. Under extravagant and rich popes, Rome was transformed into a centre of art, poetry, music, literature, education and culture. Rome became able to compete with other major European cities of the time in terms of wealth, grandeur, the arts, learning and architecture.
The Renaissance period changed the face of Rome dramatically, with works like the Pietà (Michelangelo), Pietà by Michelangelo and the frescoes of the Borgia Apartments. Rome reached the highest point of splendour under Pope Julius II (1503–1513) and his successors Pope Leo X, Leo X and Pope Clement VII, Clement VII, both members of the House of Medici, Medici family.
In this twenty-year period, Rome became one of the greatest centres of art in the world. The old St. Peter's Basilica built by Emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
(which by then was in a dilapidated state) was demolished and a new one begun. The city hosted artists like Ridolfo Ghirlandaio, Ghirlandaio, Pietro Perugino, Perugino, Sandro Botticelli, Botticelli and Donato Bramante, Bramante, who built the temple of San Pietro in Montorio and planned a great project to renovate the Apostolic Palace, Vatican. Raphael, who in Rome became one of the most famous painters of Italy, created frescoes in the Villa Farnesina, the Raphael Rooms, Raphael's Rooms, plus many other famous paintings. Michelangelo started the decoration of the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel and executed the famous statue of the Moses for the tomb of Julius II.
Its economy was rich, with the presence of several Tuscan bankers, including Agostino Chigi, who was a friend of Raphael and a patron of arts. Before his early death, Raphael also promoted for the first time the preservation of the ancient ruins. The War of the League of Cognac caused the first plunder of the city in more than five hundred years since Sack of Rome (1084), the previous sack; in 1527, the Landsknechts of Emperor Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V Sack of Rome (1527), sacked the city, bringing an abrupt end to the golden age of the Renaissance in Rome.
Beginning with the Council of Trent in 1545, the Church began the Counter-Reformation in response to the Reformation, a large-scale questioning of the Church's authority on spiritual matters and governmental affairs. This loss of confidence led to major shifts of power away from the Church. Under the popes from Pius IV to Sixtus V, Rome became the centre of a reformed Catholicism and saw the building of new monuments which celebrated the papacy. The popes and cardinals of the 17th and early 18th centuries continued the movement by having the city's landscape enriched with baroque buildings.
This was another nepotistic age; the new aristocratic families (Barberini family, Barberini, Pamphili family, Pamphili, Chigi family, Chigi, Rospigliosi family, Rospigliosi, Altieri family, Altieri, Odescalchi family, Odescalchi) were protected by their respective popes, who built huge baroque buildings for their relatives. During the Age of Enlightenment, new ideas reached the Eternal City, where the papacy supported archaeological studies and improved the people's welfare. But not everything went well for the Church during the Counter-Reformation. There were setbacks in the attempts to assert the Church's power, a notable example being in 1773 when Pope Clement XIV was forced by secular powers to have the Suppression of the Society of Jesus, Jesuit order suppressed.
Late modern and contemporary
 The rule of the Popes was interrupted by the short-lived Roman Republic (18th century), Roman Republic (1798–1800), which was established under the influence of the French Revolution. The
The rule of the Popes was interrupted by the short-lived Roman Republic (18th century), Roman Republic (1798–1800), which was established under the influence of the French Revolution. The Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
were restored in June 1800, but during Napoleon's reign Rome was Rome (department), annexed as a ''Département'' of the First French Empire, French Empire: first as ''Département du Tibre'' (1808–1810) and then as ''Département Rome'' (1810–1814). After the fall of Napoleon, the Papal States were reconstituted by a decision of the Congress of Vienna of 1814.
In 1849, Roman Republic (19th century), a second Roman Republic was proclaimed during a year of revolutions in 1848. Two of the most influential figures of the Italian unification, Giuseppe Mazzini and Giuseppe Garibaldi, fought for the short-lived republic.
Rome then became the focus of hopes of Italian reunification after the rest of Italy was united as the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
in 1861 with the temporary capital in Florence. That year Rome was declared the capital of Italy even though it was still under the Pope's control. During the 1860s, the last vestiges of the Papal States were under French protection thanks to the foreign policy of Napoleon III. French troops were stationed in the region under Papal control. In 1870 the French troops were withdrawn due to the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War. Italian troops were able to Capture of Rome, capture Rome entering the city through a breach near Porta Pia. Pope Pius IX declared himself a prisoner in the Vatican. In 1871 the capital of Italy was moved from Florence to Rome. In 1870 the population of the city was 212,000, all of whom lived with the area circumscribed by the ancient city, and in 1920, the population was 660,000. A significant portion lived outside the walls in the north and across the Tiber in the Vatican area.
 Soon after World War I in late 1922 Rome witnessed the rise of Italian Fascism led by Benito Mussolini, who led a March on Rome, march on the city. He did away with democracy by 1926, eventually declaring a new Imperial Italy (fascist), Italian Empire and allying Italy with Nazi Germany in 1938. Mussolini demolished fairly large parts of the city centre in order to build wide avenues and squares which were supposed to celebrate the fascist regime and the resurgence and glorification of classical Rome. The interwar period saw a rapid growth in the city's population which surpassed one million inhabitants soon after 1930. During World War II, due to the art treasuries and the presence of the Vatican, Rome largely escaped the tragic destiny of other European cities. However, on 19 July 1943, the Quartiere San Lorenzo, San Lorenzo district was Bombing of Rome in World War II, subject to Allied bombing raids, resulting in about 3,000 fatalities and 11,000 injuries, of whom another 1,500 died. Mussolini Fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, was arrested on 25 July 1943. On the date of the Armistice of Cassibile, Italian Armistice 8 September 1943 the city was occupied by the Germans. Allied bombing raids continued throughout 1943 and extended into 1944. Rome was liberated on 4 June 1944.
Rome developed greatly after the war as part of the "Italian economic miracle" of post-war reconstruction and modernisation in the 1950s and early 1960s. During this period, the years of ''la dolce vita'' ("the sweet life"), Rome became a fashionable city, with popular classic films such as ''Ben-Hur (1959 film), Ben Hur'', ''Quo Vadis (1951 film), Quo Vadis'', ''Roman Holiday'' and ''La Dolce Vita'' filmed in the city's iconic
Soon after World War I in late 1922 Rome witnessed the rise of Italian Fascism led by Benito Mussolini, who led a March on Rome, march on the city. He did away with democracy by 1926, eventually declaring a new Imperial Italy (fascist), Italian Empire and allying Italy with Nazi Germany in 1938. Mussolini demolished fairly large parts of the city centre in order to build wide avenues and squares which were supposed to celebrate the fascist regime and the resurgence and glorification of classical Rome. The interwar period saw a rapid growth in the city's population which surpassed one million inhabitants soon after 1930. During World War II, due to the art treasuries and the presence of the Vatican, Rome largely escaped the tragic destiny of other European cities. However, on 19 July 1943, the Quartiere San Lorenzo, San Lorenzo district was Bombing of Rome in World War II, subject to Allied bombing raids, resulting in about 3,000 fatalities and 11,000 injuries, of whom another 1,500 died. Mussolini Fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, was arrested on 25 July 1943. On the date of the Armistice of Cassibile, Italian Armistice 8 September 1943 the city was occupied by the Germans. Allied bombing raids continued throughout 1943 and extended into 1944. Rome was liberated on 4 June 1944.
Rome developed greatly after the war as part of the "Italian economic miracle" of post-war reconstruction and modernisation in the 1950s and early 1960s. During this period, the years of ''la dolce vita'' ("the sweet life"), Rome became a fashionable city, with popular classic films such as ''Ben-Hur (1959 film), Ben Hur'', ''Quo Vadis (1951 film), Quo Vadis'', ''Roman Holiday'' and ''La Dolce Vita'' filmed in the city's iconic Cinecittà Studios
Cinecittà Studios (; Italian for Cinema City) is a large film studio in Rome, Italy. With an area of 400,000 square metres (99 acres), it is the largest film studio in Europe, and is considered the hub of Italian cinema. The studios were constru ...
