Rickets on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rickets, scientific nomenclature: rachitis (from Greek , meaning 'in or of the spine'), is a condition that results in weak or soft
 Signs and symptoms of dietary deficiency rickets can include
Signs and symptoms of dietary deficiency rickets can include
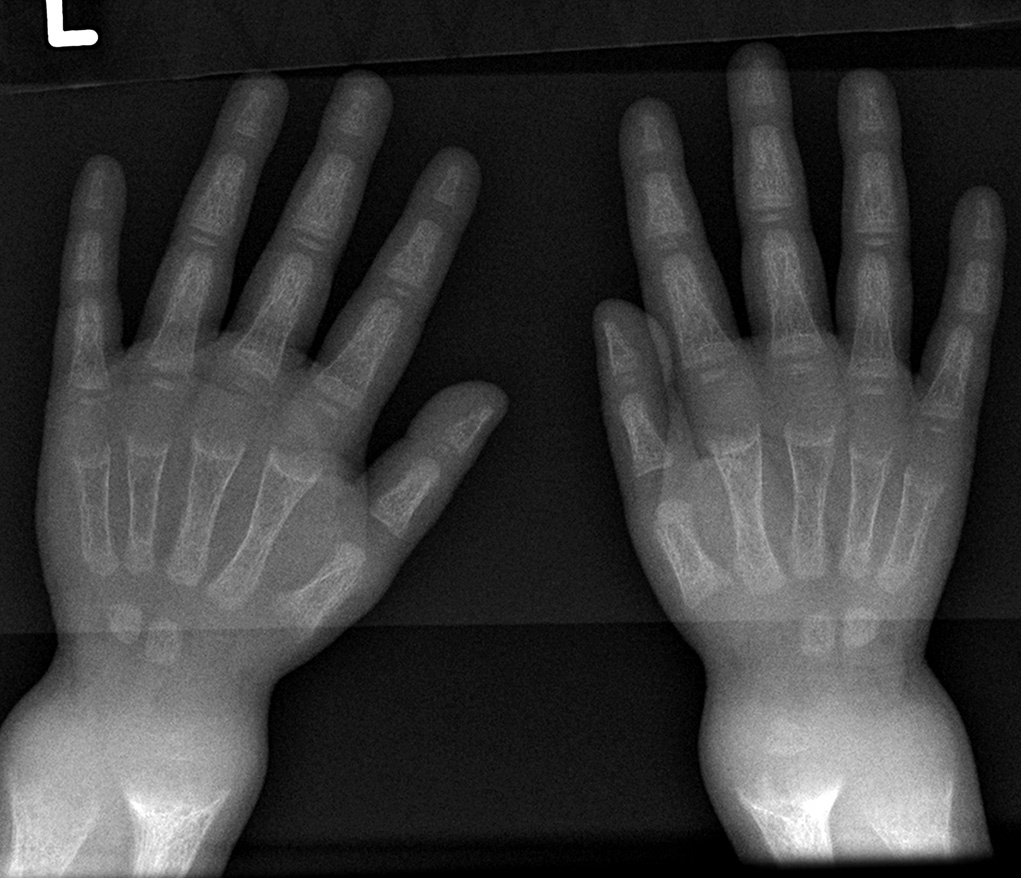
 Rickets may be diagnosed with the help of:
* Blood tests:
** Serum
Rickets may be diagnosed with the help of:
* Blood tests:
** Serum
 Greek physician
Greek physician
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s in children and may have either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving th ...
, stunted growth
Stunted growth, also known as stunting or linear growth failure, is defined as impaired growth and development manifested by low height-for-age. Stunted growth is often caused by malnutrition, and can also be caused by Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
, bone pain, large forehead
In human anatomy, the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features, two of the skull and one of the scalp. The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline, the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows. The bottom of the fo ...
, and trouble sleeping. Complications may include bone deformities, bone pseudofracture
A pseudofracture, also called a Looser zone, is a diagnostic finding in osteomalacia.
Pseudofracture also rarely occurs in Paget's disease of bone, hyperparathyroidism, renal osteodystrophy, osteogenesis imperfecta, fibrous dysplasia, and hypophosp ...
s and fractures
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
, muscle spasms
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder.
