Retinoblastoma Protein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of
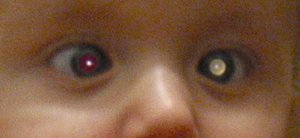 Retinoblastoma is the most intrusive intraocular cancer among children. The chance of survival and preservation of the eye depends fully on the severity. Retinoblastoma is extremely rare as there are only about 200 to 300 cases every year in the United States. Globally, only 1 in about 15,000 children have this malignancy, though rates continue to increase.
Intraocular malignancies are relatively more frequently treated than extraocular malignancies, likely due to a relatively earlier detection and subsequent treatment. Pediatricians may screen infants with annual vision tests, in which anomalies can be detected. During a red reflex test, light from an ophthalmoscope goes through transparent parts of the eye and reflects off the ocular fundus. If retinoblastoma is present, it may partially or fully impede light transversing this path. This may result in an abnormal red reflex or leucocoria, which can be a common indicator of retinoblastoma (when light is reflected by the tumor, the regular view of the red retina is blocked). The retinoblastoma may be visible as a whitish, translucent mass. If the tumor has not spread and is contained within the eye, chances of successful treatment are favorable. If initial signs are ignored or diagnosis is significantly delayed, outcomes and prognosis worsen. The effects of retinoblastoma may spread outside the eye, sometimes resulting in proptosis. Retinoblastoma that has spread may be significantly more difficult to treat.
The most common and obvious
Retinoblastoma is the most intrusive intraocular cancer among children. The chance of survival and preservation of the eye depends fully on the severity. Retinoblastoma is extremely rare as there are only about 200 to 300 cases every year in the United States. Globally, only 1 in about 15,000 children have this malignancy, though rates continue to increase.
Intraocular malignancies are relatively more frequently treated than extraocular malignancies, likely due to a relatively earlier detection and subsequent treatment. Pediatricians may screen infants with annual vision tests, in which anomalies can be detected. During a red reflex test, light from an ophthalmoscope goes through transparent parts of the eye and reflects off the ocular fundus. If retinoblastoma is present, it may partially or fully impede light transversing this path. This may result in an abnormal red reflex or leucocoria, which can be a common indicator of retinoblastoma (when light is reflected by the tumor, the regular view of the red retina is blocked). The retinoblastoma may be visible as a whitish, translucent mass. If the tumor has not spread and is contained within the eye, chances of successful treatment are favorable. If initial signs are ignored or diagnosis is significantly delayed, outcomes and prognosis worsen. The effects of retinoblastoma may spread outside the eye, sometimes resulting in proptosis. Retinoblastoma that has spread may be significantly more difficult to treat.
The most common and obvious
, Daisy's Eye Cancer Fund.
 Screening for retinoblastoma should be part of a "well baby" screening for newborns during the first 3 months of life, to include:
* The red reflex: checking for a normal reddish-orange reflection from the eye's retina with an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from about 30 cm or 1 foot, usually done in a dimly lit or dark room
* The corneal light reflex or Hirschberg test: checking for symmetrical reflection of beam of light in the same spot on each eye when a light is shined into each cornea, to help determine whether the eyes are crossed
*
Screening for retinoblastoma should be part of a "well baby" screening for newborns during the first 3 months of life, to include:
* The red reflex: checking for a normal reddish-orange reflection from the eye's retina with an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from about 30 cm or 1 foot, usually done in a dimly lit or dark room
* The corneal light reflex or Hirschberg test: checking for symmetrical reflection of beam of light in the same spot on each eye when a light is shined into each cornea, to help determine whether the eyes are crossed
*
 :1. Persistent fetal vasculature is a congenital developmental anomaly of the eye resulting from failure of the embryological, primary vitreous, and hyaloid vasculature to regress, whereby the eye is shorter, develops a cataract, and may present with whitening of the pupil.
:2. Coats disease is a typically unilateral disease characterised by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina, leading to blood vessel abnormalities in the retina and retinal detachment to mimic retinoblastoma.
