Rohini Sounding Rocket Series on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rohini is a series of 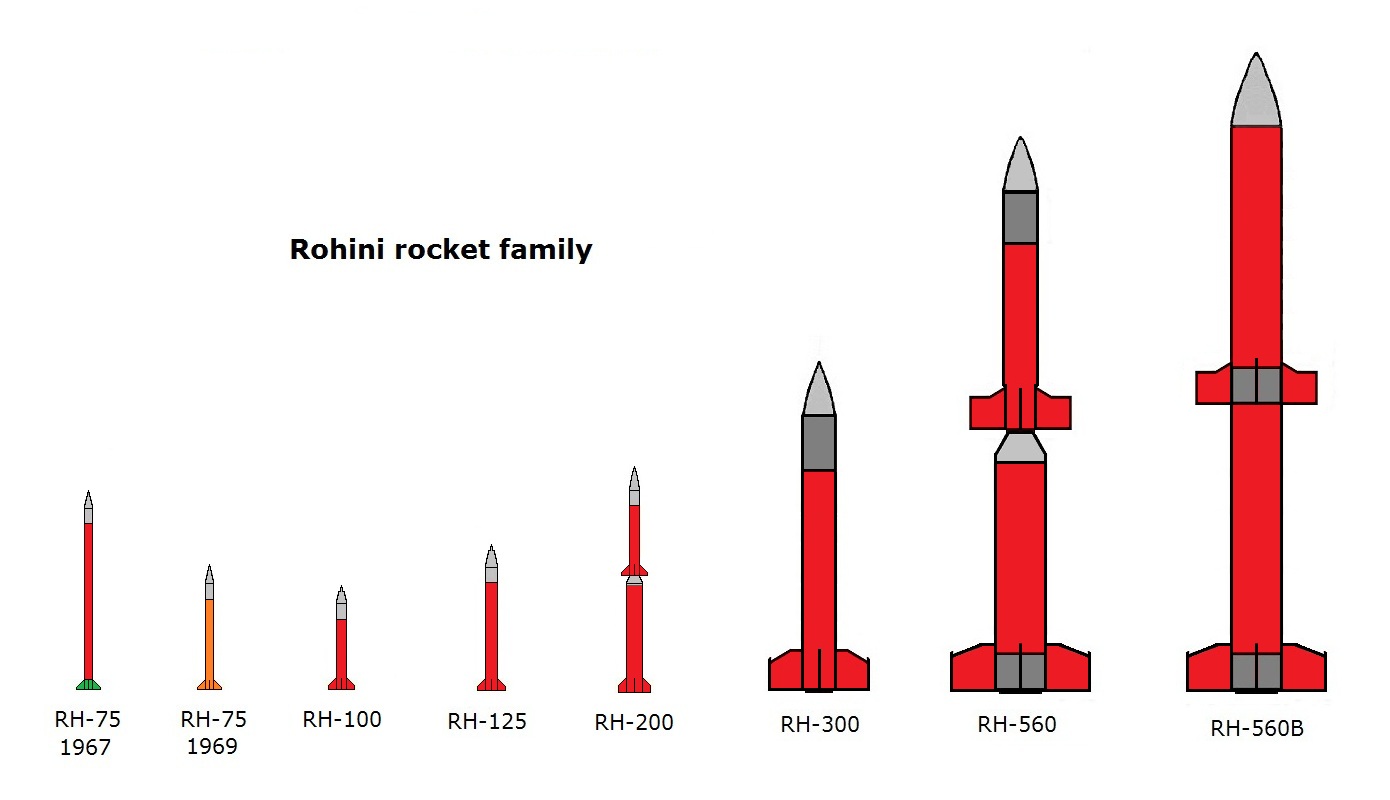 Various programs such as Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ), Leonid Meteor Shower (LMS), Indian Middle Atmosphere Programme (IMAP), Monsoon Experiment (MONEX), Middle Atmosphere Dynamics (MIDAS), and Sooryagrahan-2010 have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rocket series. It has been the forerunners for ISRO's heavier and more complex launch vehicles, with continued usage even today for atmospheric and meteorological experiment and research.
Currently, three versions are offered as operational sounding rockets , which cover a payload range of 8-100 Kg and an apogee range of 80-475 km.
Several scientific missions with national and international participation have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rockets.
Various programs such as Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ), Leonid Meteor Shower (LMS), Indian Middle Atmosphere Programme (IMAP), Monsoon Experiment (MONEX), Middle Atmosphere Dynamics (MIDAS), and Sooryagrahan-2010 have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rocket series. It has been the forerunners for ISRO's heavier and more complex launch vehicles, with continued usage even today for atmospheric and meteorological experiment and research.
Currently, three versions are offered as operational sounding rockets , which cover a payload range of 8-100 Kg and an apogee range of 80-475 km.
Several scientific missions with national and international participation have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rockets.
sounding rockets
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital flight ...
developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO ) is India's national List of government space agencies, space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru, Karnataka. It serves as the principal research and development arm of the Department of Space (DoS), ...
(ISRO) for meteorological
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture ...
and atmospheric study. These sounding rockets are capable of carrying payloads
Payload is the object or the entity that is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of t ...
of between altitudes of . The ISRO currently uses RH-200, RH-300,Mk-II, RH-560 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III rockets, which are launched from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station
Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) is India's first rocket launching station and was established on 21 November 1963. Operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), it is located in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, which ...
(TERLS) in Thumba
Thumba is a coastal area of Thiruvananthapuram city, the capital of Kerala, India.
