Romantic Literature In English on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
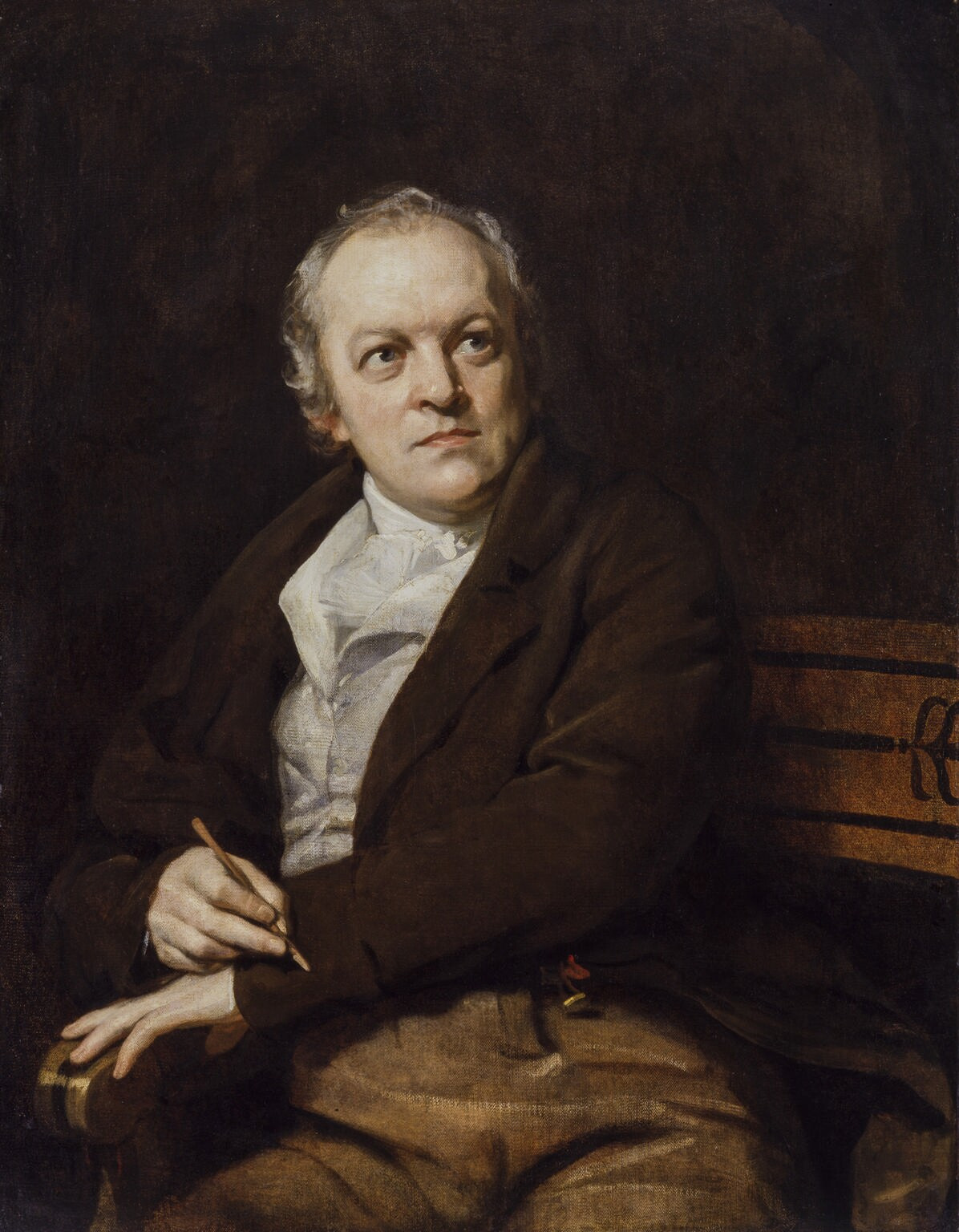

 Romantic Gothic literature made an early appearance with Washington Irving's ''The Legend of Sleepy Hollow'' (1820) and ''Rip Van Winkle'' (1819); there are picturesque "local color" elements in Washington Irving's essays and especially his travel books. From 1823, the prolific and popular novelist James Fenimore Cooper (1789–1851) began publishing his historical romances of frontier and Indian life, to create a unique form of American literature. Cooper is best remembered for his numerous sea-stories and the historical novels known as the ''Leatherstocking Tales'', with their emphasis on heroic simplicity and their fervent landscape descriptions of an already-exotic mythicized frontier peopled by "noble savages", exemplified by Uncas, from ''The Last of the Mohicans'' (1826) show the influence of Rousseau's (1712–78) philosophy. Edgar Allan Poe's tales of the macabre that first appeared in the early 1830s, and his balladic poetry was more influential in France than at home.
By the mid-19th century, the pre-eminence of literature from the British Isles began to be challenged by writers from the former American colonies. This included one of the creators of the new genre of the short story, and inventor of the detective story Edgar Allan Poe (1809–49). A major influence on American writers at this time was
Romantic Gothic literature made an early appearance with Washington Irving's ''The Legend of Sleepy Hollow'' (1820) and ''Rip Van Winkle'' (1819); there are picturesque "local color" elements in Washington Irving's essays and especially his travel books. From 1823, the prolific and popular novelist James Fenimore Cooper (1789–1851) began publishing his historical romances of frontier and Indian life, to create a unique form of American literature. Cooper is best remembered for his numerous sea-stories and the historical novels known as the ''Leatherstocking Tales'', with their emphasis on heroic simplicity and their fervent landscape descriptions of an already-exotic mythicized frontier peopled by "noble savages", exemplified by Uncas, from ''The Last of the Mohicans'' (1826) show the influence of Rousseau's (1712–78) philosophy. Edgar Allan Poe's tales of the macabre that first appeared in the early 1830s, and his balladic poetry was more influential in France than at home.