A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a musc ...
, or an abnormally curved spine. The analogous condition in adults is osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of b ...
.
The most common cause of rickets is a vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
, although hereditary genetic forms also exist. This can result from eating a diet without enough vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, dark skin, too little sun exposure, exclusive breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Orga ...
without vitamin D supplementation, celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, and certain genetic condition
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are ...
s. Other factors may include not enough calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
or phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
. The underlying mechanism involves insufficient calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature M ...
of the growth plate
The epiphyseal plate, epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with ma ...
. Diagnosis is generally based on blood tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cho ...
finding a low calcium, low phosphorus, and a high alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryo ...
together with X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
.
Prevention for exclusively breastfed babies is vitamin D supplements. Otherwise, treatment depends on the underlying cause. If due to a lack of vitamin D, treatment is usually with vitamin D and calcium. This generally results in improvements within a few weeks. Bone deformities may also improve over time. Occasionally surgery may be performed to correct bone deformities. Genetic forms of the disease typically require specialized treatment.
Rickets occurs relatively commonly in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, and Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
. It is generally uncommon in the United States and Europe, except among certain minority group
The term "minority group" has different meanings, depending on the context. According to common usage, it can be defined simply as a group in society with the least number of individuals, or less than half of a population. Usually a minority g ...
s but rates have been increasing among some populations. It begins in childhood, typically between the ages of 3 and 18 months old. Rates of disease are equal in males and females. Cases of what is believed to have been rickets have been described since the 1st century, and the condition was widespread in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. The disease was common into the 20th century. Early treatments included the use of cod liver oil.
Signs and symptoms
 Signs and symptoms of dietary deficiency rickets can include
Signs and symptoms of dietary deficiency rickets can include bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
tenderness, and a susceptibility for bone fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
s, particularly greenstick fractures. Early skeletal deformities can arise in infants such as soft, thinned skull bones – a condition known as craniotabes, which is the first sign of rickets; skull bossing Skull bossing is a descriptive term in medical physical examination indicating a protuberance of the skull, most often in the frontal bones of the forehead ("frontal bossing"). Although prominence of the skull bones may be normal, skull bossing may ...
may be present and a delayed closure of the fontanelle
A fontanelle (or fontanel) (colloquially, soft spot) is an anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising soft membranous gaps ( sutures) between the cranial bones that make up the calvaria of a fetus or an infant. Fontanelles allow ...
s.
Young children may have bowed legs
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving th ...
and thickened ankles and wrists; older children may have knock knees. Spinal curvatures of kyphoscoliosis or lumbar lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical vertebrae, cervical regio ...
may be present. The pelvic bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, isch ...
s may be deformed. A condition known as rachitic rosary can result as the thickening caused by nodules forming on the costochondral joints. This appears as a visible bump in the middle of each rib in a line on each side of the body. This somewhat resembles a rosary, giving rise to its name. The deformity of a pigeon chest may result in the presence of Harrison's groove.
Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), while levels less than 2.1 ...
, a low level of calcium in the blood can result in tetany – uncontrolled muscle spasms. Dental problems can also arise.
An X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
or radiograph
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeu ...
of an advanced patient with rickets tends to present in a classic way: the bowed legs (outward curve of long bone of the legs) and a deformed chest. Changes in the skull also occur causing a distinctive "square headed" appearance known as "caput quadratum". These deformities persist into adult life if not treated. Long-term consequences include permanent curvatures or disfiguration of the long bones, and a curved back.
Cause
Maternal deficiencies may be the cause of overt bone disease from before birth and impairment of bone quality after birth. The primary cause of congenital rickets isvitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
in the mother's blood. Vitamin D ensures that serum phosphate and calcium levels are sufficient to facilitate the mineralization of bone. Congenital rickets may also be caused by other maternal diseases, including severe osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of b ...
, untreated celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
, pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the new onset of hypertension, high blood pressure and often a significant amount of proteinuria, protein in the urine or by the new onset of high blood pressure a ...
, and premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is betwee ...