:3. Toxocariasis is a parasitic disease of the eye associated with exposure to infected puppies, which causes a retinal lesion leading to retinal detachment.
:4. Retinopathy of prematurity is associated with low-birth-weight infants who receive supplemental oxygen in the period immediately after birth, and it involves damage to the retinal tissue and may lead to retinal detachment.
:5. Congenital Cataract
:6. Norrie Disease
If the eye examination is abnormal, further testing may include imaging studies, such as computerized tomography (CT),
:1. Persistent fetal vasculature is a congenital developmental anomaly of the eye resulting from failure of the embryological, primary vitreous, and hyaloid vasculature to regress, whereby the eye is shorter, develops a cataract, and may present with whitening of the pupil.
:2. Coats disease is a typically unilateral disease characterised by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina, leading to blood vessel abnormalities in the retina and retinal detachment to mimic retinoblastoma.
:3. Toxocariasis is a parasitic disease of the eye associated with exposure to infected puppies, which causes a retinal lesion leading to retinal detachment.
:4. Retinopathy of prematurity is associated with low-birth-weight infants who receive supplemental oxygen in the period immediately after birth, and it involves damage to the retinal tissue and may lead to retinal detachment.
:5. Congenital Cataract
:6. Norrie Disease
If the eye examination is abnormal, further testing may include imaging studies, such as computerized tomography (CT),
Image:Wardrop retinoblastoma.jpg, Drawing of a large retinoblastoma
Image:Trilateral retinoblastoma.jpg, Aspect of trilateral retinoblastoma on MRI
Image:Retinoblastoma ultrasound.jpg, An ocular ultrasound of a large retinoblastoma tumor within the eye of a 3-year-old boy
Image:Retinoblastooma.jpg, Funduscopic finding of a retinoblastoma
Image:Fundus retinoblastoma.jpg, Ocular fundus aspect of retinoblastoma
Image:Retinoblastoma .jpg, Large exophytic white tumor with foci of calcification producing total exudative retinal detachment
Image:Retinoblastoma rosette.jpg, Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes in retinoblastoma
Image:Rtbl400.GIF, Retinoblastoma, 400 X magnification
Image:RB1.JPG, Crystal structure of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein bound to E2F peptide polymer
