Rogue Black Hole on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A rogue black hole is a
A rogue black hole is a
 A rogue black hole is a
A rogue black hole is a black hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. Th ...
that is not bound by any object's gravity, allowing them to float freely throughout the universe. Since black holes emit no light, the only ways to detect them are gravitational lensing
A gravitational lens is matter, such as a galaxy cluster, cluster of galaxies or a point particle, that bends light from a distant source as it travels toward an observer. The amount of gravitational lensing is described by Albert Einstein's Ge ...
or x-ray bursts
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
that occur when they destroy an object.
Intergalactic rogue black holes
These are objects without a host galactic group, caused by collisions between two galaxies or when the merging of two black holes is disrupted. It has been estimated that there could be 12 rogue supermassive black holes on the edge of theMilky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
galaxy.
Interstellar rogue black holes
Examples
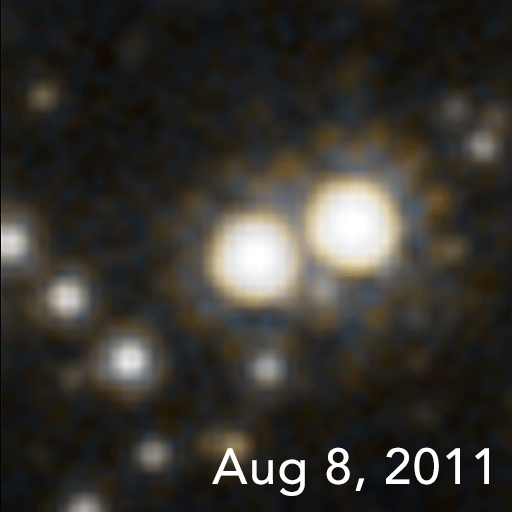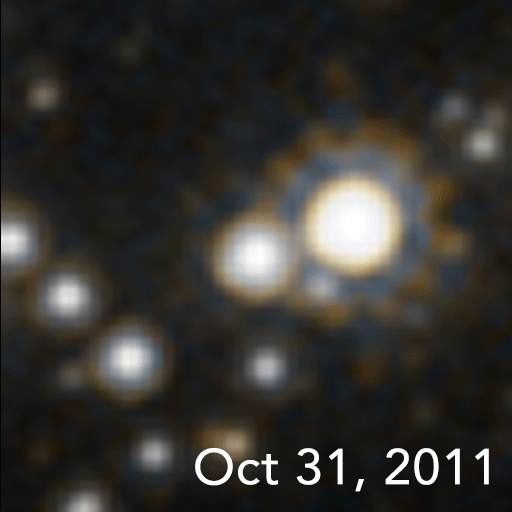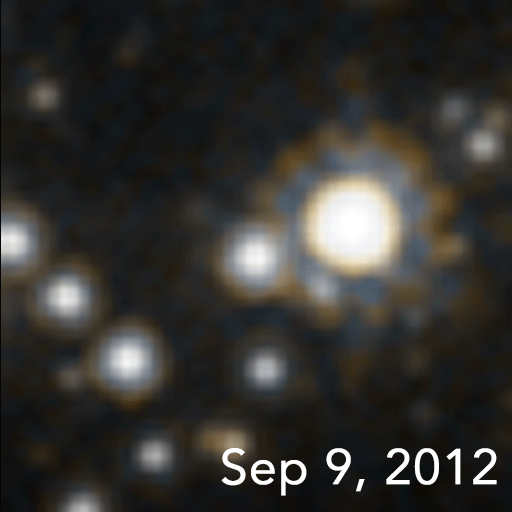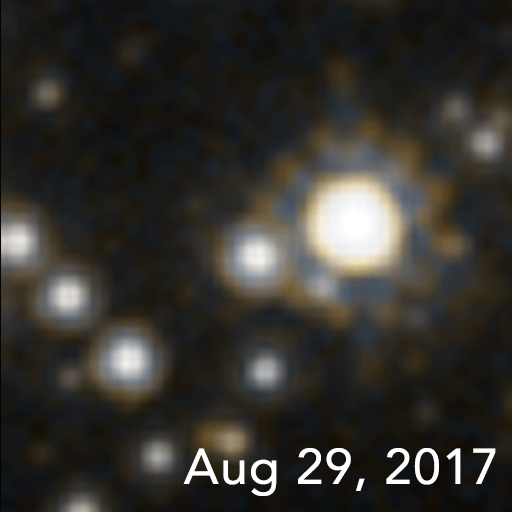
In January 2022, a team of astronomers reported of OGLE-2011-BLG-0462/MOA-2011-BLG-191, the first unambiguous detection and mass measurement of an isolatedstellar black hole
A stellar black hole (or stellar-mass black hole) is a black hole formed by the gravitational collapse of a star. They have masses ranging from about 5 to several tens of solar masses. They are the remnants of supernova explosions, which may be ...
using the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
together with the Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics
Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics (MOA) is a collaborative project between researchers in New Zealand and Japan, led by Professor Yasushi Muraki of Nagoya University. They use gravitational microlensing, microlensing to observe dark mat ...
(MOA) and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment
The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE) is a Polish astronomy, astronomical project based at the University of Warsaw that runs time-domain astronomy, a long-term variability sky survey (1992–present). The main goals are the detecti ...
(OGLE). This black hole is located 5,000 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by the International Astr ...
s away, has a mass 7.1 times that of the Sun, and moves at about 45 km/s. While there have been other candidates, they have been detected more indirectly.
See also
* Rogue star *Rogue planet
A rogue planet, also termed a free-floating planet (FFP) or an isolated planetary-mass object (iPMO), is an interstellar object of planetary mass which is not gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf.
Rogue planets may originate from ...
* Rogue extragalactic planets
*Rogue comet
An interstellar object is an astronomical object in interstellar space that is not gravitationally bound to a star. Applicable objects include asteroids, comets, and rogue planets, but not a star or stellar remnant.
This term can also be ap ...
*Tidally detached exomoon
Tidally detached exomoons, also known as orphaned exomoons or ploonets, are hypothetical exoplanets that were formerly exomoons of another planet, before being ejected from their orbits around their parent planets by tidal forces during planetary m ...
*Stellar black hole
A stellar black hole (or stellar-mass black hole) is a black hole formed by the gravitational collapse of a star. They have masses ranging from about 5 to several tens of solar masses. They are the remnants of supernova explosions, which may be ...
*Primordial black hole
In cosmology, primordial black holes (PBHs) are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang. In the inflationary era and early radiation-dominated universe, extremely dense pockets of subatomic matter may have been tightly pac ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rogue black hole Black holes Extragalactic astronomy