Roman Crimea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The

 These are the Roman client kings of the
These are the Roman client kings of the
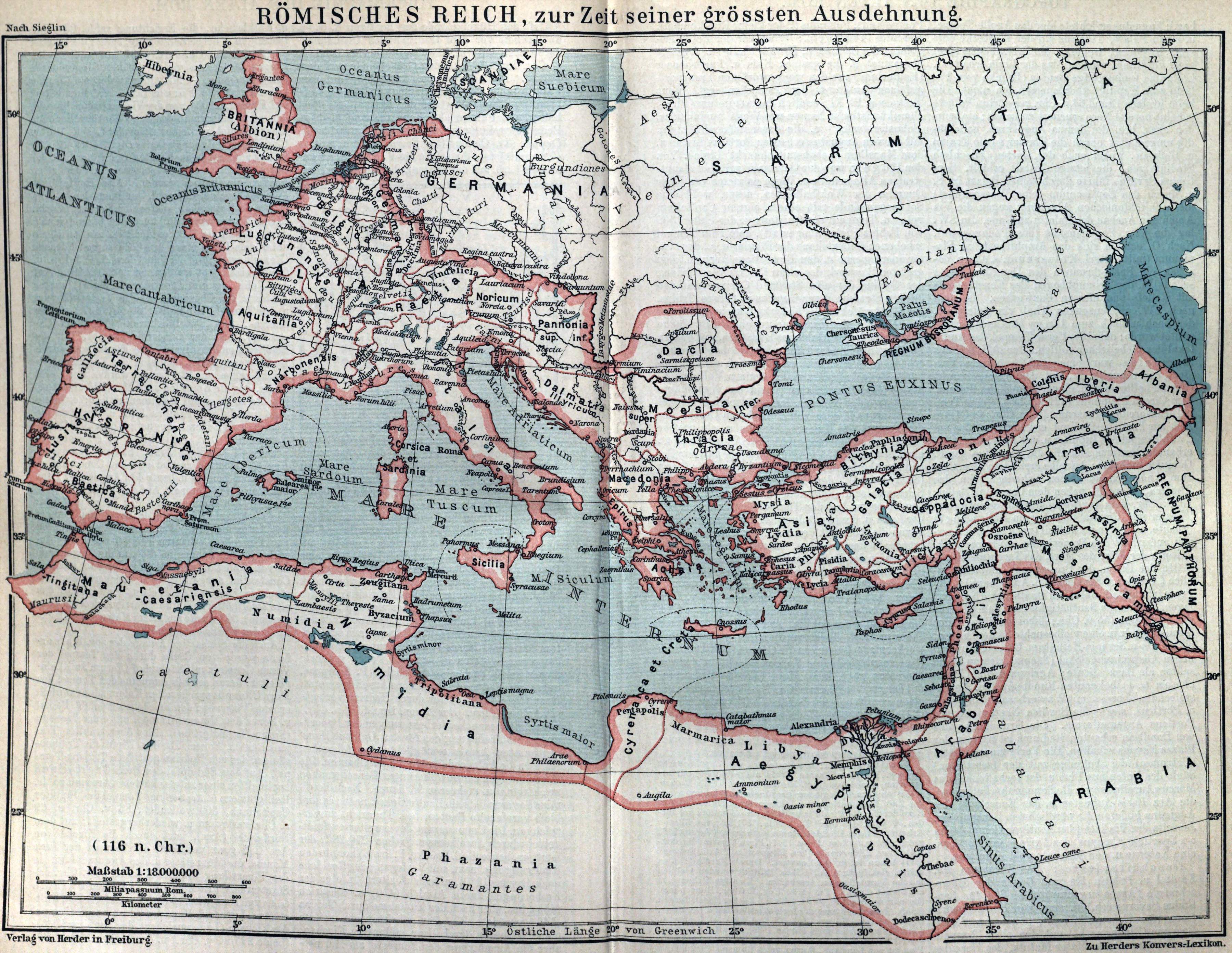
Crimean Peninsula
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrai ...
(at the time known as ''Taurica'') was under partial control of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
during the period of 47 BC to c. 340 AD. The territory under Roman control mostly coincided with the Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (; ), was an ancient Greco-Scythians, Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus, centered in the present-day ...
(although under Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
, from 62 to 68 AD; it was briefly attached to the Roman Province of Moesia Inferior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
).
Rome lost its influence in Taurica in the mid third century AD, when substantial parts of the peninsula fell to the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
, but at least nominally the kingdom survived until the 340s AD. The Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
, the eastern part of the Roman Empire that survived the loss of the western part of the empire, later regained Crimea under Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
. The Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
Empire controlled portions of the peninsula well into the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
.
Roman Empire
Rome started to dominate the Crimea peninsula (then called ''Taurica'') in the 1st century BC. The initial area of their penetration was mainly in eastern Crimea ( Bosporus kingdom) and in the westernGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
city of Chersonesos. The interior was only nominally under Roman rule.