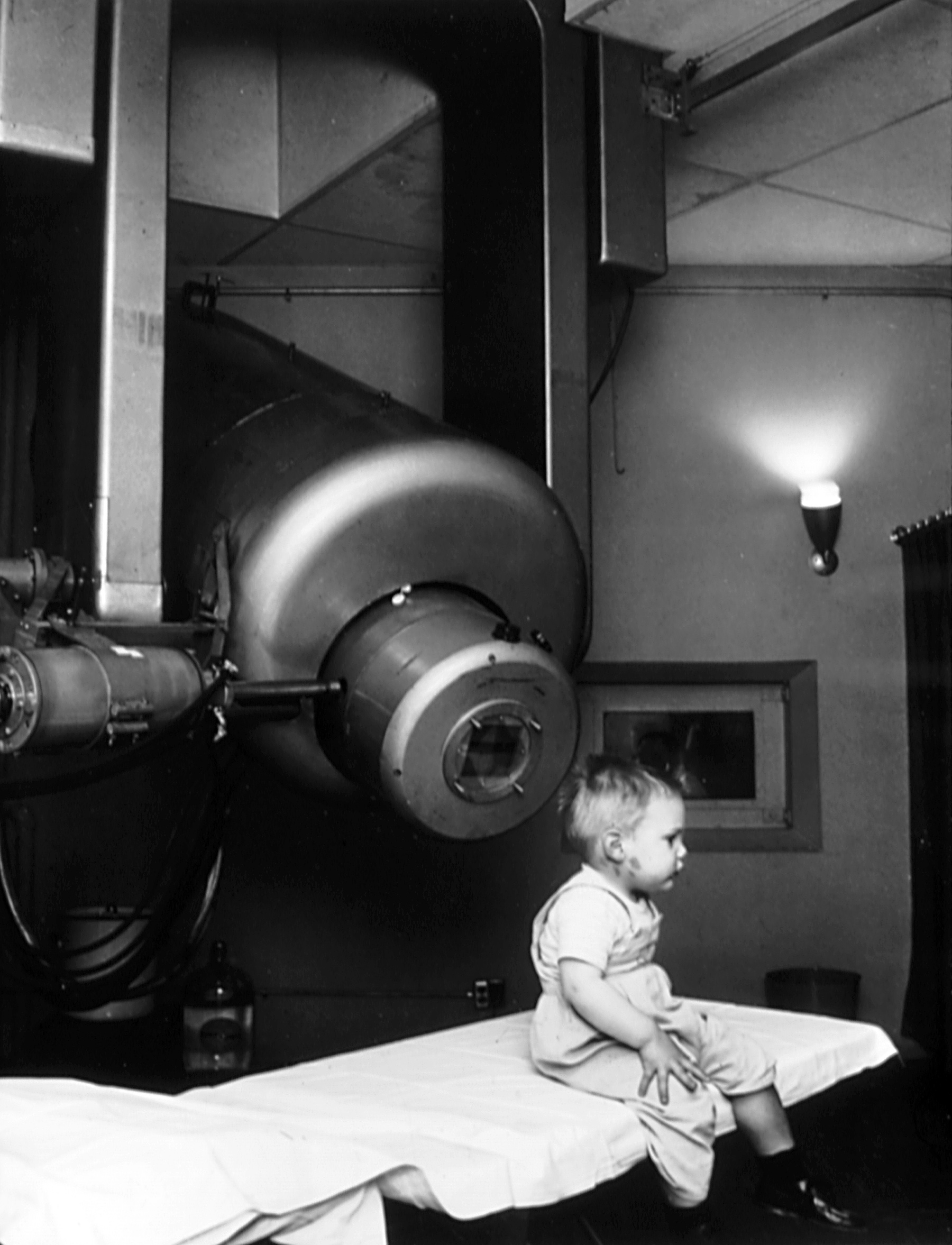 The priority of retinoblastoma treatment is to preserve the life of the child, then to preserve vision, and then to minimize complications or side effects of treatment. The exact course of treatment depends on the individual case and is decided by the ophthalmologist in discussion with the paediatric oncologist. Correct treatment also depends on the mutation type, whether it is a germline RB1 mutation, a sporadic RB1 mutation or MYCN amplification with functional RB1. Children with involvement of both eyes at diagnosis usually require multimodality therapy (chemotherapy, local therapies).
The various treatment modalities for retinoblastoma includes:
* Enucleation of the eye – Most patients with unilateral disease present with advanced intraocular disease, so usually undergo enucleation, which results in a cure rate of 95%. In bilateral Rb, enucleation is usually reserved for eyes that have failed all known effective therapies or without useful vision.
* External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) – The most common indication for EBRT is for the eye in a young child with bilateral retinoblastoma who has active or recurrent disease after completion of chemotherapy and local therapies. However, patients with hereditary disease who received EBRT therapy are reported to have a 35% risk of second cancers.
*
The priority of retinoblastoma treatment is to preserve the life of the child, then to preserve vision, and then to minimize complications or side effects of treatment. The exact course of treatment depends on the individual case and is decided by the ophthalmologist in discussion with the paediatric oncologist. Correct treatment also depends on the mutation type, whether it is a germline RB1 mutation, a sporadic RB1 mutation or MYCN amplification with functional RB1. Children with involvement of both eyes at diagnosis usually require multimodality therapy (chemotherapy, local therapies).
The various treatment modalities for retinoblastoma includes:
* Enucleation of the eye – Most patients with unilateral disease present with advanced intraocular disease, so usually undergo enucleation, which results in a cure rate of 95%. In bilateral Rb, enucleation is usually reserved for eyes that have failed all known effective therapies or without useful vision.
