Revanchism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Revanchism (, from ''revanche'', "
 Saddam Hussein's government sought to annex several territories. In the
Saddam Hussein's government sought to annex several territories. In the
 A German revanchist movement developed in response to the losses of World War I. Pan-Germanists within the
A German revanchist movement developed in response to the losses of World War I. Pan-Germanists within the
 The idea of Greater Hungary is associated with Hungarian revisionist aims at least to regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in Hungary's neighbouring countries. The outcome of the
The idea of Greater Hungary is associated with Hungarian revisionist aims at least to regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in Hungary's neighbouring countries. The outcome of the
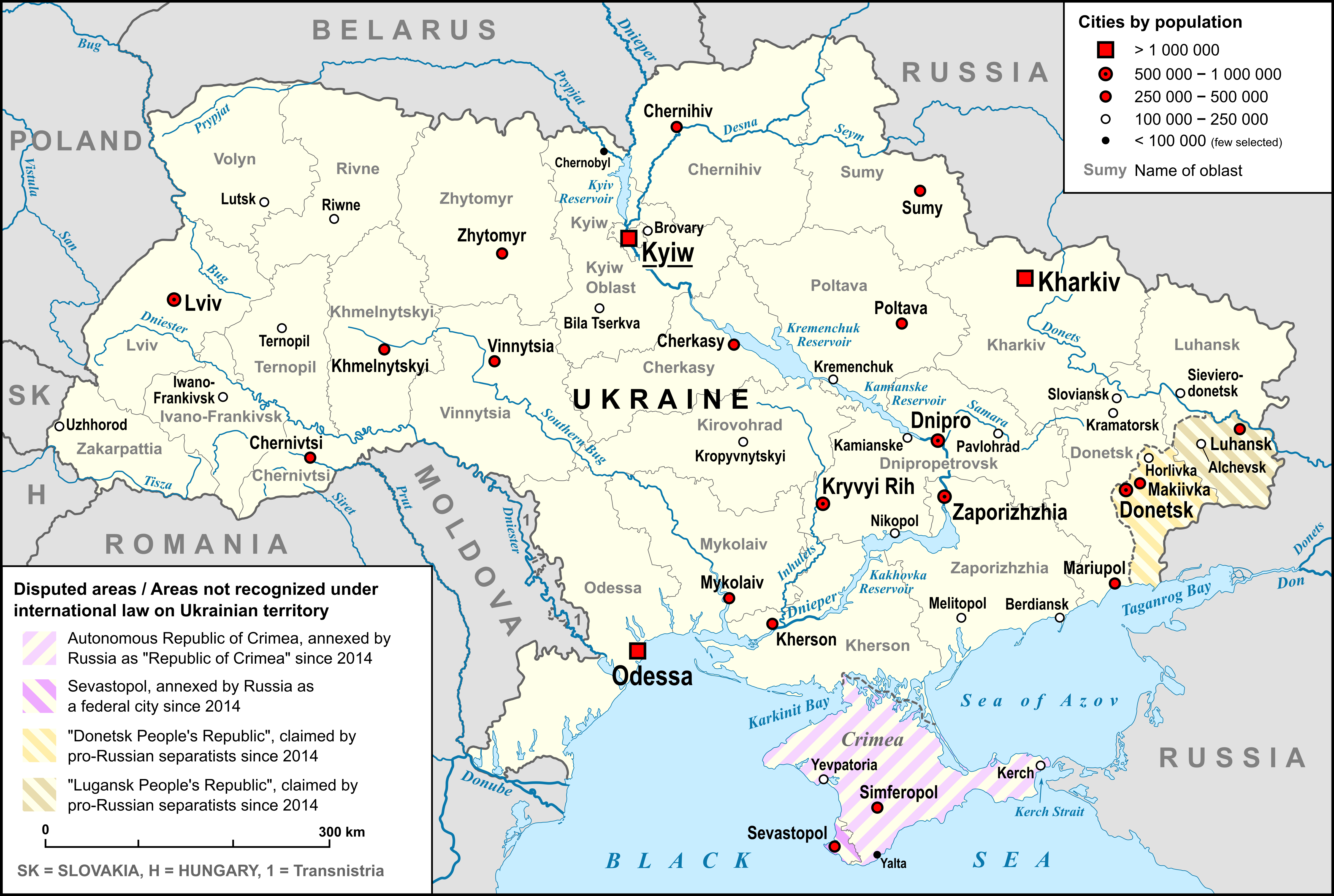 On 24 March 2021, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy signed the ''Decree No. 117/2021'' approving the "strategy of de-occupation and reintegration of the temporarily occupied territory of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol", complementing the activities of the Crimean Platform. On 10 May 2022, Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba said that "In the first months" of the
On 24 March 2021, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy signed the ''Decree No. 117/2021'' approving the "strategy of de-occupation and reintegration of the temporarily occupied territory of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol", complementing the activities of the Crimean Platform. On 10 May 2022, Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba said that "In the first months" of the
revenge
Revenge is defined as committing a harmful action against a person or group in response to a grievance, be it real or perceived. Vengeful forms of justice, such as primitive justice or retributive justice, are often differentiated from more fo ...