. The rising trend in population growth continued until the mid-1980s when the ''comune'' had more than 2.8 million residents. After this, the population declined slowly as people began to move to nearby suburbs.
Geography
Location
Rome is in theLazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
region of central Italy on the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
() river. The original settlement developed on hills that faced onto a ford beside the Tiber Island, the only natural ford of the river in this area. The Rome of the Kings was built on seven hills: the Aventine Hill
The Aventine Hill (; ; ) is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth ''rione'', or ward, of Rome.
Location and boundaries
The Aventine Hill is the southernmost of Rome's seven hills. I ...
, the Caelian Hill, the Capitoline Hill, the Esquiline Hill, the Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the ...
, the Quirinal Hill, and the Viminal Hill. Modern Rome is also crossed by another river, the Aniene, which flows into the Tiber north of the historic centre.
Although the city centre is about inland from the Tyrrhenian Sea, the city territory extends to the shore, where the south-western district of Ostia (Rome), Ostia is located. The altitude of the central part of Rome ranges from above mean sea level, above sea level (at the base of the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon) to Above mean sea level, above sea level (the peak of Monte Mario). The ''Comune'' of Rome covers an overall area of about , including many green areas.
Parks and gardens
 Public parks and nature reserves cover a large area in Rome, and the city has one of the largest areas of green space among European capitals. The most notable part of this green space is represented by the large number of villas and landscaped gardens created by the Italian aristocracy. While most of the parks surrounding the villas were destroyed during the building boom of the late 19th century, some of them remain. The most notable of these are the Villa Borghese gardens, Villa Borghese, Villa Ada, and Villa Doria Pamphili. Villa Doria Pamphili is west of the Gianicolo hill, comprising some . The Villa Sciarra (Rome), Villa Sciarra is on the hill, with playgrounds for children and shaded walking areas. In the nearby area of Trastevere, the Orto Botanico dell'Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Orto Botanico (Botanical Garden) is a cool and shady green space. The old Roman hippodrome (Circus Maximus) is another large green space: it has few trees but is overlooked by the Palatine and the Rose Garden ('roseto comunale'). Nearby is the lush Villa Celimontana, close to the gardens surrounding the Baths of Caracalla. The Villa Borghese garden is the best known large green space in Rome, with famous art galleries among its shaded walks. Overlooking Piazza del Popolo and the Spanish Steps are the gardens of Pincio and Villa Medici. There is also a notable pine wood at Castelfusano, near Ostia. Rome also has a number of regional parks of much more recent origin, including the Pineto Regional Park and the Appian Way Regional Park. There are also nature reserves at Marcigliana and at Tenuta di Castelporziano.
Public parks and nature reserves cover a large area in Rome, and the city has one of the largest areas of green space among European capitals. The most notable part of this green space is represented by the large number of villas and landscaped gardens created by the Italian aristocracy. While most of the parks surrounding the villas were destroyed during the building boom of the late 19th century, some of them remain. The most notable of these are the Villa Borghese gardens, Villa Borghese, Villa Ada, and Villa Doria Pamphili. Villa Doria Pamphili is west of the Gianicolo hill, comprising some . The Villa Sciarra (Rome), Villa Sciarra is on the hill, with playgrounds for children and shaded walking areas. In the nearby area of Trastevere, the Orto Botanico dell'Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Orto Botanico (Botanical Garden) is a cool and shady green space. The old Roman hippodrome (Circus Maximus) is another large green space: it has few trees but is overlooked by the Palatine and the Rose Garden ('roseto comunale'). Nearby is the lush Villa Celimontana, close to the gardens surrounding the Baths of Caracalla. The Villa Borghese garden is the best known large green space in Rome, with famous art galleries among its shaded walks. Overlooking Piazza del Popolo and the Spanish Steps are the gardens of Pincio and Villa Medici. There is also a notable pine wood at Castelfusano, near Ostia. Rome also has a number of regional parks of much more recent origin, including the Pineto Regional Park and the Appian Way Regional Park. There are also nature reserves at Marcigliana and at Tenuta di Castelporziano.
Climate
 Rome has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with hot, dry summers and mild, humid winters.
Its average annual temperature is above during the day and at night. In the coldest month, January, the average temperature is during the day and at night. In the warmest month, August, the average temperature is during the day and at night.
December, January and February are the coldest months, with a daily mean temperature of approximately . Temperatures during these months generally vary between during the day and between at night, with colder or warmer spells occurring frequently. Snowfall is rare but not unheard of, with light snow or flurries occurring on some winters, generally without accumulation, and major snowfalls on a very rare occurrence (the most recent ones were in 2018, 2012 and 1986).
The average relative humidity is 75%, varying from 72% in July to 77% in November. Sea temperatures vary from a low of in February to a high of in August.Monthly Tor San Lorenzo water temperature chart
Rome has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with hot, dry summers and mild, humid winters.
Its average annual temperature is above during the day and at night. In the coldest month, January, the average temperature is during the day and at night. In the warmest month, August, the average temperature is during the day and at night.
December, January and February are the coldest months, with a daily mean temperature of approximately . Temperatures during these months generally vary between during the day and between at night, with colder or warmer spells occurring frequently. Snowfall is rare but not unheard of, with light snow or flurries occurring on some winters, generally without accumulation, and major snowfalls on a very rare occurrence (the most recent ones were in 2018, 2012 and 1986).
The average relative humidity is 75%, varying from 72% in July to 77% in November. Sea temperatures vary from a low of in February to a high of in August.Monthly Tor San Lorenzo water temperature chart, seatemperature.org. The highest temperature ever recorded in Rome was on 18 July 2023.
Demographics
By 550 BC, Rome was the second largest city in Italy after only Taras (modernTaranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
) on the Salento Peninsula. It had an area of about and an estimated population of 35,000. Other sources suggest the population was just under 100,000 from 600 to 500 BC. When the Republic was founded in 509 BC the census recorded a population of 130,000. The republic included the city itself and the immediate surroundings. Other sources suggest a population of 150,000 in 500 BC. It surpassed 300,000 by 150 BC.
The size of the city at the time of the Emperor Augustus is a matter of speculation, with estimates based on grain distribution, grain imports, aqueduct capacity, city limits, population density, census reports, and assumptions about the number of unreported women, children and slaves providing a very wide range. Glenn Storey estimates 450,000 people, Whitney Oates estimates 1.2 million, Neville Morely provides a rough estimate of 800,000 and excludes earlier suggestions of 2 million. Estimates of the city's population towards and after the end of the Roman empire also vary. A.H.M. Jones estimated the population at 650,000 in the mid-fifth century. The damage caused by the sackings may have been overestimated. The population had already started to decline from the late fourth century onward, although around the middle of the fifth century it seems that Rome continued to be the most populous city of the two parts of the Empire. According to Krautheimer it was still close to 800,000 in 400 AD; had declined to 500,000 by 452, and dwindled to perhaps 100,000 in 500 AD. After the Gothic Wars, 535–552, the population may have dwindled temporarily to 30,000. During the pontificate of Pope Gregory I (590–604), it may have reached 90,000, augmented by refugees. Lancon estimates 500,000 based on the number of 'incisi' enrolled as eligible to receive bread, oil and wine rations; the number fell to 120,000 in the reform of 419. Neil Christie, citing free rations for the poorest, estimated 500,000 in the mid-fifth century and still a quarter of a million at the end of the century. Novel 36 of Emperor Valentinian III records 3.629 million pounds of pork to be distributed to the needy at 5 lbs. per month for the five winter months, sufficient for 145,000 recipients. This has been used to suggest a population of just under 500,000. Supplies of grain remained steady until the seizure of the remaining provinces of North Africa in 439 by the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
, and may have continued to some degree afterwards for a while. The city's population declined to less than 50,000 people in the Early Middle Ages from 700 AD onward. It continued to stagnate or shrink until the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
.