Location and geography
Thumba is a vast village bordering Menamkulam in the east, St. Dominic's Vettucaud in the north, and Kochuthura in the south; towards its ...
and the Satish Dhawan Space Centre
Satish Dhawan Space Centre – SDSC (formerly Sriharikota Range – SHAR) is the primary spaceport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), located in Sriharikota, Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. The spaceport is located on an isl ...
in Sriharikota
Sriharikota () is a barrier island off the Bay of Bengal coast located in the Shar Project settlement of Tirupati district in Andhra Pradesh, India. It houses the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, one of the two satellite launch centres in India (the ...
.
 Various programs such as Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ), Leonid Meteor Shower (LMS), Indian Middle Atmosphere Programme (IMAP), Monsoon Experiment (MONEX), Middle Atmosphere Dynamics (MIDAS), and Sooryagrahan-2010 have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rocket series. It has been the forerunners for ISRO's heavier and more complex launch vehicles, with continued usage even today for atmospheric and meteorological experiment and research.
Currently, three versions are offered as operational sounding rockets , which cover a payload range of 8-100 Kg and an apogee range of 80-475 km.
Several scientific missions with national and international participation have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rockets.
Various programs such as Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ), Leonid Meteor Shower (LMS), Indian Middle Atmosphere Programme (IMAP), Monsoon Experiment (MONEX), Middle Atmosphere Dynamics (MIDAS), and Sooryagrahan-2010 have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rocket series. It has been the forerunners for ISRO's heavier and more complex launch vehicles, with continued usage even today for atmospheric and meteorological experiment and research.
Currently, three versions are offered as operational sounding rockets , which cover a payload range of 8-100 Kg and an apogee range of 80-475 km.
Several scientific missions with national and international participation have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rockets.
Brief History
On November 21, 1963, the AmericanNike-Apache
The Nike Apache, also known as Argo B-13, was a two-stage sounding rocket developed by Aerolab, later Atlantic Research, for use by the United States Air Force and NASA. It became the standard NASA sounding rocket and was launched over 600 time ...
was the first sounding rocket to launch from Thumba. Following that, two-stage rockets from France (Centaure) and Russia (M-100) were launched. In 1967, the Rohini RH-75, an ISRO variant, was launched. The Rohini Sounding Rocket (RSR) Programme was established in 1975 to encompass all sounding rocket operations.
Nomenclature
The rockets in the series are designated with the letters RH (for "Rohini"), followed by a number corresponding to the diameter (in millimetres) of the rocket.Series
RH-75
The RH-75, the first sounding rocket developed by India, It weighed , had a diameter of and flew 15 times between November 1967 and September 1968.RH-100
The RH-100 was a single-stage solid-fuel rocket that was capable of carrying its payload up to an altitude of 55 km or more. When paired with a 650mm long by 40mm wide copper shaft dart used for meteorological research, it was referred to as a Menaka-I rocket.RH-125
This rocket was launched on October 9, 1971, from Sriharikota. It was a single-stage rocket using asolid propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, th ...
, carrying a payload to in altitude. It flew twice between January 1970 and October 1971.
It was used in testing and perfecting various techniques like staging, destruct system, separation devices and clustering. It was also used as a booster to the weather forecasting rockets. As such it was named as Menaka II which worked along with Menaka I.
RH-200
The RH-200 is a two-stage rocket that can reach up to a maximum altitude of . Solid motors power the first and second stages of the RH-200. A polyvinyl chloride (PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons o ...
)-based propellant had previously been employed with the RH-200 rocket. In September 2020, a new propellant based on hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB
Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) is an oligomer of butadiene terminated at each end with a hydroxyl functional group. It reacts with isocyanates to form polyurethane polymers.
HTPB is a translucent liquid with a color similar to wax paper ...
) was successfully used to launch it from the TERLS.
RH-300
The RH-300 is a single stage sounding rocket, derived from French Belier rocket engine technology. It has a launch altitude of 100 km (62 mi). A variant, the RH-300 Mk-II, has a maximum launch altitude of . It has ability to lift a payload up to 80 kilograms (20 kg of scientific payload) having volume measuring 380*500 mm in diameter. It is capable of reaching very high acceleration (20 G to M6). Numerous payloads can be tested in a single flight.RH-560
This two stage vehicle is derived from French Stromboli engine technology. Another variant, the RH-560 Mk-II, can reach a maximum launch altitude of . The RH-560 Mk-III variant's maiden flight (the flight was successful) was 12 March 2021. It achieved an apogee of 511.73 kms against the pre-flight prediction of 476 kms. The payloads were Electron and Neutral Wind Probe (ENWi),Langmuir Probe
A Langmuir probe is a device used to determine the electron temperature, electron density, and electric potential of a plasma. It works by inserting one or more electrodes into a plasma, with a constant or time-varying electric potential between ...
(LP) and Tri Methyl Aluminium (TMA).
Air-breathing propulsion version
On 23rd July 2024, ISRO successfully launched world's first air breathing rocket which is a modified version of RH-560.Applications
The RH-200 is used for meteorological studies, the RH-300 Mk-II for Middle atmospheric studies and the RH-560 Mk-II for Upper atmospheric studies and ionospheric studies. The RH-200 was used as the rocket for the first payload launch in India made by students of VIT University inVellore
Vellore ( ), also spelled Velur, is a sprawling city and the administrative headquarters of Vellore district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of the Palar River and surrounded by the Javadi Hills in the northeastern ...
.
References
{{Use Indian English, date=January 2014 Sounding rockets of India Space programme of India