Robert Fitzsimmons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Robert James Fitzsimmons (26 May 1863 – 22 October 1917) was a Cornish
 Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 4 June 1862 in
Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 4 June 1862 in
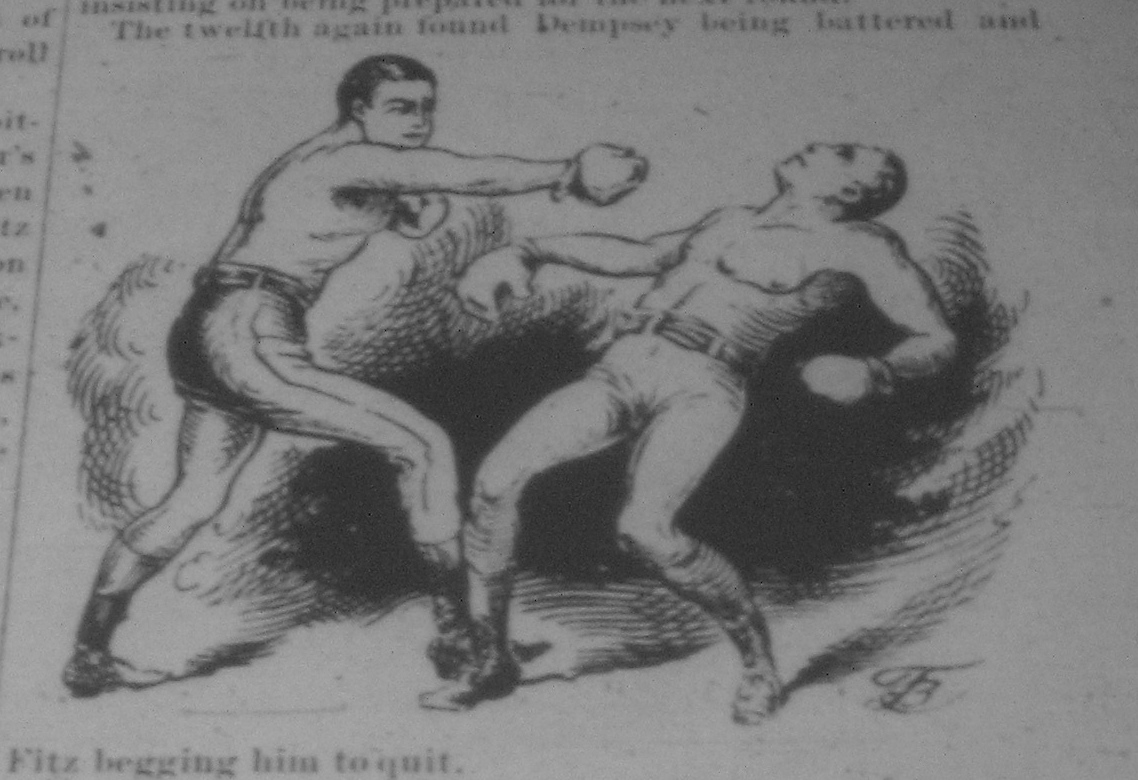 Then, on 14 January 1891, in
Then, on 14 January 1891, in
 In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, sanctioned by Judge
In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, sanctioned by Judge
Physical Culture and Self-Defense
' (Philadelphia: D. Biddle). In 1902, he and Jeffries had a rematch, once again with the World Heavyweight Championship at stake. Fitzsimmons battered Jeffries, who suffered horrible punishment. With his nose and cheek bones broken, most would have sympathized with Jeffries had he quit, but he kept going until his enormous strength and youth wore down Bob and he knocked him out cold in round eight.
Boxing Hall of Fame
On this day in boxing – Old man Bob Fitzsimmons becomes first three-weight champion – ESPN
* in the ''
Biography in the 1966 ''Encyclopaedia of New Zealand'' (birth year wrong)
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fitzsimmons, Bob 1863 births 1917 deaths 19th-century British sportsmen Burials at Graceland Cemetery (Chicago) British emigrants to New Zealand New Zealand people of Cornish descent American people of Cornish descent Immigrants to the United States English male boxers English bare-knuckle boxers English people of Irish descent Heavyweight boxers International Boxing Hall of Fame inductees Light-heavyweight boxers Middleweight boxers New Zealand male boxers New Zealand emigrants to the United States New Zealand people of English descent People associated with physical culture People from Helston World boxing champions World heavyweight boxing champions New Zealand world boxing champions World middleweight boxing champions Deaths from pneumonia in Illinois Cornish people of Irish descent
professional boxer
Professional boxing, or prizefighting, is regulated, sanctioned boxing. Professional boxing bouts are fought for a purse that is divided between the boxers as determined by contract. Most professional fights are supervised by a regulatory auth ...
who was the sport's first three-division world champion. He also achieved fame for beating "Gentleman Jim" Corbett
James John Corbett (September 1, 1866 – February 18, 1933) was an American professional boxer and a World Heavyweight Champion, best known as the only man who ever defeated John L. Sullivan (hence the " man who beat the man" concept of the ch ...