By the mid-19th century, the pre-eminence of literature from the British Isles began to be challenged by writers from the former American colonies. This included one of the creators of the new genre of the short story, and inventor of the detective story Edgar Allan Poe (1809–49). A major influence on American writers at this time was
''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', 11th ed.1910-1911
''Romanticism''
via ''Discovering Literature: Romantics and Victorians'' at the British Library
The Romantics
''In Our Time'', BBC Radio 4 discussion with Jonathan Bate, Rosemary Ashton and Nicholas Roe (Oct. 12, 2000)
The Later Romantics
''In Our Time'', BBC Radio 4 discussion with Jonathan Bate, Robert Woof & Jennifer Wallace (Apr, 15, 2004) {{DEFAULTSORT:English Literature 1798 establishments in Great Britain 1837 disestablishments in the United Kingdom English-language literature History of literature in the United Kingdom Romantic literature 18th-century British literature 19th-century British literature
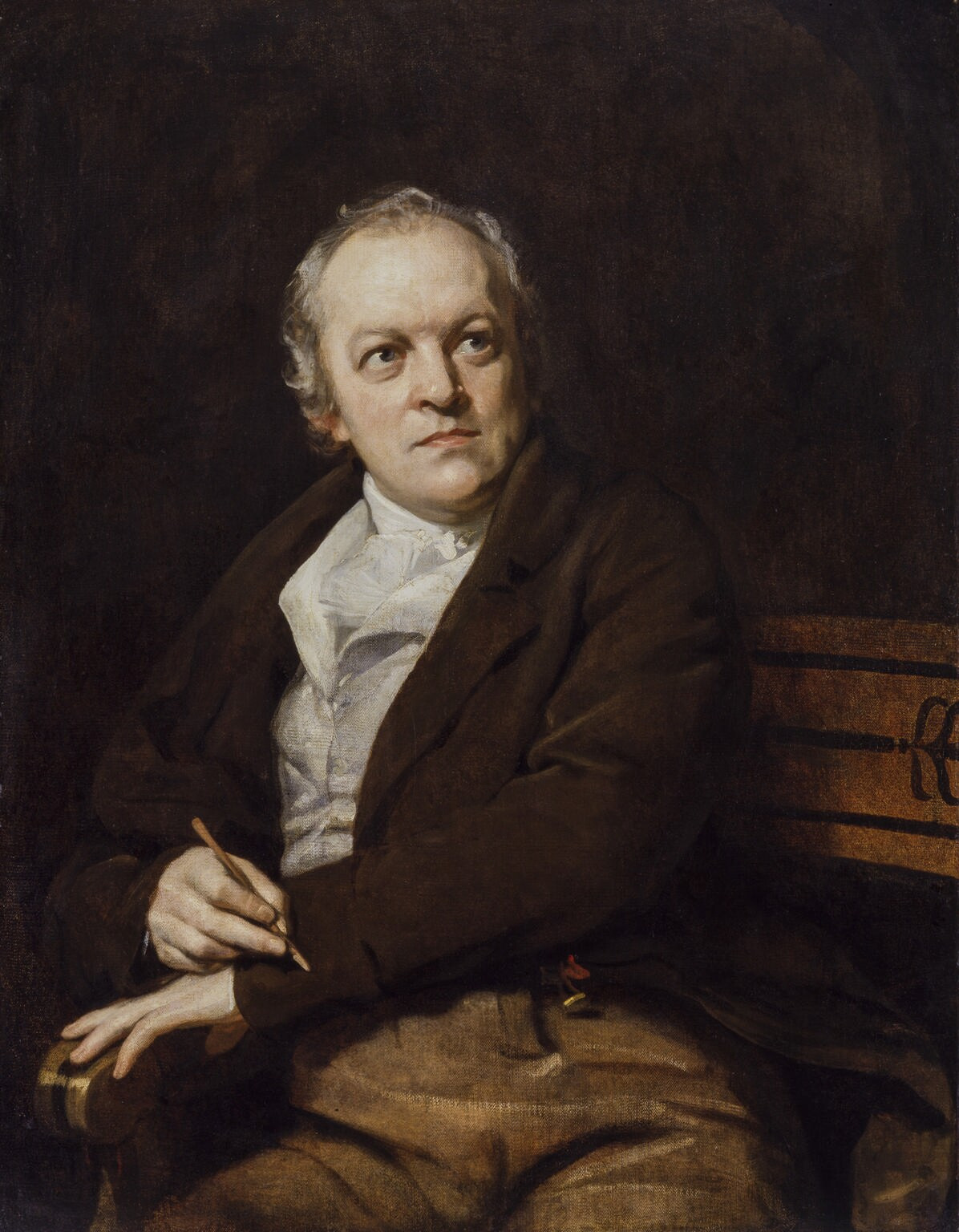
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe toward the end of the 18th century. Scholars regard the publishing of William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
's and Samuel Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge ( ; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets with his friend William Wordswort ...
's '' Lyrical Ballads'' in 1798 as probably the beginning of the movement in England, and the Coronation of Queen Victoria
The coronation of Queen Victoria, Victoria as queen of the United Kingdom took place on Thursday, 28 June 1838, just over a year after she succeeded to the throne of the United Kingdom at the age of 18. The ceremony was held in Westminster Abbey ...
in 1837 as its end. Romanticism arrived in other parts of the English-speaking world later; in the United States, about 1820.