. Rickets in children is similar to osteoporosis in the elderly, with brittle bones. Pre-natal care includes checking vitamin levels and ensuring that any deficiencies are supplemented.
Exclusively breast-fed infants may require rickets prevention by vitamin D supplementation or an increased exposure to sunlight.
In sunny countries such as Nigeria, South Africa, and Bangladesh, there is sufficient endogenous vitamin D due to exposure to the sun. However, the disease occurs among older toddlers and children in these countries, which in these circumstances is attributed to low dietary calcium intakes due to a mainly cereal-based diet.
Those at higher risk for developing rickets include:
* Breast-fed infants whose mothers are not exposed to sunlight
* Breast-fed infants who are not exposed to sunlight
* Breast-fed babies who are exposed to little sunlight
* Adolescents, in particular when undergoing the pubertal growth spurt
* Any child whose diet does not contain enough vitamin D or calcium
Diseases causing soft bones in infants, like hypophosphatasia
Hypophosphatasia (; also called deficiency of alkaline phosphatase, phosphoethanolaminuria, or Rathbun's syndrome; sometimes abbreviated HPP) is a rare, and sometimes fatal, inherited metabolic bone disease. Clinical symptoms are heterogeneous ...
or hypophosphatemia
Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or soft ...
, can also lead to rickets.
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
is allied with calcium uptake into bones; at excessive dietary levels strontium has a rachitogenic (rickets-producing) action.
Sunlight
Sunlight, especially ultraviolet light, lets human skin cells convert vitamin D from an inactive to active state. In the absence of vitamin D, dietary calcium is not properly absorbed, resulting in hypocalcaemia, leading to skeletal and dental deformities and neuromuscular symptoms, e.g. hyperexcitability. Foods that contain vitamin D include butter, eggs, fish liver oils, margarine, fortified milk and juice, portabella andshiitake
The shiitake (; ''Chinese/black mushroom'' or ''Lentinula edodes'') is a macrofungus native to East Asia, which is cultivated and consumed around the globe.
Taxonomy
The fungus was first described scientifically as '' Agaricus edodes'' by ...
mushrooms, and oily fish
Oily fish are fish species with fish oil, oil (fats) in soft tissues and in the coelomic cavity around the Gut (zoology), gut. Their fillet (cut), fillets may contain up to 30% oil, although this figure varies both within and between species. ...
es such as tuna
A tuna (: tunas or tuna) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae ( mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bul ...
, herring
Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the Order (biology), order Clupeiformes.
Herring often move in large Shoaling and schooling, schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate wate ...
, and salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
. A rare X-linked dominant ''Main Article:'' Sex linkage
X-linked dominant inheritance, sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance, is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome. As an inheritance pattern, it is less common tha ...
form exists called vitamin D-resistant rickets or X-linked hypophosphatemia.
Cases have been reported in Britain in recent years of rickets in children of many social backgrounds caused by insufficient production in the body of vitamin D because the sun's ultraviolet light was not reaching the skin due to use of strong sunblock, too much "covering up" in sunlight, or not getting out into the sun. Other cases have been reported among the children of some ethnic groups in which mothers avoid exposure to the sun for religious or cultural reasons, leading to a maternal shortage of vitamin D, and people with darker skin need more sunlight to maintain vitamin D levels.
Rickets had historically been a problem in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, especially during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
. Persistent thick fog and heavy industrial smog permeating the city blocked out significant amounts of sunlight to such an extent that up to 80 percent of children at one time had varying degrees of rickets in one form or the other. It is sometimes known "the English Disease" in some foreign languages (e.g. German: , Dutch: , Hungarian: , Swedish: ).