* External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) – The most common indication for EBRT is for the eye in a young child with bilateral retinoblastoma who has active or recurrent disease after completion of chemotherapy and local therapies. However, patients with hereditary disease who received EBRT therapy are reported to have a 35% risk of second cancers.
*
Retinoblastoma information
from
RB1 Mutation Database
NCBI Genetic Testing Registry
{{Eye tumors Ocular neoplasia Rare diseases Nervous system neoplasia Hereditary cancers Small-blue-round-cell tumors Pediatric cancers
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and 80% of retinoblastoma cases are first detected in those under 3 years old.
Though most children in high income countries survive this cancer, they may lose their vision in the affected eye(s) or need to have the eye removed.
Almost half of children with retinoblastoma have a hereditary genetic defect associated with it. In other cases, retinoblastoma is caused by a congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
mutation in the chromosome 13 gene 13q14 ( retinoblastoma protein).
Signs and symptoms
sign
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or me ...
of retinoblastoma is an abnormal appearance of the retina as viewed through the pupil, the medical term for which is leukocoria, also known as amaurotic cat's eye reflex. Other signs and symptoms include deterioration of vision, a red and irritated eye with glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
, and faltering growth or delayed development. Some children with retinoblastoma can develop a squint, commonly referred to as "cross-eyed" or "wall-eyed" (strabismus
Strabismus is an eye disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is pointed at an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
). Retinoblastoma presents with advanced disease in developing countries and eye enlargement is a common finding.
Depending on the position of the tumors, they may be visible during a simple eye examination using an ophthalmoscope to look through the pupil. A positive diagnosis is usually made only with an examination under anesthetic ( EUA). A white eye reflection is not always a positive indication of retinoblastoma and can be caused by light being reflected badly or by other conditions such as Coats' disease
Coats' disease is a rare congenital, nonhereditary eye disorder, causing full or partial blindness, characterized by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina. Coats' disease can also fall under glaucoma.
It can have a similar p ...
.
The presence of the photographic fault red eye in only one eye and not in the other may be a sign of retinoblastoma. A clearer sign is "white eye" or "cat's eye" (leukocoria).Introduction to White Eye, Daisy's Eye Cancer Fund.
Cause
Mutation of genes, found in chromosomes, can affect the way in which cells grow and develop within the body. Alterations in RB1 or MYCN can give rise to retinoblastoma.RB1
In children with the heritable genetic form of retinoblastoma, a mutation occurs in the '' RB1'' gene on chromosome 13.'' RB1'' was the first tumor suppressor gene cloned. Although'' RB1'' interacts with over 100 cell proteins, its negative regulator effect on the cell cycle principally arises from binding and inactivation of thetranscription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
'' E2F'', thus repressing the transcription of genes which are required for the S phase.
The defective ''RB1 ''gene can be inherited from either parent; in some children, however, the mutation occurs in the early stages of fetal development. The expression of the'' RB1 ''allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
is autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
dominant with 90% penetrance.
Inherited forms of retinoblastomas are more likely to be bilateral. In addition, inherited uni- or bilateral retinoblastomas may be associated with pineoblastoma and other malignant midline supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs) with a dismal outcome; retinoblastoma concurrent with a PNET is known as trilateral retinoblastoma. A 2014 meta-analysis showed that 5-year survival of trilateral retinoblastoma increased from 6% before 1995 to 57% by 2014, attributed to early detection and improved chemotherapy.
The development of retinoblastoma can be explained by the two-hit model. According to the two-hit model, both alleles need to be affected, so two events are necessary for the retinal cell or cells to develop into tumors. The first mutational event can be inherited ( germline or constitutional), which will then be present in all cells in the body. The second “hit” results in the loss of the remaining normal allele (gene) and occurs within a particular retinal cell. In the sporadic, nonheritable form of retinoblastoma, both mutational events occur within a single retinal cell after fertilization (somatic events); sporadic retinoblastoma tends to be unilateral.