(the man who beat John L. Sullivan
John Lawrence Sullivan (October 15, 1858 – February 2, 1918), known simply as John L. among his admirers, and dubbed the "Boston Strong Boy" by the press, was an American boxer. He is recognized as the first heavyweight champion of gloved ...
), and he is in ''The Guinness Book of World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a British reference book published annually, listi ...
'' as the lightest heavyweight
Heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports and professional wrestling.
Boxing Professional
Male boxers who weigh over are considered heavyweights by 2 of the 4 major professional boxing organizations: the International Boxing Federation an ...
champion, weighing just 167 pounds when he won the title. Nicknamed Ruby Robert and The Freckled Wonder, he took pride in his lack of scars and appeared in the ring wearing heavy woollen underwear to conceal the disparity between his trunk and leg-development.
Considered one of the hardest punchers in boxing history, Fitzsimmons is ranked No. 8 on ''The Ring The Ring may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*The Ring (franchise), ''The Ring'' (franchise), a Japanese horror media franchise
Literature
* ''The Ring'', a 1967 novel by Richard Chopping
* ''The Ring'', a 1988 book by Daniel Keys Moran
* ''The R ...
'' magazine's list of 100 greatest punchers of all time. Boxing writer and founder of ''The Ring'' magazine, Nat Fleischer
Nathaniel Stanley Fleischer (November 3, 1887 – June 25, 1972) was a noted American boxing writer and collector.
Career
Fleischer was born in New York City. After he graduated from City College of New York in 1908, Fleischer worked for the ''N ...
, ranked Fitzsimmons the third greatest heavyweight
Heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports and professional wrestling.
Boxing Professional
Male boxers who weigh over are considered heavyweights by 2 of the 4 major professional boxing organizations: the International Boxing Federation an ...
of all time and regarded him as the greatest pound for pound
Pound for pound is a ranking used in combat sports, such as boxing, wrestling, or mixed martial arts, adjusted to compensate for weight class. As fighters in different weight classes do not compete directly, determining the best fighter pound for ...
knockout
A knockout (abbreviated to KO or K.O.) is a fight-ending, winning criterion in several full-contact combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, Muay Thai, mixed martial arts, karate, some forms of taekwondo and other sports involving striking, ...
puncher in boxing history.
Early life
 Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 4 June 1862 in
Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 4 June 1862 in Helston
Helston () is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated at the northern end of the The Lizard, Lizard Peninsula approximately east of Penzance and south-west of Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth.Ordnance Survey: ...
, Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, the youngest of seven boys and five girls born to James and Jane () Fitzsimmons. Not long before his birth, his parents had moved from his father's native Ireland to Cornwall, where his mother came from, in order for his father to find work as a policeman.Ingram 2012, p. 37. Fitzsimmons received his early education at the National school in Helston. In 1873, the family moved again; James, Jane and their youngest five children sailed on the ''Adamant'' for the 93-day journey to Lyttelton, New Zealand
Lyttelton ( or ''Riritana'') is a port town on the north shore of Lyttelton Harbour / Whakaraupō, at the northwestern end of Banks Peninsula and close to Christchurch, on the eastern coast of the South Island of New Zealand.
As a landing point ...
.
They settled in Timaru
Timaru (; ) is a port city in the southern Canterbury Region of New Zealand, located southwest of Christchurch and about northeast of Dunedin on the eastern Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of the South Island. The Timaru urban area is home to peo ...