Skin color theory
Rickets is often a result of vitamin D3 deficiency. The correlation between human skin color and latitude is thought to be the result of positive selection to varying levels of solar ultraviolet radiation. Northern latitudes have selection for lighter skin that allows UV rays to produce vitamin D from 7-dehydrocholesterol. Conversely, latitudes near the equator have selection for darker skin that can block the majority of UV radiation to protect from toxic levels of vitamin D, as well as skin cancer. An anecdote often cited to support this hypothesis is that Arctic populations whose skin is relatively darker for their latitude, such as the Inuit, have a diet that is historically rich in vitamin D. Since these people acquire vitamin D through their diet, there is not a positive selective force to synthesize vitamin D from sunlight. Environment mismatch: vitamin D deficiency arises from a mismatch between an individual's previous and current environment. This risk of mismatch increases with advances in transportation methods and increases in urban population size at high latitudes. Similar to the environmental mismatch when dark-skinned people live at high latitudes, Rickets can also occur in religious communities that require long garments with hoods and veils. These hoods and veils act as sunlight barriers that prevent individuals from synthesizing vitamin D naturally from the sun. In a study by Mithal et al., vitamin D insufficiency of various countries was measured by lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D. 25(OH) D is an indicator of vitamin D insufficiency that can be easily measured. These percentages should be regarded as relative vitamin D levels, and not as predicting evidence for development of rickets. Asian immigrants living in Europe have an increased risk for vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D insufficiency was found in 40% of non-Western immigrants in the Netherlands, and in more than 80% of Turkish and Moroccan immigrants. The Middle East, despite high rates of sun-exposure, has the highest rates of rickets worldwide. This fact can be explained by limited sun exposure due to cultural practices and lack of vitamin D supplementation for breast-feeding women. Up to 70% and 80% of adolescent girls in Iran and Saudi Arabia, respectively, have vitamin D insufficiency. Socioeconomic factors that limit a vitamin D rich diet also plays a role. In the United States, vitamin D insufficiency varies dramatically by ethnicity. Among females aged 70 years and older, the prevalence of low serum 25(OH) D levels was 28.5% for non-Hispanic whites, 55% for Mexican Americans, and 68% for non-Hispanic blacks. Among males, the prevalence was 23%, 45%, and 58%, respectively. A systematic review published in theCochrane Library
The Cochrane Library (named after Archie Cochrane) is a collection of databases in medicine and other healthcare specialties provided by Cochrane and other organizations. At its core is the collection of Cochrane Reviews, a database of systema ...
looked at children up to three years old in Turkey and China and found a beneficial association between vitamin D and rickets. In Turkey, children getting vitamin D had only a 4% chance of developing rickets compared to children who received no medical intervention. In China, a combination of vitamin D, calcium and nutritional counseling was linked to a decreased risk of rickets.
Parents can supplement their nutritional intake with vitamin D enhanced beverages if they feel their child is at risk for vitamin D deficiency.
A 2019 review linked rickets disease to exclusive consumption of Neocate baby formula.
Diagnosis

 Rickets may be diagnosed with the help of:
* Blood tests:
** Serum
Rickets may be diagnosed with the help of:
* Blood tests:
** Serum calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
may show low levels of calcium, serum phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
may be low, and serum alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryo ...
may be high from bones or changes in the shape or structure of the bones. This can show enlarged limbs and joints.
* A bone density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although medicine#Clinical practice, clinically it is measured by ...
scan may be undertaken.
* Radiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiog ...
typically show widening of the zones of provisional calcification of the metaphyses
The metaphysis (: metaphyses) is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epip ...
secondary to unmineralized osteoid. Cupping, fraying, and splaying of metaphyses typically appears with growth and continued weight bearing. These changes are seen predominantly at sites of rapid growth, including the proximal humerus, distal radius, distal femur and both the proximal and the distal tibia. Therefore, a skeletal survey for rickets can be accomplished with anteroposterior radiographs of the knees, wrists, and ankles.
In veterinary practice, rickets, osteodystrophy and mineral metabolism disorders are diagnosed using an ultrasound echosteometer in the design М.М. Orlov and А.V. Savinkov.
Types
* Vitamin D-related rickets **Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
** Vitamin D-dependent rickets (VDDR)
*** Type 1: insufficiency in activation
**** VDDR1A: 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency
**** VDDR1B: CYP2R1 deficiency
*** Type 2: resistance to calcitriol
**** VDDR2A: calcitriol receptor mutation
**** VDDR2B: unknown nuclear ribonucleoprotein interfering with signal transduction
*** Type 3: excessive inactivation (CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by ''CYP3A4'' gene. It organic redox reaction, oxidizes small foreign organic molecules ( ...
mutation, dominant)
* Hypocalcemia-related rickets
** Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), while levels less than 2.1 ...
** Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three mo ...
(CKD-BMD)
* Hypophosphatemia-related rickets
** Congenital
*** Vitamin D-resistant rickets
*** Autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets (ADHR)
*** Autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets (ARHR)
** Hypophosphatemia
Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or soft ...