Several methods have been developed to detect the ''RB1'' gene mutations. Attempts to correlate gene mutations to the stage at presentation have not shown convincing evidence of a correlation.
MYCN
Not all retinoblastoma cases are with RB1 inactivation. There are cases reported with only one RB1 mutation or even two functional RB1 alleles, which indicates other oncogenic lesions of retinoblastoma. Somatic amplification of the '' MYCN'' oncogene is responsible for some cases of nonhereditary, early-onset, aggressive, unilateral retinoblastoma. MYCN can act as a transcription factor and promotes proliferation by regulating the expression of cell cycle genes. Although ''MYCN'' amplification accounted for only 1.4% of retinoblastoma cases, researchers identified it in 18% of infants diagnosed at less than 6 months of age. Median age at diagnosis for ''MYCN'' retinoblastoma was 4.5 months, compared with 24 months for those who had nonfamilial unilateral disease with two ''RB1 ''gene mutations.Diagnosis
 Screening for retinoblastoma should be part of a "well baby" screening for newborns during the first 3 months of life, to include:
* The red reflex: checking for a normal reddish-orange reflection from the eye's retina with an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from about 30 cm or 1 foot, usually done in a dimly lit or dark room
* The corneal light reflex or Hirschberg test: checking for symmetrical reflection of beam of light in the same spot on each eye when a light is shined into each cornea, to help determine whether the eyes are crossed
*
Screening for retinoblastoma should be part of a "well baby" screening for newborns during the first 3 months of life, to include:
* The red reflex: checking for a normal reddish-orange reflection from the eye's retina with an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from about 30 cm or 1 foot, usually done in a dimly lit or dark room
* The corneal light reflex or Hirschberg test: checking for symmetrical reflection of beam of light in the same spot on each eye when a light is shined into each cornea, to help determine whether the eyes are crossed
* Eye examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. ...
: checking for any structural abnormalities
Classification
The two forms of the disease are aheritable
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of Phenotypic trait, traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cell (biology), cells or orga ...
form and nonheritable form (all cancers are considered genetic in that mutations of the genome are required for their development, but this does not imply that they are heritable, or transmitted to offspring). Approximately 40% of patients have a heritable form of retinoblastoma, carrying a mutation in the ''RB1'' gene. If no history of the disease exists within the family, the disease is labeled "sporadic", but this does not necessarily indicate that it is the nonheritable form. Bilateral retinoblastomas are commonly heritable, while unilateral retinoblastomas are commonly nonheritable.
In about two-thirds of cases, only one eye is affected (unilateral retinoblastoma); in the other third, tumors develop in both eyes (bilateral retinoblastoma). The number and size of tumors on each eye may vary. In certain cases, the pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
or the suprasellar or parasellar region (or in very rare cases other midline intracranial locations) is also affected (trilateral retinoblastoma). The position, size, and quantity of tumors are considered when choosing the type of treatment for the disease.
Differential diagnosis
 :1. Persistent fetal vasculature is a congenital developmental anomaly of the eye resulting from failure of the embryological, primary vitreous, and hyaloid vasculature to regress, whereby the eye is shorter, develops a cataract, and may present with whitening of the pupil.
:2. Coats disease is a typically unilateral disease characterised by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina, leading to blood vessel abnormalities in the retina and retinal detachment to mimic retinoblastoma.
:3. Toxocariasis is a parasitic disease of the eye associated with exposure to infected puppies, which causes a retinal lesion leading to retinal detachment.
:4. Retinopathy of prematurity is associated with low-birth-weight infants who receive supplemental oxygen in the period immediately after birth, and it involves damage to the retinal tissue and may lead to retinal detachment.
:5. Congenital Cataract
:6. Norrie Disease
If the eye examination is abnormal, further testing may include imaging studies, such as computerized tomography (CT),
:1. Persistent fetal vasculature is a congenital developmental anomaly of the eye resulting from failure of the embryological, primary vitreous, and hyaloid vasculature to regress, whereby the eye is shorter, develops a cataract, and may present with whitening of the pupil.