When the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
annexed Rome in 1870, the city had a population of about 225,000. Less than half the city within the walls was built up in 1881 when the population recorded was 275,000. This increased to 600,000 by the eve of World War I. The Fascism, Fascist regime of Mussolini tried to block an excessive demographic rise of the city but failed to prevent it from reaching one million people by the early 1930s. Population growth continued after the Second World War, helped by a post-war economic boom. A construction boom also created many suburbs during the 1950s and 1960s.
In mid-2010, there were 2,754,440 residents in the city proper, while some 4.2 million people lived in the greater Rome area (which can be approximately identified with its administrative metropolitan city, with a population density of about 800 inhabitants/km2 stretching over more than ). Minors (children ages 18 and younger) totalled 17.00% of the population compared to pensioners who number 20.76%. This compares with the Italian average of 18.06% (minors) and 19.94% (pensioners). The average age of a Roman resident is 43 compared to the Italian average of 42. In the five years between 2002 and 2007, the population of Rome grew by 6.54%, while Italy as a whole grew by 3.56%. The current birth rate of Rome is 9.10 births per 1,000 inhabitants compared to the Italian average of 9.45 births.
The urban area of Rome extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of around 3.9 million. Between 3.2 and 4.2 million people live in the Rome metropolitan area.
Origin groups
 According to the 2011 statistics conducted by ISTAT, approximately 9.5% of the population consists of non-Italians. About half of the immigrant population consists of those of various other European origins (chiefly Romanian, Polish, Ukrainian, and Albanian) numbering a combined total of 131,118 or 4.7% of the population. The remaining 4.8% are those with non-European origins, chiefly Filipinos (26,933), Bangladeshis (12,154), and Chinese (10,283).
The Esquilino (rione of Rome), Esquilino ''Rioni of Rome, rione'', off Termini Station (Rome), Termini Railway Station, has evolved into a largely immigrant neighbourhood. It is perceived as Rome's Chinatown. Immigrants from more than a hundred different countries reside there. A commercial district, Esquilino contains restaurants featuring many kinds of international cuisine. There are wholesale clothes shops. Of the 1,300 or so commercial premises operating in the district 800 are Chinese-owned; around 300 are run by immigrants from other countries around the world; 200 are owned by Italians.
Summary table
According to the 2011 statistics conducted by ISTAT, approximately 9.5% of the population consists of non-Italians. About half of the immigrant population consists of those of various other European origins (chiefly Romanian, Polish, Ukrainian, and Albanian) numbering a combined total of 131,118 or 4.7% of the population. The remaining 4.8% are those with non-European origins, chiefly Filipinos (26,933), Bangladeshis (12,154), and Chinese (10,283).
The Esquilino (rione of Rome), Esquilino ''Rioni of Rome, rione'', off Termini Station (Rome), Termini Railway Station, has evolved into a largely immigrant neighbourhood. It is perceived as Rome's Chinatown. Immigrants from more than a hundred different countries reside there. A commercial district, Esquilino contains restaurants featuring many kinds of international cuisine. There are wholesale clothes shops. Of the 1,300 or so commercial premises operating in the district 800 are Chinese-owned; around 300 are run by immigrants from other countries around the world; 200 are owned by Italians.
Summary table
Language
Rome's historic contribution to language in a worldwide sense is extensive. Through the process of Romanization (cultural), Romanization, the peoples of Italy, Gallia, the Iberian Peninsula and Dacia developed languages which derive directly from Latin and were adopted in large areas of the world, all through cultural influence, colonisation and migration. Moreover, also modern English, because of the Norman Conquest, borrowed a large percentage of its vocabulary from the Latin language. The Latin alphabet, Roman or Latin alphabet is the most widely used writing system in the world used by the greatest number of languages. The medieval Roman dialect belonged to the southern family of Italian dialects, and was thus much closer to the Neapolitan language than to the Florentine. A typical example of Romanesco of that period is ' ("Life ofCola di Rienzo
Nicola di Lorenzo Gabrini (1313 8 October 1354), commonly known as Cola di Rienzo () or Rienzi, was an Italian politician and leader, who styled himself as the "tribune of the Roman people".
During his lifetime, he advocated for the unificatio ...
"), written by an anonymous Roman during the 14th century. Starting with the 16th century, the Roman dialect underwent a stronger and stronger influence from the Tuscan dialect (from which modern Italian derives) starting with the reigns of the two House of Medici, Medici popes (Leo X and Clement VII) and with the Sack of Rome (1527), Sack of Rome in 1527, two events which provoked a large immigration from Tuscany. Therefore, current Romanesco has grammar and roots that are rather different from other dialects in Central Italy.
Religion

Romulus and Remus
In Roman mythology, Romulus and (, ) are twins in mythology, twin brothers whose story tells of the events that led to the Founding of Rome, founding of the History of Rome, city of Rome and the Roman Kingdom by Romulus, following his frat ...
, according to tradition. Other deities such as Vesta (mythology), Vesta and Minerva were honoured. Rome was also the base of several mystery cults, such as Mithraic Mysteries, Mithraism. Later, after Saint Peter, St Peter and Paul the Apostle, St Paul were martyred in the city, and the first Christians began to arrive, Rome became Christian, and the Old St. Peter's Basilica was constructed in 313 AD. Despite some interruptions (such as the Avignon Papacy, Avignon papacy), Rome has for centuries been the home of the Roman Catholic Church and the Pope, Bishop of Rome, otherwise known as the Pope.
Despite the fact that Rome is home to the Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
and St. Peter's Basilica, Rome's cathedral is the Archbasilica of Saint John Lateran, in the south-east of the city centre. There are around 900 churches in Rome in total. Aside from the cathedral itself, some others of note include the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore, the Basilica of Saint Paul Outside the Walls, the Basilica di San Clemente, San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane and the Church of the Gesu, Church of the Gesù. There are also the ancient Catacombs of Rome underneath the city. Numerous highly important religious educational institutions are also in Rome, such as the Pontifical Lateran University, Pontifical Biblical Institute, Pontifical Gregorian University, and Pontifical Oriental Institute.
Since the end of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
, Rome is also the centre of an important Jewish community, which was once based in Trastevere, and later in the Roman Ghetto. There lies also the major synagogue in Rome, the ''Great Synagogue of Rome, Tempio Maggiore''.
The territory of Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
is part of the ''Mons Vaticanus'' (Vatican Hill), and of the adjacent former Vatican Fields, where St. Peter's Basilica, the Apostolic Palace, the Sistine Chapel, and museums were built, along with various other buildings. The area was part of the Roman rione of Borgo (rione of Rome), Borgo until 1929. Being separated from the city on the west bank of the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
, the area was a suburb that was protected by being included within the walls of Pope Leo IV, Leo IV, later expanded by the current fortification walls of Pope Paul III, Paul III, Pope Pius IV, Pius IV, and Pope Urban VIII, Urban VIII. When the Lateran Treaty of 1929 that created the Vatican state was being prepared, the boundaries of the proposed territory were influenced by the fact that much of it was all but enclosed by this loop.
Rome has been a major Christian pilgrimage site since the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. People from all over the Christian world visit Vatican City, within the city of Rome, the seat of the papacy. The city became a major pilgrimage site during the Middle Ages. Apart from brief periods as an independent city during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, Rome kept its status as Papal capital and holy city for centuries, even when the Papacy briefly relocated to Avignon
Avignon (, , ; or , ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the Communes of France, commune had a ...
(1309–1377). Catholics believe that the Vatican is the last resting place of St. Peter. Pilgrimages to Rome can involve visits to many sites, both within Vatican City and in Italian territory. A popular stopping point is the scala sancta, Pilate's stairs: these are, according to the Christian tradition, the steps that led up to the praetorium of Pontius Pilate in Jerusalem, which Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
stood on during his Passion (Christianity), Passion on his way to trial.