(typically secondary to malabsorption)
** Fanconi's syndrome
* Secondary to other diseases
** Tumor-induced osteomalacia
** McCune–Albright syndrome
McCune–Albright syndrome is a complex genetic disorder affecting the bone, skin and endocrine systems. It is a mosaic disease arising from somatic activating mutations in '' GNAS'', which encodes the alpha-subunit of the Gs heterotrimeric G ...
** Epidermal nevus syndrome
Epidermal nevus syndrome, also known as Feuerstein and Mims syndrome, and Solomon's syndromeFreedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . is a rare disease that was first described in 1968 a ...
** Dent's disease
Differential diagnosis
Osteochondrodysplasias, also known as genetic bone diseases, may mimic the clinical picture of rickets in regard to the features of bone deformities. The radiologic picture and the laboratory findings of serum calcium, phosphate and alkaline phosphatase are important differentiating factors. Blount's disease is an important differential diagnosis because it causes knee deformities in a similar fashion to rickets namely bow legs orgenu varum
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving th ...
. Infants with rickets can have bone fractures. This sometimes leads to child abuse allegations. This issue appears to be more common for solely nursing infants of black mothers, in winter in temperate climates, suffering poor nutrition and no vitamin D supplementation. People with darker skin produce less vitamin D than those with lighter skin, for the same amount of sunlight.
Treatment
Diet and sunlight
Treatment involves increasing dietary intake of calcium, phosphates and vitamin D. Exposure to ultraviolet B light (most easily obtained when the sun is highest in the sky), cod liver oil, halibut-liver oil, and viosterol are all sources of vitamin D. A sufficient amount of ultraviolet B light in sunlight each day and adequate supplies of calcium and phosphorus in the diet can prevent rickets. Darker-skinned people need to be exposed longer to the ultraviolet rays. The replacement of vitamin D has been proven to correct rickets using these methods of ultraviolet light therapy and medicine. Recommendations are for 400international unit
In pharmacology, the international unit (IU) is a unit of measurement for the effect or biological activity of a substance, for the purpose of easier comparison across similar ''forms'' of substances. International units are used to quantify vi ...
s (IU) of vitamin D a day for infants and children. Children who do not get adequate amounts of vitamin D are at increased risk of rickets. Vitamin D is essential for allowing the body to uptake calcium for use in proper bone calcification and maintenance.
Supplementation
Sufficient vitamin D levels can also be achieved through dietary supplementation and/or exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3, colecalciferol or calciol, is a type of vitamin D that is produced by the skin when exposed to UV light, UVB light; it is found in certain foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Cholecalcife ...
) is the preferred form since it is more readily absorbed than vitamin D2. Most dermatologists
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the Human skin, skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A List of dermatologists, ...
recommend vitamin D supplementation as an alternative to unprotected ultraviolet exposure due to the increased risk of skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
associated with sun exposure. Endogenous production with full body exposure to sunlight is approximately 250 μg (10,000 IU) per day.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is the largest professional association of pediatricians in the United States. It is headquartered in Itasca, Illinois, and maintains an office in Washington, D.C. The AAP has published hundreds of poli ...
(AAP), all infants, including those who are exclusively breast-fed, may need vitamin D supplementation until they start drinking at least of vitamin D-fortified milk or formula a day.
Despite this recommendation, a recent Cochrane systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
has found limited evidence that vitamin D plus calcium, or calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
alone compared to vitamin D improves healing in children with nutritional rickets.
Surgery
Occasionally surgery is needed to correct severe and persistent deformities of the lower limbs, especially around the knees namelygenu varum
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving th ...
and genu valgum
Genu valgum, commonly called "knock-knee", is a condition in which the knees angle in and touch each other when the human leg, legs are straightened. Individuals with severe valgus deformity, valgus deformities are typically unable to touch thei ...