The Romantic period was one of social change in England because of the depopulation of the countryside and the rapid growth of overcrowded industrial cities
An industrial city or industrial town is a town or city in which the municipal economy, at least historically, is centered around industry, with important factories or other production facilities in the town. It has been part of most countries' ...
between 1798 and 1832. The movement of so many people in England was the result of two forces: the Agricultural Revolution, which involved enclosure
Enclosure or inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or "common land", enclosing it, and by doing so depriving commoners of their traditional rights of access and usage. Agreements to enc ...
s that drove workers and their families off the land; and the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, which provided jobs "in the factories and mills, operated by machines driven by steam-power
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
". Indeed, Romanticism may be seen in part as a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, though it was also a revolt against the aristocratic social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
, as well as a reaction against the scientific rationalization of nature. The French Revolution had an important influence on the political thinking of many Romantic figures at this time as well.
England
18th-century precursors
The Romantic movement in English literature of the early 19th century has its roots in 18th-century poetry, theGothic novel
Gothic fiction, sometimes referred to as Gothic horror (primarily in the 20th century), is a literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name of the genre is derived from the Renaissance era use of the word "gothic", as a pejorative to mean ...
and the novel of sensibility. Cuddon, p. 588 This includes the pre-Romantic graveyard poets from the 1740s, whose works are characterized by gloomy meditations on mortality, "skulls and coffins, epitaphs and worms". To this was added by later practitioners, a feeling for the " sublime" and uncanny, and an interest in ancient English poetic forms and folk poetry. These concepts are often considered precursors of the Gothic genre. Gothic poets include Thomas Gray
Thomas Gray (26 December 1716 – 30 July 1771) was an English poet, letter-writer, and classics, classical scholar at Cambridge University, being a fellow first of Peterhouse then of Pembroke College, Cambridge, Pembroke College. He is widely ...
(1716–71), whose ''Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard
''Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard'' is a poem by Thomas Gray, completed in 1750 and first published in 1751. The poem's origins are unknown, but it was partly inspired by Gray's thoughts following the death of the poet Richard West in 1742 ...
'' (1751) is "the best known product of this kind of sensibility"; William Cowper
William Cowper ( ; – 25 April 1800) was an English poet and Anglican hymnwriter.
One of the most popular poets of his time, Cowper changed the direction of 18th-century nature poetry by writing of everyday life and scenes of the Engli ...
(1731–1800); Christopher Smart (1722–71); Thomas Chatterton
Thomas Chatterton (20 November 1752 – 24 August 1770) was an English poet whose precocious talents ended in suicide at age 17. He was an influence on Romantic artists of the period such as Shelley, Keats, Wordsworth and Coleridge.
Alth ...
(1752–70); Robert Blair (1699–1746), author of '' The Grave'' (1743), "which celebrates the horror of death"; and Edward Young (1683–1765), whose ''The Complaint, or Night-Thoughts on Life, Death and Immortality'' (1742–45) is another "noted example of the graveyard genre". Other precursors of Romanticism are the poets James Thomson (1700–48) and James Macpherson (1736–96).
The sentimental novel
The sentimental novel or the novel of sensibility is an 18th- and 19th-century literary genre which presents and celebrates the concepts of sentiment, sentimentalism, and sensibility. Sentimentalism, which is to be distinguished from sensi ...
or "novel of sensibility" developed during the second half of the 18th century. It celebrates the emotional and intellectual concepts of sentiment, sentimentalism and sensibility. Sentimentalism, which is to be distinguished from sensibility, was a fashion in both poetry and prose fiction which began in reaction to the rationalism of the Augustan Age. Sentimental novels relied on emotional response both from their readers and characters. Scenes of distress and tenderness are common, and the plot is arranged to advance emotions rather than action. The result is a valorization of "fine feeling", displaying the characters as models for refined, sensitive emotional effect. The ability to display feelings was thought to show character and experience, and to shape social life and relations. Famous sentimental novels in English include Samuel Richardson
Samuel Richardson (baptised 19 August 1689 – 4 July 1761) was an English writer and printer known for three epistolary novels: '' Pamela; or, Virtue Rewarded'' (1740), '' Clarissa: Or the History of a Young Lady'' (1748) and '' The Histo ...
's ''Pamela, or Virtue Rewarded
''Pamela; or, Virtue Rewarded'' is an epistolary novel first published in 1740 by the English writer Samuel Richardson. Considered one of the first true English novels, it serves as Richardson's version of conduct literature about marriage. ...
'' (1740), Oliver Goldsmith
Oliver Goldsmith (10 November 1728 – 4 April 1774) was an Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish poet, novelist, playwright, and hack writer. A prolific author of various literature, he is regarded among the most versatile writers of the Georgian e ...
's '' The Vicar of Wakefield'' (1766), Laurence Sterne
Laurence Sterne (24 November 1713 – 18 March 1768) was an Anglo-Irish novelist and Anglican cleric. He is best known for his comic novels ''The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman'' (1759–1767) and ''A Sentimental Journey Thro ...
's ''Tristram Shandy Tristram may refer to:
Literature
* the title character of ''The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman'', a novel by Laurence Sterne
* the title character of '' Tristram of Lyonesse'', an epic poem by Algernon Charles Swinburne
*"Tristr ...
'' (1759–67) and '' A Sentimental Journey'' (1768), Henry Brooke's '' The Fool of Quality'' (1765–70), Henry Mackenzie's '' The Man of Feeling'' (1771) and Maria Edgeworth
Maria Edgeworth (1 January 1768 – 22 May 1849) was a prolific Anglo-Irish novelist of adults' and children's literature. She was one of the first realist writers in children's literature and a significant figure in the evolution of the novel i ...
's '' Castle Rackrent'' (1800).
Foreign influences were the Germans Goethe
Johann Wolfgang (von) Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German polymath who is widely regarded as the most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a wide-ranging influence on Western literature, literary, Polit ...