, a town 147 km (91 miles) south-west of Lyttelton populated mainly by Cornish immigrants, and James Fitzsimmons established a blacksmith's forge in the town. Once Fitzsimmons had completed his education at the Timaru Main School, he took on a range of jobs. He wanted to join the crew of the ''Isabella Ridley'', and do some service as a sailor, hoping that it would toughen him up for a career in boxing, but the ship was badly damaged in storms while still docked in Timaru. Instead, he took on a range of jobs; as a butcher's delivery boy, a carriage painter, striker at an iron foundry, and a decorator, before becoming an apprentice at his family's blacksmith's forge with his brother Jarrett. His time working in the blacksmith's forge helped to develop his upper body, particularly his arms and shoulders. During his time working in the blacksmith's forge, there are stories that Fitzsimmons was not averse to fighting quarrelsome, often drunk, customers, and it was suggested that this even boosted business, as customers returned to the forge, hoping to see a fight.
Amateur career
In the early 1880sJem Mace
James "Jem" Mace (8 April 1831 – 30 November 1910) was an English boxing champion, primarily during the bare-knuckle era. He was born at Beeston, Norfolk, Beeston, Norfolk. Although nicknamed "The Gypsy", he denied Romani people, Romani eth ...
, an English bare-knuckle boxer
Bare-knuckle boxing (also known as bare-knuckle or bare-knuckle fighting) is a full-contact combat sport based on punching without any form of padding on the hands. The sport as it is known today originated in 17th-century England and, although s ...
, travelled to Timaru
Timaru (; ) is a port city in the southern Canterbury Region of New Zealand, located southwest of Christchurch and about northeast of Dunedin on the eastern Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of the South Island. The Timaru urban area is home to peo ...
and hosted both his boxing school, and the first boxing championships held in New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
in 1880. Fitzsimmons entered the tournament and knocked out four opponents on his way to winning the lightweight
Lightweight is a weight class in combat sports and rowing (sport), rowing.
Boxing Professional boxing
The lightweight division is over 130 pounds (59 kilograms) and up to 135 pounds (61.2 kilograms) boxing weight classes, weight class in the spor ...
title. He knocked out five opponents in the subsequent competition in 1881 to capture the middleweight
Middleweight is a weight class in combat sports.
Boxing Professional
In professional boxing, the middleweight division is contested above and up to .
Early boxing history is less than exact, but the middleweight designation seems to have beg ...
championship. During one of these tournaments, it is often suggested that Fitzsimmons defeated Herbert Slade
Herbert Augustus Slade (10 January 1851 – 6 April 1913), also known as "Maori" Slade, the Big Maori, the Maori Mauler or the Australian Giant, was a New Zealand Boxing, boxer of Irish people, Irish and Māori people, Māori descent, who fought ...
, a professional heavyweight boxer who was touring with Mace, but Slade was touted as being undefeated in 1883, and it is possible that it was Slade's brother that Fitzsimmons beat. After these tournaments, Fitzsimmons boxed at least six times in New Zealand, including some bare knuckle bouts, but it is unclear if he received payment for his fights during this time.
Professional career
Move to Australia
Boxing record books show Fitzsimmons officially began boxing professionally in 1883, inAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. He beat Jim Crawford there in a bare knuckle fight by getting a knockout
A knockout (abbreviated to KO or K.O.) is a fight-ending, winning criterion in several full-contact combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, Muay Thai, mixed martial arts, karate, some forms of taekwondo and other sports involving striking, ...
in three rounds. Fitzsimmons had his first 28 definite professional fights in Australia, where he lost the Australian middleweight title to Mick Dooley (rumours spoke of a fixed bout) and where he also won a fight by knockout while on the floor: when Edward Starlight Robins dropped Fitzsimmons to the canvas in round nine of their fight, he also broke his hand and could not continue, therefore the referee declared Fitzsimmons the winner by a knockout.
By this stage, Fitzsimmons had established his own style
Style, or styles may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Style'' (2001 film), a Hindi film starring Sharman Joshi, Riya Sen, Sahil Khan and Shilpi Mudgal
* ''Style'' (2002 film), a Tamil drama film
* ''Style'' (2004 film), a Burmese film
* '' ...
. He developed a certain movement and caginess from one of the greatest bare-knuckle fighters, Jem Mace
James "Jem" Mace (8 April 1831 – 30 November 1910) was an English boxing champion, primarily during the bare-knuckle era. He was born at Beeston, Norfolk, Beeston, Norfolk. Although nicknamed "The Gypsy", he denied Romani people, Romani eth ...
. Mace encouraged Fitzsimmons to develop his punching technique, drawing on the enormous power he had gained from blacksmithing. Fitzsimmons delivered short, accurate and occasionally conclusive punches. He soon built up a reputation as by far the hardest puncher in boxing.
