Right Libertarianism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Right-libertarianism,Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971)
"The Left and Right Within Libertarianism"
. ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press
p. 4
. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. ..In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces ''laissez-faire'' liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: Sage Publications
p. 1006
. . also known as libertarian capitalism, or right-wing libertarianism, "It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Murray Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism). There is a complex debate within this tradition between those like Robert Nozick, who advocate a 'minimal state', and those like Rothbard who want to do away with the state altogether and allow all transactions to be governed by the market alone. From an anarchist perspective, however, both positions—the minimal state (minarchist) and the no-state ('anarchist') positions—neglect the problem of economic domination; in other words, they neglect the hierarchies, oppressions, and forms of exploitation that would inevitably arise in laissez-faire 'free' market. ..Anarchism, therefore, has no truck with this right-wing libertarianism, not only because it neglects economic inequality and domination, but also because in practice (and theory) it is highly inconsistent and contradictory. The individual freedom invoked by right-wing libertarians is only narrow economic freedom within the constraints of a capitalist market, which, as anarchists show, is no freedom at all. is a
"The Greening of Politics: Toward a New Kind of Political Practice"
. ''Green Perspectives: Newsletter of the Green Program Project'' (1). "We have permitted cynical political reactionaries and the spokesmen of large corporations to pre-empt these basic libertarian American ideals. We have permitted them not only to become the specious voice of these ideals such that individualism has been used to justify egotism; the pursuit of happiness to justify greed, and even our emphasis on local and regional autonomy has been used to justify parochialism, insularism, and exclusivity—often against ethnic minorities and so-called deviant individuals. We have even permitted these reactionaries to stake out a claim to the word libertarian, a word, in fact, that was literally devised in the 1890s in France by Elisée Reclus as a substitute for the word anarchist, which the government had rendered an illegal expression for identifying one's views. The propertarians, in effect—acolytes of Ayn Rand, the earth mother of greed, egotism, and the virtues of property—have appropriated expressions and traditions that should have been expressed by radicals but were willfully neglected because of the lure of European and Asian traditions of socialism, socialisms that are now entering into decline in the very countries in which they originated".Fernandez, Frank (2001)
''Cuban Anarchism. The History of a Movement''
Sharp Press. p. 9. "Thus, in the United States, the once exceedingly useful term "libertarian" has been hijacked by egotists who are in fact enemies of liberty in the full sense of the word.""The Week Online Interviews Chomsky"
''Anarchism: A Very Short Introduction''
. Oxford University Press. p. 62. "For a century, anarchists have used the word 'libertarian' as a synonym for 'anarchist', both as a noun and an adjective. The celebrated anarchist journal ''Le Libertaire'' was founded in 1896. However, much more recently the word has been appropriated by various American free-market philosophers." it continues to be widely used to refer to
"150 years of Libertarian"
. ''Anarchist Writers''. The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 31 January 2020.The Anarchist FAQ Editorial Collective (17 May 2017)
"160 years of Libertarian"
. ''Anarchist Writers''. Anarchist FAQ. Retrieved 31 January 2020. and more generally libertarian communism/
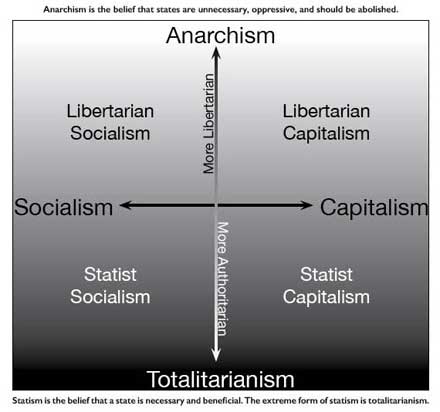 People described as being ''left-libertarian'' or ''right-libertarian'' generally tend to call themselves simply ''libertarians'' and refer to their philosophy as ''libertarianism''. In light of this, some authors and political scientists classify the forms of
People described as being ''left-libertarian'' or ''right-libertarian'' generally tend to call themselves simply ''libertarians'' and refer to their philosophy as ''libertarianism''. In light of this, some authors and political scientists classify the forms of
''Collection of Essays and Tracts in Theology, from Various Authors, with Biographical and Critical Notices''
publicado por Oliver Everett, 13 Cornhill, 1824 (ver, Writings of Dr. Cogan, 205). The
"De l'être-humain mâle et femelle – Lettre à P.J. Proudhon"
(in French).Woodcock, George (1962). ''Anarchism: A History of Libertarian Ideas and Movements''. Meridian Books. p. 280. "He called himself a "social poet," and published two volumes of heavily didactic verse—Lazaréennes and Les Pyrénées Nivelées. In New York, from 1858 to 1861, he edited an anarchist paper entitled ''Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social'', in whose pages he printed as a serial his vision of the anarchist Utopia, entitled L'Humanisphére." to mean a form of
"The Left and Right Within Libertarianism"
. ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press
p. 4
. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. ..In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces ''laissez-faire'' liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: Sage Publications
p. 1006
. . also known as libertarian capitalism, or right-wing libertarianism, "It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Murray Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism). There is a complex debate within this tradition between those like Robert Nozick, who advocate a 'minimal state', and those like Rothbard who want to do away with the state altogether and allow all transactions to be governed by the market alone. From an anarchist perspective, however, both positions—the minimal state (minarchist) and the no-state ('anarchist') positions—neglect the problem of economic domination; in other words, they neglect the hierarchies, oppressions, and forms of exploitation that would inevitably arise in laissez-faire 'free' market. ..Anarchism, therefore, has no truck with this right-wing libertarianism, not only because it neglects economic inequality and domination, but also because in practice (and theory) it is highly inconsistent and contradictory. The individual freedom invoked by right-wing libertarians is only narrow economic freedom within the constraints of a capitalist market, which, as anarchists show, is no freedom at all. is a
libertarian
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according ...
political philosophy
Political philosophy studies the theoretical and conceptual foundations of politics. It examines the nature, scope, and Political legitimacy, legitimacy of political institutions, such as State (polity), states. This field investigates different ...
that supports capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
property rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership), is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their Possession (law), possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely ...
and market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
*Marketing, the act of sat ...
distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
of natural resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. ...
. The term ''right-libertarianism'' is used to distinguish this class of views on the nature of property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ...
and capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
from left-libertarianism
Left-libertarianism, also known as left-wing libertarianism, is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that stresses both individual freedom and social equality. Left-libertarianism represents several related yet distinct approaches to ...
, a variant of libertarianism that combines self-ownership
Self-ownership, also known as sovereignty of the individual or individual sovereignty, is the concept of property in one's own person, expressed as the moral or natural right of a person to have bodily integrity and be the exclusive controlle ...
with an egalitarian approach to property and income. In contrast to socialist libertarianism, capitalist libertarianism supports free-market capitalism
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any o ...
. Like other forms of libertarianism, it supports civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties of ...
, especially natural law
Natural law (, ) is a Philosophy, philosophical and legal theory that posits the existence of a set of inherent laws derived from nature and universal moral principles, which are discoverable through reason. In ethics, natural law theory asserts ...
, negative rights
Negative and positive rights are rights that oblige either inaction (''negative rights'') or action (''positive rights''). These obligations may be of either a legal or moral character. The notion of positive and negative rights may also be ap ...
, the non-aggression principle, and a significant transformation or outright elimination of the modern welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the State (polity), state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal oppor ...
.
Right-libertarian political thought is characterized by the strict priority given to liberty
Liberty is the state of being free within society from oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one's way of life, behavior, or political views. The concept of liberty can vary depending on perspective and context. In the Constitutional ...
, with the need to maximize the realm of individual freedom and minimize the scope of government authority. Right-libertarians typically see the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
as the principal threat to liberty. This anti-statism
Anti-statism is an approach to social, economic or political philosophy that opposes the influence of the state over society. It emerged in reaction to the formation of modern sovereign states, which anti-statists considered to work against the ...
differs from anarcho-socialist theory (but not individualist anarchist theory) in that it is based upon private property norms and strong individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and a ...
that places less emphasis on human sociability or cooperation. Right-libertarian philosophy is also rooted in the ideas of individual rights
Individual rights, also known as natural rights, are rights held by individuals by virtue of being human. Some theists believe individual rights are bestowed by God. An individual right is a moral claim to freedom of action.
Group rights, also k ...
and ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( , from , ) is a type of economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies or regulations). As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' ...
'' economics. The right-libertarian theory of individual rights generally follows the homestead principle
The homestead principle is the principle by which one gains ownership of an unowned natural resource by performing an act of original appropriation. Appropriation could be enacted by putting an unowned resource to active use (as with using i ...
and the labor theory of property
The labor theory of property, also called the labor theory of appropriation, labor theory of ownership, labor theory of entitlement, and principle of first appropriation, is a theory of natural law that holds that property originally comes about ...
, stressing self-ownership and that people have an absolute right to the property that their labor produces. Economically, right-libertarians make no distinction between capitalism and free markets and view any attempt to dictate the market process as counterproductive, emphasizing the mechanisms and self-regulating nature of the market whilst portraying government intervention
A market intervention is a policy or measure that modifies or interferes with a market, typically done in the form of state action, but also by philanthropic and political-action groups. Market interventions can be done for a number of reas ...
and attempts to redistribute wealth
Redistribution of income and wealth is the transfer of income and wealth (including physical property) from some individuals to others through a social mechanism such as taxation, welfare, public services, land reform, monetary policies, confi ...
as criminally immoral, unnecessary, and counter-productive. Although all right-libertarians oppose government intervention, there is a division between anarcho-capitalists
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by pri ...
, who view the state as an unnecessary evil and want property rights protected without statutory law through market-generated tort, contract and property law; and minarchists, who support the need for a minimal state, often referred to as a night-watchman state
A night-watchman state, also referred to as a minimal state or minarchy, whose proponents are known as minarchists, is a model of a state that is limited and minimal, whose functions depend on libertarian theory. Right-libertarians support i ...
, to provide its citizens with courts
A court is an institution, often a government entity, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and administer justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law.
Courts gene ...
, military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
, and police
The police are Law enforcement organization, a constituted body of Law enforcement officer, people empowered by a State (polity), state with the aim of Law enforcement, enforcing the law and protecting the Public order policing, public order ...
.Marshall, Peter (2008). '' Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism''. London: Harper Perennial. p. 565. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. ..In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces ''laissez-faire'' liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".
Like libertarians of all varieties, right-libertarians refer to themselves simply as ''libertarians''. Being the most common type of libertarianism in the United States
In the United States, libertarianism is a political philosophy promoting individual liberty. According to common meanings of Conservatism in the United States, conservatism and Modern liberalism in the United States, liberalism in the United S ...
, right-libertarianism has become the most common referent of ''libertarianism'' there since the late 20th century while historically and elsewhereBookchin, Murray (January 1986)"The Greening of Politics: Toward a New Kind of Political Practice"
. ''Green Perspectives: Newsletter of the Green Program Project'' (1). "We have permitted cynical political reactionaries and the spokesmen of large corporations to pre-empt these basic libertarian American ideals. We have permitted them not only to become the specious voice of these ideals such that individualism has been used to justify egotism; the pursuit of happiness to justify greed, and even our emphasis on local and regional autonomy has been used to justify parochialism, insularism, and exclusivity—often against ethnic minorities and so-called deviant individuals. We have even permitted these reactionaries to stake out a claim to the word libertarian, a word, in fact, that was literally devised in the 1890s in France by Elisée Reclus as a substitute for the word anarchist, which the government had rendered an illegal expression for identifying one's views. The propertarians, in effect—acolytes of Ayn Rand, the earth mother of greed, egotism, and the virtues of property—have appropriated expressions and traditions that should have been expressed by radicals but were willfully neglected because of the lure of European and Asian traditions of socialism, socialisms that are now entering into decline in the very countries in which they originated".Fernandez, Frank (2001)
''Cuban Anarchism. The History of a Movement''
Sharp Press. p. 9. "Thus, in the United States, the once exceedingly useful term "libertarian" has been hijacked by egotists who are in fact enemies of liberty in the full sense of the word.""The Week Online Interviews Chomsky"
Z Magazine
ZNetwork, formerly known as Z Communications, is a left-wing activist-oriented media group founded in 1986 by Michael Albert and Lydia Sargent.Max Elbaum''Revolution in the Air: Sixties Radicals Turn to Lenin, Mao and Che'' London, England, UK; ...