:2. Coats disease is a typically unilateral disease characterised by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina, leading to blood vessel abnormalities in the retina and retinal detachment to mimic retinoblastoma.
:3. Toxocariasis is a parasitic disease of the eye associated with exposure to infected puppies, which causes a retinal lesion leading to retinal detachment.
:4. Retinopathy of prematurity is associated with low-birth-weight infants who receive supplemental oxygen in the period immediately after birth, and it involves damage to the retinal tissue and may lead to retinal detachment.
:5. Congenital Cataract
:6. Norrie Disease
If the eye examination is abnormal, further testing may include imaging studies, such as computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI), and ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
. CT and MRI can help define the structure abnormalities and reveal any calcium depositions. Ultrasound can help define the height and thickness of the tumor. Bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
examination or lumbar puncture may also be done to determine any metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
to bones or the brain.
Morphology
Gross and microscopic appearances of retinoblastoma are identical in both hereditary and sporadic types. Macroscopically, viable tumor cells are found near blood vessels, while zones of necrosis are found in relatively avascular areas. Microscopically, both undifferentiated and differentiated elements may be present. Undifferentiated elements appear as collections of small, round cells with hyperchromatic nuclei; differentiated elements include Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes, Homer Wright rosettes, and fleurettes from photoreceptor differentiation.Genetic testing
Identifying the ''RB1'' gene mutation that led to a child's retinoblastoma can be important in the clinical care of the affected individual and in the care of (future) siblings and offspring. It may run in the family. # Bilaterally affected individuals and 13-15% of unilaterally affected individuals, are expected to show an ''RB1'' mutation in blood. By identifying the ''RB1'' mutation in the affected individual, (future) siblings, children, and other relatives can be tested for the mutation; if they do not carry the mutation, child relatives are not at risk of retinoblastoma, so need not undergo the trauma and expense of examinations under anaesthetic. For the 85% of unilaterally affected patients found not to carry either of their eye tumor'' RB1'' mutations in blood, neither molecular testing nor clinical surveillance of siblings is required. # If the ''RB1'' mutation of an affected individual is identified, amniotic cells in an at-risk pregnancy can be tested for the family mutation; any fetus that carries the mutation can be delivered early, allowing early treatment of any eye tumors, leading to better visual outcomes. # For cases of unilateral retinoblastoma where no eye tumor is available for testing, if no ''RB1'' mutation is detected in blood after high-sensitivity molecular testing (i.e. >93%'' RB1'' mutation detection sensitivity), the risk of a germline ''RB1'' mutation is reduced to less than 1%, a level at which only clinic examination (and not examinations under anaesthetic) is recommended for the affected individual and their future offspring (National Retinoblastoma Strategy, Canadian Guidelines for Care).Imaging
Traditional ultrasound B scan can detect calcifications in the tumour while high-frequency ultrasound B scan is able to provide higher resolution than the traditional ultrasound and determine the proximity of the tumour with front portion of the eye. MRI scan can detect high-risk features such as optic nerve invasion; choroidal invasion, scleral invasion, and intracranial invasion. CT scan is generally avoided because radiation can stimulate the formation of more eye tumours in those with RB1 genetic mutation.Staging
In order to properly diagnose retinoblastoma, there must be guidelines to follow to properly classify the risk of the tumor. The ''Reese Ellsworth Classification System,'' by Dr. Algernon Reese and Dr. Robert Ellsworth, is universally used to determine the size, location, and multi-focality of the tumor. The system was originally used to decide the best treatment result by using external beam radiotherapy, as well as, the likeliness of salvaging the globe of the eye. Due tochemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
not being part of the ''Reese Ellsworth Classification System,'' there needed to be an updated classification system to foresee the treatment outcomes of chemotherapy. The International Classification for Intraocular Retinoblastoma is now the current system being used, and it was created by Murphree and associates. According to Reese and Ellsworth, there were different groups that had various features in order to classify the globe salvage as very favorable to the category of very unfavorable. In order to salvage the affected eye, the disc diameter had to be around 4DD and behind the equator to have higher favorability. If the tumor was around ten in disc diameter and involved roughly 50% of the retina, it was considered unfavorable to salvage the globe which could result in enucleation. According to Murphree, the different groups were classified from very low risk to very high risk which was determined by features of the given tumor. Very low risk means that the tumor has to be less than 3mm and there must be no seeding of the vitreous or sub-retinal area. When a patient is very high risk, the tumor presents itself with multiple features and is going to have to be treated with conservative treatment modalities or enucleation.