In addition, Rome hosts multiple Buddhist temples, and a variety of Reconstructionist Roman religion, Roman modern pagan temples held by the Pietas Comunità Gentile, Associazione Tradizionale Pietas which every year takes part in the religious festivities of the Natale di Roma, historically known as ''Dies Romana'' and also referred to as Romaia, the festival linked to the foundation of Rome, celebrated on 21 April.Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives - Life of Romulus''12.2
(from LacusCurtius) According to
legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess certain qualities that give the ...
, Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
is said to have founded the city of Rome on 21 April, 753 BC. From this date, the Roman chronology derived its system, known by the Latin phrase ''Ab Urbe condita'', meaning ''"from the founding of the City"'', which counted the years from this presumed foundation.
Government
 Rome constitutes a comune ''comune, speciale'', named ''"Roma Capitale"'', and is the largest both in terms of land area and population among the 8,101 ''comuni'' of Italy. It is governed by a mayor and a city council. The seat of the ''comune'' is the ''Palazzo Senatorio'' on the Capitoline Hill, the historic seat of the city government. The local administration in Rome is commonly referred to as ''"Campidoglio"'', the Italian name of the hill. ''Palazzo Senatorio'', seat of the municipality of Rome, has been a town hall since AD 1144, making it the oldest town hall in the world.
Since 1972, the city has been divided into administrative areas, called ''municipi'' (sing. ''municipio'') (until 2001 named ''circoscrizioni''). They were created for administrative reasons to increase decentralisation in the city. Each ''municipio'' is governed by a president and a council of twenty-five members who are elected by its residents every five years. The ''municipi'' frequently cross the boundaries of the traditional, non-administrative divisions of the city. The municipi were originally 20, then 19, and in 2013, their number was reduced to 15.
Rome is also divided into differing types of non-administrative units. The historic centre is divided into 22 ''Rioni of Rome, rioni'', all of which are located within the Aurelian Walls except Prati and Borgo (rione of Rome), Borgo. These originate from the 14 regions of Augustan Rome, which evolved in the Middle Ages into the 14 regions of Medieval Rome, medieval rioni. In the
Rome constitutes a comune ''comune, speciale'', named ''"Roma Capitale"'', and is the largest both in terms of land area and population among the 8,101 ''comuni'' of Italy. It is governed by a mayor and a city council. The seat of the ''comune'' is the ''Palazzo Senatorio'' on the Capitoline Hill, the historic seat of the city government. The local administration in Rome is commonly referred to as ''"Campidoglio"'', the Italian name of the hill. ''Palazzo Senatorio'', seat of the municipality of Rome, has been a town hall since AD 1144, making it the oldest town hall in the world.
Since 1972, the city has been divided into administrative areas, called ''municipi'' (sing. ''municipio'') (until 2001 named ''circoscrizioni''). They were created for administrative reasons to increase decentralisation in the city. Each ''municipio'' is governed by a president and a council of twenty-five members who are elected by its residents every five years. The ''municipi'' frequently cross the boundaries of the traditional, non-administrative divisions of the city. The municipi were originally 20, then 19, and in 2013, their number was reduced to 15.
Rome is also divided into differing types of non-administrative units. The historic centre is divided into 22 ''Rioni of Rome, rioni'', all of which are located within the Aurelian Walls except Prati and Borgo (rione of Rome), Borgo. These originate from the 14 regions of Augustan Rome, which evolved in the Middle Ages into the 14 regions of Medieval Rome, medieval rioni. In the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, under Pope Sixtus V, they again reached fourteen, and their boundaries were finally defined under Pope Benedict XIV in 1743.
Rome is the principal town of the Metropolitan City of Rome
Metropolitan City of Rome Capital () is an area of local government at the level of metropolitan city in the Lazio region of Italy. It comprises the territory of the city of Rome and 120 other ''comuni'' (: ''comune'') in the hinterland of the c ...
, operative since 1 January 2015. The Metropolitan City replaced the old Province of Rome, provincia di Roma, which included the city's metropolitan area and extends further north until Civitavecchia. The Metropolitan City of Rome is the largest by area in Italy. At , its dimensions are comparable to the region of Liguria. Moreover, the city is also the capital of the Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
region.
Rome is the national capital of Italy and is the seat of the Politics of Italy, Italian Government. The official residences of the President of Italy, President of the Italian Republic and the Prime Minister of Italy, Italian Prime Minister, the seats of both houses of the Parliament of Italy, Italian Parliament and that of the Constitutional Court of Italy, Italian Constitutional Court are located in the historic centre. The state ministries are spread out around the city; these include the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which is located in Palazzo della Farnesina near the Olympic stadium.
International relations
Among the global cities, Rome is unique in having two sovereign entities located entirely within its city limits, the Holy See, represented by the Vatican City State, and the territorially smaller Sovereign Military Order of Malta. The Vatican is an enclave of the Italiancapital city
A capital city, or just capital, is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state (polity), state, province, department (administrative division), department, or other administrative division, subnational division, usually as its ...
and a sovereign possession of the Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop ...
, which is the Diocese of Rome and the supreme government of the Roman Catholic Church. For this reason, Rome has sometimes been described as the capital of two states. Rome is the seat of the so-called "Polo Romano" made up by three main international agencies of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
: the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
, the World Food Programme
The World Food Programme (WFP) is an international organization within the United Nations that provides food assistance worldwide. It is the world's largest humanitarian organization and the leading provider of school meals. Founded in 1961 ...
and the International Fund for Agricultural Development
The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) is an international financial institution and a specialised agency of the United Nations that works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries. It is the on ...
.
Rome has traditionally been involved in the process of European political integration. The Treaties of the EU are located in Palazzo della Farnesina. In 1957 the city hosted the signing of the Treaties of Rome, Treaty of Rome, which established the European Economic Community (predecessor to the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
), and also played host to the official signing of the proposed Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe, European Constitution in July 2004. Rome is the seat of the European Olympic Committee and of the NATO Defense College. The city is the place where the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, Statute of the International Criminal Court and the European Convention on Human Rights were formulated. The city hosts also other important international entities such as the International Development Law Organization, the International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property and the UNIDROIT (International Institute for the Unification of Private Law).
Twin towns and sister cities
Since April 1956, Rome is exclusively and reciprocally twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Paris, France : ''Solo Parigi è degna di Roma; solo Roma è degna di Parigi.'' : ''Seule Paris est digne de Rome; seule Rome est digne de Paris.'' : "Only Paris is worthy of Rome; only Rome is worthy of Paris." Rome's other partner cities are:Economy
As the capital of Italy, Rome hosts all the principal institutions of the nation, including the Presidency of the Republic, the government (and its single ), the Parliament, the main judicial Courts, and the diplomatic representatives of all the countries for the states of Italy and Vatican City. Many international institutions are located in Rome, notably cultural and scientific ones, such as the American Institute, the British School, the French Academy, the Scandinavian Institutes, and the German Archaeological Institute. There are also specialised agencies of the United Nations, such as theFood and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
. Rome also hosts major international and worldwide political and cultural organisations, such as the International Fund for Agricultural Development
The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) is an international financial institution and a specialised agency of the United Nations that works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries. It is the on ...
, World Food Programme
The World Food Programme (WFP) is an international organization within the United Nations that provides food assistance worldwide. It is the world's largest humanitarian organization and the leading provider of school meals. Founded in 1961 ...
, the NATO Defence College, and the International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property.