. 23 February 2002. "The term libertarian as used in the US means something quite different from what it meant historically and still means in the rest of the world. Historically, the libertarian movement has been the anti-statist wing of the socialist movement. In the US, which is a society much more dominated by business, the term has a different meaning. It means eliminating or reducing state controls, mainly controls over private tyrannies. Libertarians in the US don't say let's get rid of corporations. It is a sort of ultra-rightism."Ward, Colin (2004)''Anarchism: A Very Short Introduction''
. Oxford University Press. p. 62. "For a century, anarchists have used the word 'libertarian' as a synonym for 'anarchist', both as a noun and an adjective. The celebrated anarchist journal ''Le Libertaire'' was founded in 1896. However, much more recently the word has been appropriated by various American free-market philosophers." it continues to be widely used to refer to
anti-state
Anti-statism is an approach to Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic or political philosophy that opposes the influence of the State (polity), state over society. It emerged in reaction to the formation of modern sovereign state ...
forms of socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
such as anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. A ...
Marshall, Peter (2009). '' Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism''. p. 641. "The word 'libertarian' has long been associated with anarchism and has been used repeatedly throughout this work. The term originally denoted a person who upheld the doctrine of the freedom of the will; in this sense, Godwin was not a 'libertarian', but a 'necessitarian'. It came however to be applied to anyone who approved of liberty in general. In anarchist circles, it was first used by Joseph Déjacque as the title of his anarchist journal ''Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social'' published in New York in 1858. At the end of the last century, the anarchist Sebastien Faure took up the word, to stress the difference between anarchists and authoritarian socialists".The Anarchist FAQ Editorial Collective (11 December 2008)"150 years of Libertarian"
. ''Anarchist Writers''. The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 31 January 2020.The Anarchist FAQ Editorial Collective (17 May 2017)
"160 years of Libertarian"
. ''Anarchist Writers''. Anarchist FAQ. Retrieved 31 January 2020. and more generally libertarian communism/
libertarian Marxism
Libertarian socialism is an anti-authoritarian and anti-capitalist political current that emphasises self-governance and workers' self-management. It is contrasted from other forms of socialism by its rejection of state ownership and from other ...
and libertarian socialism
Libertarian socialism is an anti-authoritarian and anti-capitalist political current that emphasises self-governance and workers' self-management. It is contrasted from other forms of socialism by its rejection of state ownership and from other ...
. Around the time of Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
, who popularized the term ''libertarian'' in the United States during the 1960s, anarcho-capitalist movements started calling themselves ''libertarian'', leading to the rise of the term ''libertarian capitalist'' (mainly used by proponents) and ''right-libertarian'' (mainly used by opponents) to distinguish them. Rothbard himself acknowledged the co-opting of the term "libertarian" and boasted of its "capture ..from the enemy" after statists had captured the term "liberal" from the champions of liberty.
Definition
 People described as being ''left-libertarian'' or ''right-libertarian'' generally tend to call themselves simply ''libertarians'' and refer to their philosophy as ''libertarianism''. In light of this, some authors and political scientists classify the forms of
People described as being ''left-libertarian'' or ''right-libertarian'' generally tend to call themselves simply ''libertarians'' and refer to their philosophy as ''libertarianism''. In light of this, some authors and political scientists classify the forms of libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
into two groups, namely left-libertarianism
Left-libertarianism, also known as left-wing libertarianism, is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that stresses both individual freedom and social equality. Left-libertarianism represents several related yet distinct approaches to ...
and right-libertarianism, to distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ...
and capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
.
The term ''libertarian'' was first used by late Enlightenment freethinkers, referring to those who believed in free will
Free will is generally understood as the capacity or ability of people to (a) choice, choose between different possible courses of Action (philosophy), action, (b) exercise control over their actions in a way that is necessary for moral respon ...
, as opposed to necessity, a now-disused philosophy that posited a kind of determinism. The word ''libertarian'' is first recorded in 1789 coined by the British historian William Belsham
William Belsham (1752 – 1827) was an English political writer and historian, noted as a supporter of the Whig Party and its principles. He justified the American Revolution in excusing Americans in their resistance to the demands of England, a ...
, in a discussion against free will from the author's deterministic point of view. This debate between libertarianism in a philosophical-metaphysical sense and determinism
Determinism is the Metaphysics, metaphysical view that all events within the universe (or multiverse) can occur only in one possible way. Deterministic theories throughout the history of philosophy have developed from diverse and sometimes ov ...
would continue into the early nineteenth century, especially in the field of Protestant theology.Jared Sparks, ''Collection of Essays and Tracts in Theology, from Various Authors, with Biographical and Critical Notices''
publicado por Oliver Everett, 13 Cornhill, 1824 (ver, Writings of Dr. Cogan, 205). The
Merriam-Webster Dictionary
''Webster's Dictionary'' is any of the US English language dictionaries edited in the early 19th century by Noah Webster (1758–1843), a US lexicographer, as well as numerous related or unrelated dictionaries that have adopted the Webster's n ...
, in English, attests to this ancient use of the word libertarian by describing its meaning as "an advocate of the doctrine of free will "and, taking a broad definition, also says that he is" a person who holds the principles of individual freedom especially in thought and action ".
Many decades later, ''libertarian'' was a term used by the French libertarian communist Joseph Déjacque
Joseph Déjacque (; 27 December 1821 – 18 November 1865) was a French political journalist and poet. A house painter by trade, during the 1840s, he became involved in the French labour movement and taught himself how to write poetry. He was ...
Déjacque, Joseph (1857)"De l'être-humain mâle et femelle – Lettre à P.J. Proudhon"
(in French).Woodcock, George (1962). ''Anarchism: A History of Libertarian Ideas and Movements''. Meridian Books. p. 280. "He called himself a "social poet," and published two volumes of heavily didactic verse—Lazaréennes and Les Pyrénées Nivelées. In New York, from 1858 to 1861, he edited an anarchist paper entitled ''Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social'', in whose pages he printed as a serial his vision of the anarchist Utopia, entitled L'Humanisphére." to mean a form of
left-wing politics
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social ...
that has been frequently used to refer to anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. A ...
and libertarian socialism
Libertarian socialism is an anti-authoritarian and anti-capitalist political current that emphasises self-governance and workers' self-management. It is contrasted from other forms of socialism by its rejection of state ownership and from other ...
since the mid- to late 19th century. With the modern development of right-libertarian ideologies such as anarcho-capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by pri ...
and minarchism
A night-watchman state, also referred to as a minimal state or minarchy, whose proponents are known as minarchists, is a model of a state that is limited and minimal, whose functions depend on libertarian theory. Right-libertarians support it ...
co-opting the term ''libertarian'' in the mid-20th century to instead advocate ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( , from , ) is a type of economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies or regulations). As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' ...
'' capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
and strong private property rights
Property rights are constructs in economics for determining how a resource or economic good is used and owned, which have developed over ancient and modern history, from Abrahamic law to Article 17 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Re ...
such as in land, infrastructure and natural resources, the terms ''left-libertarianism'' and ''right-libertarianism'' have been used more often as to differentiate between the two. Socialist libertarianism has been included within a broad left-libertarianism while right-libertarianism mainly refers to ''laissez-faire'' capitalism such as Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
's anarcho-capitalism and Robert Nozick
Robert Nozick (; November 16, 1938 – January 23, 2002) was an American philosopher. He held the Joseph Pellegrino Harvard University Professor, University Professorship at Harvard University,
Right-libertarianism has been described as combining individual freedom and opposition to the state, with strong support for
p. 27
. .Mudde, Cas (2016)
''The Populist Radical Right: A Reader''
(1st ed.). Routledge. . Mark Bevir holds that there are three types of libertarianism, namely left, right and According to contemporary American libertarian
According to contemporary American libertarian
"Libertarianism Is Unique and Belongs Neither to the Right Nor the Left: A Critique of the Views of Long, Holcombe, and Baden on the Left, Hoppe, Feser, and Paul on the Right"
. ''
"Telling stories about post-war Britain: popular individualism and the 'crisis' of the 1970s"
. ''Twentieth Century British History''. 28 (2): 268–304. radical right and
"Real World Politics and Radical Libertarianism"
LewRockwell.com. . Retrieved 25 January 2020.Teles, Steven; Kenney, Daniel A. "Spreading the Word: The Diffusion of American Conservatism in Europe and Beyond". In Kopsten, Jeffrey; Steinmo, Sven, eds. (2007)
''Growing Apart?: America and Europe in the Twenty-First Century''
.
"Libertarianism"
. ''
''Betrayal of the American Right''
. Auburn, Alabama:
"Found Cause"
. ''
"Ayn Rand Is Dead"
. ''National Review''. pp. 35–36. Retrieved 16 March 2020. While ''libertarian'' was popularized by the libertarian socialist
"New-Paradigm Libertarianism: a Very Brief Explanation"
. PhilPapers. Retrieved 26 June 2019. It is commonly referred to as a continuation or radicalization of
"The Minarchist's Dilemma"
. '' Strike The Root''. Retrieved 26 June 2019. Some minarchists argue that a state is inevitable, believing anarchy to be futile. Others argue that anarchy is immoral because it implies that the non-aggression principle is optional and not sufficient to enforce the non-aggression principle because the enforcement of laws under anarchy is open to competition. Another common justification is that private defense agencies and court firms would tend to represent the interests of those who pay them enough. Right-libertarians such as anarcho-capitalists argue that the state violates the non-aggression principle by its nature because governments use force against those who have not stolen or vandalized private property, assaulted anyone, or committed fraud. Others argue that monopolies tend to be corrupt and inefficient and that private defense and court agencies would have to have a good reputation to stay in business. Linda and Morris Tannehill argue that no coercive monopoly of force can arise on a truly free market and that a government's citizenry can desert them in favor of a competent protection and defense agency. Philosopher Moshe Kroy argues that the disagreement between anarcho-capitalists who adhere to
 Anarcho-capitalism advocates the elimination of
Anarcho-capitalism advocates the elimination of
(2011). ''Libertarian Papers''. 3 (3). Anarcho-capitalists support
"The New Right and Anarcho-Capitalism"
. London: Harper Perennial. . Autarchism promotes the principles of
"Are Libertarians 'Anarchists'?"
Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 1 April 2020. Many anarchist activists and scholars deny that anarcho-capitalism is a form of anarchism, or that capitalism is compatible with anarchism,Davis, Laurence (2019). "Individual and Community". In Levy, Carl; Adams, Matthew S. (eds.). ''The Palgrave Handbook of Anarchism''. Cham: Springer. pp. 47–70. . . regarding it instead as right-libertarian. Anarcho-capitalists are distinguished from anarchists and minarchists. The latter advocate a night-watchman state limited to protecting individuals from aggression and enforcing private property. On the other hand, anarchists support
 Conservative libertarianism combines ''
Conservative libertarianism combines ''
pp. 110–111
. This can also be understood as promoting
(1975). National Book Foundation. Retrieved 8 March 2012. . where he argued that only a minimal state limited to the narrow functions of protection against "force, fraud, theft, and administering courts of law" could be justified without violating people's rights.
 Traditionally, liberalism's primary emphasis was placed on securing the freedom of the individual by limiting the power of the government and maximizing the power of free market forces. As a political philosophy, it advocated
Traditionally, liberalism's primary emphasis was placed on securing the freedom of the individual by limiting the power of the government and maximizing the power of free market forces. As a political philosophy, it advocated
 Paleolibertarianism was developed by American libertarian theorists
Paleolibertarianism was developed by American libertarian theorists
"What Is Classical Liberalism?"
National Center for Policy Analysis. Retrieved 26 June 2019. . With other forms of right-libertarianism there are significant differences. Edwin van de Haar argues that "confusingly, in the United States the term libertarianism is sometimes also used for or by classical liberals. But this erroneously masks the differences between them". Classical liberalism refuses to give priority to liberty over order and therefore does not exhibit the hostility to the state which is the defining feature of libertarianism. As such, right-libertarians believe classical liberals favor too much state involvement, arguing that they do not have enough respect for individual property rights and lack sufficient trust in the workings of the
 At least partly reflective of some of the social and cultural concerns that lay beneath Rothbard's outreach to paleoconservatives is
At least partly reflective of some of the social and cultural concerns that lay beneath Rothbard's outreach to paleoconservatives is  Walter Block identifies Feser, Hoppe, and Paul as "right-libertarians". Rothbard's outreach to conservatives was partly triggered by his perception of negative reactions within the Libertarian Party to
Walter Block identifies Feser, Hoppe, and Paul as "right-libertarians". Rothbard's outreach to conservatives was partly triggered by his perception of negative reactions within the Libertarian Party to
"With Liberty and Justice for Some"
. In Zimmerman, Michael; Callicott, Baird; Warren, Karen; Klaver, Irene; Clark, John. ''Environmental Philosophy: From Animal Rights to Radical Ecology'' (4th ed.). Pearson. . including the view that it has no explicit theory of liberty. It has been argued that ''laissez-faire'' capitalism does not necessarily produce the best or most efficient outcome, nor does its philosophy of individualism and policies of
free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
s and private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
. Property rights have been the issue that has divided libertarian philosophies. According to Jennifer Carlson, right-libertarianism is the dominant form of libertarianism in the United States
In the United States, libertarianism is a political philosophy promoting individual liberty. According to common meanings of Conservatism in the United States, conservatism and Modern liberalism in the United States, liberalism in the United S ...