, Schiller and August Wilhelm Schlegel, and French philosopher and writer Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Republic of Geneva, Genevan philosopher (''philosophes, philosophe''), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment through ...
(1712–78). Cuddon, pp. 588–9. Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January ew Style, NS1729 – 9 July 1797) was an Anglo-Irish Politician, statesman, journalist, writer, literary critic, philosopher, and parliamentary orator who is regarded as the founder of the Social philosophy, soc ...
's '' A Philosophical Enquiry into the Origin of Our Ideas of the Sublime and Beautiful'' (1757) is another important influence.Drabble
A drabble is a short work of fiction of precisely one hundred words in length."Winner ...
, pp. 957–8. The changing landscape, brought about by the expansion of the city and depopulation of the countryside, was another influence on the growth of the Romantic movement. The poor condition of workers, the new class conflicts and the pollution of the environment led to a reaction against urbanism
Urbanism is the study of how inhabitants of urban areas, such as towns and cities, interact with the built environment. It is a direct component of disciplines such as urban planning, a profession focusing on the design and management of urban ...
and industrialization, and an emphasis on the beauty and value of nature.
Horace Walpole
Horatio Walpole, 4th Earl of Orford (; 24 September 1717 – 2 March 1797), better known as Horace Walpole, was an English Whig politician, writer, historian and antiquarian.
He had Strawberry Hill House built in Twickenham, southwest London ...
's 1764 novel ''The Castle of Otranto
''The Castle of Otranto'' is a novel by Horace Walpole. First published in 1764, it is generally regarded as the first Gothic novel. In the second edition, Walpole applied the word 'Gothic' to the novel in the subtitle – ''A Gothic Story''. Se ...
'' created the Gothic fiction
Gothic fiction, sometimes referred to as Gothic horror (primarily in the 20th century), is a literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name of the genre is derived from the Renaissance era use of the word "gothic", as a pejorative to mean me ...
genre by combining elements of horror and romance. Ann Radcliffe introduced the brooding figure of the gothic villain
A villain (also known as a " black hat", "bad guy" or "baddy"; The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.126 "baddy (also baddie) noun (pl. -ies) ''informal'' a villain or criminal in a book, film, etc.". the feminine form is villai ...
, which developed into the Byronic hero. Her most popular and influential work, '' The Mysteries of Udolpho'' (1795), is frequently cited as the archetypal Gothic novel. '' Vathek'' (1786) by William Beckford and '' The Monk'' (1796) by Matthew Lewis were other notable early works in the gothic and horror literary genres. The first English short stories were gothic tales like Richard Cumberland's "remarkable narrative" ''The Poisoner of Montremos'' (1791).
Romantic poetry
The physical landscape is prominent in the poetry of this period. The Romantics, and especially Wordsworth, are often described as "nature poets". However, these "nature poems" reveal wider concerns in that they are often meditations on "an emotional problem or personal crisis". The poet, painter and printmakerWilliam Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake has become a seminal figure in the history of the Romantic poetry, poetry and visual art of the Roma ...
(1757–1827) was an early writer of his kind. Largely disconnected from the major streams of the literature of his time, Blake was generally unrecognized during his lifetime but is now considered a seminal figure in the history of both the poetry and visual arts of the Romantic Age. Considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, Blake is held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and creativity, and for the philosophical and mystical undercurrents within his work. Among his most important works are '' Songs of Innocence'' (1789) and '' Songs of Experience'' (1794), "and profound and difficult 'prophecies'" such as '' Visions of the Daughters of Albion'' (1793), '' The Book of Urizen'' (1794), '' Milton'' (1804–1810) and '' Jerusalem The Emanation of the Giant Albion'' (1804–1820).
After Blake, among the earliest Romantics were the Lake Poets
The Lake Poets were a group of English poets who all lived in the Lake District of England, United Kingdom, in the first half of the nineteenth century. As a group, they followed no single "school" of thought or literary practice then known. They ...
, a small group of friends, including William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
(1770–1850), Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge ( ; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets with his friend William Wordsworth ...
(1772–1834), Robert Southey (1774–1843) and journalist Thomas De Quincey (1785–1859). However, at the time, Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European literature, European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'' (18 ...
(1771–1832) was the most famous poet. Scott achieved immediate success with his long narrative poem '' The Lay of the Last Minstrel'' in 1805, followed by the full epic poem
In poetry, an epic is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. With regard to ...
'' Marmion'' in 1808. Both were set in the distant Scottish past.
The early Romantic poets brought a new form of emotionalism and introspection
Introspection is the examination of one's own conscious thoughts and feelings. In psychology, the process of introspection relies on the observation of one's mental state, while in a spiritual context it may refer to the examination of one's s ...
, and their emergence is marked by the first romantic manifesto in English literature, the ''Preface'' to '' Lyrical Ballads'' (1798). In it Wordsworth discusses what he sees as the elements of a new type of poetry, one based on the "real language of men", and which avoids the poetic diction of much 18th-century poetry. Here, Wordsworth gives his famous definition of poetry, as "the spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings" which "takes its origin from emotion recollected in tranquility". The poems in ''Lyrical Ballads'' were mostly by Wordsworth, though Coleridge contributed one of the great poems of English literature, the long '' Rime of the Ancient Mariner'', a tragic ballad about the survival of one sailor through a series of supernatural events on his voyage through the South Seas
Today the term South Seas, or South Sea, most commonly refers to the portion of the Pacific Ocean south of the equator. The term South Sea may also be used synonymously for Oceania, or even more narrowly for Polynesia or the Polynesian Triangle ...