Winning the Middleweight title
Moving on to theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Fitzsimmons fought four more times in 1890, winning three and drawing one.
New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, he won his first world title from Jack (Nonpareil) Dempsey. Fitzsimmons knocked out Dempsey (from whom the later Jack Dempsey
William Harrison "Jack" Dempsey (June 24, 1895 – May 31, 1983), nicknamed Kid Blackie and The Manassa Mauler, was an American boxer who competed from 1914 to 1927, and world heavyweight champion from 1919 to 1926.
One of the most iconic athl ...
took his name) in the 13th round to become the World Middleweight Champion Championship recognition
1884–1910
Champions were recognized by public acclamation. A champion in that era was a fighter who had a notable win over another fighter and kept winning afterward. Retirements or disputed results could lead to a cha ...
. Fitzsimmons knocked Dempsey down at least 13 times and by the finish left him in such a pitiable condition that he begged him to quit. Since Dempsey would not do so, Fitzsimmons knocked him out and then carried him to his corner. On 22 July, police broke off his fight with Jim Hall after he had knocked Hall down several times.
Fitzsimmons spent the next two years fighting non-title bouts and exhibitions
An exhibition, in the most general sense, is an organized presentation and display of a selection of items. In practice, exhibitions usually occur within a cultural or educational setting such as a museum, art gallery, park, library, exhibition ...
until giving Hall a chance at the title in 1893. He retained the crown by a knockout in round four. He spent the rest of that year doing exhibitions, and on 2 June, he had scheduled a two-way exhibition where he would demonstrate in public how to hit the boxing bag and then how to box against a real opponent. Reportedly, two freak accidents happened that day: Fitzsimmons hit the bag so hard that it broke, and then his opponent of that day allegedly slipped, getting hit in the head and the boxing exhibition was cancelled.
At a public sparring
Sparring is a form of training common to many combat sports. It can encompass a range of activities and techniques such as punching, kicking, grappling, throwing, wrestling or submission work dependent on style. Although the precise form varies, ...
performance on 16 November 1894 at Jacob's Opera House, Syracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, United States. With a population of 148,620 and a Syracuse metropolitan area, metropolitan area of 662,057, it is the fifth-most populated city and 13 ...
, Fitzsimmons knocked out sparring partner Con Riordan, who was carried off unconscious and died several hours later. Two months later Fitzsimmons was charged with manslaughter
Manslaughter is a common law legal term for homicide considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is sometimes said to have first been made by the ancient Athenian lawmaker Draco in the 7th ce ...
but was acquitted
In common law jurisdictions, an acquittal means that the criminal prosecution has failed to prove that the accused is guilty beyond a reasonable doubt of the charge presented. It certifies that the accused is free from the charge of an o ...
.
Fitzsimmons vs. Sharkey
After vacating the Middleweight title, Fitzsimmons began campaigning atheavyweight
Heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports and professional wrestling.
Boxing Professional
Male boxers who weigh over are considered heavyweights by 2 of the 4 major professional boxing organizations: the International Boxing Federation an ...
(the light heavyweight
Light heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports.
Boxing
Professional
In professional boxing, the division is above and up to , falling between super middleweight and cruiserweight (boxing), cruiserweight.
The light heavyweight class has ...
division did not exist at that time). On 2 December 1896, the San Francisco Athletic Club
The San Francisco Athletic Club was a boxing academy in San Francisco, California, known as the main training center for young boxers in the San Francisco Bay Area. The Club was opened in 1885 by Alex Greggains who had been a former middleweight ...
sponsored a fight at the Mechanics' Pavilion in San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
between Fitzsimmons and Tom Sharkey
Thomas "Sailor Tom" Sharkey (November 26, 1873 – April 17, 1953) was an Irish professional boxer who laid claim to the world heavyweight title by defeating Bob Fitzsimmons on December 2, 1896 in a highly controversial fight. Sharkey's recor ...
. Unable to find a referee, they called on former lawman Wyatt Earp
Wyatt Berry Stapp Earp (March 19, 1848 – January 13, 1929) was an American lawman in the American West, including Dodge City, Kansas, Dodge City, Wichita, Kansas, Wichita, and Tombstone, Arizona, Tombstone. Earp was involved in the gunfight ...
. He had officiated 30 or so matches in earlier days, though not under the Marquess of Queensberry rules
The Marquess of Queensberry Rules, also known as Queensberry Rules, are a set of generally accepted rules governing the sport of boxing. Drafted in London in 1865 and published in 1867, they were so named because the 9th Marquess of Queensberry ...
