Roman Thrace on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the
 With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the
With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the
 As it was an interior province, far from the borders of the Empire, and having a major Roman road ( Via Egnatia) that passed through the region, Thrace remained peaceful and prosperous until the
As it was an interior province, far from the borders of the Empire, and having a major Roman road ( Via Egnatia) that passed through the region, Thrace remained peaceful and prosperous until the
Map
of the Roman state according to the Compilation notitia dignitatum
Place-names
in the Compilation notitia dignitatum {{Late Roman Provinces, state=expanded Late Roman provinces Greece under Roman rule 40s establishments in the Roman Empire States and territories established in the 40s
 Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
. Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
and early Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
as the Sapaean kingdom
The Thracian kingdom, also called the Sapaean kingdom, was an ancient Thracian state in the southeastern Balkans that existed from the middle of the 1st century BC to 46 AD. Succeeding the Classical and Hellenistic era Odrysian kingdom of Th ...
. Roman emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
annexed the kingdom as a Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
in 46 AD.
Confines
From the perspective ofclassical Greece
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in ancient Greece,The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." ( Thomas R. Mar ...
, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia and Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Thracian kingdom as it stood during the 5th to 1st centuries BC.
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, by order of emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
, in AD 46, ''Thracia'' (formally ''provincia Thracia'' "Thracian province", "eparchy of the Thracians") was established as a Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
. After the administrative reforms of the 3rd century, ''Thracia'' was reduced to the territory of the six small provinces of the Diocese of Thrace. Later still, the medieval Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
theme of Thracia
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkans, Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical Greece, Classical and Hellenistic period, Hellenis ...
contained only what today is Eastern Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically in Southeast Europe. Turkish Thrace accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest c ...
.
Under the Principate
The Odrysian kingdom of Thrace became a Roman client kingdom c. 20 BC, while the Greekcity-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
s on the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
coast came under Roman control as '' civitates foederatae'' ("allied" cities with internal autonomy). After the death of the Thracian king Rhoemetalces III in 46 AD and an unsuccessful anti-Roman revolt, the kingdom was annexed as the Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
of Thracia.
The new province encompassed not only the lands of the former Odrysian realm, but also the north-eastern portion of the province of Macedonia as well as the islands of Thasos, Samothrace and Imbros in the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
. To the north, Thracia bordered the province of Moesia Inferior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
; initially, the provincial boundary ran at a line north of the Haeumus Mountains, including the cities of Nicopolis ad Istrum and Marcianopolis in Thracia, but by the end of the 2nd century AD the border had moved south along the Haemus. The area of the Thracian Chersonese (modern Gallipoli Peninsula) was excluded from its governor's purview and administered as part of the emperor's personal domains. The province's first capital, where the Roman governor resided, was Heraclea Perinthus. Thracia was an imperial province, headed initially by a '' procurator'', and, after c. 107/109, by a '' legatus Augusti pro praetore''. Otherwise, the internal structure of the old Thracian kingdom was retained and only gradually superseded by Roman institutions. The old tribal-based ''strategiai'' ("generalcies"), headed by a ''strategos
''Strategos'' (), also known by its Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized form ''strategus'', is a Greek language, Greek term to mean 'military General officer, general'. In the Hellenistic world and in the Byzantine Empire, the term was also use ...
'' ("general"), were retained as the main administrative divisions, but some villages were grouped together into ''kōmarchiai'' ("village headships") or subordinated to neighbouring cities (the two Roman colonies of '' colonia Claudia Aprensis'' and '' colonia Flavia Pacis Deueltensium'' and several Greek cities, many of whom were founded by Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
), which were set apart. In the mid-1st century, the ''strategiai'' numbered fifty, but the progressive expansion of the cities and the land assigned to them reduced their number: by the early 2nd century, they had decreased to fourteen, and c. 136 they were abolished altogether as official administrative divisions.
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
(r. 193–211), frequently traveled through Thrace during his military campaigns from 193 to 198, first during his war with Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was a Roman usurper from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a ...
and later against the Parthians. The city of Perinthus, which backed Severus, was granted the prestigious title of '' neokoros'' twice, alongside the permission to hold crown festivals in his honor. Severus also allowed Anchialus to organize ''seuereia'' festivals, possibly as a reward for its support during the civil war.
Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis, was a period in History of Rome, Roman history during which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressure of repeated Barbarian invasions ...
, when it was repeatedly raided by Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
from beyond the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
. During the campaigns to confront these raiders, Emperor Decius
Gaius Messius Quintus Trajanus Decius ( 201June 251), known as Trajan Decius or simply Decius (), was Roman emperor from 249 to 251.
A distinguished politician during the reign of Philip the Arab, Decius was proclaimed emperor by his troops a ...
(r. 249–251) fell in the Battle of Abritus in 251. Thracia suffered especially heavily in the great Gothic seaborne raids of 268–270, and it was not until 271 that Emperor Aurelian
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disinte ...
(r. 270–275) was able to secure the Balkan provinces against Gothic raids for some time to come.
Generally, the provincial and urban policy of Roman emperors, with the foundation of several cities of Greek type (city-state), contributed more to the progress of Hellenization than to the Romanization of Thrace. So by the end of Roman antiquity, the phenomenon of Romanization occurs only upon the Lower Moesia, while Thrace lying south of the Haemus mountains had been almost completely Hellenized.
As regards the Thracian dispersion outside the borders (''extra fines provinciae''), from epigraphic evidence we know the presence of many Thracians (mostly soldiers) throughout the Roman Empire from Syria and Arabia to Britain.
Late antiquity
Under the administrative reforms ofDiocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
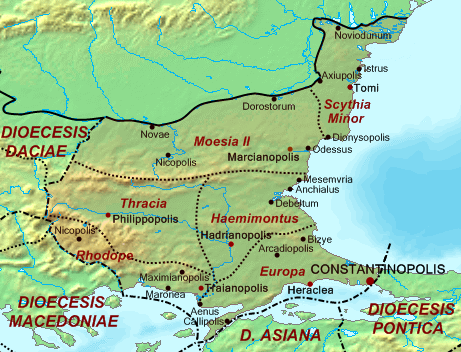
(r. 284–305), Thracia's territory was divided into four smaller provinces: ''Thracia'', '' Haemimontus'', '' Rhodope'' and '' Europa''.
The new province of Thracia comprised the northwestern portion of the old province, i.e. the upper valley of the Hebrus river between Haemus and Rhodope and including Philippopolis (in Thracia), which had become the provincial capital in the early 3rd century. It was headed by a governor with the rank of '' consularis''.
The four Thracian provinces, along with the two provinces of Moesia Inferior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
, were grouped into the diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
of Thraciae, which in turn was part of the Prefecture of the East. Militarily, the entire region was under the control of the ''magister militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the e ...
per Thracias''.Soustal (1991), pp. 62–63
See also
*Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
* List of Roman governors of Thracia
* Thraco-Roman
The term Thraco-Roman describes the Romanization (cultural), Romanized culture of Thracians under the rule of the Roman Empire.
The Odrysian kingdom of Thrace became a Roman client kingdom c. 20 BC, while the Greek city-states on the Black Sea coa ...
Notes
References
Sources
*External links
Map
of the Roman state according to the Compilation notitia dignitatum
Place-names
in the Compilation notitia dignitatum {{Late Roman Provinces, state=expanded Late Roman provinces Greece under Roman rule 40s establishments in the Roman Empire States and territories established in the 40s