, and involves the symbolically significant slaying of an albatross. Coleridge is also especially remembered for ''Kubla Khan
"Kubla Khan: or A Vision in a Dream" () is a poem written by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, completed in 1797 and published in 1816. It is sometimes given the subtitles "A Vision in a Dream" and "A Fragment." According to Coleridge's preface to "Kub ...
'', '' Frost at Midnight'', '' Dejection: An Ode'', '' ''Christabel'''', as well as the major prose work, '' Biographia Literaria''. His critical work, especially on Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
, was highly influential, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking culture. Coleridge and Wordsworth, along with Carlyle, were major influences through Emerson, on American transcendentalism
Transcendentalism is a philosophical, spiritual, and literary movement that developed in the late 1820s and 1830s in the New England region of the United States. "Transcendentalism is an American literary, political, and philosophical movement of ...
. Among Wordsworth's most important poems are ''Michael
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* he He ..., a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name
* Michael (bishop elect)">Michael (surname)">he He ..., a given nam ...
'', '' Lines Written a Few Miles Above Tintern Abbey'' , '' Resolution and Independence'', '' Ode: Intimations of Immortality'' and the long, autobiographical epic ''The Prelude
''The Prelude or, Growth of a Poet's Mind; An Autobiographical Poem '' is an autobiographical poem in blank verse by the English poet William Wordsworth. Intended as the introduction to the more philosophical poem ''The Recluse,'' which Wordswort ...
''. ''The Prelude'' was begun in 1799, but published posthumously in 1850. Wordsworth's poetry is noteworthy for how he "inverted the traditional hierarchy of poetic genres, subjects, and style by elevating humble and rustic life and the plain ..into the main subject and medium of poetry in general", and how, in Coleridge's words, he awakens in the reader a "freshness of sensation" in his depiction of familiar, commonplace objects.
Robert Southey (1774–1843) was another of the so-called "Lake Poets
The Lake Poets were a group of English poets who all lived in the Lake District of England, United Kingdom, in the first half of the nineteenth century. As a group, they followed no single "school" of thought or literary practice then known. They ...
", and Poet Laureate for 30 years from 1813 to his death in 1843, although his fame has been long eclipsed by that of his contemporaries and friends William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
and Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge ( ; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets with his friend William Wordsworth ...
. Thomas De Quincey (1785–1859) was an English essay
An essay ( ) is, generally, a piece of writing that gives the author's own argument, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of a Letter (message), letter, a term paper, paper, an article (publishing), article, a pamphlet, and a s ...
ist, best known for his '' Confessions of an English Opium-Eater'' (1821), an autobiographical account of his laudanum use and its effect on his life. William Hazlitt
William Hazlitt (10 April 177818 September 1830) was an English essayist, drama and literary criticism, literary critic, painter, social commentator, and philosopher. He is now considered one of the greatest critics and essayists in the history ...
(1778–1830), friend of both Coleridge and Wordsworth, is another important essayist at this time, though today he is best known for his literary criticism, especially '' Characters of Shakespear's Plays'' (1817–18).

Second generation
The second generation of Romantic poets includesLord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
(1788–1824), Percy Bysshe Shelley
Percy Bysshe Shelley ( ; 4 August 1792 – 8 July 1822) was an English writer who is considered one of the major English Romantic poets. A radical in his poetry as well as in his political and social views, Shelley did not achieve fame durin ...
(1792–1822) and John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tub ...
(1795–1821). Byron, however, was still influenced by 18th-century satirists and was, perhaps the least "romantic" of the three, preferring "the brilliant wit of Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
to what he called the 'wrong poetical system' of his Romantic contemporaries". Byron achieved enormous fame and influence throughout Europe with works exploiting the violence and drama of their exotic and historical settings. Goethe
Johann Wolfgang (von) Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German polymath who is widely regarded as the most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a wide-ranging influence on Western literature, literary, Polit ...
called Byron "undoubtedly the greatest genius of our century". A trip to Europe resulted in the first two cantos of ''Childe Harold's Pilgrimage
''Childe Harold's Pilgrimage: A Romaunt'' is a long narrative poem in four parts written by Lord Byron. The poem was published between 1812 and 1818. Dedicated to " Ianthe", it describes the travels and reflections of a young man disillusioned ...
'' (1812), a mock-heroic epic of a young man's adventures in Europe, but also a sharp satire against London society. The poem contains elements thought to be autobiographical, as Byron generated some of the storyline from experience gained during his travels between 1809 and 1811. However, despite the success of ''Childe Harold'' and other works, Byron was forced to leave England for good in 1816 and seek asylum on the Continent, because, among other things, of his alleged incestuous affair with his half-sister Augusta Leigh
Augusta Maria Leigh (''née'' Byron; 26 January 1783 – 12 October 1851) was the only surviving daughter of John Byron (British Army officer), John "Mad Jack" Byron, the poet Lord Byron's father, by his first wife, Amelia Osborne, Marchiones ...
.Drabble
A drabble is a short work of fiction of precisely one hundred words in length."Winner ...
, p. 156. Here he joined Percy Bysshe and Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley ( , ; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction# ...
, with his secretary John William Polidori on the shores of Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva is a deep lake on the north side of the Alps, shared between Switzerland and France. It is one of the List of largest lakes of Europe, largest lakes in Western Europe and the largest on the course of the Rhône. Sixty percent () ...
, during the "Year Without a Summer
The year 1816 is known as the Year Without a Summer because of severe climate abnormalities that caused average global temperatures to decrease by . Summer temperatures in Europe were the coldest of any on record between 1766 and 2000, resultin ...
". Polidori's ''The Vampyre
"The Vampyre" is a short work of prose fiction written in 1819 by John William Polidori, taken from the story told by Lord Byron as part of a contest among Polidori, Mary Shelley, Lord Byron, and Percy Shelley. The same contest produced the n ...