. Right-libertarians "see strong private property rights as the basis for freedom and thus are—to quote the title of Brian Doherty's text on libertarianism in the United States—" Radicals for Capitalism".
Herbert Kitschelt and Anthony J. McGann contrast right-libertarianism—"a strategy that combines pro-market positions with opposition to hierarchical authority, support of unconventional political participation, and endorsement of feminism and of environmentalism"—with right-authoritarianism.Kitschelt, Herbert; McGann, Anthony J. (1997) 995
Year 995 (Roman numerals, CMXCV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Japan
* 17 May - Fujiwara no Michitaka (imperial regent) dies.
* 3 June: Fujiwara no Michikane gains power and becomes Rege ...
'' The Radical Right in Western Europe: A Comparative Analysis''. University of Michigan Pressp. 27
. .Mudde, Cas (2016)
''The Populist Radical Right: A Reader''
(1st ed.). Routledge. . Mark Bevir holds that there are three types of libertarianism, namely left, right and
consequentialist libertarianism
Consequentialist libertarianism, also known as consequentialist liberalism or libertarian consequentialism, is a libertarian political philosophy and position that is supportive of a free market and strong private property rights only on the grou ...
as promoted by Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek (8 May 1899 – 23 March 1992) was an Austrian-born British academic and philosopher. He is known for his contributions to political economy, political philosophy and intellectual history. Hayek shared the 1974 Nobe ...
.
Walter Block
Walter Edward Block (born August 21, 1941) is an American Austrian School economist and anarcho-capitalist theorist. He was the Harold E. Wirth Eminent Scholar Endowed Chair in Economics at the School of Business at Loyola University New Orlean ...
, left-libertarians and right-libertarians agree with certain libertarian premises, but "where heydiffer is in terms of the logical implications of these founding axioms".Block, Walter (2010)"Libertarianism Is Unique and Belongs Neither to the Right Nor the Left: A Critique of the Views of Long, Holcombe, and Baden on the Left, Hoppe, Feser, and Paul on the Right"
. ''
Journal of Libertarian Studies
The Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, that is a center for Austrian economics, right-wing libertarian thought and the paleolibertarian and anarc ...
''. 22. pp. 127–170. Although some libertarians may reject the political spectrum
A political spectrum is a system to characterize and classify different Politics, political positions in relation to one another. These positions sit upon one or more Geometry, geometric Coordinate axis, axes that represent independent political ...
, especially the left–right political spectrum
The left–right political spectrum is a system of classifying political positions, ideologies and political parties, parties, with emphasis placed upon issues of social equality and social hierarchy. In addition to positions on the left and on ...
, right-libertarianism and several right-oriented strands of libertarianism in the United States have been described as being right-wing, New Right,Robinson, Emily; ''et al.'' (2017)"Telling stories about post-war Britain: popular individualism and the 'crisis' of the 1970s"
. ''Twentieth Century British History''. 28 (2): 268–304. radical right and
reactionary
In politics, a reactionary is a person who favors a return to a previous state of society which they believe possessed positive characteristics absent from contemporary.''The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought'' Third Edition, (1999) p. 729. ...
.
American libertarian activist and politician David Nolan David Nolan may refer to:
* David Nolan (politician) (1943–2010), co-founder of the United States Libertarian Party
* David Nolan (American author) (born 1946), American author
* David Nolan (British author) (born 1964), British author of ''I ...
, the principal founder of the Libertarian Party, developed what is now known as the Nolan Chart
The Nolan Chart is a political spectrum diagram created by United States, American Libertarian Party (United States), libertarian activist David Nolan (libertarian), David Nolan in 1969, charting political views along two axes, representing econo ...
to replace the traditional left-right political spectrum. The Nolan Chart has been used by several modern American libertarians and right-libertarians who reject the traditional political spectrum for its lack of inclusivity and see themselves as north-of-center. It is used in an effort to quantify typical libertarian views that support both free markets and social liberties and reject what they see as restrictions on economic and personal freedom imposed by the left and the right, respectively, although this latter point has been criticized. Other libertarians reject the separation of personal and economic liberty or argue that the Nolan Chart gives no weight to foreign policy.
Since the resurgence of neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
in the 1970s, right-libertarianism has spread beyond North America via think tanks and political parties.Gregory, Anthony (24 April 2007)"Real World Politics and Radical Libertarianism"
LewRockwell.com. . Retrieved 25 January 2020.Teles, Steven; Kenney, Daniel A. "Spreading the Word: The Diffusion of American Conservatism in Europe and Beyond". In Kopsten, Jeffrey; Steinmo, Sven, eds. (2007)
''Growing Apart?: America and Europe in the Twenty-First Century''
.
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessme ...
. pp. 136–169. In the United States, libertarianism is increasingly viewed as this capitalist free-market position.
Terminology
As a term, ''right-libertarianism'' is used by some political analysts, academics and media sources, especially in the United States, to describe the libertarian philosophy which is supportive offree-market capitalism
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any o ...
and strong right to property
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership), is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely and is typicall ...
, in addition to supporting limited government
In political philosophy, limited government is the concept of a government limited in power. It is a key concept in the history of liberalism.Amy Gutmann, "How Limited Is Liberal Government" in Liberalism Without Illusions: Essays on Liberal ...
and self-ownership
Self-ownership, also known as sovereignty of the individual or individual sovereignty, is the concept of property in one's own person, expressed as the moral or natural right of a person to have bodily integrity and be the exclusive controlle ...
, being contrasted with left-wing views which do not support the former. In most of the world, this particular political position is mostly known as classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited governmen ...
, economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
and neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
. It is mainly associated with right-wing politics
Right-wing politics is the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that view certain social orders and Social stratification, hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position b ...
, support for free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
s and private ownership
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
of capital goods. Furthermore, it is usually contrasted with similar ideologies such as social democracy
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achi ...
and social liberalism
Social liberalism is a political philosophy and variety of liberalism that endorses social justice, social services, a mixed economy, and the expansion of civil and political rights, as opposed to classical liberalism which favors limited g ...
which generally favor alternative forms of capitalism such as mixed economies
A mixed economy is an economic system that includes both elements associated with capitalism, such as private businesses, and with socialism, such as nationalized government services.
More specifically, a mixed economy may be variously de ...
, state capitalism
State capitalism is an economic system in which the state undertakes business and commercial economic activity and where the means of production are nationalized as state-owned enterprises (including the processes of capital accumulation, ...
and welfare capitalism
Welfare capitalism is capitalism that includes social welfare policies and/or the practice of businesses providing welfare services to their employees. Welfare capitalism in this second sense, or industrial paternalism, was centered on indust ...
.
Peter Vallentyne
Peter Vallentyne (; born March 25, 1952) is an American philosopher who is Florence G. Kline Professor of Philosophy at the University of Missouri in Columbia, Missouri. He holds dual citizenship in the United States and Canada.
Biography
Vall ...
writes that libertarianism, defined as being about self-ownership
Self-ownership, also known as sovereignty of the individual or individual sovereignty, is the concept of property in one's own person, expressed as the moral or natural right of a person to have bodily integrity and be the exclusive controlle ...
, is not a right-wing doctrine in the context of the typical left–right political spectrum
The left–right political spectrum is a system of classifying political positions, ideologies and political parties, parties, with emphasis placed upon issues of social equality and social hierarchy. In addition to positions on the left and on ...
because on social issues it tends to be left-wing, opposing laws restricting consensual sexual relationships between or drug use by adults as well as laws imposing religious views or practices and compulsory military service. He defines right-libertarianism as holding that unowned natural resources "may be appropriated by the first person who discovers them, mixes her labor with them, or merely claims them—without the consent of others, and with little or no payment to them". He contrasts this with left-libertarianism
Left-libertarianism, also known as left-wing libertarianism, is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that stresses both individual freedom and social equality. Left-libertarianism represents several related yet distinct approaches to ...
, where such "unappropriated natural resources belong to everyone in some egalitarian manner". Vallentyne, Peter (20 July 2010)"Libertarianism"
. ''
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') is a freely available online philosophy resource published and maintained by Stanford University, encompassing both an online encyclopedia of philosophy and peer-reviewed original publication ...
''. Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
. Retrieved 26 December 2012. Similarly, Charlotte and Lawrence Becker maintain that right-libertarianism most often refers to the political position that because natural resources are originally unowned, they may be appropriated at will by private parties without the consent of, or owing to, others.
Samuel Edward Konkin III
Samuel Edward Konkin III (July 8, 1947 – February 23, 2004), also known as SEK3, was a Canadian-American libertarian philosopher and Austrian school economist. As the author of the publication ''New Libertarian Manifesto'', he was a proponen ...
, who characterized agorism
Samuel Edward Konkin III (July 8, 1947 – February 23, 2004), also known as SEK3, was a Canadian-American libertarian philosopher and Austrian school economist. As the author of the publication ''New Libertarian Manifesto'', he was a proponen ...
as a form of left-libertarianism and strategic branch of left-wing market anarchism, defined right-libertarianism as an "activist, organization, publication or tendency which supports parliamentarianism
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of the legisl ...
exclusively as a strategy for reducing or abolishing the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
, typically opposes Counter-Economics
Counter-economics is an economic theory and revolutionary method consisting of direct action carried out through the black market or the gray market. As a term, it was originally used by American libertarian activists and theorists Samuel Edward ...
, either opposes the Libertarian Party or works to drag it right and prefers coalitions with supposedly 'free-market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
' conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilizati ...
".
Anthony Gregory maintains that libertarianism "can refer to any number of varying and at times mutually exclusive political orientations". While holding that the important distinction for libertarians is not left or right, but whether they are "government apologists who use libertarian rhetoric to defend state aggression", he describes right-libertarianism as having and maintaining interest in economic freedom, preferring a conservative lifestyle, viewing private business as a "great victim of the state" and favoring a non-interventionist
Non-interventionism or non-intervention is commonly understood as "a foreign policy of political or military non-involvement in foreign relations or in other countries' internal affairs". This is based on the grounds that a state should not inter ...
foreign policy, sharing the Old Right's "opposition to empire".
Old Right
Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
, whose writings and personal influence helped create some strands of right-libertarianism, wrote about the Old Right in the United States, a loose coalition of individuals formed in the 1930s to oppose the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
at home and military interventionism abroad, that they "did not describe or think of themselves as conservatives: they wanted to repeal and overthrow, not conserve". Rothbard, Murray (2007)''Betrayal of the American Right''
. Auburn, Alabama:
Mises Institute
The Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, that is a center for Austrian economics, right-wing libertarian thought and the paleolibertarian and ana ...
. p. xi. . Bill Kauffman has also written about such "old right libertarians". Kauffman, Bill (18 May 2009)"Found Cause"
. ''
The American Conservative
''The American Conservative'' (''TAC'') is a bimonthly magazine published by the American Ideas Institute. The magazine was founded in 2002 by Pat Buchanan, Scott McConnell and Taki Theodoracopulos to advance an anti- neoconservative perspect ...
''. Retrieved 15 March 2020. Peter Marshall dates right-libertarianism and anarcho-capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by pri ...
in particular back to the Old Right and as being popularized again by the New Right.
Individuals who are seen in this Old Right libertarian tradition include Frank Chodorov
Frank Chodorov (February 15, 1887 – December 28, 1966) was an American intellectual, author, and member of the Old Right, a group of classically liberal thinkers who were non-interventionist in foreign policy and opposed to both the America ...
, John T. Flynn
John Thomas Flynn (October 25, 1882 – April 13, 1964) was an American journalist best known for his opposition to President Franklin D. Roosevelt and to American entry into World War II. In September 1940, Flynn helped establish the America Fi ...
, Garet Garrett
Garet Garrett (February 19, 1878 – November 6, 1954), born Edward Peter Garrett, was an American journalist and author, known for his opposition to the New Deal and U.S. involvement in World War II.
Overview
Garrett was born February 1 ...
, Rose Wilder Lane, H. L. Mencken
Henry Louis Mencken (September 12, 1880 – January 29, 1956) was an American journalist, essayist, satirist, cultural critic, and scholar of American English. He commented widely on the social scene, literature, music, prominent politicians, ...
, Albert Jay Nock and Isabel Paterson. What those thinkers had in common was opposition to the rise of the managerial state during the Progressive Era
The Progressive Era (1890s–1920s) was a period in the United States characterized by multiple social and political reform efforts. Reformers during this era, known as progressivism in the United States, Progressives, sought to address iss ...
and its expansion in connection with the New Deal and the Fair Deal
The Fair Deal was a set of proposals put forward by U.S. President Harry S. Truman to Congress in 1945 and in his January 1949 State of the Union Address. More generally, the term characterizes the entire domestic agenda of the Truman adminis ...
whilst challenging imperialism
Imperialism is the maintaining and extending of Power (international relations), power over foreign nations, particularly through expansionism, employing both hard power (military and economic power) and soft power (diplomatic power and cultura ...
and military interventionism. However, ''Old Right'' was a label about which many or most of these figures might have been skeptical as most thought of themselves effectively as classical liberals rather than the national defense
National security, or national defence (national defense in American English), is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived ...
and social conservatism
Social conservatism is a political philosophy and a variety of conservatism which places emphasis on Tradition#In political and religious discourse, traditional social structures over Cultural pluralism, social pluralism. Social conservatives ...
of thinkers associated with the later movement conservatism
Movement conservatism is a term used by political analysts to describe conservatives in the United States since the mid-20th century and the New Right. According to George H. Nash in 2009, the movement comprises a coalition of five distinct im ...
, with Chodorov famously writing: "As for me, I will punch anyone who calls me a conservative in the nose. I am a radical". Their opposition and resistance to the state approached philosophical anarchism with Nock and amounted to statelessness
In international law, a stateless person is someone who is "not considered as a national by any state under the operation of its law". Some stateless people are also refugees. However, not all refugees are stateless, and many people who are s ...
in Chodorov's case. On the other hand, Lew Rockwell and Jeffrey Tucker identifies the Old Right as being culturally conservative, arguing that " gorous social authority—as embodied in the family, church, and other mediating institutions—is a bedrock of the virtuous society" and that " e egalitarian ethic is morally reprehensible and destructive of private property and social authority". Rockwell, Lew; Tucker, Jeffrey (28 May 1990)"Ayn Rand Is Dead"
. ''National Review''. pp. 35–36. Retrieved 16 March 2020. While ''libertarian'' was popularized by the libertarian socialist
Benjamin Tucker
Benjamin Ricketson Tucker (; April 17, 1854 – June 22, 1939) was an American individualist anarchist and self-identified socialist. Tucker was the editor and publisher of the American individualist anarchist periodical ''Liberty'' (1881–19 ...
around the late 1870s and early 1880s, H. L. Mencken and Albert Jay Nock were the first prominent figures in the United States to describe themselves as ''libertarian'' as a synonym for '' liberal''. They believed that Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
had co-opted the word ''liberal'' for his New Deal policies which they opposed and used ''libertarian'' to signify their allegiance to classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited governmen ...
, individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and a ...
and limited government
In political philosophy, limited government is the concept of a government limited in power. It is a key concept in the history of liberalism.Amy Gutmann, "How Limited Is Liberal Government" in Liberalism Without Illusions: Essays on Liberal ...
.
In the 1960s, Rothbard started publishing '' Left and Right: A Journal of Libertarian Thought'', believing that the left–right political spectrum had gone "entirely askew" since conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilizati ...
were sometimes more statist
In political science, statism or etatism (from French, ''état'' 'state') is the doctrine that the political authority of the state is legitimate to some degree. This may include economic and social policy, especially in regard to taxation an ...
than liberals and tried to reach out to leftists and go beyond left and right. In 1971, Rothbard wrote about right-libertarianism which he described as supporting free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold Economic liberalism, economically liberal positions, while economic nationalist politica ...
, property rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership), is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their Possession (law), possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely ...
and self-ownership
Self-ownership, also known as sovereignty of the individual or individual sovereignty, is the concept of property in one's own person, expressed as the moral or natural right of a person to have bodily integrity and be the exclusive controlle ...
. Rothbard would later describe it as anarcho-capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by pri ...
and paleolibertarianism
Paleolibertarianism (also known as the "Paleo strategy") is a right-libertarian political activism strategy aimed at uniting libertarians and paleoconservatives. It was developed by American anarcho-capitalist theorists Murray Rothbard and L ...
.
Philosophy
Right-libertarianism developed in the United States in the mid-20th century from the works of European liberal writers such asJohn Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
, Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek (8 May 1899 – 23 March 1992) was an Austrian-born British academic and philosopher. He is known for his contributions to political economy, political philosophy and intellectual history. Hayek shared the 1974 Nobe ...
and Ludwig von Mises
Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (; ; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian-American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical l ...
and is the most popular conception of libertarianism in the United States
In the United States, libertarianism is a political philosophy promoting individual liberty. According to common meanings of Conservatism in the United States, conservatism and Modern liberalism in the United States, liberalism in the United S ...
today.Lester, J. C. (22 October 2017)"New-Paradigm Libertarianism: a Very Brief Explanation"
. PhilPapers. Retrieved 26 June 2019. It is commonly referred to as a continuation or radicalization of
classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited governmen ...
.Boaz, David (1998). ''Libertarianism: A Primer''. Free Press. pp. 22–26. The most important of these early right-libertarian philosophers were modern American libertarians such as Robert Nozick
Robert Nozick (; November 16, 1938 – January 23, 2002) was an American philosopher. He held the Joseph Pellegrino Harvard University Professor, University Professorship at Harvard University,Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
.
Although often sharing the left-libertarian advocacy for social freedom, right-libertarians also value capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
while rejecting institutions that intervene the free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
on the grounds that such interventions represent unnecessary coercion of individuals and therefore a violation of their economic freedom. Anarcho-capitalist
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of Sovereign state, centralized states in favor of Stateless society, stateless societies, where systems of p ...
s seek complete elimination of the state in favor of private defense agencies while minarchists defend night-watchman state
A night-watchman state, also referred to as a minimal state or minarchy, whose proponents are known as minarchists, is a model of a state that is limited and minimal, whose functions depend on libertarian theory. Right-libertarians support i ...
s which maintain only those functions of government necessary to safeguard natural rights, understood in terms of self-ownership or autonomy.
Right-libertarians are economic liberals of either the Austrian School
The Austrian school is a Heterodox economics, heterodox Schools of economic thought, school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result primarily from the motivat ...
(majority) or the Chicago school of economics
The Chicago school of economics is a Neoclassical economics, neoclassical Schools of economic thought, school of economic thought associated with the work of the faculty at the University of Chicago, some of whom have constructed and populari ...
(minority) and support ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( , from , ) is a type of economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies or regulations). As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' ...
'' capitalism which they define as the free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
in opposition to state capitalism
State capitalism is an economic system in which the state undertakes business and commercial economic activity and where the means of production are nationalized as state-owned enterprises (including the processes of capital accumulation, ...
and interventionism. Right-libertarianism and its individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and a ...
have been discussed as part of the New Right in relation to neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
and Thatcherism
Thatcherism is a form of British conservative ideology named after Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party leader Margaret Thatcher that relates to not just her political platform and particular policies but also her personal character a ...
. In the 20th century, New Right liberal conservatism
Liberal conservatism is a political ideology combining conservative policies with liberal stances, especially on economic issues but also on social and ethical matters, representing a brand of political conservatism strongly influenced by libe ...
influenced by right-libertarianism marginalized other forms of conservatism.
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') is a freely available online philosophy resource published and maintained by Stanford University, encompassing both an online encyclopedia of philosophy and peer-reviewed original publication ...
'' describes right-libertarian philosophy as follows:
Libertarianism is often thought of as 'right-wing' doctrine. This, however, is mistaken for at least two reasons. First, on social—rather than economic—issues, libertarianism tends to be 'left-wing'. It opposes laws that restrict consensual and private sexual relationships between adults (e.g., gay-sex, non-marital sex, and deviant sex), laws that restrict drug use, laws that impose religious views or practices on individuals, and compulsory military service. Second, in addition to the better-known version of libertarianism—right-libertarianism—, there is also a version known as 'left-libertarianism. Both endorse full self-ownership, but they differ with respect to the powers agents have to appropriate unappropriated natural resources (land, air, water, etc.).Right-libertarians are distinguished from left-libertarians by their relation to
property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ...
and capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
. While both left-libertarianism and right-libertarianism share general antipathy towards power by a government authority, the latter exempts power wielded through free-market capitalism
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any o ...
. Historically, libertarians such as Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer (27 April 1820 – 8 December 1903) was an English polymath active as a philosopher, psychologist, biologist, sociologist, and anthropologist. Spencer originated the expression "survival of the fittest", which he coined in '' ...
and Max Stirner
Johann Kaspar Schmidt (; 25 October 1806 – 26 June 1856), known professionally as Max Stirner (; ), was a German post-Hegelian philosopher, dealing mainly with the Hegelian notion of social alienation and self-consciousness. Stirner is oft ...
supported the protection of an individual's freedom from powers of government and private ownership
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
. While condemning governmental encroachment on personal liberties, right-libertarians support freedoms on the basis of their agreement with private property rights and the abolishment of public amenities is a common theme in right-libertarian writings.
While associated with free-market capitalism, right-libertarianism is not opposed in principle to voluntary egalitarianism
Egalitarianism (; also equalitarianism) is a school of thought within political philosophy that builds on the concept of social equality, prioritizing it for all people. Egalitarian doctrines are generally characterized by the idea that all hum ...
and socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
. However, right-libertarians believe that their advocated economic system would prove superior and that people would prefer it to socialism. For Nozick, it does not imply support of capitalism, but merely that capitalism is compatible with libertarianism, something which is rejected by anti-capitalist
Anti-capitalism is a political ideology and Political movement, movement encompassing a variety of attitudes and ideas that oppose capitalism. Anti-capitalists seek to combat the worst effects of capitalism and to eventually replace capitalism ...
libertarians.
According to Stephen Metcalf, Nozick expressed serious misgivings about capitalism, going so far as to reject much of the foundations of the theory on the grounds that personal freedom can sometimes only be fully actualized via a collectivist politics and that wealth is at times justly redistributed via taxation to protect the freedom of the many from the potential tyranny of an overly selfish and powerful few. Nozick suggested that citizens who are opposed to wealth redistribution which fund programs they object to should be able to opt-out by supporting alternative government-approved charities with an added 5% surcharge. Nonetheless, Nozick did not stop from self-identifying as a libertarian in a broad sense and Julian Sanchez has argued that his views simply became more nuanced.
Non-aggression principle
The non-aggression principle (NAP) is often described as the foundation of several present-day libertarian philosophies, including right-libertarianism. The NAP is a moral stance which forbids actions that are inconsistent with capitalistprivate property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
and property rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership), is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their Possession (law), possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely ...
. It defines aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In h ...
and initiation of force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
as violation of these rights. The NAP and property rights are closely linked since what constitutes aggression depends on what it is considered to be one's property. The principle has been used rhetorically to oppose policies such as military draft
Conscription, also known as the draft in the United States and Israel, is the practice in which the compulsory enlistment in a national service, mainly a military service, is enforced by law. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it contin ...
s, taxation and victimless crime
A victimless crime is an illegal act that typically either directly involves only the perpetrator or occurs between consenting adults. Because it is consensual in nature, whether there involves a victim is a matter of debate. Definitions of vi ...
laws.
Property rights
While there is debate on whether right-libertarianism andleft-libertarianism
Left-libertarianism, also known as left-wing libertarianism, is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that stresses both individual freedom and social equality. Left-libertarianism represents several related yet distinct approaches to ...
or socialist libertarianism "represent distinct ideologies as opposed to variations on a theme", right-libertarianism is most in favor of capitalist private property and property rights. Right-libertarians maintain that unowned natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. ...
s "may be appropriated by the first person who discovers them, mixes his labor with them, or merely claims them—without the consent of others, and with little or no payment to them". This contrasts with left-libertarianism in which "unappropriated natural resources belong to everyone in some egalitarian manner". Right-libertarians believe that natural resources are originally unowned and therefore private parties may appropriate them at will without the consent of, or owing to, others (e.g. a land value tax
A land value tax (LVT) is a levy on the value of land (economics), land without regard to buildings, personal property and other land improvement, improvements upon it. Some economists favor LVT, arguing it does not cause economic efficiency, ec ...
).
Right-libertarians are also referred to as propertarian
Propertarianism, or proprietarianism, is a political philosophy that reduces all questions of law to the right to own property. On property rights, it advocates private property on the basis of Lockean sticky property norms, where an owner kee ...
s because they hold that societies in which private property rights are enforced are the only ones that are both ethical and lead to the best possible outcomes. They generally support free-market capitalism
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any o ...
and are not opposed to any concentrations of economic power, provided it occurs through non-coercive means.
State
There is a debate amongst right-libertarians as to whether or not thestate
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
is legitimate. While anarcho-capitalists advocate its abolition, minarchists support minimal states, often referred to as night-watchman states. Minarchists maintain that the state is necessary for the protection of individuals from aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In h ...