According to the Global city#GaWC study, GaWC study of world cities, Rome is a "Beta +" city. The city was ranked in 2024 as 31st in the Global Cities Index, second highest in Italy after Milan. With a 2005 GDP of €94.376 billion (US$121.5 billion), the city produces 6.7% of the national GDP (more than any other single city in Italy), and its unemployment rate, lowered from 11.1% to 6.5% between 2001 and 2005, is now one of the lowest rates of all the European Union capital cities. Rome's economy grows at around 4.4% annually and continues to grow at a higher rate in comparison to any other city in the rest of the country. This means that were Rome a country, it would be the world's 52nd richest country by GDP, near to the size to that of Egypt. Rome also had a 2003 GDP per capita of €29,153 (US$37,412), which was second in Italy (after Milan), and is more than 134.1% of the EU average GDP per capita. Rome, on the whole, has the highest total earnings in Italy, reaching €47,076,890,463 in 2008, yet, in terms of average workers' incomes, the city places itself 9th in Italy, with €24,509. On a global level, Rome's workers receive the 30th highest wages in 2009, coming three places higher than in 2008, in which the city ranked 33rd. The Rome area had a List of cities by GDP, GDP amounting to $167.8 billion, and $38,765 per capita.
Although the economy of Rome is characterised by the absence of heavy industry, and it is largely dominated by service (economics), services, high-technology companies (IT, aerospace, defence, telecommunications), research, construction and commercial activities (especially banking), and the huge development of tourism are very dynamic and extremely important to its economy. Rome's international airport, Fiumicino, is the largest in Italy, and the city hosts the head offices of the vast majority of the major Italian companies, as well as the headquarters of three of the world's 100 largest companies: Enel
Enel S.p.A. is an Italian multinational manufacturer and distributor of electricity and gas. Enel was first established as a public body at the end of 1962, and then transformed into a limited company in 1992. In 1999, following the liberali ...
, Eni
Eni is an Italian oil and gas corporation.
Eni or ENI may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* Escuela Nacional de Inteligencia, the Argentine intelligence academy
* Groupe des écoles nationales d’ingénieurs (Groupe ENI), a French engi ...
, and Telecom Italia.
Universities, national radio and television and the movie industry in Rome are also important parts of the economy: Rome is also the hub of the Cinema of Italy, Italian film industry, thanks to the Cinecittà studios, working since the 1930s. The city is also a centre for banking and insurance as well as electronics, energy, transport, and aerospace industries. Numerous international companies and agencies headquarters, government ministries, conference centres, sports venues, and museums are located in Rome's principal business districts: the Esposizione Universale Roma (EUR); the ''Torrino'' (further south from the EUR); the ''Magliana''; the ''Parco de' Medici-Laurentina'' and the so-called ''Tiburtina-valley'' along the ancient Via Tiburtina.
Tourism
Rome today is one of the most important tourist destinations of the world, due to the incalculable immensity of its archaeological and artistic treasures, as well as for the charm of its unique traditions, the beauty of its panoramic views, and the majesty of its magnificent "villas" (parks). Among the most significant resources are the many museums – Capitoline Museums, Vatican Museums, the Vatican Museums and the and others dedicated to modern and contemporary art – aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts, fountains, churches, palaces, historical buildings, the monuments and ruins of theRoman Forum
A forum (Latin: ''forum'', "public place outdoors", : ''fora''; English : either ''fora'' or ''forums'') was a public square in a municipium, or any civitas, of Ancient Rome reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, alon ...
, and the Catacombs. Rome is the third most visited city in the EU, after London and Paris, and receives an average of 7–10 million tourists a year, which sometimes doubles on holy years. The Colosseum (4 million tourists) and the Vatican Museums (4.2 million tourists) are the 39th and 37th (respectively) most visited places in the world, according to a recent study.
Rome is a major archaeological hub, and one of the world's main centres of archaeology, archaeological research. There are numerous cultural and research institutes located in the city, such as the American Academy in Rome, and The Swedish Institute at Rome. Rome contains numerous List of ancient monuments in Rome, ancient sites, including the Roman Forum, Forum Romanum, Trajan's Market, Trajan's Forum, the Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; , ultimately from Ancient Greek word "kolossos" meaning a large statue or giant) is an Ellipse, elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphi ...
, and the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon, to name but a few. The Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; , ultimately from Ancient Greek word "kolossos" meaning a large statue or giant) is an Ellipse, elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphi ...
, arguably one of Rome's most iconic archaeological sites, is regarded as a Wonders of the World, wonder of the world.I H Evans (reviser), ''Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable'' (Centenary edition Fourth impression (corrected); London: Cassell, 1975), p. 1163
Rome contains a vast collection of art, sculpture, fountains, mosaics, frescos, and paintings, from all different periods. Rome first became a major artistic centre during ancient Rome, with forms of important Roman art such as Architecture of ancient Rome, architecture, painting, sculpture and mosaic work. Metalworking, Metal-work, coin die and gem engraving, ivory carvings, figurine glass, Ancient Roman pottery, pottery, and book illustrations are considered to be 'minor' forms of Roman artwork. Rome later became a major centre of Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
art, since the popes spent vast sums of money for the constructions of grandiose basilicas, palaces, piazzas and public buildings in general. Rome became one of Europe's major centres of Renaissance artwork, second only to Florence, and able to compare to other major cities and cultural centres, such as Paris and Venice. The city was affected greatly by the Italian Baroque, baroque, and Rome became the home of numerous artists and architects, such as Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Bernini, Caravaggio, Annibale Carracci, Carracci, Francesco Borromini, Borromini and Pietro da Cortona, Cortona. In the late 18th century and early 19th century, the city was one of the centres of the Grand Tour, when wealthy, young English and other European aristocrats visited the city to learn about Culture of ancient Rome, ancient Roman culture, art, philosophy, and architecture. Rome hosted a great number of neoclassical and rococo artists, such as Giovanni Paolo Pannini, Pannini and Bernardo Bellotto. Today, the city is a major artistic centre, with numerous art institutes and museums.
Rome has a growing stock of contemporary and modern art and architecture. The National Gallery of Modern Art has works by Balla, Morandi, Pirandello, Carrà, De Chirico, De Pisis, Guttuso, Fontana, Burri, Mastroianni, Turcato, Kandisky, and Cézanne on permanent exhibition. 2010 saw the opening of Rome's newest arts foundation, a contemporary art and architecture gallery designed by acclaimed Iraqi architect Zaha Hadid. Known as MAXXI – National Museum of the 21st Century Arts it restores a dilapidated area with striking modern architecture. Maxxi features a campus dedicated to culture, experimental research laboratories, international exchange and study and research. It is one of Rome's most ambitious modern architecture projects alongside Renzo Piano's Auditorium Parco della Musica and Massimiliano Fuksas' Rome Convention Center, Centro Congressi Italia EUR, in the EUR district, due to open in 2016. The convention centre features a huge translucent container inside which is suspended a steel and teflon structure resembling a cloud and which contains meeting rooms and an auditorium with two piazzas open to the neighbourhood on either side.
Education
 Rome is a nationwide and major international centre for higher education, containing numerous academies, colleges and universities. It boasts a large variety of academies and colleges, and has always been a major worldwide intellectual and educational centre, especially during Ancient Rome and the
Rome is a nationwide and major international centre for higher education, containing numerous academies, colleges and universities. It boasts a large variety of academies and colleges, and has always been a major worldwide intellectual and educational centre, especially during Ancient Rome and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, along with Florence. According to the City Brands Index, Rome is considered the world's second most historically, educationally and culturally interesting and beautiful city.
Rome has many universities and colleges. Its first university, Sapienza University of Rome, La Sapienza (founded in 1303), is one of the largest in the world, with more than 140,000 students attending; in 2005 it ranked as Europe's 33rd best university and in 2013 the Sapienza University of Rome ranked as the 62nd in the world and the top in Italy in its ''World University Rankings''. and has been ranked among Europe's 50 and the world's 150 best colleges. In order to decrease the overcrowding of La Sapienza, two new public universities were founded during the last decades: University of Rome Tor Vergata, Tor Vergata in 1982, and Roma Tre University, Roma Tre in 1992. Rome hosts also the LUISS School of Government, Italy's most important graduate university in the areas of international affairs and European studies as well as LUISS Business School, Italy's most important business school. Rome Istituto superiore per le industrie artistiche (ISIA), ISIA was founded in 1973 by Giulio Carlo Argan and is Italy's oldest institution in the field of industrial design.