. Surgical correction of rachitic deformities can be achieved through osteotomies or guided growth surgery. Guided growth surgery has almost replaced the use of corrective osteotomies. The functional results of guided growth surgery in children with rickets are satisfactory. While bone osteotomies work through acute/immediate correction of the limb deformity, guided growth works through gradual correction.
Epidemiology
In developed countries, rickets is arare disease
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, the term orphan disease describes a rare disease whose rarity results in little or no funding or research for treatments, without financi ...
(incidence of less than 1 in 200,000). Recently, cases of rickets have been reported among children who are not fed enough vitamin D.
In 2013/2014 there were fewer than 700 cases in England. In 2019 the number of cases hospitalised was said to be the highest in 50 years.
Rickets occurs relatively commonly in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, Africa, and Asia.
History
 Greek physician
Greek physician Soranus of Ephesus
Soranus of Ephesus (; 1st/2nd century AD) was a Ancient Greek medicine, Greek physician. He was born in Ephesus but practiced in Alexandria and subsequently in Rome, and was one of the chief representatives of the Methodic school of medicine. Se ...
, one of the chief representatives of the Methodic school
The Methodic school (''Methodics'', ''Methodists'', or ''Methodici'', ) was a branch of medical thought in ancient Greece and Rome. It arose in reaction to both the Empiric school and the Dogmatic school (sometimes referred to as the Rationalist ...
of medicine who practiced in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
and subsequently in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, reported deformation of the bones in infants as early as the first and second centuries AD. The first use of the word 'rickets' is the handwritten entry for 25 February 1632 in 'Receipt Books' of the Fairfax Family which lists five remedies for 'rickets in children'. The word 'rickets' first occurred in print in 1634 in the Annual Bill of Mortality of the City of London. Rickets was not defined as a specific medical condition until 1645, when an English physician Daniel Whistler gave the earliest known description of the disease.
In 1650, a treatise on rickets was published by Francis Glisson
Francis Glisson (1597 – 14 October 1677) was a British physician, anatomist, and writer on medical subjects. He did important work on the anatomy of the liver, and he wrote an early pediatric text on rickets. An experiment he performed he ...
, a physician at Caius College, Cambridge
Gonville and Caius College, commonly known as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348 by Edmund Gonville, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges an ...
, who said it had first appeared about 30 years previously in the counties of Dorset
Dorset ( ; Archaism, archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north and the north-east, Hampshire to the east, t ...
and Somerset
Somerset ( , ), Archaism, archaically Somersetshire ( , , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east ...
.
In 1857, John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology and early germ theory, in part because of hi ...
suggested rickets, then widespread in Britain, was being caused by the adulteration of bakers' bread with alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium ...
.
German pediatrician Kurt Huldschinsky successfully demonstrated in the winter of 1918–1919 how rickets could be treated with ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
lamps.
Between 1918 and 1920, the role of diet in the development of rickets was determined by Edward Mellanby.
In 1923, American physician Harry Steenbock demonstrated that irradiation by ultraviolet light increased the vitamin D content of foods and other organic materials. Steenbock's irradiation technique was used for foodstuffs, but most memorably for milk.
By 1945, rickets had all but been eliminated in the United States.
However, beginning around 2003, rickets reemerged as an issue in the US for some populations causing the American Academy of Pediatrics
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is the largest professional association of pediatricians in the United States. It is headquartered in Itasca, Illinois, and maintains an office in Washington, D.C. The AAP has published hundreds of poli ...
recommended that all infants have Vitamin D intake of 200 IU per day.
Etymology
The word ''rickets'' may be from theOld English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
word ('to twist'), although because this is conjectured, several major dictionaries simply say "origin unknown". The name ''rickets'' is plural in form but usually singular in construction. The Greek word (, meaning 'in or of the spine') was later adopted as the scientific term for rickets, due chiefly to the words' similarity in sound.
See also
* Hypervitaminosis DReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Skeletal disorders Vitamin D Vitamin deficiencies Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate