Robert Brothers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Les Frères Robert were two French brothers. Anne-Jean Robert (1758–1820) and Nicolas-Louis Robert (1760–1828) were the engineers who built the world's first


/ref>
Coupe Aeronautique Gordon Bennett, More than 100 years.
/ref> In Beuvry a stone monument was erected to commemorate the 200th anniversary landing of the brothers. A celebration festival ''la ducasse du Ballon'' is now held at the end of every September. (See image of ''Les frères Robert'' monument at Ville de Beuvry )
Images at Fiddlers Green
U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission. Accessed 23 February 2007. {{DEFAULTSORT:Robert Brothers 18th-century French inventors French balloonists 18th-century French engineers Aviation pioneers French aviators Brother duos History of ballooning
hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
balloon
A balloon is a flexible membrane bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. For special purposes, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), ...
for professor Jacques Charles
Jacques Alexandre César Charles (12 November 1746 – 7 April 1823) was a French people, French inventor, scientist, mathematician, and balloonist.
Charles wrote almost nothing about mathematics, and most of what has been credited to him was due ...
, which flew from central Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
on 27 August 1783. They went on to build the world's first manned hydrogen balloon, and on 1 December 1783 Nicolas-Louis accompanied Jacques Charles on a 2-hour, 5-minute flight. Their barometer and thermometer made it the first balloon flight to provide meteorological measurements of the atmosphere above the Earth's surface.
The brothers subsequently experimented with an elongated elliptical shape for the hydrogen envelope in a balloon they attempted to power and steer by means of oars and umbrella
An umbrella or parasol is a folding canopy supported by wooden or metal ribs that is mounted on a wooden, metal, or plastic pole. It is usually designed to protect a person against rain. The term ''umbrella'' is traditionally used when protec ...
s. In September 1784 the brothers flew 186 km from Paris to Beuvry, the world's first flight of more than 100 km.
Career
Background
The Robert brothers were skilled engineers with a workshop at the ''Place des Victoires
The Place des Victoires (; English: Victory Square, 'Square of Victories') is a circular Town square, square in central Paris, located a short distance northeast of the Palais-Royal and straddling the border between the 1st arrondissement of Pari ...
'' in Paris, who worked with professor Jacques Charles to build the first usable hydrogen balloon in 1783. Charles conceived the idea that hydrogen would be a suitable lifting agent for balloons because, as a chemist, he had studied the work of his contemporaries Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "inflammable air". He described the density of inflammable a ...
, Joseph Black and Tiberius Cavallo.

First hydrogen balloon
Jacques Charles designed the hydrogen balloon and the Robert brothers invented the methodology for constructing the lightweight, airtight gas bag. They dissolvedrubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
in a solution of turpentine
Turpentine (which is also called spirit of turpentine, oil of turpentine, terebenthine, terebenthene, terebinthine and, colloquially, turps) is a fluid obtainable by the distillation of resin harvested from living trees, mainly pines. Principall ...
and varnish
Varnish is a clear Transparency (optics), transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not to be confused with wood stain. It usually has a yellowish shade due to the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmente ...
ed the sheets of silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
that were stitched together to make the main envelope. They used alternate strips of red and white silk, but the discolouration of the varnishing/rubberising process left a red and yellow result.
Jacques Charles and the Robert brothers launched their balloon, the world's first hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
-filled balloon
A balloon is a flexible membrane bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. For special purposes, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), ...
(called '' Le Globe''), on 27 August 1783, from the Champ-de-Mars (now the site of the Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower from 1887 to 1889.
Locally nicknamed "''La dame de fe ...
); Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
was among the crowd of onlookers. The balloon was comparatively small, a 35 cubic-metre sphere of rubberised silk, and only capable of lifting about 9 kg. It was filled with hydrogen that had been made by pouring nearly a quarter of a tonne of sulphuric acid onto half a tonne of scrap iron. The hydrogen gas was fed into the envelope through lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
pipes; but as it was not passed through cold water, great difficulty was experienced in filling the balloon completely (the gas was hot when produced, but as it cooled in the balloon, it contracted). Daily progress bulletins were issued on the inflation; and the crowd was so great that on the 26th the balloon was moved secretly by night to the Champ-de-Mars, a distance of 4 kilometres.
The balloon flew northwards for 45 minutes, pursued by chasers on horseback, and landed 21 kilometres away in the village of Gonesse where the reportedly terrified local peasants attacked it with pitchforks or knives and destroyed it. The project was funded by a subscription organised by Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond
Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond (17 May 174118 July 1819) was a French geologist, volcanologist and traveller.