") is the political manifestation of the will to reverse the territorial losses which are incurred by a country, frequently after a war or after a social movement
A social movement is either a loosely or carefully organized effort by a large group of people to achieve a particular goal, typically a Social issue, social or Political movement, political one. This may be to carry out a social change, or to re ...
. As a term, ''revanchism'' originated in 1870s France in the aftermath of the Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
among nationalists who wanted to avenge the French defeat and reclaim the lost territories of Alsace-Lorraine.
Revanchism draws its strength from patriotic and retributionist thought and is often motivated by economic or geopolitical factors. Extreme revanchist ideologues often represent a hawkish stance, suggesting that their desired objectives can be achieved through the positive outcome of another war. It is linked with irredentism
Irredentism () is one State (polity), state's desire to Annexation, annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by Ethnicity, ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the ...
, the conception that a part of the cultural and ethnic nation remains "unredeemed" outside the borders of its appropriate nation-state.
Revanchist politics often rely on the identification of a nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
with a nation state, mobilizing sentiments of ethnic nationalism to claim territories outside of where members of the ethnic group currently live. Such claims are often presented as being based on ancient or even autochthonous occupation of a territory since " time immemorial".
Historical and current examples
Americas
Argentina
Argentina considers the British-controlledFalkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ...
to be part of the Tierra del Fuego Province. In 1994, Argentina's claim to the territories was added to its constitution.
During the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, the Argentine fascist ideology Nacionalista and organizations such as the Alliance of Nationalist Youth openly supported plans to annex Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the Argentina–Paraguay border, south and southwest, Brazil to the Brazil–Paraguay border, east and northeast, and Boli ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
and some southern and eastern parts of Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
, which they claimed belonged to Argentina via past territories of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata.
Mexico
Some Mexican nationalists consider theSouthwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural list of regions of the United States, region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacen ...
to be Mexican territory that must be returned. The territory belonged to Mexico until 1836 when Texas established itself as its own nation. Texas citizens then voted to join the United States in the Texas annexation
The Republic of Texas was annexation, annexed into the United States and Admission to the Union, admitted to the Union as the List of U.S. states by date of admission to the Union, 28th state on December 29, 1845.
The Republic of Texas Texas ...
(1845) leading to the 1846–48 Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
and, as a consequence of the war, the Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession () is the region in the modern-day Western United States that Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United S ...
of further territory that now constitutes much of the western US.
In 1865, as the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
ended, Maximilian "was actively recruiting Confederate refugees to colonize northern Mexico and bring their slaves with them. Grant foresaw that Maximilian was creating a base from which diehard rebels would carry on a revanchist war against the United States and create an obstacle protecting Maximilian's empire against invasion by U.S. forces".
Asia
China
The People's Republic of China (PRC) has used historical claims in theSouth China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
(SCS) as justification for island building activities and revised territorial claims. The "nine-dash line
The nine-dash line, also referred to as the eleven-dash line by Taiwan, is a set of line segments on various maps that accompanied the claims of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC, "Mainland China") and the Taiwan, Republic of China (RO ...
" map extends the area that the PRC identifies as within its sovereign territory disregarding several international laws of the sea. In addition to civil and military confrontations in the SCS, other territorial disputes have affected Japan, India, and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
. See also Chinese irredentism.
Iraq
Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
(1980–1988), Saddam claimed that Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
had the right to hold sovereignty to the east bank of the Shatt al-Arab river held by Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.
The Iraqi government, echoing claims made by Iraqi nationalists for years, justified the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait in 1990 by claiming that Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
had always been an integral part of Iraq and only became an independent nation due to the interference of the British government.
It has been suspected that Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
intended to invade and annex a portion of Saudi Arabia's Eastern Province on the justification that the Saudi region of Al-Hasa had been part of the Ottoman province of Basra that the British had helped Saudi Arabia conquer in 1913.
Philippines
The Philippines maintains a "dormant claim" on portions of North Borneo as part of its territory, which is currently administered as part ofMalaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
's Sabah
Sabah () is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah has land borders with the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and Indonesia's North Kalima ...
state. The Philippines' territorial claim is based on the disputed territory being formerly administered by the Sultanate of Sulu
The Sultanate of Sulu (; ; ) is a Sunni Muslim subnational monarchy in the Philippines, Republic of the Philippines that includes the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Zamboanga City and certain portions of Palawan in today's Philippines. H ...
under the 1878 Lease Agreement signed between the Sultan of Sulu Jamalul Azam and Baron de Overbeck of North Borneo Chartered Company
Turkey
The 21st century has seen a domestic trend in Turkish politics, where the revival of Ottoman traditions and culture has been accompanied by the rise of the Justice and Development Party (AKP, founded in 2001) which came to power in 2002, along with claims to territory once held by theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. The use of the ideology by Justice and Development Party has mainly supported a greater influence of Ottoman culture in domestic social policy which has caused issues with the secular and republican credentials of modern Turkey. The AKP have used slogans such as ' ("descendant of the Ottomans") to refer to their supporters and also their former leader Recep Tayyip Erdoğan
Recep Tayyip Erdoğan (born 26 February 1954) is a Turkish politician who is the 12th and current president of Turkey since 2014. He previously served as the 25th prime minister of Turkey, prime minister from 2003 to 2014 as part of the Jus ...
(who was elected President in 2014) during their election campaigns. These domestic ideals have also seen a revival of neo-Ottomanism in the AKP's foreign policy. Besides acting as a clear distinction between them and ardent supporters of secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on naturalistic considerations, uninvolved with religion. It is most commonly thought of as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state and may be broadened ...
, the social Ottomanism advocated by the AKP has served as a basis for their efforts to transform Turkey's existing parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their Election, democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of t ...
into a presidential system
A presidential, strong-president, or single-executive system (sometimes also congressional system) is a form of government in which a head of government (usually titled " president") heads an executive branch that derives its authority and l ...
, favouring a strong centralised leadership similar to that of the Ottoman era. Critics have thus accused Erdoğan of acting like an "Ottoman sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
".
The rise in Ottomanism has also been accompanied by claims to territories held by Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, with prominent examples including in 2015, a crowd of Turkish youth rallying in Armenian populated districts of Istanbul chanted "We must turn these districts into Armenian and Kurdish cemeteries." In September 2015, a 'Welcome' sign was installed in Iğdır and written in four languages, Turkish, Kurdish, English, and Armenian. The Armenian portion of the sign was protested by the "Fight against Armenian groundless allegations" alliance (ASIMDER) who demanded its removal. In October 2015, the Armenian writing on the 'Welcome' sign was heavily vandalized. The Armenian portion of the sign was ultimately removed in June 2016. The Mayor of Igdir also claimed that the existence of the Armenian state was a "historical mistake", and that Armenia is actually Turkish territory, illegally occupied by Armenians, waiting to be re-integrated into Turkey.
Europe
France
The instance of revanchism that gave these groundswells of opinion their modern name came in the 1870s. French revanchism was a deep sense of bitterness, hatred and demand for revenge against Germany, especially because of the loss of Alsace and Lorraine following defeat in theFranco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
. Paintings that emphasized the humiliation of the defeat came in high demand, such as those by Alphonse-Marie-Adolphe de Neuville.
Georges Clemenceau, of the Radical Republicans, opposed participation in the scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa was the invasion, conquest, and colonialism, colonisation of most of Africa by seven Western European powers driven by the Second Industrial Revolution during the late 19th century and early 20th century in the era of ...
and other adventures that would divert the Republic from objectives related to the "blue line of the Vosges" in Alsace-Lorraine. After the governments of Jules Ferry had pursued a number of colonies in the early 1880s, Clemenceau lent his support to Georges Ernest Boulanger, a popular figure, nicknamed ''Général Revanche'', who it was felt might overthrow the Republic in 1889. This ultranationalist tradition influenced French politics up to 1921 and was one of the major reasons France went to great pains to woo the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, resulting in the Franco-Russian Alliance of 1894 and, after more accords, the Triple Entente of the three great Allied powers of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
: France, Great Britain, and Russia.
French revanchism influenced the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
of 1919 following the end of World War I, which restored Alsace-Lorraine to France and extracted reparations from the defeated Germany. The conference was not only opened on the anniversary of the proclamation of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
; the treaty also had to be signed by the new German government in the same room, the Hall of Mirrors
The Hall of Mirrors () is a grand Baroque architecture, Baroque style gallery and one of the most emblematic rooms in the royal Palace of Versailles near Paris, France. The grandiose ensemble of the hall and its adjoining salons was intended to ...
.
Germany
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
called for the reclamation of the property of a German state due to pre-war borders or because of the territory's historical relation to Germanic peoples. The movement called for the reincorporation of Alsace-Lorraine, the Polish Corridor and the Sudetenland (see Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
, Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
parts of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
until its dismemberment after World War I). Those claims, supported by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
, led to World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, with the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
. This irredentism had also been characteristic of the Völkisch movement
The ''Völkisch'' movement ( , , also called Völkism) was a Pan-Germanism, Pan-German Ethnic nationalism, ethno-nationalist movement active from the late 19th century through the dissolution of the Nazi Germany, Third Reich in 1945, with remn ...
in general and of the Pan-German League (''Alldeutscher Verband''). The ''Verband'' wanted to uphold German " racial hygiene" and were against breeding with, in their eyes, inferior races like the Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
and Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
.''Antisemitism: A Historical Encyclopedia of Prejudice and Persecution'', Volume 1. Richard S. Levy, 528–529, ABC-CLIO 2005
Greece
Greek revanchism refers to the political sentiment or movement advocating for the restoration or reclaiming of territories historically or culturally once associated withGreece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, but currently under the control of other states. Stemming from unresolved territorial disputes, Greek revanchism often manifests in nationalist rhetoric, diplomatic tensions, and occasional military confrontations. Historical grievances, such as the population exchanges between Greece and Turkey following World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, also fuel revanchist sentiments. While Greek revanchism has influenced foreign policy decisions and public discourse, it remains a contentious and complex issue in the broader context of regional geopolitics and international relations.
Hungary
 The idea of Greater Hungary is associated with Hungarian revisionist aims at least to regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in Hungary's neighbouring countries. The outcome of the
The idea of Greater Hungary is associated with Hungarian revisionist aims at least to regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in Hungary's neighbouring countries. The outcome of the Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (; ; ; ), often referred to in Hungary as the Peace Dictate of Trianon or Dictate of Trianon, was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference. It was signed on the one side by Hungary ...
of 1920 is to this day remembered in Hungary as the Trianon trauma. According to a study, two-thirds of Hungarians agreed in 2020 that parts of neighbouring countries should belong to them.
Poland
In the 1920s and 1930s,Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
was trying to reclaim ethnic Polish lands that had been seized by German, Russian and Austro-Hungarian empires:
Russia
The annexation of the Crimean peninsula by the Russian Federation in April 2014, together with accusations by Western and Ukrainian leaders that Russia is supporting separatist actions by ethnic Russians in the secessionist Donbas region, has been cited by a number of prominent media outlets in the West as evidence of a revanchist policy on the part of the Kremlin and Russian PresidentVladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
. The invasion of Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
in 2022 has the same origins.
Some Russian nationalists consider Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
to be Russian territory that must be returned. Alaska was legally sold to the United States by Russia in 1867.
Spain
Spain cededGibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
to Britain under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
of 1713. Spain's claim to Gibraltar became government policy under the regime of the dictator Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (born Francisco Paulino Hermenegildo Teódulo Franco Bahamonde; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general and dictator who led the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist forces i ...
and has remained in place under successive governments following the Spanish transition to democracy.
Sweden
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
lost Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
to Russia at the conclusion of the Finnish War
The Finnish War (; ; ) was fought between the Gustavian era, Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a result of the war, the eastern third of Sweden was established a ...
(1808–09), ending nearly 600 years of Swedish rule. For most of the rest of the 1800s there was talk, but few practical plans and little political will, of reclaiming Finland from Russia. Since Sweden was never able to challenge Russia's military might on its own, no attempts were made.
During the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
in 1853 to 1856, the Allied nations initiated talks with Sweden to allow troop and fleet movements through Swedish ports to be used against Russia. In return, the Allies would help Sweden reclaim Finland with the help of an expeditionary force. In the end, the plans fell through and Sweden never became involved in the fighting.
Ukraine
 On 24 March 2021, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy signed the ''Decree No. 117/2021'' approving the "strategy of de-occupation and reintegration of the temporarily occupied territory of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol", complementing the activities of the Crimean Platform. On 10 May 2022, Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba said that "In the first months" of the
On 24 March 2021, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy signed the ''Decree No. 117/2021'' approving the "strategy of de-occupation and reintegration of the temporarily occupied territory of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol", complementing the activities of the Crimean Platform. On 10 May 2022, Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba said that "In the first months" of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
"the victory for us looked like withdrawal of Russian forces to the positions they occupied before February 24 and payment for inflicted damage. Now if we are strong enough on the military front and we win the battle for Donbas, which will be crucial for the following dynamics of the war, of course the victory for us in this war will be the liberation of the rest of our territories", including Donbas and Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
.
See also
Further reading
* Alexander B. Murphy. 1990. “Historical Justifications for Territorial Claims.” ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'' 80(4):531–548.References
Bibliography
* * * {{Authority control Political theories Aftermath of the Franco-Prussian War