In ancient times Crimea was known as "Chersonesus Taurica", from the name of the Tauri, who were descendants of the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
. Many Greek colonists settled in Taurica: their most renowned colony was Chersonesos. In 114 BC the Bosporus kingdom accepted the overlordship of Mithridates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and ...
, king of Pontus, as a protection from tribes of Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
. For nearly five centuries after the defeat of Mithridates by the Roman Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
, Crimea was under the suzerainty of Rome.
The main Roman settlement was Charax, a castrum
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified milita ...
probably built around 60–65, and the main naval Roman base was in Chersonesos.
When the Romans arrived at Taurica, they set up their camp and built a fortress and a temple of Jupiter Dolichenus on the coast of the harbor of Balaklava
Balaklava ( Ukrainian and , , ) is a settlement on the Crimean Peninsula and part of the city of Sevastopol. It is an administrative center of Balaklavsky District that used to be part of the Crimean Oblast before it was transferred to Sevast ...
, then called ''Symbolon Limen''.
Tiberius Julius Aspurgus (8 BC – 38) founded a line of Bosporan Kings which endured with some interruptions until 341. Originally called Aspurgus, he adopted the Roman names "Tiberius Julius" because he received Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cu ...
and enjoyed the patronage of the first two Roman Emperors, Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
and Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
. All of the following kings adopted these two Roman names followed by a third name, mostly of Pontic, Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
or Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4t ...
origin. Bosporan kings struck coinage throughout the kingdom period, which included gold stater
The stater (; ) was an ancient coin used in various regions of Greece. The term is also used for similar coins, imitating Greek staters, minted elsewhere in ancient Europe.
History
The stater, as a Greek silver currency, first as ingots, and ...
s bearing portraits of the respective Roman Emperors.
In 67, Emperor Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
prepared a military expedition to conquer for Rome all the northern shores of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
from the Caucasus to what is now Romania-Moldova-Ukraine, but his death stopped the project. For this reason, he probably put Taurica under direct Roman rule and created the Charax castrum. He extended the Roman province of Lower Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
to Tyras, Olbia
Olbia (, ; ; ) is a city and communes of Italy, commune of 61,000 inhabitants in the Italy, Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called in the Roman age, Civita in the Middle ...
and Taurica (the peninsula of Crimea).
Taurica enjoyed a relative golden period under Roman leadership during the 2nd century AD, with huge commerce of wheat, clothing, wine and slaves of the Black Sea slave trade:
The region was temporarily conquered by the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
in 250. The last client king of the Roman Empire in Taurica was Tiberius Julius Rhescuporis VI, who died in 342. Rhescuporis seems to have minted coins as late as 341, indicating that there was some extent of political control over the remnants of the kingdom at this point. The remnants of the Bosporan kingdom were finally swept away with the invasion of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
in 375/6.
Charax
The largest Roman military settlement inTaurica
The recorded history of the Crimean Peninsula, historically known as ''Tauris'', ''Taurica'' (), and the ''Tauric Chersonese'' (, "Tauric Peninsula"), begins around the 5th century BCE when several Greeks in pre-Roman Crimea, Greek colonies were ...
was Charax. It was situated on a four-hectare area at the western ridge of "Ai Todor", close to the modern Yalta
Yalta (: ) is a resort town, resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Crime ...
castle of Swallow's Nest.
When in 62–66 AD the Roman garrisons were installed in Taurica, Charax became one of their strongholds. The Romans built a fortress and stationed a sub-unit (vexillatio) of the "Ravenna squadron". Charax was a very important strategic point, because it allowed the Romans to establish control over the navigation along the Crimean coast.
The military camp
A military camp or bivouac is a semi-permanent military base, for the lodging of an army. Camps are erected when a military force travels away from a major installation or fort during training or operations, and often have the form of large cam ...
was fully developed under Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolida ...
with the intention of protecting Chersonesos and other Bosporean trade emporiums from the Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
. By the end of the 1st century, the Roman forces were evacuated from the Crimea peninsula.
Several decades later the camp was restored by a vexillatio of the Legio I Italica: it hosted a detachment of the Legio XI Claudia
Legio XI Claudia ("Claudius' Eleventh Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. The legion was levied by Julius Caesar for his campaign against the Nervii. XI ''Claudia'' dates back to the two legions (the other was the XIIth) recruit ...
at the end of the 2nd century. In this century, new stone walls were added to the fortress and a new Roman road was built, connecting Charax to Chersonesos.
The camp was abandoned by the Romans at the end of the 3rd century.
Roman client kings

 These are the Roman client kings of the
These are the Roman client kings of the Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (; ), was an ancient Greco-Scythians, Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus, centered in the present-day ...
:
* Pharnaces 64 BC – 47 BC
* Mithridates I 47 BC – 44 BC
* Asander
Asander or Asandros (; lived 4th century BC) was the son of Philotas (father of Parmenion), Philotas and brother of Parmenion and Agathon (son of Philotas), Agathon. He was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian general under Alexander the Great, a ...