, breach of contract
Breach of contract is a legal cause of action and a type of civil wrong, in which a binding agreement or bargained-for exchange is not honored by one or more of the parties to the contract by non-performance or interference with the other part ...
, fraud and theft. They believe the only legitimate governmental institutions are courts, military and police, although some expand this list to include the executive and legislative
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers ...
branches, fire department
A fire department (North American English) or fire brigade (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), also known as a fire company, fire authority, fire district, fire and rescue, or fire service in some areas, is an organi ...
s and prisons. These minarchists justify the state on the grounds that it is the logical consequence
Logical consequence (also entailment or logical implication) is a fundamental concept in logic which describes the relationship between statement (logic), statements that hold true when one statement logically ''follows from'' one or more stat ...
of adhering to the non-aggression principle.Gregory, Anthony (10 May 2004)"The Minarchist's Dilemma"
. '' Strike The Root''. Retrieved 26 June 2019. Some minarchists argue that a state is inevitable, believing anarchy to be futile. Others argue that anarchy is immoral because it implies that the non-aggression principle is optional and not sufficient to enforce the non-aggression principle because the enforcement of laws under anarchy is open to competition. Another common justification is that private defense agencies and court firms would tend to represent the interests of those who pay them enough. Right-libertarians such as anarcho-capitalists argue that the state violates the non-aggression principle by its nature because governments use force against those who have not stolen or vandalized private property, assaulted anyone, or committed fraud. Others argue that monopolies tend to be corrupt and inefficient and that private defense and court agencies would have to have a good reputation to stay in business. Linda and Morris Tannehill argue that no coercive monopoly of force can arise on a truly free market and that a government's citizenry can desert them in favor of a competent protection and defense agency. Philosopher Moshe Kroy argues that the disagreement between anarcho-capitalists who adhere to
Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
's view of human consciousness and the nature of values
In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of some thing or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live ( normative ethics), or to describe the significance of different a ...
and minarchists who adhere to Ayn Rand
Alice O'Connor (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum; , 1905March 6, 1982), better known by her pen name Ayn Rand (), was a Russian-born American writer and philosopher. She is known for her fiction and for developing a philosophical system which s ...
's view of human consciousness and the nature of values over whether or not the state is moral is not due to a disagreement over the correct interpretation of a mutually held ethical stance. He argues that the disagreement between these two groups is instead the result of their disagreement over the nature of human consciousness and that each group is making the correct interpretation of their differing premises. According to Kroy, these two groups are not making any errors with respect to deducing the correct interpretation of any ethical stance because they do not hold the same ethical stance.
Taxation as theft
The idea of taxation as theft is a viewpoint found in a number of political philosophies. Under this view, government transgressesproperty rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership), is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their Possession (law), possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely ...
by enforcing compulsory tax collection. Right-libertarians see taxation as a violation of the non-aggression principle.
Schools of thought
Anarcho-capitalism
 Anarcho-capitalism advocates the elimination of
Anarcho-capitalism advocates the elimination of centralized state
A unitary state is a (sovereign) state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or sub-state units). Such units exer ...
s in favor of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
, contracts, free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
s, individual sovereignty, private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
, the right-libertarian interpretation of self-ownership
Self-ownership, also known as sovereignty of the individual or individual sovereignty, is the concept of property in one's own person, expressed as the moral or natural right of a person to have bodily integrity and be the exclusive controlle ...
and voluntaryism
Voluntaryism (,"Voluntaryism"
. '' statute A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wil ...
, anarcho-capitalists hold that society tends to contractually self-regulate and civilize through participation in the free market which they describe as a voluntary society. In an anarcho-capitalist society, courts, . '' statute A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wil ...
law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
and all other security services would be provided by privately funded competitors rather than through taxation and money would be privately and competitively provided in an open market
The term open market is used generally to refer to an economic situation close to free trade. In a more specific, technical sense, the term refers to interbank trade in securities.
In economic theory
Economists judge the "openness" of markets a ...
. Under anarcho-capitalism, personal and economic activities would be regulated by private law
Private law is that part of a legal system that governs interactions between individual persons. It is distinguished from public law, which deals with relationships between both natural and artificial persons (i.e., organizations) and the st ...
rather than through politics."Review of Kosanke's Instead of Politics – Don Stacy"(2011). ''Libertarian Papers''. 3 (3). Anarcho-capitalists support
wage labour
Wage labour (also wage labor in American English), usually referred to as paid work, paid employment, or paid labour, refers to the socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer in which the worker sells their labour power under ...
and believe that neither protection of person and property nor victim compensation requires a state.Marshall, Peter (2008). ''Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism''"The New Right and Anarcho-Capitalism"
. London: Harper Perennial. . Autarchism promotes the principles of
individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and a ...
, the moral ideology of individual liberty and self-reliance whilst rejecting compulsory government and supporting the elimination of government in favor of ruling oneself to the exclusion of rule by others.
The most well-known version of anarcho-capitalism was formulated in the mid-20th century by Austrian School economist and paleolibertarian
Paleolibertarianism (also known as the "Paleo strategy") is a right-libertarian political activism strategy aimed at uniting libertarians and paleoconservatives. It was developed by American anarcho-capitalist theorists Murray Rothbard and Lew ...
Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
. Widely regarded as its founder, Rothbard combined the free-market approach from the Austrian School with the human rights views and a rejection of the state from 19th-century American individualist anarchists and mutualists such as Lysander Spooner
Lysander Spooner (January 19, 1808 – May 14, 1887) was an American abolitionist, entrepreneur, lawyer, essayist, natural rights legal theorist, pamphleteer, political philosopher, and writer often associated with the Boston anarchist tr ...
and Benjamin Tucker
Benjamin Ricketson Tucker (; April 17, 1854 – June 22, 1939) was an American individualist anarchist and self-identified socialist. Tucker was the editor and publisher of the American individualist anarchist periodical ''Liberty'' (1881–19 ...
, although rejecting their anti-capitalism
Anti-capitalism is a political ideology and movement encompassing a variety of attitudes and ideas that oppose capitalism. Anti-capitalists seek to combat the worst effects of capitalism and to eventually replace capitalism with an alternati ...
and socialist economics
Socialist economics comprises the economic theories, practices and norms of hypothetical and existing socialist economic systems. A socialist economic system is characterized by social ownership and operation of the means of production that m ...
, along with the labor theory of value
The labor theory of value (LTV) is a theory of value that argues that the exchange value of a good or service is determined by the total amount of " socially necessary labor" required to produce it. The contrasting system is typically known as ...
and the normative implications they derived from it. In Rothbardian anarcho-capitalism, exemplified in ''For a New Liberty
''For a New Liberty: The Libertarian Manifesto'' (1973; second edition 1978; third edition 1985) is a book by American economist and historian Murray Rothbard, in which the author promotes anarcho-capitalism. The work has been credited as an infl ...
'', there would first be the implementation of a mutually agreed-upon libertarian "legal code which would be generally accepted and which the courts would pledge themselves to follow". This legal code would recognize contracts, individual sovereignty, private property, self-ownership, and tort law as part of the principle of non-aggression In the tradition following David D. Friedman
David Director Friedman (; born February 12, 1945) is an American economist, physicist, legal scholar, and anarcho-capitalist theorist. Although his academic training was in chemistry and physics and not law or economics, he is known for his t ...
, exemplified in '' The Machinery of Freedom'', anarcho-capitalists do not rely upon the idea of natural law
Natural law (, ) is a Philosophy, philosophical and legal theory that posits the existence of a set of inherent laws derived from nature and universal moral principles, which are discoverable through reason. In ethics, natural law theory asserts ...
or natural rights
Some philosophers distinguish two types of rights, natural rights and legal rights.
* Natural rights are those that are not dependent on the laws or customs of any particular culture or government, and so are ''universal'', ''fundamental rights ...
(deontological libertarianism
Natural-rights libertarianism is the theory that all individuals possess certain natural or moral rights, mainly a right of individual sovereignty and that therefore acts of initiation of force and fraud are rights-violations and that is suffici ...
) and follow consequentialist libertarianism
Consequentialist libertarianism, also known as consequentialist liberalism or libertarian consequentialism, is a libertarian political philosophy and position that is supportive of a free market and strong private property rights only on the grou ...
, presenting economic justifications for a free-market capitalist
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production, and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a market ...
society.
While some authors consider anarcho-capitalism a form of individualist anarchism
Individualist anarchism or anarcho-individualism is a collection of anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hi ...
, many others disagree with this as individualist anarchism is largely socialistic. Rothbard argued that individualist anarchism is different from anarcho-capitalism and other capitalist theories due to the individualist anarchists retaining the labor theory of value and socialist economics.Rothbard, Murray (1950s)"Are Libertarians 'Anarchists'?"
Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 1 April 2020. Many anarchist activists and scholars deny that anarcho-capitalism is a form of anarchism, or that capitalism is compatible with anarchism,Davis, Laurence (2019). "Individual and Community". In Levy, Carl; Adams, Matthew S. (eds.). ''The Palgrave Handbook of Anarchism''. Cham: Springer. pp. 47–70. . . regarding it instead as right-libertarian. Anarcho-capitalists are distinguished from anarchists and minarchists. The latter advocate a night-watchman state limited to protecting individuals from aggression and enforcing private property. On the other hand, anarchists support
personal property
Personal property is property that is movable. In common law systems, personal property may also be called chattels or personalty. In civil law (legal system), civil law systems, personal property is often called movable property or movables—a ...
(defined in terms of possession and use, i.e. mutualist usufruct
Usufruct () is a limited real right (or ''in rem'' right) found in civil law and mixed jurisdictions that unites the two property interests of ''usus'' and ''fructus'':
* ''Usus'' (''use'', as in usage of or access to) is the right to use or en ...
) and oppose capital concentration, interest, monopoly, private ownership of productive property such as the means of production
In political philosophy, the means of production refers to the generally necessary assets and resources that enable a society to engage in production. While the exact resources encompassed in the term may vary, it is widely agreed to include the ...
(capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
, land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of Earth not submerged by the ocean or another body of water. It makes up 29.2% of Earth's surface and includes all continents and islands. Earth's land sur ...
and the means of labor
The means of labor (also called instruments of labor) is a concept in Marxist political economy that refers to "all those things with the aid of which man acts upon the subject of his labor, and transforms it." (Institute of Economics of the Aca ...
), profit
Profit may refer to:
Business and law
* Profit (accounting), the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market
* Profit (economics), normal profit and economic profit
* Profit (real property), a nonpossessory inter ...
, rent, usury
Usury () is the practice of making loans that are seen as unfairly enriching the lender. The term may be used in a moral sense—condemning taking advantage of others' misfortunes—or in a legal sense, where an interest rate is charged in e ...
and wage slavery
Wage slavery is a term used to criticize exploitation of labour by business, by keeping wages low or stagnant in order to maximize profits. The situation of wage slavery can be loosely defined as a person's dependence on wages (or a salary) f ...
which are viewed as inherent to capitalism. Anarchism's emphasis on anti-capitalism, egalitarianism
Egalitarianism (; also equalitarianism) is a school of thought within political philosophy that builds on the concept of social equality, prioritizing it for all people. Egalitarian doctrines are generally characterized by the idea that all hum ...
and for the extension of community and individuality sets it apart from anarcho-capitalism and other types of right-libertarianism.Jennings, Jeremy (1993). "Anarchism". In Eatwell, Roger; Wright, Anthony (eds.). ''Contemporary Political Ideologies''. London: Pinter. pp. 127–146. . " ..anarchism does not stand for the untrammelled freedom of the individual (as the 'anarcho-capitalists' appear to believe) but, as we have already seen, for the extension of individuality ''and'' community" (p. 143).Gay, Kathlyn; Gay, Martin (1999). ''Encyclopedia of Political Anarchy''. ABC-CLIO. p. 15. . "For many anarchists (of whatever persuasion), anarcho-capitalism is a contradictory term, since 'traditional' anarchists oppose capitalism".Morriss, Andrew (2008). "Anarcho-capitalism". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). ''The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism''. Sage; Cato Institute. pp. 13–14. . . . "Social anarchists, those anarchists with communitarian leanings, are critical of anarcho-capitalism because it permits individuals to accumulate substantial power through markets and private property."Franks, Benjamin (August 2013). Freeden, Michael; Stears, Marc (eds.). "Anarchism". ''The Oxford Handbook of Political Ideologies''. Oxford University Press: 385–404. . "Individualisms that defend or reinforce hierarchical forms such as the economic-power relations of anarcho-capitalism ..are incompatible with practices of social anarchism. ..Increasingly, academic analysis has followed activist currents in rejecting the view that anarcho-capitalism has anything to do with social anarchism" (pp. 393–394).
Ruth Kinna
Ruth Ellen Kinna (born March 1961) is a historian and theorist of anarchism. She is Professor of Political Philosophy in the Department of Politics, History and International Relations of Loughborough University. She is also one of the two co-e ...
writes that ''anarcho-capitalism'' is a term coined by Rothbard to describe "a commitment to unregulated private property and laissez-faire economics, prioritizing the liberty-rights of individuals, unfettered by government regulation, to accumulate, consume and determine the patterns of their lives as they see fit". According to Kinna, anarcho-capitalists "will sometimes label themselves market anarchists because they recognize the negative connotations of 'capitalism'. But the literatures of anarcho-capitalism draw on classical liberal theory, particularly the Austrian School—Friedrich von Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek (8 May 1899 – 23 March 1992) was an Austrian-born British academic and philosopher. He is known for his contributions to political economy, political philosophy and intellectual history. Hayek shared the 1974 Nobe ...
and Ludwig von Mises
Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (; ; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian-American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical l ...
—rather than recognizable anarchist traditions. Ayn Rand
Alice O'Connor (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum; , 1905March 6, 1982), better known by her pen name Ayn Rand (), was a Russian-born American writer and philosopher. She is known for her fiction and for developing a philosophical system which s ...
's laissez-faire, anti-government, corporate philosophy—Objectivism
Objectivism is a philosophical system named and developed by Russian-American writer and philosopher Ayn Rand. She described it as "the concept of man as a heroic being, with his own happiness as the moral purpose of his life, with productive a ...
—is sometimes associated with anarcho-capitalism".Kinna, Ruth, ed. (2012). ''The Bloomsbury Companion to Anarchism''. New York: Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 330–331. . Other scholars similarly associate anarcho-capitalism with anti-state liberal schools such as neo-classical liberalism, radical neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
and right-libertarianism. Anarcho-capitalism is usually seen as part of the New Right.
Conservative libertarianism
 Conservative libertarianism combines ''
Conservative libertarianism combines ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( , from , ) is a type of economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies or regulations). As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' ...
'' economics and conservative values. It advocates the greatest possible economic liberty and the least possible government regulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. F ...
of social life whilst harnessing this to traditionalist conservatism
Traditionalist conservatism, often known as classical conservatism, is a political philosophy, political and social philosophy that emphasizes the importance of transcendent moral principles, manifested through certain posited natural laws t ...
, emphasizing authority and duty.
Conservative libertarianism prioritizes liberty as its main emphasis, promoting free expression
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recognise ...
, freedom of choice
Freedom of choice describes an individual's opportunity and autonomy to perform an action selected from at least two available options, unconstrained by external parties.
In politics
In the abortion debate, for example, the term "freedom of c ...
and ''laissez-faire'' capitalism to achieve cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
and social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives fro ...
conservative ends whilst rejecting liberal social engineering.Piper, J. Richard (1997). ''Ideologies and Institutions: American Conservative and Liberal Governance Prescriptions Since 1933''. Rowman & Littlefield
Rowman & Littlefield Publishing Group is an American independent academic publishing company founded in 1949. Under several imprints, the company offers scholarly books for the academic market, as well as trade books. The company also owns ...
pp. 110–111
. This can also be understood as promoting
civil society
Civil society can be understood as the "third sector" of society, distinct from government and business, and including the family and the private sphere.conservatism
Conservatism is a Philosophy of culture, cultural, Social philosophy, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, Convention (norm), customs, and Value (ethics and social science ...
and libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
, representing the conservative wing of libertarianism and vice versa. Fusionism combines traditionalist and social conservatism
Social conservatism is a political philosophy and a variety of conservatism which places emphasis on Tradition#In political and religious discourse, traditional social structures over Cultural pluralism, social pluralism. Social conservatives ...
with ''laissez-faire'' economics. This is most closely associated with Frank Meyer. Hans-Hermann Hoppe
Hans-Hermann Hoppe (; ; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American academic associated with Austrian School economics, anarcho-capitalism, right-wing libertarianism, and opposition to democracy. He is professor emeritus of economics at th ...
is a cultural conservative right-libertarian, whose belief in the rights of property owners to establish private covenant communities, from which homosexuals and political dissidents may be "physically removed", has proven particularly divisive. Hoppe also garnered controversy due to his support for restrictive limits on immigration which critics argue is at odds with libertarianism.
Minarchism
Within right-libertarian philosophy, minarchism is supportive of anight-watchman state
A night-watchman state, also referred to as a minimal state or minarchy, whose proponents are known as minarchists, is a model of a state that is limited and minimal, whose functions depend on libertarian theory. Right-libertarians support i ...
, a model of a state whose only functions are to provide its citizens with courts, military and police, protecting them from aggression, breach of contract, fraud and theft whilst enforcing property law
Property law is the area of law that governs the various forms of ownership in real property (land) and personal property. Property refers to legally protected claims to resources, such as land and personal property, including intellectual prope ...
s. 19th-century Britain has been described by historian Charles Townshend
Charles Townshend (27 August 1725 – 4 September 1767) was a British politician who held various titles in the Parliament of Great Britain. His establishment of the controversial Townshend Acts is considered one of the key causes of the Amer ...
as standard-bearer of this form of government among European countries.
As a term, ''night-watchman state'' () was coined by German socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
Ferdinand Lassalle
Ferdinand Johann Gottlieb Lassalle (born Lassal; 11 April 1825 – 31 August 1864) was a German jurist, philosopher, socialist, and political activist. Remembered as an initiator of the German labour movement, he developed the theory of state s ...
, an advocate of social-democratic
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, socia ...
state socialism
State socialism is a political and economic ideology within the socialist movement that advocates state ownership of the means of production. This is intended either as a temporary measure, or as a characteristic of socialism in the transition ...
, to criticize the bourgeois state
The capitalist state is the state, its functions and the form of organization it takes within capitalist socioeconomic systems.Jessop, Bob (January 1977). "Recent Theories of the Capitalist State". ''Soviet Studies''. 1: 4. pp. 353–373. Thi ...
. Austrian School economist Ludwig von Mises
Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (; ; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian-American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical l ...
, a classical liberal who greatly influenced right-libertarianism, later opined that Lassalle tried to make limited government look ridiculous, but that it was no more ridiculous than governments that concerned themselves with "the preparation of sauerkraut, with the manufacture of trouser buttons, or with the publication of newspapers".
Robert Nozick
Robert Nozick (; November 16, 1938 – January 23, 2002) was an American philosopher. He held the Joseph Pellegrino Harvard University Professor, University Professorship at Harvard University,National Book Award
The National Book Awards (NBA) are a set of annual U.S. literary awards. At the final National Book Awards Ceremony every November, the National Book Foundation presents the National Book Awards and two lifetime achievement awards to authors. ...
in category Philosophy and Religion for his book ''Anarchy, State, and Utopia
''Anarchy, State, and Utopia'' is a 1974 book by the American political philosopher Robert Nozick. It won the 1975 US National Book Award in category Philosophy and Religion, has been translated into 11 languages, and was named one of the "100 m ...
'' (1974),"National Book Awards – 1975"(1975). National Book Foundation. Retrieved 8 March 2012. . where he argued that only a minimal state limited to the narrow functions of protection against "force, fraud, theft, and administering courts of law" could be justified without violating people's rights.
Neo-classical liberalism
 Traditionally, liberalism's primary emphasis was placed on securing the freedom of the individual by limiting the power of the government and maximizing the power of free market forces. As a political philosophy, it advocated
Traditionally, liberalism's primary emphasis was placed on securing the freedom of the individual by limiting the power of the government and maximizing the power of free market forces. As a political philosophy, it advocated civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties of ...
under the rule of law
The essence of the rule of law is that all people and institutions within a Body politic, political body are subject to the same laws. This concept is sometimes stated simply as "no one is above the law" or "all are equal before the law". Acco ...
, with an emphasis on economic freedom. Closely related to economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
, it developed in the early 19th century, emerging as a response to urbanization and to the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
in Europe and the United States. It advocated a limited government
In political philosophy, limited government is the concept of a government limited in power. It is a key concept in the history of liberalism.Amy Gutmann, "How Limited Is Liberal Government" in Liberalism Without Illusions: Essays on Liberal ...
and held a belief in ''laissez-faire'' economic policy.
Built on ideas that had already arisen by the end of the 18th century such as selected ideas of John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
,Steven M. Dworetz (1994). ''The Unvarnished Doctrine: Locke, Liberalism, and the American Revolution''. Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptised 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the field of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as the "father of economics"——— or ...
, Thomas Robert Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English economist, cleric, and scholar influential in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
, Jean-Baptiste Say
Jean-Baptiste () is a male French name, originating with Saint John the Baptist, and sometimes shortened to Baptiste. The name may refer to any of the following:
Persons
* Charles XIV John of Sweden, born Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, was K ...
and David Ricardo
David Ricardo (18 April 1772 – 11 September 1823) was a British political economist, politician, and member of Parliament. He is recognized as one of the most influential classical economists, alongside figures such as Thomas Malthus, Ada ...
, it drew on classical economics
Classical economics, also known as the classical school of economics, or classical political economy, is a school of thought in political economy that flourished, primarily in Britain, in the late 18th and early-to-mid 19th century. It includ ...
and economic ideas as espoused by Smith in ''The Wealth of Nations
''An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'', usually referred to by its shortened title ''The Wealth of Nations'', is a book by the Scottish people, Scottish economist and moral philosophy, moral philosopher Adam Smith; ...
'' and stressed the belief in progress
Progress is movement towards a perceived refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. It is central to the philosophy of progressivism, which interprets progress as the set of advancements in technology, science, and social organization effic ...
, natural law
Natural law (, ) is a Philosophy, philosophical and legal theory that posits the existence of a set of inherent laws derived from nature and universal moral principles, which are discoverable through reason. In ethics, natural law theory asserts ...
and utilitarianism
In ethical philosophy, utilitarianism is a family of normative ethical theories that prescribe actions that maximize happiness and well-being for the affected individuals. In other words, utilitarian ideas encourage actions that lead to the ...
. These liberals were more suspicious than conservatives of all but the most minimal government and adopted Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes ( ; 5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679) was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', in which he expounds an influential formulation of social contract theory. He is considered t ...
's theory of government, believing government had been created by individuals to protect themselves from one another.Quinton, A. (1995). "Conservativism". In Goodin, R. E.; Pettit, P. eds. ''A Companion to Contemporary Political Philosophy''. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 246. The term ''classical liberalism'' was applied in retrospect to distinguish earlier 19th-century liberalism from the newer ''social liberalism
Social liberalism is a political philosophy and variety of liberalism that endorses social justice, social services, a mixed economy, and the expansion of civil and political rights, as opposed to classical liberalism which favors limited g ...
''.
Neoliberalism emerged in the era following World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
during which social liberalism was the mainstream form of liberalism while Keynesianism
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongl ...
and social democracy
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achi ...
were the dominant ideologies in the Western world. It was led by neoclassical economists
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption, and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a goo ...
such as Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek (8 May 1899 – 23 March 1992) was an Austrian-born British academic and philosopher. He is known for his contributions to political economy, political philosophy and intellectual history. Hayek shared the 1974 Nobe ...
and Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and ...
, who advocated the reduction of the state and a return to classical liberalism, hence the term ''neo-classical liberalism'', not to be confused with the more left-leaning neoclassical liberalism, an American bleeding-heart libertarian school originating in Arizona. However, it did accept some aspects of social liberalism such as some degree of welfare provision by the state, but on a greatly reduced scale. Hayek and Friedman used the term ''classical liberalism'' to refer to their ideas, but others use the term to refer to all liberalism before the 20th century, not to designate any particular set of political views and therefore see all modern developments as being by definition not classical.
In the late 19th century, classical liberalism developed into neo-classical liberalism which argued for government to be as small as possible to allow the exercise of individual freedom
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and ad ...
. In its most extreme form, neo-classical liberalism advocated social Darwinism
Charles Darwin, after whom social Darwinism is named
Social Darwinism is a body of pseudoscientific theories and societal practices that purport to apply biological concepts of natural selection and survival of the fittest to sociology, economi ...
.Mayne, Alan James (1999). ''From Politics Past to Politics Future: An Integrated Analysis of Current and Emergent Paradigmss''. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 124. . Right-libertarianism has been influenced by these schools of liberalism. It has been commonly referred to as a continuation or radicalization of classical liberalism and referred to as neo-classical liberalism.
Neolibertarianism
The concept of neolibertarianism gained a small following in the mid-2000s among right-leaning commentators who distinguished themselves fromneoconservatives
Neoconservatism (colloquially neocon) is a political movement which began in the United States during the 1960s among liberal hawks who became disenchanted with the increasingly pacifist Democratic Party along with the growing New Left and ...
by their support for individual liberties and from libertarians by their support for foreign interventionism
Interventionism, in international politics, is the interference of a state or group of states into the domestic affairs of another state for the purposes of Coercion (international relations), coercing that state to do something or refrain from d ...
.
Paleolibertarianism
 Paleolibertarianism was developed by American libertarian theorists
Paleolibertarianism was developed by American libertarian theorists Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
and Lew Rockwell. Combining conservative cultural values and social philosophy with a libertarian opposition to government intervention, it overlaps with paleoconservatism..
In the United States, paleolibertarianism is a controversial current due its connections to the alt-right
The alt-right (abbreviated from alternative right) is a Far-right politics, far-right, White nationalism, white nationalist movement. A largely Internet activism, online phenomenon, the alt-right originated in the United States during the late ...
and the Tea Party movement
The Tea Party movement was an American fiscally conservative political movement within the Republican Party that began in 2007, catapulted into the mainstream by Congressman Ron Paul's presidential campaign. The movement expanded in resp ...
. Besides their anti-gun control
Gun control, or firearms regulation, is the set of laws or policies that regulate the manufacture, sale, transfer, possession, modification, or use of firearms and ammunition by civilians.
Most countries allow civilians to own firearms, bu ...
stance in regard to gun laws and politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
in support of the right to keep and bear arms
The right to keep and bear arms (often referred to as the right to bear arms) is a legal right for people to possess weapons (arms) for the preservation of life, liberty, and property. The purpose of gun rights is for Self-defense#Armed, self ...
, these movements, especially the Old Right and paleoconservatism, are united by an anti-leftist stance. In the essay "Right-Wing Populism: A Strategy for the Paleo Movement", Rothbard reflected on the ability of paleolibertarians to engage in an "outreach to redneck
''Redneck'' is a derogatory term mainly applied to white Americans perceived to be crass and unsophisticated, closely associated with rural whites of the southern United States.Harold Wentworth, and Stuart Berg Flexner, ''Dictionary of American ...
s" founded on libertarianism and social conservatism. He cited former Louisiana State Representative David Duke
David Ernest Duke (born July 1, 1950) is an American politician, neo-Nazi, conspiracy theorist, and former grand wizard of the Knights of the Ku Klux Klan. From 1989 to 1992, he was a member of the Louisiana House of Representatives for the ...
and former United States Senator Joseph McCarthy
Joseph Raymond McCarthy (November 14, 1908 – May 2, 1957) was an American politician who served as a Republican Party (United States), Republican United States Senate, U.S. Senator from the state of Wisconsin from 1947 until his death at age ...
as models for the new movement.
In Europe, paleolibertarianism has some significant overlap with right-wing populism
Right-wing populism, also called national populism and right populism, is a political ideology that combines right-wing politics with populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric employs anti- elitist sentiments, opposition to the Establis ...
. Former European Union-parliamentarian Janusz Korwin-Mikke
Janusz Ryszard Korwin-Mikke (; born 27 October 1942), also known by his initials JKM or simply as Korwin, is a Polish far-right politician, paleolibertarian and author. He was a member of the European Parliament from 2014 until 2018. He was the ...
from KORWiN supports both ''laissez-faire'' economics and anti-immigration
Opposition to immigration, also known as anti-immigration, is a political position that seeks to restrict immigration. In the modern sense, immigration refers to the entry of people from one state or territory into another state or territory in ...
and anti-feminist positions.
Propertarianism
Propertarianism advocates the replacement of states with contractual relationships. Propertarian ideals are most commonly cited to advocate for a state or other governance body whose main or only job is to enforce contracts andprivate property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
.
Propertarianism is generally considered right-libertarian because it "reduce all human rights to rights of property, beginning with the natural right of self-ownership".
As a term, ''propertarian'' appears to have been coined in 1963 by Edward Cain, who wrote:
Since their use of the word "liberty" refers almost exclusively to property, it would be helpful if we had some other word, such as "propertarian", to describe them. ..Novelist Ayn Rand is not a conservative at all but claims to be very relevant. She is a radical capitalist, and is the closest to what I mean by a propertarian.
Comparison to classical liberalism
Some forms of right-libertarianism are an outgrowth or as a variant ofclassical liberal
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, eco ...
thought.Goodman, John C. (20 December 2005)"What Is Classical Liberalism?"
National Center for Policy Analysis. Retrieved 26 June 2019. . With other forms of right-libertarianism there are significant differences. Edwin van de Haar argues that "confusingly, in the United States the term libertarianism is sometimes also used for or by classical liberals. But this erroneously masks the differences between them". Classical liberalism refuses to give priority to liberty over order and therefore does not exhibit the hostility to the state which is the defining feature of libertarianism. As such, right-libertarians believe classical liberals favor too much state involvement, arguing that they do not have enough respect for individual property rights and lack sufficient trust in the workings of the
free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
and its spontaneous order
Spontaneous order, also named self-organization in the hard sciences, is the spontaneous emergence of order out of seeming chaos. The term "self-organization" is more often used for physical changes and biological processes, while "spontaneous ...
leading to support of a much larger state. Right-libertarians also disagree with classical liberals as being too supportive of central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
s and monetarist
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of policy-makers in controlling the amount of money in circulation. It gained prominence in the 1970s, but was mostly abandoned as a direct guidance to monetary ...
policies.
By country
Since the 1970s, right-libertarianism has spread beyond the United States. With the foundation of the Libertarian Party in 1971, many countries followed the example and led to the creation oflibertarian parties
This is a list of libertarian political parties.
Active parties by country
Defunct parties by country
Organizations associated with Libertarian parties
See also
* Liberal parties by country
* List of libertarian organizations
* Lists ...
advocating this type of libertarianism, along with classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited governmen ...
, economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
and neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
, around the world, including the United Kingdom, Israel and South Africa. Internationally, the majority of those libertarian parties are grouped within the International Alliance of Libertarian Parties
The International Alliance of Libertarian Parties (IALP) is an alliance of libertarian political parties around the world. Its mission is to promote libertarian politics internationally.
At the 2014 Libertarian National Convention in the United ...
. There also exists the European Party for Individual Liberty at the European level.
Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
was the founder and co-founder of a number of right-libertarian and right-libertarian-leaning journals and organizations. Rothbard was the founder of the Center for Libertarian Studies
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentrici ...
in 1976, the ''Journal of Libertarian Studies
The Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, that is a center for Austrian economics, right-wing libertarian thought and the paleolibertarian and anarc ...
'' and co-founder of the Mises Institute
The Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, that is a center for Austrian economics, right-wing libertarian thought and the paleolibertarian and ana ...
in 1982, including the founding in 1987 of the Mises Institute's ''Review of Austrian Economics'', a heterodox economics
Heterodox economics is a broad, relative term referring to schools of economic thought which are not commonly perceived as belonging to mainstream economics. There is no absolute definition of what constitutes heterodox economic thought, as it i ...
journal later renamed the ''Quarterly Journal of Austrian Economics
The ''Quarterly Journal of Austrian Economics'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering heterodox economics published by the Ludwig von Mises Institute.Lee, Frederic S., and Cronin, Bruce C. (2010)"Research Quality Rankings of Heter ...
''.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, right-libertarianism emerged and became more prominent in British politics after the 1980sneoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
and the economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
of the premiership of Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
, albeit not as prominent as in the United States during the 1970s and the presidency
A presidency is an administration or the executive, the collective administrative and governmental entity that exists around an office of president of a state or nation. Although often the executive branch of government, and often personified b ...
of Republican Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
during the 1980s.
Prominent British right-libertarians include former director of the Libertarian Alliance Sean Gabb and philosopher Stephen R. L. Clark, who are seen as rightists. Gabb has called himself "a man of the right" and Clark self-identifies as an "anarcho-conservative". Gabb has also articulated a libertarian defense of the British Empire. At the same time, Gabb has given a generally appreciative commentary of left-libertarian Kevin Carson
Mutualism is an anarchist school of thought and economic theory that advocates for workers' control of the means of production, a free market made up of individual artisans, sole proprietorships and workers' cooperatives, and occupation and u ...
's work on organization theory and Clark has supported animal rights
Animal rights is the philosophy according to which many or all Animal consciousness, sentient animals have Moral patienthood, moral worth independent of their Utilitarianism, utility to humans, and that their most basic interests—such as ...
, gender inclusiveness and non-judgmental attitude toward some unconventional sexual arrangements.
Apart from the Libertarian Party, there is also a right-libertarian faction of the mainstream Conservative Party that espouses Thatcherism
Thatcherism is a form of British conservative ideology named after Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party leader Margaret Thatcher that relates to not just her political platform and particular policies but also her personal character a ...
.
United States
Right-libertarianism is the dominant form and better known version of libertarianism in the United States, especially when compared withleft-libertarianism
Left-libertarianism, also known as left-wing libertarianism, is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that stresses both individual freedom and social equality. Left-libertarianism represents several related yet distinct approaches to ...
. Robert Nozick
Robert Nozick (; November 16, 1938 – January 23, 2002) was an American philosopher. He held the Joseph Pellegrino Harvard University Professor, University Professorship at Harvard University,Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School,Ronald Hamowy, ed., 2008, The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism', Cato Institute, Sage, , p. 62: "a leading economist of the Austri ...
have been described as the most noted advocate of this type of libertarianism. Unlike Rothbard, who argued for the abolition of the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
, Nozick argued for a night-watchman state
A night-watchman state, also referred to as a minimal state or minarchy, whose proponents are known as minarchists, is a model of a state that is limited and minimal, whose functions depend on libertarian theory. Right-libertarians support i ...
. To this day, there remains a division between anarcho-capitalists
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by pri ...
that advocate its abolition and minarchists who support a night-watchman state. According to Nozick, only such a minimal state could be justified without violating people's rights. Nozick argued that a night-watchman state provides a framework that allows for any political system that respects fundamental individual rights and therefore morally justifies the existence of a state.
Already a radical classical liberal
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, eco ...
and anti-interventionist strongly influenced by the Old Right, especially its opposition to the managerial state whilst being more unequivocally anti-war
An anti-war movement is a social movement in opposition to one or more nations' decision to start or carry on an armed conflict. The term ''anti-war'' can also refer to pacifism, which is the opposition to all use of military force during conf ...
and anti-imperialist
Anti-imperialism in political science and international relations is opposition to imperialism or neocolonialism. Anti-imperialist sentiment typically manifests as a political principle in independence struggles against intervention or influenc ...
, Rothbard had become the doyen of right-libertarianism. Before his departure from the New Left
The New Left was a broad political movement that emerged from the counterculture of the 1960s and continued through the 1970s. It consisted of activists in the Western world who, in reaction to the era's liberal establishment, campaigned for freer ...
, with which he helped build for a few years a relationship with other libertarians, Rothbard considered liberalism and libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
to be left-wing, radical
Radical (from Latin: ', root) may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Classical radicalism, the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and Latin America in the 19th century
*Radical politics ...
and revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates for, a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective to describe something producing a major and sudden impact on society.
Definition
The term—bot ...
whereas conservatism to be right-wing, reactionary
In politics, a reactionary is a person who favors a return to a previous state of society which they believe possessed positive characteristics absent from contemporary.''The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought'' Third Edition, (1999) p. 729. ...
and counter-revolutionary
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution has occurred, in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "c ...
. As for socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
, especially state socialism
State socialism is a political and economic ideology within the socialist movement that advocates state ownership of the means of production. This is intended either as a temporary measure, or as a characteristic of socialism in the transition ...
, Rothbard argued that it was not the opposite of libertarianism, but rather that it pursued liberal ends through conservative means, putting it in the political center. By the time of his death in 1995, Rothbard had involved the segment of the libertarian movement loyal to him in an alliance with the growing paleoconservative
Paleoconservatism is a political philosophy and a strain of conservatism in the United States stressing American nationalism, Christian ethics, regionalism, traditionalist conservatism, and non-interventionism. Paleoconservatism's concerns over ...
movement, seen by many observers, libertarian and otherwise, as flirting with racism and social reaction. Suggesting that libertarians needed a new cultural profile that would make them more acceptable to social and cultural conservatives, Rothbard criticized the tendency of proponents of libertarianism to appeal to "'free spirits,' to people who don't want to push other people around, and who don't want to be pushed around themselves" in contrast to "the bulk of Americans", who "might well be tight-assed conformists, who want to stamp out drugs in their vicinity, kick out people with strange dress habits." While emphasizing that it was relevant as a matter of strategy, Rothbard argued that the failure to pitch the libertarian message to Middle America might result in the loss of "the tight-assed majority".
 At least partly reflective of some of the social and cultural concerns that lay beneath Rothbard's outreach to paleoconservatives is
At least partly reflective of some of the social and cultural concerns that lay beneath Rothbard's outreach to paleoconservatives is paleolibertarianism
Paleolibertarianism (also known as the "Paleo strategy") is a right-libertarian political activism strategy aimed at uniting libertarians and paleoconservatives. It was developed by American anarcho-capitalist theorists Murray Rothbard and L ...
. In an early statement of this position, Lew Rockwell and Jeffrey Tucker arguing for a specifically Christian libertarianism
Christian libertarianism is the synthesis of Christian beliefs with libertarian political philosophy, with a focus on beliefs about free will, human nature, and God-given inalienable rights.
As with some other forms of libertarianism, Christian ...
. Later, Rockwell would no longer consider himself a "paleolibertarian" and was "happy with the term libertarian." While distancing himself from the paleolibertarian alliance strategy, Rockwell affirmed paleoconservatives for their "work on the immigration issue" and maintained that "porous borders in Texas and California" could be seen as "reducing liberty, not increasing it, through a form of publicly subsidized right to trespass."
Hans-Hermann Hoppe
Hans-Hermann Hoppe (; ; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American academic associated with Austrian School economics, anarcho-capitalism, right-wing libertarianism, and opposition to democracy. He is professor emeritus of economics at th ...
argued that "libertarians must be conservatives." Hoppe acknowledged what he described as "the importance, under clearly stated circumstances, of discriminating against communists, democrats, and habitual advocates of alternative, non-family centered lifestyles, including homosexuals." He disagreed with Walter Block
Walter Edward Block (born August 21, 1941) is an American Austrian School economist and anarcho-capitalist theorist. He was the Harold E. Wirth Eminent Scholar Endowed Chair in Economics at the School of Business at Loyola University New Orlean ...
and argued that libertarianism need not be seen as requiring open borders
An open border is a border that enables free movement of people and often of goods between jurisdictions with no restrictions on movement and is lacking a border control. A border may be an open border due to intentional legislation allowing fr ...
. Hoppe attributed "open border enthusiasm" to "egalitarianism". While defending market anarchy in preference to both, Hoppe argued for the superiority of monarchy to democracy by maintaining that monarchs are likely to be better stewards of the territory they claim to own than are democratic politicians, whose time horizons may be shorter.
Defending the fusion of traditionalist conservatism
Traditionalist conservatism, often known as classical conservatism, is a political philosophy, political and social philosophy that emphasizes the importance of transcendent moral principles, manifested through certain posited natural laws t ...
with libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
and rejecting the view that libertarianism means support for a liberal culture, Edward Feser
Edward Charles Feser (; born April 16, 1968) is an American Catholic philosopher. He is an Associate Professor of Philosophy at Pasadena City College in Pasadena, California.
Education
Feser holds a Ph.D. in philosophy from the University of Ca ...
implies that a central issue for those who share his viewpoint is "the preservation of traditional morality—particularly traditional sexual morality, with its idealization of marriage and its insistence that sexual activity be confined within the bounds of that institution, but also a general emphasis on dignity and temperance over self-indulgence and dissolute living."
California Governor Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
appealed to right-libertarians in a 1975 interview with ''Reason
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing valid conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, religion, scien ...
'' by stating to "believe the very heart and soul of conservatism is libertarianism." However, President Reagan, Reaganomics
Reaganomics (; a portmanteau of ''Reagan'' and ''economics'' attributed to Paul Harvey), or Reaganism, were the Neoliberalism, neoliberal economics, economic policies promoted by United States President, U.S. President Ronald Reagan during the ...
and policies of the Reagan administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following his landslide victory over ...
have been criticized by libertarians, including right-libertarians such as Rothbard, who argued that the Reagan presidency
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the List of presidents of the United States, 40th president of the United States began with First inauguration of Ronald Reagan, his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Rep ...
has been "a disaster for libertarianism in the United States" and Reagan himself was "a dramatic failure". Among other reasons, this was because Reagan turned the United States' big trade deficit into debt and the United States became a debtor nation for the first time since World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
under Reagan. Ron Paul
Ronald Ernest Paul (born August 20, 1935) is an American author, activist, and politician who served as the U.S. representative for Texas's 22nd congressional district from 1976 to 1977, and again from 1979 to 1985, as well as for Texas' ...
was one of the first elected officials in the nation to support Reagan's presidential campaign and actively campaigned for Reagan in 1976 and 1980. Paul quickly became disillusioned with the Reagan administration's policies after Reagan's election in 1980 and later recalled being the only Republican to vote against the Reagan budget proposals in 1981, aghast that "in 1977, Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
proposed a budget with a $38 billion deficit, and every Republican in the House voted against it. In 1981, Reagan proposed a budget with a $45 billion deficit—which turned out to be $113 billion—and Republicans were cheering his great victory. They were living in a storybook land." Paul expressed his disgust with the political culture of both major parties in a speech delivered in 1984 upon resigning from the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
to prepare for a failed run for the Senate and eventually apologized to his libertarian friends for having supported Reagan. By 1987, Paul was ready to sever all ties to the Republican Party as explained in a blistering resignation letter. While affiliated with both Libertarian
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according ...
and Republican parties at different times, Paul stated to have always been a libertarian at heart.
 Walter Block identifies Feser, Hoppe, and Paul as "right-libertarians". Rothbard's outreach to conservatives was partly triggered by his perception of negative reactions within the Libertarian Party to
Walter Block identifies Feser, Hoppe, and Paul as "right-libertarians". Rothbard's outreach to conservatives was partly triggered by his perception of negative reactions within the Libertarian Party to Ron Paul 1988 presidential campaign
The Ron Paul presidential campaign of 1988 began in early 1987 when former Congressman Ron Paul of Texas announced his candidacy for the 1988 presidential nomination of the Libertarian Party. He joined the third party after leaving the Repub ...
because of Paul's conservative appearance and his discomfort with abortion. Nonetheless, Paul himself did not make cultural issues central to his public persona during his 2008
2008 was designated as:
*International Year of Languages
*International Year of Planet Earth
*International Year of the Potato
*International Year of Sanitation
The Great Recession, a worldwide recession which began in 2007, continued throu ...
and 2012
2012 was designated as:
*International Year of Cooperatives
*International Year of Sustainable Energy for All
Events January
*January 4 – The Cicada 3301 internet hunt begins.
* January 12 – Peaceful protests begin in the R ...
presidential campaigns for the Republican presidential nomination and focused on a simple message of support for personal freedom and civil liberties, commitment to fiscal discipline and opposition to war, although he did continue to take what some regarded as a conservative position regarding immigration, arguing for some restrictions on cross-border freedom of movement.
Paul's fellow libertarian anti-militarist Justin Raimondo
Justin Raimondo (born Dennis Raimondo; November 18, 1951 – June 27, 2019) was an American author and the editorial director of Antiwar.com. He described himself as a "conservative- paleo-libertarian."
Early life
Born in White Plains, New ...
, a co-founder of Antiwar.com, described himself as a "conservative paleolibertarian". Unlike Feser and Rockwell, Raimondo's ''Reclaiming the American Right'' argued for a resurgence of Old Right political attitudes and did not focus on the social and cultural issues that are of central importance to Feser and Rockwell.
Free State Project
One of the most prominent groups dedicated to promulgating and instituting right-libertarian values is theFree State Project
The Free State Project (FSP) is an American political migration movement founded in 2001 to recruit at least 20,000 libertarians to move to a single low-population state to make the state a stronghold for libertarian ideas. New Hampshire was s ...
. The Free State Project is an activist libertarian movement formed in 2001. It is working to bring libertarians to the state of New Hampshire to protect and advance liberty. , the project website showed that 19,988 people have pledged to move and 6,232 people identified as Free Staters in New Hampshire.
Free State Project participants interact with the political landscape in New Hampshire in various ways. In 2017, there were 17 Free Staters in the New Hampshire House of Representatives, and in 2021, the New Hampshire Liberty Alliance
The New Hampshire Liberty Alliance (NHLA) is a nonpartisan, libertarian coalition in New Hampshire. The organization supports libertarian candidates for state and local offices, and other libertarian causes and organizations.
Just before the Nov ...
, which ranks bills and elected representatives based on their adherence to what they see as libertarian principles, scored 150 (out of 380 rated) representatives as "A−" or above rated representatives. Participants also engage with other like-minded activist groups such as Rebuild New Hampshire, Young Americans for Liberty
Young Americans for Liberty (YAL) is a Libertarianism in the United States, libertarian student activism organization headquartered in Austin, Texas. Formed in 2008 in the aftermath of the Ron Paul 2008 presidential campaign, YAL establishes ch ...
, and Americans for Prosperity
Americans for Prosperity (AFP), founded in 2004, is a Libertarian conservatism, libertarian conservative political advocacy group in the United States affiliated with brothers Charles Koch and the late David Koch. As the Koch family's primary pol ...
.
Criticism
Criticism of right-libertarianism includes ethical, economic, environmental, pragmatic and philosophical concerns,Friedman, Jeffrey (1993). "What's Wrong with Libertarianism". ''Critical Review''. 11 (3). p. 427.Sterba, James P. (October 1994). "From Liberty to Welfare". ''Ethics''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Blackwell. 105 (1): 237–241.Partridge, Ernest (2004)"With Liberty and Justice for Some"
. In Zimmerman, Michael; Callicott, Baird; Warren, Karen; Klaver, Irene; Clark, John. ''Environmental Philosophy: From Animal Rights to Radical Ecology'' (4th ed.). Pearson. . including the view that it has no explicit theory of liberty. It has been argued that ''laissez-faire'' capitalism does not necessarily produce the best or most efficient outcome, nor does its philosophy of individualism and policies of
deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a ...
prevent the abuse of natural resources.
Use of the NAP as a justification for right-libertarianism has been criticized as circular reasoning
Circular reasoning (, "circle in proving"; also known as circular logic) is a fallacy, logical fallacy in which the reasoner begins with what they are trying to end with. Circular reasoning is not a formal logical fallacy, but a pragmatic defect ...
and as a rhetorical obfuscation of the coercive nature of right-libertarian property law enforcement, with critics arguing that the principle redefines aggression in their own terms.
Jeffrey H. Reiman criticized right-libertarians' support of private property, arguing that "the holders of large amounts of property have great power to dictate the terms upon which others work for them and thus in effect the power to 'force' others to be resources for them".
See also
* Anarchism and capitalism *Conservative liberalism
Conservative liberalism, also referred to as right-liberalism, is a variant of liberalism combining liberal values and policies with conservative stances, or simply representing the right wing of the liberal movement. In the case of modern con ...
* Constitutionalism
Constitutionalism is "a compound of ideas, attitudes, and patterns of behavior elaborating the principle that the authority of government derives from and is limited by a body of fundamental law".
Political organizations are constitutional to ...
* Criticism of democracy
Democracy, its functions, and its development have been criticized throughout history. Some critics call upon the constitutional regime to be true to its own highest principles; others reject the values promoted by constitutional democracy.
...
* Debates within libertarianism
Libertarianism is variously defined by sources as there is no general consensus among scholars on the definition nor on how one should use the term as a historical category. Scholars generally agree that libertarianism refers to the group of pol ...
* Fiscal conservatism
In American political theory, fiscal conservatism or economic conservatism is a political and economic philosophy regarding fiscal policy and fiscal responsibility with an ideological basis in capitalism, individualism, limited government, ...
* Free banking
* Freedom of association
Freedom of association encompasses both an individual's right to join or leave groups voluntarily, the right of the group to take collective action to pursue the interests of its members, and the right of an association to accept or decline membe ...
* Issues in anarchism
* Labor mobility
Labor or worker mobility is the geographical and occupational movement of workers. Impediments to mobility are easily divided into two distinct classes with one being personal and the other being systemic. Personal impediments include physical loc ...
* Market fundamentalism
Market fundamentalism, also known as free-market fundamentalism, is a term applied to a strong belief in the ability of unregulated '' laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalist policies to solve most economic and social problems. It is often us ...
* Objectivist movement
The Objectivist movement is a Social movement, movement of individuals who seek to study and advance Objectivism, the philosophy expounded by novelist-philosopher Ayn Rand. The movement began informally in the 1950s and consisted of students who ...
* Outline of libertarianism
* Patriot movement
* Republican Liberty Caucus
The Republican Liberty Caucus (RLC) is a political action organization dedicated to promoting the ideals of Individual freedom, individual liberty, limited government and free market economics within the Republican Party (United States), Republi ...
* Sovereign citizen movement
The sovereign citizen movement (also SovCit movement or SovCits) is a loose group of anti-government activists, conspiracy theory, conspiracy theorists, vexatious litigants, tax protesters and financial scammers found mainly in English-speakin ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{neoliberalism LibertarianismLibertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
Libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
Libertarianism by form
Libertarianism in the United States