Life
He was born at Montélimar. He was educated at the Jesuit's College at Lyon and afterwards at Grenoble where he studied law and ...
.

First manned hydrogen balloon flight
At 13:45 on 1 December 1783, Professor Jacques Charles (after whom the gas balloon came to be called a ''Charlière'' ) and the Robert brothers launched a new manned balloon from the Jardin des Tuileries in Paris, amid vast crowds and excitement. The balloon was held on ropes and led to its final launch place by four of the leading noblemen in France, the Marechal de Richelieu, Marshal de Biron, the Bailiff of Suffren, and the Duke of Chaulnes. Jacques Charles was accompanied by Nicolas-Louis Robert as co-pilot of the 380-cubic-metre, hydrogen-filled, balloon. The envelope was fitted with a hydrogen release valve and was covered with a net from which the basket was suspended. Sand ballast was used to control altitude. They ascended to a height of about 1,800 feet (550 m) and landed at sunset in Nesles-la-Vallée after a 2-hour, 5-minute flight covering 36 km. The chasers on horseback, who were led by the Duc de Chartres, held down the craft while both Charles and Nicolas-Louis alighted. Jacques Charles then decided to ascend again, but alone this time because the balloon had lost some of its hydrogen. The balloon ascended rapidly to an altitude of approximately 3,000 metres, rising into the sunlight again, so that Charles then saw a second sunset. He began suffering from aching pain in his ears so he 'valved' to release gas, and descended to land gently about 3 km away at Tour du Lay. Unlike the Robert brothers, Charles never flew again. They carried a barometer and a thermometer to measure the pressure and the temperature of the air, making this not only the first manned hydrogen balloon flight but also the first balloon flight to provide meteorological measurements of the atmosphere above the Earth's surface. It is reported that 400,000 spectators witnessed the launch, and that hundreds had paid one crown each to help finance the construction and receive access to a "special enclosure" for a "close-up view" of the take-off. Among the "special enclosure" crowd wasBenjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
, the diplomatic representative of the United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguo ...
. Also present was Joseph Montgolfier, whom Charles honoured by asking him to release the small, bright green, pilot balloon to assess the wind and weather conditions.
This event took place ten days after the world's first manned balloon flight by Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier
Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier () (30 March 1754 – 15 June 1785) was a French chemistry and physics teacher, and one of the first pioneers of aviation. He made the first manned free balloon flight with François Laurent d'Arlandes on 21 Nov ...
using a Montgolfier brothers
The Montgolfier brothers – Joseph-Michel Montgolfier (; 26 August 1740 – 26 June 1810) and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier (; 6 January 1745 – 2 August 1799) – were aviation pioneers, balloonists and paper manufacturers from the Communes o ...
hot air balloon
A hot air balloon is a lighter-than-air aircraft consisting of a bag, called an envelope, which contains heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule), which carri ...
. Simon Schama wrote in ''Citizens
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality; ...
'':

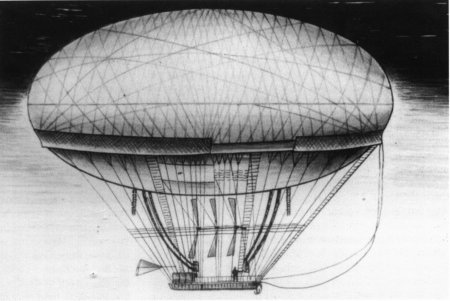
Attempted dirigible: the elongated balloon
The next project of Jacques Charles and the brothers was to build an elongated, steerable craft that followedJean Baptiste Meusnier
Jean Baptiste Marie Charles Meusnier de la Place (Tours, 19 June 1754 — le Pont de Cassel, near Mainz, 13 June 1793) was a French mathematician, engineer and Revolutionary general. He is best known for Meusnier's theorem on the curvature o ...
's proposals (1783–85) for a dirigible balloon. The design incorporated Meusnier's internal ''ballonnet'' (air cells), a rudder, and an ineffective parasol-paddle based method of propulsion.
On 15 July 1784 the brothers flew for 45 minutes from Saint-Cloud
Saint-Cloud () is a French commune in the western suburbs of Paris, France, from the centre of Paris. Like other communes of Hauts-de-Seine such as Marnes-la-Coquette, Neuilly-sur-Seine and Vaucresson, Saint-Cloud is one of France's wealthie ...
to Meudon
Meudon () is a French Communes of France, commune located in the Hauts-de-Seine Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, on the left bank of the Seine. It is located from the Kilometre Zero, center of P ...
with M. Collin-Hullin and Louis Philippe II, the Duke of Chartres in their elongated balloon which was called ''La Caroline''. It was fitted with oars for propulsion and direction, but they proved useless. The absence of a gas release valve meant that the duke had to slash the ''ballonnet'' to prevent rupture when they reached an altitude of about 4,500 metres.