47 BC, then 44 BC – 17 BC
* Scribonius 17 BC – 16 BC
* Dynamis with Asander 47 BC, then 44 BC – 17 BC, then with Polemon from 16 BC until her death in 14 BC
* Polemon I 16 BC – 8 BC
* Aspurgus 8 BC – 38 AD
* Rhescuporis I 14 – 42 AD
* Polemon II 38 – 41 AD
* Mithridates II 42 – 46 AD
* Cotys I 46 – 78
** Roman Province 63 – 68
* Rhescuporis II
file:Monete ellenistiche, regno di tracia, Rescuporide II, in bronzo, 12-18 dc.jpg, Coin of Rhescuporis II of Thracia
Rhescuporis II (Greek language, Greek: Ρησκούπορις) was king of the Sapaean kingdom of Thrace from 12 to 19 AD. He rul ...
78 – 93
* Sauromates I 93 – 123
* Cotys II 123 – 131
* Rhoemetalces 131 – 153
* Eupator 154 – 170
* Sauromates II 172 – 210
* Rhescuporis III 211 – 228
* Cotys III 228 – 234
* Sauromates III 229 – 232
* Rhescuporis IV 233 – 234
* Chedosbios 233 – 234 (?)
* Ininthimeus 234 – 239
* Rhescuporis V 240 – 276
* Pharsanzes 253 – 254
* Teiranes 276 – 278
* Sauromates IV 276
* Theothorses 279 – 309
* Rhadamsades 309 – 322
* Rhescuporis VI 314 – 341
Episcopal sees
Ancient episcopal sees of Roman Crimea (Zechia) that are listed in the ''Annuario Pontificio
The ''Annuario Pontificio'' ( Italian for ''Pontifical Yearbook'') is the annual directory of the Holy See of the Catholic Church. It lists the popes in chronological order and all officials of the Holy See's departments. It also provides nam ...
'' as titular see
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbi ...
s include:
* Bosporus
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait ( ; , colloquially ) is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental bo ...
, Byzantine? Archbishopric
* Chersonesus in Zechia
* Matrega
Phanagoria (; ) was the largest Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the Taman peninsula, spread over two plateaus along the eastern shore of the Cimmerian Bosporus.
The city was a large Emporia (ancient Greece), emporium for all the traffic be ...
* Nicopsis (Tuapse)
* Phulli (Stary Krym), ?Archbishopric
* Soldaia
* Sugdaea
* Tanais
Byzantine Empire
TheByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
(Eastern Roman Empire) re-established Roman control of the region under Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
().
In the 6th century, probably at the end of the reign of Justinian I, the status of Roman Crimea changed. Taurica became the Province of Chersonesos, which also included Bosporos and the southern coast of Crimea.
This enlargement of Byzantine Taurica resulted in the elevation of the ranks of its governors. In the second half of the 6th century, the military and civil authorities in the region were entrusted to the military deputy, "''doux Chersonos''".
Furthermore, the city of Chersonnesos was used by the Romans as a place of banishment: St. Clement of Rome died there in exile in 99 AD, having first preached the Gospel in the region. Another exile, the Emperor Justinian II, spent the years to there - after he returned to power (in 705) he allegedly destroyed the city in revenge.
Most of Roman Crimea fell under Khazar
The Khazars ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a nomadic Turkic people who, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, an ...
overlordship in the late 7th century.
In the mid-8th century, the Khazars put down the rebellious Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were either a Greuthungi- Gothic tribe or a Western Germanic tribe that bore the name '' Gothi'', a title applied to various Germanic tribes that remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the ...
and their city, Doros (modern Mangup), was occupied. A Khazar ''tudun'' (ruler) was resident at Chersonesos already in 690, despite the fact that this town was nominally subject to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. The Byzantine emperors controlled the southern shores of the Crimea peninsula (the theme of Cherson) until the 13th century. Control then passed to the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
, one of the successor states to the Byzantine Empire after the sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusaders sacked and destroyed most of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the city, the Latin Empire ( ...
in 1204. Another offshoot, the Crimea-based Principality of Theodoro, endured from the 14th century until 1475, when the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
conquered it.
Many series of Roman coins survive from the 1st century BC to about 300, and also some from the Byzantine period.
See also
* History of Crimea * Italians of Crimea * Strait of Kerch *List of Kings of Cimmerian Bosporus
The Bosporan kings were the rulers of the Bosporan Kingdom, an ancient Hellenistic period, Hellenistic Greco-Scythians, Scythian state centered on the Kerch Strait (the Cimmerian Bosporus) and ruled from the city of Panticapaeum. Panticapaeum was ...
Notes
Bibliography
* * * {{Territories with limited Roman Empire occupation & presenceCrimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
Ancient history of Ukraine
Ancient Crimea
1st-century BC establishments in the Roman Republic
340 disestablishments
340s disestablishments in the Roman Empire
States and territories established in the 1st century BC
States and territories disestablished in the 4th century
Ukraine in the Roman era