 Rome contains many pontifical university, pontifical universities and other institutes, including the British School at Rome, the French Academy in Rome, French School in Rome, the Pontifical Gregorian University (the oldest Society of Jesus, Jesuit university in the world, founded in 1551), Istituto Europeo di Design, the Lorenzo de' Medici School, Scuola Lorenzo de' Medici, the Link Link Campus, Campus of Malta, and the Università Campus Bio-Medico. Rome is also the location of two American Universities; The American University of Rome and John Cabot University as well as St. John's University (Italy), St. John's University branch campus, John Felice Rome Center, a campus of Loyola University Chicago and Temple University Rome, a campus of Temple University. The Roman Colleges are several seminary, seminaries for students from foreign countries studying for the Catholic priesthood, priesthood at the Pontifical Universities. Examples include the Venerable English College, the Pontifical North American College, the Scots College (Rome), Scots College, and the Pontifical Croatian College of St. Jerome. Rome's major libraries include: the , opened in 1604, making it Italy's first public library; the Biblioteca Vallicelliana, established in 1565; the Biblioteca Casanatense, opened in 1701; the National Central Library (Rome), National Central Library, one of the two national libraries in Italy, which contains 4,126,002 volumes; The Biblioteca del Ministero degli Affari Esteri, specialised in diplomacy, foreign affairs and modern history; the Biblioteca dell'Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana; the Biblioteca Don Bosco, one of the largest and most modern of all Salesian libraries; the Biblioteca e Museo teatrale del Burcardo, a museum-library specialised in history of drama and theatre; the Biblioteca della Società Geografica Italiana, which is based in the Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana and is the most important geographical library in Italy, and one of Europe's most important; and the Vatican Library, one of the oldest and most important libraries in the world, which was formally established in 1475, though in fact much older and has 75,000 codex, codices, as well as 1.1 million printed books, which include some 8,500 Incunabulum, incunabula. There are also many specialist libraries attached to various foreign cultural institutes in Rome, among them that of the American Academy in Rome, the French Academy in Rome and the Bibliotheca Hertziana – Max Planck Institute of Art History, a German library, often noted for excellence in the arts and sciences.
Rome contains many pontifical university, pontifical universities and other institutes, including the British School at Rome, the French Academy in Rome, French School in Rome, the Pontifical Gregorian University (the oldest Society of Jesus, Jesuit university in the world, founded in 1551), Istituto Europeo di Design, the Lorenzo de' Medici School, Scuola Lorenzo de' Medici, the Link Link Campus, Campus of Malta, and the Università Campus Bio-Medico. Rome is also the location of two American Universities; The American University of Rome and John Cabot University as well as St. John's University (Italy), St. John's University branch campus, John Felice Rome Center, a campus of Loyola University Chicago and Temple University Rome, a campus of Temple University. The Roman Colleges are several seminary, seminaries for students from foreign countries studying for the Catholic priesthood, priesthood at the Pontifical Universities. Examples include the Venerable English College, the Pontifical North American College, the Scots College (Rome), Scots College, and the Pontifical Croatian College of St. Jerome. Rome's major libraries include: the , opened in 1604, making it Italy's first public library; the Biblioteca Vallicelliana, established in 1565; the Biblioteca Casanatense, opened in 1701; the National Central Library (Rome), National Central Library, one of the two national libraries in Italy, which contains 4,126,002 volumes; The Biblioteca del Ministero degli Affari Esteri, specialised in diplomacy, foreign affairs and modern history; the Biblioteca dell'Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana; the Biblioteca Don Bosco, one of the largest and most modern of all Salesian libraries; the Biblioteca e Museo teatrale del Burcardo, a museum-library specialised in history of drama and theatre; the Biblioteca della Società Geografica Italiana, which is based in the Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana and is the most important geographical library in Italy, and one of Europe's most important; and the Vatican Library, one of the oldest and most important libraries in the world, which was formally established in 1475, though in fact much older and has 75,000 codex, codices, as well as 1.1 million printed books, which include some 8,500 Incunabulum, incunabula. There are also many specialist libraries attached to various foreign cultural institutes in Rome, among them that of the American Academy in Rome, the French Academy in Rome and the Bibliotheca Hertziana – Max Planck Institute of Art History, a German library, often noted for excellence in the arts and sciences.
Culture
Architecture
Fountains and aqueducts
Rome is a city known for its numerous fountains, built-in all different styles, from Classical and Medieval, to Baroque and Neoclassical. The city has had fountains for more than two thousand years, and they have provided drinking water and decorated the piazzas of Rome. During theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, in 98 AD, according to Sextus Julius Frontinus, the Roman consul who was named ''Curator Aquarum, curator aquarum'' or guardian of the water of the city, Rome had nine aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts which fed 39 monumental fountains and 591 public basins, not counting the water supplied to the Imperial household, baths, and owners of private villas. Each of the major fountains was connected to two different aqueducts, in case one was shut down for service.
During the 17th and 18th century, the Roman popes reconstructed other degraded Roman aqueducts and built new display fountains to mark their termini, launching the golden age of the Roman fountain. The fountains of Rome, like the paintings of Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, were expressions of the new style of Baroque art. In these fountains, sculpture became the principal element, and the water was used simply to animate and decorate the sculptures. They, like baroque gardens, were "a visual representation of confidence and power".
Statues
Rome is well known for its statues but, in particular, the talking statues of Rome. These are usually ancient statues which have become popular soapboxes for political and social discussion, and places for people to (often satirically) voice their opinions. There are two main talking statues: the Pasquino and the Marforio, yet there are four other noted ones: il Babuino, Madama Lucrezia, il Facchino and Abbot Luigi. Most of these statues are ancient Roman or classical, and most of them also depict mythical gods, ancient people or legendary figures; il Pasquino represents Menelaus, Abbot Luigi is an unknown Roman magistrate, il Babuino is supposed to be Silenus, Marforio represents Oceanus, Madama Lucrezia is a bust of Isis, and il Facchino is the only non-Roman statue, created in 1580, and not representing anyone in particular. They are often, due to their status, covered with placards or graffiti expressing political ideas and points of view. Other statues in the city, which are not related to the talking statues, include those of the Ponte Sant'Angelo, or several monuments scattered across the city, such as that to Giordano Bruno in the Campo de'Fiori.Obelisks and columns
 The city hosts eight ancient Egyptian and five ancient Rome, ancient Roman obelisks, together with a number of more modern obelisks; there was also formerly (until 2005) an Aksumite Empire, ancient Ethiopian obelisk in Rome. The city contains some of obelisks in piazzas, such as in Piazza Navona, Saint Peter's Square, St Peter's Square, Piazza di Monte Citorio, Piazza Montecitorio, and Piazza del Popolo, and others in villas, thermae parks and gardens, such as in Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana, the Baths of Diocletian, and the Pincian Hill. Moreover, the centre of Rome hosts also Trajan's column, Trajan's and Column of Marcus Aurelius, Antonine Column, two ancient Roman columns with spiral relief. The Column of Marcus Aurelius is located in Piazza Colonna and it was built around 180 AD by
The city hosts eight ancient Egyptian and five ancient Rome, ancient Roman obelisks, together with a number of more modern obelisks; there was also formerly (until 2005) an Aksumite Empire, ancient Ethiopian obelisk in Rome. The city contains some of obelisks in piazzas, such as in Piazza Navona, Saint Peter's Square, St Peter's Square, Piazza di Monte Citorio, Piazza Montecitorio, and Piazza del Popolo, and others in villas, thermae parks and gardens, such as in Villa Mattei, Villa Celimontana, the Baths of Diocletian, and the Pincian Hill. Moreover, the centre of Rome hosts also Trajan's column, Trajan's and Column of Marcus Aurelius, Antonine Column, two ancient Roman columns with spiral relief. The Column of Marcus Aurelius is located in Piazza Colonna and it was built around 180 AD by Commodus
Commodus (; ; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was Roman emperor from 177 to 192, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father Marcus Aurelius and then ruling alone from 180. Commodus's sole reign is commonly thought to mark the end o ...
in memory of his parents. The Column of Marcus Aurelius was inspired by Trajan's Column at Trajan's Forum, which is part of the Imperial Fora.