. The fight may have been the most anticipated fight on American soil that year. Fitzsimmons was favoured to win, and bets flowed heavily his way. Earp entered the ring still armed with his customary Colt .45 and drew a lot of attention when he had to be disarmed. He later said he forgot he was wearing it. Fitzsimmons was taller and quicker than Sharkey and dominated the fight from the opening bell. In the eighth round, Fitzsimmons hit Sharkey with his famed "solar plexus punch," an uppercut
The uppercut (formerly known as the undercut) is a punch used in boxing that starts low and travels upwards vertically aiming at the opponent's chin or upper abdomen (so-called " solar plexus"). It is, along with the cross, one of the two main p ...
under the heart that could render a man temporarily helpless. The punch caught Sharkey, Earp, and most of the crowd by surprise, and Sharkey dropped, clutched his groin, and rolled on the canvas, screaming foul.
Earp stopped the bout, ruling that Fitzsimmons had hit Sharkey with a low blow. His ruling was greeted with loud boos and catcalls. Very few witnessed the foul Earp ruled on. He awarded the decision to Sharkey, who attendants carried out as "...limp as a rag."
Winning the heavyweight title
 In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, sanctioned by Judge
In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, sanctioned by Judge Roy Bean
Phantly Roy Bean Jr. (c. 1825 – March 16, 1903) was an American saloon-keeper and Justice of the Peace in Val Verde County, Texas, who called himself "The Only Law West of the Pecos". According to legend, he held court in his saloon along ...
, against the Irish fighter Peter Maher. On 17 March 1897, in Carson City, Nevada
Carson City, officially the Carson City Consolidated Municipality, is an Independent city (United States), independent city and the capital of the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 58,63 ...
, he knocked out American Jim Corbett
Edward James Corbett (25 July 1875 – 19 April 1955) was an Anglo-Indian hunter and author. He gained fame through hunting and killing several man-eating tigers and leopards in Northern India, as detailed in his bestselling 1944 memoir '' M ...
, generally recognised as the legitimate World Heavyweight Champion
At boxing's beginning, the heavyweight division had no weight limit, and historically the weight class has gone with vague or no definition. During the 19th century many heavyweights were 170 pounds (12 st 2 lb, 77 kg) or less, tho ...
(having won the title from John L. Sullivan
John Lawrence Sullivan (October 15, 1858 – February 2, 1918), known simply as John L. among his admirers, and dubbed the "Boston Strong Boy" by the press, was an American boxer. He is recognized as the first heavyweight champion of gloved ...
in 1892) in round 14 in what is considered Nevada's first World Championship
A world championship is generally an international competition open to elite competitors from around the world, representing their nations, and winning such an event will be considered the highest or near highest achievement in the sport, game ...
prize fight. This constituted a remarkable achievement, as Jim Corbett, a skilled boxer, weighed one stone 3 pounds (17 lb) more than Fitzsimmons. He out-boxed Fitzsimmons for several rounds, knocked him down in the sixth round and badly damaged his face with his jab, left hook and right hand, but Fitzsimmons kept coming and Corbett began to tire. In the 14th round, Fitzsimmons won the title with his "solar plexus" punch. Corbett collapsed in agony. Fitzsimmons' "solar plexus" punch became legendary, although he himself may never have used the phrase. The entire fight was filmed by Enoch J. Rector
Enoch J. Rector (October 9, 1863 – January 26, 1957) was an American boxing film promoter and early cinema technician. He was a partner in Woodville Latham's Kinetoscope Exhibition Company (later the Lambda Company) during the mid-1890s, w ...
and released to cinemas as ''The Corbett-Fitzsimmons Fight
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
'', the longest film ever released at the time. It was also the first time in history a full boxing match was recorded and it was the world's first feature film. Using her maiden name, it was covered by Nellie Verrill Mighels Davis
Nellie Mighels Davis (née Verrill; September 10, 1844 – June 24, 1945) was a US civic leader and journalist. In 1897, she was the first woman to report a boxing prize fight ( Fitzsimmons/ Corbett) in the United States. She was also the firs ...
, the first woman to report a prize fight.
Fitzsimmons spent the rest of 1897 and 1898 doing stage tours. In 1899, Fitzsimmons fought James J. Jeffries
James Jackson Jeffries (April 15, 1875 – March 3, 1953) was an American professional boxer and List of world heavyweight boxing champions, world heavyweight champion.