'' was published in 1819, creating the literary vampire genre. This short story was inspired by the life of Lord Byron and his poem '' The Giaour'' (1813). Between 1819 and 1824, Byron published his unfinished epic satire ''Don Juan
Don Juan (), also known as Don Giovanni ( Italian), is a legendary fictional Spanish libertine who devotes his life to seducing women.
The original version of the story of Don Juan appears in the 1630 play (''The Trickster of Seville and t ...
'', which, though initially condemned by the critics, "was much admired by Goethe who translated part of it".
Shelley is perhaps best known for poems such as '' Ozymandias'', '' Ode to the West Wind'', '' To a Skylark'', '' Music, When Soft Voices Die'', ''The Cloud'', '' The Masque of Anarchy'' and '' Adonais'', an elegy written on the death of Keats. Shelley's early profession of atheism, in the tract '' The Necessity of Atheism'', led to his expulsion from Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
, and branded him as a radical agitator and thinker, setting an early pattern of marginalization
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. In the EU context, the Euro ...
and ostracism
Ostracism (, ''ostrakismos'') was an Athenian democratic procedure in which any citizen could be expelled from the city-state of Athens for ten years. While some instances clearly expressed popular anger at the citizen, ostracism was often us ...
from the intellectual and political circles of his time. Similarly, Shelley's 1821 essay '' A Defence of Poetry'' displayed a radical view of poetry, in which poets act as "the unacknowledged legislators of the world", because, of all of artists, they best perceive the undergirding structure of society. His close circle of admirers, however, included the most progressive thinkers of the day, including his future father-in-law, philosopher William Godwin
William Godwin (3 March 1756 – 7 April 1836) was an English journalist, political philosopher and novelist. He is considered one of the first exponents of utilitarianism and the first modern proponent of anarchism. Godwin is most famous fo ...
. Works like '' Queen Mab'' (1813) reveal Shelley "as the direct heir to the French and British revolutionary intellectuals of the 1790s." Shelley became an idol of the next three or four generations of poets, including important Victorian and Pre-Raphaelite
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (PRB), later known as the Pre-Raphaelites, was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, ...
poets such as Robert Browning
Robert Browning (7 May 1812 – 12 December 1889) was an English poet and playwright whose dramatic monologues put him high among the Victorian literature, Victorian poets. He was noted for irony, characterization, dark humour, social commentar ...
and Dante Gabriel Rossetti
Gabriel Charles Dante Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882), generally known as Dante Gabriel Rossetti ( ; ), was an English poet, illustrator, painter, translator, and member of the Rossetti family. He founded the Pre-Raphaelite Brother ...
, as well as later W. B. Yeats
William Butler Yeats (, 13 June 186528 January 1939), popularly known as W. B. Yeats, was an Irish poet, dramatist, writer, and literary critic who was one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. He was a driving force behind the ...
. Shelley's influential poem '' The Masque of Anarchy'' (1819) calls for nonviolence in protest and political action. It is perhaps the first modern statement of the principle of nonviolent protest. Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (2October 186930January 1948) was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalism, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethics, political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful Indian ...
's passive resistance was influenced and inspired by Shelley's verse, and Gandhi would often quote the poem to vast audiences.
Though John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tub ...
shared Byron and Shelley's radical politics, "his best poetry is not political", but is especially noted for its sensuous music and imagery, along with a concern with material beauty and the transience of life. Among his most famous works are '' The Eve of St. Agnes'', '' Ode to Psyche'', '' La Belle Dame sans Merci'', ''Ode to a Nightingale
"Ode to a Nightingale" is a poem by John Keats written either in the garden of the Spaniards Inn, Hampstead, London or, according to Keats' friend Charles Armitage Brown, under a plum tree in the garden of Keats' house at Keats House, Wentworth P ...
'', ''Ode on a Grecian Urn'', ''Ode on Melancholy'', ''To Autumn'' and the incomplete ''Hyperion (poem), Hyperion'', a "philosophical" poem in blank verse, which was "conceived on the model of John Milton, Milton's ''Paradise Lost''". Keats' letters "are among the finest in English" and important "for their discussion of his aesthetic ideas", including 'negative capability. Keats has always been regarded as a major Romantic, "and his stature as a poet has grown steadily through all changes of fashion".
Other poets
Another important poet in this period was John Clare (1793–1864). Clare was the son of a farm labourer, who came to be known for his celebratory representations of the English countryside and his lamentation for the changes taking place in rural England. His poetry underwent a major re-evaluation in the late 20th century and he is often now considered to be among the most important 19th-century poets. His biographer Jonathan Bate states that Clare was "the greatest labouring-class poet that England has ever produced. No one has ever written more powerfully of nature, of a rural childhood, and of the alienated and unstable self". George Crabbe (1754–1832) was an English poet who, during the Romantic period, wrote "closely observed, realistic portraits of rural life ..in the heroic couplets of the Augustan literature, Augustan age".Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
, who was an admirer of Crabbe's poetry, described him as "nature's sternest painter, yet the best". Modern critic Frank Whitehead has said that "Crabbe, in his verse tales in particular, is an important – indeed, a major – poet whose work has been and still is seriously undervalued". Crabbe's works include ''The Village (poem), The Village'' (1783), ''Poems'' (1807), ''The Borough (poem), The Borough'' (1810), and his poetry collections ''Tales'' (1812) and ''Tales of the Hall'' (1819).