Bridges
 The city of Rome contains numerous famous bridges which cross the
The city of Rome contains numerous famous bridges which cross the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
. The only bridge to remain unaltered until today from the classical age is Pons Fabricius, Ponte dei Quattro Capi, which connects the Isola Tiberina with the left bank. The other surviving – albeit modified – ancient Roman bridges crossing the Tiber are Pons Cestius, Ponte Cestio, Ponte Sant'Angelo and Ponte Milvio. Considering Ponte Nomentano, also built during ancient Rome, which crosses the Aniene, currently there are five ancient Roman bridges still remaining in the city. Other noteworthy bridges are Ponte Sisto, the first bridge built in the Renaissance above Roman foundations; Ponte Rotto, actually the only remaining arch of the ancient ''Pons Aemilius'', collapsed during the flood of 1598 and demolished at the end of the 19th century; and Ponte Vittorio Emanuele II, a modern bridge connecting Corso Vittorio Emanuele and Borgo. Most of the city's public bridges were built in Classical or Renaissance style, but also in Baroque, Neoclassical and Modern styles. According to the Encyclopædia Britannica, the finest ancient bridge remaining in Rome is the Ponte Sant'Angelo, which was completed in 135 AD, and was decorated with ten statues of the angels, designed by Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Bernini in 1688.
Catacombs
 Rome has an extensive amount of ancient catacombs, or underground burial places under or near the city, of which there are at least forty, some discovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, they include Religion in ancient Rome, pagan and Jewish burials, either in separate catacombs or mixed together. The first large-scale catacombs were excavated from the 2nd century onwards. Originally they were carved through tuff, a soft volcanic rock, outside the boundaries of the city, because Roman law forbade burial places within city limits. Currently, maintenance of the catacombs is in the hands of the Pope, Papacy which has invested in the Salesians of Don Bosco the supervision of the Catacombs of St. Callixtus on the outskirts of Rome.
Rome has an extensive amount of ancient catacombs, or underground burial places under or near the city, of which there are at least forty, some discovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, they include Religion in ancient Rome, pagan and Jewish burials, either in separate catacombs or mixed together. The first large-scale catacombs were excavated from the 2nd century onwards. Originally they were carved through tuff, a soft volcanic rock, outside the boundaries of the city, because Roman law forbade burial places within city limits. Currently, maintenance of the catacombs is in the hands of the Pope, Papacy which has invested in the Salesians of Don Bosco the supervision of the Catacombs of St. Callixtus on the outskirts of Rome.
Entertainment and performing arts
Rome is an important centre for music, and it has an intense musical scene, including several prestigious music conservatories and theatres. It hosts the Accademia Nazionale di Santa Cecilia (founded in 1585), for which new concert halls have been built in the new Parco della Musica, one of the largest musical venues in the world. Rome also has an opera house, the Teatro dell'Opera di Roma, as well as several minor musical institutions. The city also played host to the Eurovision Song Contest 1991, Eurovision Song Contest in 1991 and the MTV Europe Music Awards 2004, MTV Europe Music Awards in 2004. Rome has also had a major impact on music history. The Roman School was a group of composers of predominantly church music, which were active in the city during the 16th and 17th centuries, therefore spanning the late Renaissance music, Renaissance and early Baroque music, Baroque eras. The term also refers to the music they produced. Many of the composers had a direct connection to the Holy See, Vatican and the Sistine Chapel, papal chapel, though they worked at several churches; stylistically they are often contrasted with the Venetian School (music), Venetian School of composers, a concurrent movement which was much more progressive. By far the most famous composer of the Roman School is Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina, whose name has been associated for four hundred years with smooth, clear, polyphony, polyphonic perfection. However, there were other composers working in Rome, and in a variety of styles and forms. Between 1960 and 1970 Rome was considered to be as a "new Hollywood" because of the many actors and directors who worked there; Via Vittorio Veneto had transformed into a glamour place where you could meet famous people.Fashion
 Rome is also widely recognised as a world fashion capital. Although not as important as Milan, Rome is the fourth most important centre for fashion in the world, according to the 2009 Global Language Monitor after
Rome is also widely recognised as a world fashion capital. Although not as important as Milan, Rome is the fourth most important centre for fashion in the world, according to the 2009 Global Language Monitor after Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
, New York City, New York, and Paris, and beating London.
Major luxury fashion houses and jewellery chains, such as Valentino SpA, Valentino, Bulgari, Fendi
Fendi Srl () is an Culture of Italy, Italian luxury goods, luxury fashion house producing fur, ready-to-wear, leather goods, shoes, fragrances, eyewear, timepieces and accessories. Founded in Rome in 1925 by fashion designers Edoardo Fendi and ...
, Laura Biagiotti, Brioni (brand), Brioni, and Renato Balestra, are headquartered or were founded in the city. Also, other major labels, such as Gucci, Chanel, Prada, Dolce & Gabbana, Armani, and Versace have luxury boutiques in Rome, primarily along its prestigious and upscale Via Condotti, Via dei Condotti.
Cuisine

 Rome's cuisine has evolved through centuries and periods of social, cultural, and political changes. Rome became a major gastronomical centre during the Ancient Rome, ancient age. Ancient Roman cuisine was highly influenced by Ancient Greek culture, and after, the empire's enormous expansion exposed Romans to many new, provincial culinary habits and cooking techniques.
Later, during the
Rome's cuisine has evolved through centuries and periods of social, cultural, and political changes. Rome became a major gastronomical centre during the Ancient Rome, ancient age. Ancient Roman cuisine was highly influenced by Ancient Greek culture, and after, the empire's enormous expansion exposed Romans to many new, provincial culinary habits and cooking techniques.
Later, during the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, Rome became well known as a centre of high-cuisine, since some of the best chefs of the time worked for the popes. An example of this was Bartolomeo Scappi, who was a chef working for Pope Pius IV, Pius IV; he acquired fame in 1570 when his cookbook ''Opera dell'arte del cucinare'' was published. In the book he lists approximately 1,000 recipes of the Renaissance cuisine and describes cooking techniques and tools, giving the first known picture of a fork.
The Testaccio, Rome's trade and slaughterhouse area, was often known as the "belly" or "slaughterhouse" of Rome, and was inhabited by butchers, or ''vaccinari''.Eyewitness Travel (2006), pg. 312 – 313 The most common or ancient Roman cuisine included the "fifth quarter". The old-fashioned ''coda alla vaccinara'' (oxtail cooked in the way of butchers) is still one of the city's most popular meals and is part of most of Rome's restaurants' menus. Lamb is also a very popular part of Roman cuisine, and is often roasted with spices and herbs.
In the modern age, the city developed its own peculiar cuisine, based on products of the nearby Roman Campagna, Campagna, artichoke, globe artichokes are common. In parallel, Roman Jews – present in the city since the 1st century BC – developed their own cuisine, the ''cucina giudaico-romanesca''. The Roman cuisine widely use offal, resulting in dishes such as the entrail-based rigatoni with sauce. is a meat dish based on lamb from the Roman cuisine.
Examples of Roman dishes include ''saltimbocca alla romana'' – a veal cutlet, Roman-style, topped with raw ham and sage and simmered with white wine and butter; ''carciofi alla romana'' – artichokes Roman-style, outer leaves removed, stuffed with mint, garlic, breadcrumbs and braised; ''carciofi alla giudia'' – artichokes fried in olive oil, typical of Roman Jewish cooking, outer leaves removed, stuffed with mint, garlic, breadcrumbs and braised; ''Carbonara, spaghetti alla carbonara'' – spaghetti with bacon, egg (food), eggs and ; ''cacio e pepe, spaghetti cacio e pepe'' – spaghetti with and black pepper; and ''Gnocchi alla romana, gnocchi di semolino alla romana'' – semolina dumpling, Roman-style.