He was known for his enormous strength and stamina. Jeffries fought out of ...
at the Coney Island Athletic Club near Brooklyn
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelv ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. Most people gave Jeffries little chance, even though at over 15 stones (95 kg) he massively outweighed his opponent and was far younger, but Jeffries lifted the World Heavyweight Championship from Fitzsimmons with an 11th-round knockout.
In June 1901 Fitzsimmons took part in a wrestling
Wrestling is a martial art, combat sport, and form of entertainment that involves grappling with an opponent and striving to obtain a position of advantage through different throws or techniques, within a given ruleset. Wrestling involves di ...
match against Gus Ruhlin. He lost and went back to boxing. He then enjoyed legitimate boxing knockouts of leading contenders Ruhlin and Tom Sharkey
Thomas "Sailor Tom" Sharkey (November 26, 1873 – April 17, 1953) was an Irish professional boxer who laid claim to the world heavyweight title by defeating Bob Fitzsimmons on December 2, 1896 in a highly controversial fight. Sharkey's recor ...
.
In 1901 he published a book Physical Culture and Self-Defense
' (Philadelphia: D. Biddle). In 1902, he and Jeffries had a rematch, once again with the World Heavyweight Championship at stake. Fitzsimmons battered Jeffries, who suffered horrible punishment. With his nose and cheek bones broken, most would have sympathized with Jeffries had he quit, but he kept going until his enormous strength and youth wore down Bob and he knocked him out cold in round eight.
Winning the Light Heavyweight title
In November 1903, Fitzsimmons made history by defeating World Light Heavyweight Champion George Gardiner (also known as Gardner) by a decision in 20 rounds, becoming the first boxer to win titles in three weight-divisions. Soon afterward, he went back to the Heavyweights, where he kept fighting until 1914, with mixed results. In 1907 at age 44, Fitzsimmons fought much younger Jack Johnson, during the time period in which reigning champion James J. Jeffries refused to fight Johnson. The bout between Johnson and Fitzsimmons ended in victory for Johnson with a second roundknockout
A knockout (abbreviated to KO or K.O.) is a fight-ending, winning criterion in several full-contact combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, Muay Thai, mixed martial arts, karate, some forms of taekwondo and other sports involving striking, ...
.Ken Burns, ''Unforgivable Blackness''
Retirement
Although Fitzsimmons became a world champion in each of theMiddleweight
Middleweight is a weight class in combat sports.
Boxing Professional
In professional boxing, the middleweight division is contested above and up to .
Early boxing history is less than exact, but the middleweight designation seems to have beg ...
, Light Heavyweight and Heavyweight divisions, historians do ''not'' consider him the first world Light Heavyweight Champion to become World Heavyweight Champion, because he won the Heavyweight title before winning the Light Heavyweight belt. Michael Spinks
Michael Spinks (born July 22, 1956) is an American former professional boxer who competed from 1977 to 1988. He held world championships in two weight classes, including the undisputed light heavyweight title from 1983 to 1985, and the lineal ...
counts as the first Light Heavyweight World Champion to win the Heavyweight belt as well. However, Fitzsimmons was the first Middleweight Champion to win the Heavyweight title and the only Heavyweight Champion to drop down and win the Light Heavyweight title. Fitzsimmons and later Henry Armstrong
Henry Jackson Jr. (December 12, 1912 – October 22, 1988) was an American professional boxer and a world boxing champion who fought under the name Henry Armstrong. He is the only fighter to ever hold world championships in three divisions (fea ...
were the only men to win undisputed world championship in three different weight classes. After his retirement, Fitzsimmons moved back to his home country of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and settled in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
.
Fitzsimmons had a final professional record of 69 wins with 57 by knockout, 12 losses, 14 draws, and 6 no contests (22 newspaper decisions). His exact record remains unknown, as the boxing world often kept records poorly during his era.
Personal life
Fitzsimmons married four times and had six children, two of whom died in infancy. His son Robert, fighting under the moniker "Young Bob Fitzsimmons", enjoyed a moderately successfulprofessional boxing
Professional boxing, or prizefighting, is regulated, sanctioned boxing. Professional boxing bouts are fought for a purse that is divided between the boxers as determined by contract. Most professional fights are supervised by a regulatory auth ...
career as a heavyweight
Heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports and professional wrestling.