Female poets
Female writers were increasingly active in all genres throughout the 18th century, and by the 1790s women's poetry was flourishing. Notable poets later in the period include, Anna Laetitia Barbauld, Joanna Baillie, Susanna Blamire and Hannah More. Other women poets include, Mary Alcock ( – 1798) and Mary Robinson (poet), Mary Robinson (1758–1800), both of whom "highlighted the enormous discrepancy between life for the rich and the poor", and Felicia Hemans (1793–1835), author of nineteen individual books during her lifetime and who continued to be republished widely after her death in 1835. More interest has been shown in recent years in Dorothy Wordsworth (1771–1855), William's sister, who "was modest about her writing abilities, [but] she produced poems of her own; and her journals and travel narratives certainly provided inspiration for her brother". In the past decades, there has been substantial scholarly and critical work done on women poets of this period, both to make them available in print or online, and second, to assess them and position them within the literary tradition. In particular, Felicia Hemans, although sticking to its forms, began a process of undermining the Romantic tradition, a deconstruction that was continued by Letitia Elizabeth Landon (1802–1838). Landon's novel forms of metrical romance and dramatic monologue was much copied and had a long and lasting influence on Victorian poetry. Her work is now frequently classified as post-romantic. She also produced three completed novels, a tragedy, and numerous short stories.Romantic novel
Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley ( , ; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction# ...
(1797–1851) is remembered as the author of ''Frankenstein'' (1818). The plot of this is said to have come from a waking dream she had, in the company of Percy Shelley, Lord Byron, and John Polidori, following a conversation about galvanism and the feasibility of returning a corpse or assembled body parts to life, and on the experiments of the 18th-century natural philosopher and poet Erasmus Darwin, who was said to have animated dead matter. Sitting around a log fire at Byron's villa, the company also amused themselves by reading German ghost stories, prompting Byron to suggest they each write their own supernatural tale.
Jane Austen's works critique the sentimental novel, novels of sensibility of the second half of the 18th century and are part of the transition to 19th-century Literary realism, realism. Her plots, though fundamentally comic, highlight the dependence of women on marriage to secure social standing and economic security. Austen brings to light the hardships women faced, since they usually did not inherit money, could not work and were largely dependent on their husbands. She reveals not only the difficulties women faced in her day, but also what was expected of men and of the careers they had to follow. This she does with wit and humour and with endings where all characters, good or bad, receive exactly what they deserve. Her work brought her little personal fame and only a few positive reviews during her lifetime, but the publication in 1869 of her nephew's ''A Memoir of Jane Austen'' introduced her to a wider public, and by the 1940s she had become accepted as a major writer. The second half of the 20th century saw a proliferation of Austen scholarship and the emergence of a Janeite fan culture. Austen's works include ''Sense and Sensibility'' (1811), ''Pride and Prejudice'' (1813), ''Mansfield Park'' (1814), ''Emma (novel), Emma'' (1815), ''Northanger Abbey'' (1817) and ''Persuasion (novel), Persuasion'' (1817).
Drama
Byron, Keats and Percy Shelley all wrote for the stage, but with little success in England, with Shelley's ''The Cenci'' perhaps the best known work produced, though that was not played in a public theatre in England until a century after his death. Byron's plays, along with dramatizations of his poems and Scott's novels, were much more popular on the Continent, and especially in France, and through these versions, several were turned into operas, many still performed today. If contemporary poets had little success on the stage, the period was a legendary one for performances of Shakespeare, and went some way to restoring his original texts and removing the Augustan "improvements" to them. The greatest actor of the period, Edmund Kean, restored the tragic ending to ''King Lear''; Coleridge said that, “Seeing him act was like reading Shakespeare by flashes of lightning.”Wales
Wales had its own Romantic movement, especially in Welsh-language literature, Welsh literature (which was rarely translated or known outside Wales). The countryside and history of Wales exerted an influence on the Romantic imagination of Britons, especially in travel writings, and the poetry of Wordsworth.Damian Walford Davies, Lynda Pratt, eds. (2007) ''Wales and the Romantic Imagination'' The "poetry and bardic vision" of Edward Williams (1747–1826), better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg, bear the hallmarks of Romanticism. "His Romantic image of Wales and its past had a far-reaching effect on the way in which the Welsh envisaged their own national identity during the nineteenth century."Scotland
James Macpherson was the first Scottish poet to gain an international reputation. Claiming to have found poetry written by the ancient bard Ossian, he published "translations" that acquired international popularity, being proclaimed as a Celtic equivalent of the Classical antiquity, Classical Epic poetry, epics. ''Fingal'', written in 1762, was speedily translated into many European languages, and its appreciation of natural beauty and treatment of the ancient legend have been credited, more than any single work, with bringing about the Romantic movement in European, and especially in German literature, through its influence on Johann Gottfried von Herder and Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. It was also popularised in France by figures that included Napoleon. Eventually it became clear that the poems were not direct translations from the Gaelic, but flowery adaptations made to suit the aesthetic expectations of his audience. Both Robert Burns (1759–96) andWalter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European literature, European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'' (18 ...
(1771–1832) were highly influenced by the Ossian cycle. Robert Burns (1759–1796) was a pioneer of the Romanticism, Romantic movement, and after his death he became a cultural icon in Scotland. As well as writing poems, Burns also collected Folk music, folk songs from across Scotland, often revising or Literary adaptation, adapting them. His ''Poems, Chiefly in the Scottish Dialect, Poems, chiefly in the Scottish Dialect'' was published in 1786. Among poems and songs of Burns that remain well known across the world are, ''Auld Lang Syne''; ''A Red, Red Rose''; ''A Man's A Man for A' That''; ''To a Louse''; ''To a Mouse''; ''The Battle of Sherramuir''; ''Tam o' Shanter'' and ''Ae Fond Kiss (song), Ae Fond Kiss''.