Cinema
 Rome hosts the
Rome hosts the Cinecittà Studios
Cinecittà Studios (; Italian for Cinema City) is a large film studio in Rome, Italy. With an area of 400,000 square metres (99 acres), it is the largest film studio in Europe, and is considered the hub of Italian cinema. The studios were constru ...
, the largest film and television production facility in continental Europe and the centre of the Cinema of Italy, Italian cinema, where many of today's biggest box office hits are filmed. The studio complex is from the centre of Rome and is part of one of the biggest production communities in the world, second only to Hollywood, Los Angeles, California, Hollywood, with well over 5,000 professionals – from period costume makers to visual effects specialists. More than 3,000 productions have been made on its lot.
Founded in 1937 by Benito Mussolini, the studios were bombed by the Allies of World War II, Western Allies during the Second World War. In the 1950s, Cinecittà was the filming location for several large American film productions, and subsequently became the studio most closely associated with Federico Fellini. Today, Cinecittà is the only studio in the world with pre-production, production, and full post-production facilities on one lot, allowing directors and producers to walk in with their script and "walkout" with a completed film.
Sports
Association football is the most popular sport in Rome, as in the rest of the country. The city hosted the final games of the 1934 FIFA World Cup, 1934 and 1990 FIFA World Cup. The latter took place in the Stadio Olimpico, which is also the shared home stadium for local Serie A clubs SS Lazio, founded in 1900, and AS Roma, founded in 1927, whose rivalry in the Derby della Capitale has become a staple of Roman sports culture. Footballers who play for these teams and are also born in the city tend to become especially popular, as has been the case with players such as Francesco Totti and Daniele De Rossi (both for AS Roma), and Alessandro Nesta (for SS Lazio). Rome hosted the
Rome hosted the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad () and commonly known as Rome 1960 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 25 August to 11 September 1960 in Rome, Italy. Rome had previously been awar ...
, with great success, using many ancient sites such as the Villa Borghese gardens, Villa Borghese and the Baths of Caracalla, Thermae of Caracalla as venues. For the Olympic Games many new facilities were built, notably the new large Olympic Stadium (which was then enlarged and renewed to host several matches and the final of the 1990 FIFA World Cup), the Stadio Flaminio, the Villaggio Olimpico (Olympic Village, created to host the athletes and redeveloped after the games as a residential district), ecc. Rome made a Rome bid for the 2020 Summer Olympics, bid to host the 2020 Summer Olympics but it was withdrawn.
Further, Rome hosted the EuroBasket 1991 and is home to the internationally recognised basketball team Virtus Roma. Rugby union is gaining wider acceptance. Until 2011 the Stadio Flaminio was the home stadium for the Italy national rugby union team, which has been playing in the Six Nations Championship since 2000. The team now plays home games at the Stadio Olimpico because the Stadio Flaminio needs works of renovation in order to improve both its capacity and safety. Rome is home to local rugby union teams such as Rugby Roma Olimpic, Rugby Roma (winner of five Italian championships), Unione Rugby Capitolina and S.S. Lazio Rugby 1927 (rugby union branch of the multisport club S.S. Lazio).
Every May, Rome hosts the Italian Open (tennis), Italian Open, an ATP Masters 1000 tournaments, ATP Masters 1000 tennis tournament, on the clay courts of the Foro Italico. Cycling was popular in the post-World War II period, although its popularity has faded. Rome has hosted the final portion of the Giro d'Italia three times, in 1911, 1950, and 2009. Other local sports teams include volleyball (M. Roma Volley), handball or water polo, waterpolo.
Transport


 A three-line metro system called the ''Rome Metro, Metropolitana'' operates in Rome. Construction on the first branch started in the 1930s. The line had been planned to quickly connect the Roma Termini railway station, main railway station with the newly planned E42 area in the southern suburbs, where 1942 the List of world expositions, World Fair was supposed to be held. The event never took place because of war, but the area was later partly redesigned and renamed EUR, Rome, Esposizione Universale Roma in the 1950s to serve as a modern business district. The line was finally opened in 1955, and it is now the south part of the B Line.
The A line opened in 1980 from Ottaviano to Anagnina stations, later extended in stages (1999–2000) to Battistini. In the 1990s, an extension of the B line was opened from Termini to Rebibbia. The A and B lines intersect at Roma Termini station. A new branch of the B line (B1) opened on 13 June 2012 after an estimated building cost of €500 million. B1 connects to line B at Piazza Bologna and has four stations over a distance of .
A third line, the C line, is under construction with an estimated cost of €3 billion and will have 30 stations over a distance of . It will partly replace the existing Roma Termini railway station, Termini-Pantano rail line. It will feature full automated, driverless trains. The first section with 15 stations connecting Pantano with the quarter of Centocelle in the eastern part of the city, opened on 9 November 2014. The end of the work was scheduled in 2015, but archaeological findings often delay underground construction work.
A fourth line, D line, is also planned. It will have 22 stations over a distance of . The first section was projected to open in 2015 and the final sections before 2035, but due to the city's financial crisis, the project has been put on hold.
Above-ground public transport in Rome is made up of a bus, tram and urban train network (FR lines). The bus network has in excess of 350 bus lines and over eight thousand bus stops, whereas the more-limited tram system has of track and 192 stops. There are also trolleybuses.
A three-line metro system called the ''Rome Metro, Metropolitana'' operates in Rome. Construction on the first branch started in the 1930s. The line had been planned to quickly connect the Roma Termini railway station, main railway station with the newly planned E42 area in the southern suburbs, where 1942 the List of world expositions, World Fair was supposed to be held. The event never took place because of war, but the area was later partly redesigned and renamed EUR, Rome, Esposizione Universale Roma in the 1950s to serve as a modern business district. The line was finally opened in 1955, and it is now the south part of the B Line.
The A line opened in 1980 from Ottaviano to Anagnina stations, later extended in stages (1999–2000) to Battistini. In the 1990s, an extension of the B line was opened from Termini to Rebibbia. The A and B lines intersect at Roma Termini station. A new branch of the B line (B1) opened on 13 June 2012 after an estimated building cost of €500 million. B1 connects to line B at Piazza Bologna and has four stations over a distance of .
A third line, the C line, is under construction with an estimated cost of €3 billion and will have 30 stations over a distance of . It will partly replace the existing Roma Termini railway station, Termini-Pantano rail line. It will feature full automated, driverless trains. The first section with 15 stations connecting Pantano with the quarter of Centocelle in the eastern part of the city, opened on 9 November 2014. The end of the work was scheduled in 2015, but archaeological findings often delay underground construction work.
A fourth line, D line, is also planned. It will have 22 stations over a distance of . The first section was projected to open in 2015 and the final sections before 2035, but due to the city's financial crisis, the project has been put on hold.
Above-ground public transport in Rome is made up of a bus, tram and urban train network (FR lines). The bus network has in excess of 350 bus lines and over eight thousand bus stops, whereas the more-limited tram system has of track and 192 stops. There are also trolleybuses.
See also
* Outline of Rome *SPQR
SPQR or S.P.Q.R., an initialism for (; ), is an emblematic phrase referring to the government of the Roman Republic. It appears on documents made public by an inscription in stone or metal, in dedications of monuments and public works, and on ...
* Tourism in Italy
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * *External links
Comune of Rome
APT (official Tourist Office) of the City of Rome
Rome Museums – official site
.
Capitoline Museums
* {{Authority control Rome, Ancient city of Rome, Capitals in Europe Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, Catholic pilgrimage sites Holy cities Places in the deuterocanonical books New Testament cities Populated places established in the 8th century BC 8th-century BC establishments in Italy World Heritage Sites in Italy