Boxing Professional
Male boxers who weigh over are considered heavyweights by 2 of the 4 major professional boxing organizations: the International Boxing Federation an ...
between 1919 and 1931.
In the early 1900s, Fitzsimmons, alongside his third wife and actress
An actor (masculine/gender-neutral), or actress (feminine), is a person who portrays a character in a production. The actor performs "in the flesh" in the traditional medium of the theatre or in modern media such as film, radio, and television. ...
Julia May Gifford, created and starred in a play surrounding their "would be divorce" titled "A Fight For Love" by Hal Reid.
Death
Fitzsimmons died ofpneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
on 22 October 1917 in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, survived by his fourth wife. His grave lies in the Graceland Cemetery
Graceland Cemetery is a large historic garden cemetery located in the north side community area of Uptown, in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Established in 1860, its main entrance is at the intersection of Clark Street and Irving Park R ...
, Uptown
Uptown may refer to:
Neighborhoods or regions in several cities
United States
* Uptown, Chicago, Illinois
* Uptown Manhattan, New York City, New York
* Uptown, Richmond, Virginia
* Uptown, Dallas, Texas
* Uptown, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania
* Upt ...
. Having four wives, a gambling habit, and a susceptibility to confidence tricksters
A scam, or a confidence trick, is an attempt to defraud a person or group after first gaining their trust. Confidence tricks exploit victims using a combination of the victim's credulity, naivety, compassion, vanity, confidence, irresponsibili ...
, he did not hold on to the money he made.
Legacy
In 1954, Fitzsimmons was inducted into the World Boxing Hall of Fame (WBHF) and ''The Ring'' magazine's Boxing Hall of Fame. In 1971,Nat Fleischer
Nathaniel Stanley Fleischer (November 3, 1887 – June 25, 1972) was a noted American boxing writer and collector.
Career
Fleischer was born in New York City. After he graduated from City College of New York in 1908, Fleischer worked for the ''N ...
ranked Fitzsimmons the third greatest heavyweight
Heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports and professional wrestling.
Boxing Professional
Male boxers who weigh over are considered heavyweights by 2 of the 4 major professional boxing organizations: the International Boxing Federation an ...
of all time and regarded him as the greatest pound for pound
Pound for pound is a ranking used in combat sports, such as boxing, wrestling, or mixed martial arts, adjusted to compensate for weight class. As fighters in different weight classes do not compete directly, determining the best fighter pound for ...
knockout
A knockout (abbreviated to KO or K.O.) is a fight-ending, winning criterion in several full-contact combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, Muay Thai, mixed martial arts, karate, some forms of taekwondo and other sports involving striking, ...
puncher in boxing history. Charley Rose named him the greatest light-heavyweight
Light heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports.
Boxing
Professional
In professional boxing, the division is above and up to , falling between super middleweight and cruiserweight (boxing), cruiserweight.
The light heavyweight class has ...
of all time.
The statue ''Peace'' on the Dewey Arch was modelled on Fitzsimmons by the sculptor Daniel Chester French
Daniel Chester French (April 20, 1850 – October 7, 1931) was an American sculpture, sculptor in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. His works include ''The Minute Man'', an 1874 statue in Concord, Massachusetts, and his Statue of Abr ...
. A statue of Fitzsimmons has also stood in the city centre of Timaru
Timaru (; ) is a port city in the southern Canterbury Region of New Zealand, located southwest of Christchurch and about northeast of Dunedin on the eastern Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of the South Island. The Timaru urban area is home to peo ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, since 1987. It was commissioned by New Zealand millionaire boxing fan Bob Jones and sculpted by Margriet Windhausen.
The International Boxing Hall of Fame
The International Boxing Hall of Fame (IBHOF), located in Canastota, New York, right next to exit 34 of the New York State Thruway, honors boxers, trainers and other contributors to the sport worldwide. Inductees are selected on ballots cre ...
has made Fitzsimmons a member in its "Old Timer" category as one of the inaugural inductees of the 1990 class.
In 2003, ''The Ring The Ring may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*The Ring (franchise), ''The Ring'' (franchise), a Japanese horror media franchise
Literature
* ''The Ring'', a 1967 novel by Richard Chopping
* ''The Ring'', a 1988 book by Daniel Keys Moran
* ''The R ...
'' named Fitzsimmons number eight on their list of greatest punchers of all time.