One of the most important British novelists of the early 19th century was Sir Walter Scott, who was not only highly popular, but "the greatest single influence on fiction in the 19th century ..[and] a European figure". Scott's novel writing career was launched in 1814 with ''Waverley (novel), Waverley'', often called the first historical novel, and was followed by ''Ivanhoe''. The Waverley Novels, including ''The Antiquary'', ''Old Mortality'', ''The Heart of Midlothian'', and whose subject is Scottish history, are now generally regarded as Scott's masterpieces.Drabble
A drabble is a short work of fiction of precisely one hundred words in length."Winner ...
, p. 890. He was one of the most popular novelists of the era, and his historical romances inspired a generation of painters, composers, and writers throughout Europe, including Franz Schubert, Felix Mendelssohn and J. M. W. Turner. His novels also inspired many operas, of which the most famous are ''Lucia di Lammermoor'' (1835) by Donizetti, and Bizet's ''La jolie fille de Perth'', ''The Fair Maid of Perth'' (1867). However, today his contemporary, Jane Austen, is widely read and the source for films and television series, while Scott is comparatively neglected.
America
The European Romantic movement reached America in the early 19th century. American Romanticism was just as multifaceted and individualistic as it was in Europe. Like the Europeans, the American Romantics demonstrated a high level of moral enthusiasm, commitment to individualism and the unfolding of the self, an emphasis on intuitive perception, and the assumption that the natural world was inherently good, while human society was filled with corruption. Romanticism became popular in American politics, philosophy and art. The movement appealed to the revolutionary spirit of America as well as to those longing to break free of the strict religious traditions of early settlement. The Romantics rejected rationalism and religious intellect. It appealed to those in opposition of Calvinism, which includes the belief that the destiny of each individual is preordained. Romantic Gothic literature made an early appearance with Washington Irving's ''The Legend of Sleepy Hollow'' (1820) and ''Rip Van Winkle'' (1819); there are picturesque "local color" elements in Washington Irving's essays and especially his travel books. From 1823, the prolific and popular novelist James Fenimore Cooper (1789–1851) began publishing his historical romances of frontier and Indian life, to create a unique form of American literature. Cooper is best remembered for his numerous sea-stories and the historical novels known as the ''Leatherstocking Tales'', with their emphasis on heroic simplicity and their fervent landscape descriptions of an already-exotic mythicized frontier peopled by "noble savages", exemplified by Uncas, from ''The Last of the Mohicans'' (1826) show the influence of Rousseau's (1712–78) philosophy. Edgar Allan Poe's tales of the macabre that first appeared in the early 1830s, and his balladic poetry was more influential in France than at home.
By the mid-19th century, the pre-eminence of literature from the British Isles began to be challenged by writers from the former American colonies. This included one of the creators of the new genre of the short story, and inventor of the detective story Edgar Allan Poe (1809–49). A major influence on American writers at this time was
Romantic Gothic literature made an early appearance with Washington Irving's ''The Legend of Sleepy Hollow'' (1820) and ''Rip Van Winkle'' (1819); there are picturesque "local color" elements in Washington Irving's essays and especially his travel books. From 1823, the prolific and popular novelist James Fenimore Cooper (1789–1851) began publishing his historical romances of frontier and Indian life, to create a unique form of American literature. Cooper is best remembered for his numerous sea-stories and the historical novels known as the ''Leatherstocking Tales'', with their emphasis on heroic simplicity and their fervent landscape descriptions of an already-exotic mythicized frontier peopled by "noble savages", exemplified by Uncas, from ''The Last of the Mohicans'' (1826) show the influence of Rousseau's (1712–78) philosophy. Edgar Allan Poe's tales of the macabre that first appeared in the early 1830s, and his balladic poetry was more influential in France than at home.
By the mid-19th century, the pre-eminence of literature from the British Isles began to be challenged by writers from the former American colonies. This included one of the creators of the new genre of the short story, and inventor of the detective story Edgar Allan Poe (1809–49). A major influence on American writers at this time was Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
.
The Romantic movement gave rise to New England Transcendentalism, which portrayed a less restrictive relationship between God and Universe. The publication of Ralph Waldo Emerson's 1836 essay ''Nature (essay), Nature'' is usually considered the watershed moment at which transcendentalism became a major cultural movement. The new philosophy presented the individual with a more personal relationship with God. Transcendentalism and Romanticism appealed to Americans in a similar fashion, for both privileged feeling over reason, individual freedom of expression over the restraints of tradition and custom. It often involved a rapturous response to nature. It encouraged the rejection of harsh, rigid Calvinism, and promised a new blossoming of American culture.
The romantic American novel developed fully with Nathaniel Hawthorne's (1804–1864) ''The Scarlet Letter'' (1850), a stark drama of a woman cast out of her community for committing adultery. Hawthorne's fiction had a profound impact on his friend Herman Melville (1819–1891). In ''Moby-Dick'' (1851), an adventurous whaling voyage becomes the vehicle for examining such themes as obsession, the nature of evil, and human struggle against the elements. By the 1880s, however, psychological and social realism were competing with Romanticism in the novel.
See also
* Irish literature * Literature of Northern Ireland * Post-romanticismReferences
Cited sources
* * * *External links
* British Women Romantic Poets, 1789 - 183''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', 11th ed.1910-1911
''Romanticism''
via ''Discovering Literature: Romantics and Victorians'' at the British Library
The Romantics
''In Our Time'', BBC Radio 4 discussion with Jonathan Bate, Rosemary Ashton and Nicholas Roe (Oct. 12, 2000)
The Later Romantics
''In Our Time'', BBC Radio 4 discussion with Jonathan Bate, Robert Woof & Jennifer Wallace (Apr, 15, 2004) {{DEFAULTSORT:English Literature 1798 establishments in Great Britain 1837 disestablishments in the United Kingdom English-language literature History of literature in the United Kingdom Romantic literature 18th-century British literature 19th-century British literature