On 19 September 1784 the brothers and M. Collin-Hullin flew for 6 hours 40 minutes, covering from Paris to Beuvry near Béthune
Béthune ( ; archaic and ''Bethwyn'' historically in English) is a town in northern France, Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department.
Geography
Béthune is located in the Provinces of Fran ...
. En route they passed over Saint-Just-en-Chaussée and the region of Clermont de l'Oise. This was the first flight over 100 kilometers as well as over 100 miles.Freres Robert at Beuvry/ref>
Commemoration
In October 2001 the CIA (FAI's Commission Internationale d'Aérostation) announced that the Robert brothers had been inducted to the Federal Aviation Administration 'Balloon and Airship Hall of Fame' for their work in developing the first usable hydrogen balloons. In 1933 the mayor of Nesles-la-Vallée erected a stèle monument to Jacques Charles and Nicholas-Louis Robert. The inscription reads ''On board the First Balloon Inflated with Hydrogen, Charles and Robert, who left Paris, landed in this meadow on the first of December 1785.'' (''A Bord du Premier Ballon Gonfle a L'Hydrogene, Charles et Robert partis de Paris ont atterri dans cette prairie Le Premier de Decembre 1785.'') In 1983 the 200th anniversary of ballooning was commemorated by special issue ofpostage stamp
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage (the cost involved in moving, insuring, or registering mail). Then the stamp is affixed to the f ...
s by countries around the world.
*Images of the original hydrogen balloon were published in Central Africa Republic, Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, France, Malagasy Republic
The Malagasy Republic (, ) was a state situated in Southeast Africa on the island of Madagascar. It was established in 1958 as an autonomous republic within the newly created French Community, became fully independent in 1960, and existed un ...
, Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the Argentina–Paraguay border, south and southwest, Brazil to the Brazil–Paraguay border, east and northeast, and Boli ...
, Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
, Republic of Upper Volta
The Republic of Upper Volta () was a landlocked West African country established on 11 December 1958 as a self-governing state within the French Community. Before becoming autonomous, it had been part of the French Union as the French Upper V ...
, Zaire
Zaire, officially the Republic of Zaire, was the name of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1971 to 18 May 1997. Located in Central Africa, it was, by area, the third-largest country in Africa after Sudan and Algeria, and the 11th-la ...
.
*Images of the elongated balloon were published in Central Africa Republic, Paraguay, Upper Volta.
The ''Coupe Charles et Robert'' was an international ballooning event that was run in 1983 in parallel with the Gordon Bennett Cup (ballooning)./ref> In Beuvry a stone monument was erected to commemorate the 200th anniversary landing of the brothers. A celebration festival ''la ducasse du Ballon'' is now held at the end of every September. (See image of ''Les frères Robert'' monument at Ville de Beuvry )
See also
* History of ballooning *Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier
Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier () (30 March 1754 – 15 June 1785) was a French chemistry and physics teacher, and one of the first pioneers of aviation. He made the first manned free balloon flight with François Laurent d'Arlandes on 21 Nov ...
, the first manned balloon flight using a Montgolfier
The Montgolfier brothers – Joseph-Michel Montgolfier (; 26 August 1740 – 26 June 1810) and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier (; 6 January 1745 – 2 August 1799) – were aviation pioneers, balloonists and paper manufacturers from the Communes o ...
hot-air balloon, 10 days before the Charles hydrogen balloon
* Jean-Pierre Blanchard
Jean-Pierre rançoisBlanchard (; 4 July 1753 – 7 March 1809) was a French inventor, best known as a pioneer of gas balloon flight, who distinguished himself in the conquest of the air in a balloon. Notable for his successful hydrogen balloo ...
* Timeline of aviation - 18th century
This is a list of aviation-related events during the 18th century (January 1, 1701 – December 31, 1800):
1700s–1770s
*1709
**Portuguese Father Bartolomeu de Gusmão demonstrates a practical model of a hot-air balloon made of a paper envelop ...
* List of firsts in aviation
References
;AttributionExternal links
Images at Fiddlers Green
U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission. Accessed 23 February 2007. {{DEFAULTSORT:Robert Brothers 18th-century French inventors French balloonists 18th-century French engineers Aviation pioneers French aviators Brother duos History of ballooning