In 2006, he was inducted into the Australian National Boxing Hall of Fame
The Australian National Boxing Hall of Fame is a sports hall of fame which was founded in 2001 and began inducting boxers into the Hall of Fame in 2003. Since then annual induction dinners have been held across Australia.
Inductees are nominated ...
as an honorary international.
Works
*Professional boxing record
All information in this section is derived fromBoxRec
BoxRec or boxrec.com is a website dedicated to holding updated records of professional and amateur boxers, both male and female. It also maintains a MediaWiki-based encyclopedia of boxing.
The objective of the site is to document every profess ...
, unless otherwise stated. Official record
Allnewspaper decision
A newspaper decision was a type of decision in professional boxing. It was rendered by a consensus of sportswriters attending a bout after it had ended inconclusively with a " no decision", as many regions had not adopted the National Sporting Club ...
s are officially regarded as “no decision” bouts and are not counted in the win/loss/draw column.
Unofficial record
Record with the inclusion ofnewspaper decision
A newspaper decision was a type of decision in professional boxing. It was rendered by a consensus of sportswriters attending a bout after it had ended inconclusively with a " no decision", as many regions had not adopted the National Sporting Club ...
s in the win/loss/draw column.
Titles in boxing
Major world titles
*World middleweight champion Championship recognition
1884–1910
Champions were recognized by public acclamation. A champion in that era was a fighter who had a notable win over another fighter and kept winning afterward. Retirements or disputed results could lead to a cha ...
(160 lbs)
* World light-heavyweight champion (175 lbs)
*World heavyweight champion
At boxing's beginning, the heavyweight division had no weight limit, and historically the weight class has gone with vague or no definition. During the 19th century many heavyweights were 170 pounds (12 st 2 lb, 77 kg) or less, tho ...
(200+ lbs)
Regional/International titles
* Australian middleweight championAmateur titles
*New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
lightweight
Lightweight is a weight class in combat sports and rowing (sport), rowing.
Boxing Professional boxing
The lightweight division is over 130 pounds (59 kilograms) and up to 135 pounds (61.2 kilograms) boxing weight classes, weight class in the spor ...
champion
*New Zealand middleweight
Middleweight is a weight class in combat sports.
Boxing Professional
In professional boxing, the middleweight division is contested above and up to .
Early boxing history is less than exact, but the middleweight designation seems to have beg ...
champion
See also
*List of heavyweight boxing champions
At boxing's beginning, the heavyweight division had no weight class (boxing), weight limit, and historically the weight class has gone with vague or no definition. During the 19th century many heavyweights were 170 Pound (mass), pounds (12 st ...
* List of light heavyweight boxing champions
This is a chronological list of world light heavyweight boxing champions, as recognized by four of the better-known sanctioning organizations:
Championship recognition
1903–1910
The light-heavyweight division was created in 1903, the brainc ...
* List of middleweight boxing champions Championship recognition
1884–1910
Champions were recognized by public acclamation. A champion in that era was a fighter who had a notable win over another fighter and kept winning afterward. Retirements or disputed results could lead to a cha ...
* List of boxing triple champions
In boxing, a triple champion is a boxer who has won world titles in three weight classes. For most of the 20th century it was a remarkable and rare achievement accomplished by only a handful of fighters. Beginning in the 1970s, triple champions h ...
Notes and references
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
* *Boxing Hall of Fame
On this day in boxing – Old man Bob Fitzsimmons becomes first three-weight champion – ESPN
* in the ''
Dictionary of New Zealand Biography
The ''Dictionary of New Zealand Biography'' (DNZB) is an encyclopedia or biographical dictionary containing biographies of over 3,000 deceased New Zealanders. It was first published as a series of print volumes from 1990 to 2000, went online ...
''
Biography in the 1966 ''Encyclopaedia of New Zealand'' (birth year wrong)
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fitzsimmons, Bob 1863 births 1917 deaths 19th-century British sportsmen Burials at Graceland Cemetery (Chicago) British emigrants to New Zealand New Zealand people of Cornish descent American people of Cornish descent Immigrants to the United States English male boxers English bare-knuckle boxers English people of Irish descent Heavyweight boxers International Boxing Hall of Fame inductees Light-heavyweight boxers Middleweight boxers New Zealand male boxers New Zealand emigrants to the United States New Zealand people of English descent People associated with physical culture People from Helston World boxing champions World heavyweight boxing champions New Zealand world boxing champions World middleweight boxing champions Deaths from pneumonia in Illinois Cornish people of Irish descent