International Classification for Intraocular Retinoblastoma
Treatment
 The priority of retinoblastoma treatment is to preserve the life of the child, then to preserve vision, and then to minimize complications or side effects of treatment. The exact course of treatment depends on the individual case and is decided by the ophthalmologist in discussion with the paediatric oncologist. Correct treatment also depends on the mutation type, whether it is a germline RB1 mutation, a sporadic RB1 mutation or MYCN amplification with functional RB1. Children with involvement of both eyes at diagnosis usually require multimodality therapy (chemotherapy, local therapies).
The various treatment modalities for retinoblastoma includes:
* Enucleation of the eye – Most patients with unilateral disease present with advanced intraocular disease, so usually undergo enucleation, which results in a cure rate of 95%. In bilateral Rb, enucleation is usually reserved for eyes that have failed all known effective therapies or without useful vision.
* External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) – The most common indication for EBRT is for the eye in a young child with bilateral retinoblastoma who has active or recurrent disease after completion of chemotherapy and local therapies. However, patients with hereditary disease who received EBRT therapy are reported to have a 35% risk of second cancers.
*
The priority of retinoblastoma treatment is to preserve the life of the child, then to preserve vision, and then to minimize complications or side effects of treatment. The exact course of treatment depends on the individual case and is decided by the ophthalmologist in discussion with the paediatric oncologist. Correct treatment also depends on the mutation type, whether it is a germline RB1 mutation, a sporadic RB1 mutation or MYCN amplification with functional RB1. Children with involvement of both eyes at diagnosis usually require multimodality therapy (chemotherapy, local therapies).
The various treatment modalities for retinoblastoma includes:
* Enucleation of the eye – Most patients with unilateral disease present with advanced intraocular disease, so usually undergo enucleation, which results in a cure rate of 95%. In bilateral Rb, enucleation is usually reserved for eyes that have failed all known effective therapies or without useful vision.
* External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) – The most common indication for EBRT is for the eye in a young child with bilateral retinoblastoma who has active or recurrent disease after completion of chemotherapy and local therapies. However, patients with hereditary disease who received EBRT therapy are reported to have a 35% risk of second cancers.
* Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation, radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. The word "brachytherapy" comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word , meaning "short-distance" or "s ...
involves the placement of a radioactive implant (plaque), usually on the sclera adjacent to the base of a tumor. It used as the primary treatment, or more frequently, in patients with small tumors or in those who had failed initial therapy including previous EBRT therapy.
* Thermotherapy involves the application of heat directly to the tumor, usually in the form of infrared radiation. It is also used for small tumors.
* Laser photocoagulation is recommended only for small posterior tumors. An argon or diode laser or a xenon arc is used to coagulate all the blood supply to the tumor.
* Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy can be used in many ways, including whole body exposure for therapeutic health benefits or may be used locally to treat ...
induces damage to the vascular endothelium with secondary thrombosis and infarction of the tumor tissue by rapidly freezing it. It may be used as primary therapy for small peripheral tumors or for small recurrent tumors previously treated with other methods.
* Systemic chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
has become forefront of treatment in the past decade, in the search for globe-preserving measures and to avoid the adverse effects of EBRT therapy. The common indications for chemotherapy for intraocular retinoblastoma include tumors that are large and that cannot be treated with local therapies alone in children with bilateral tumors. It is also used in patients with unilateral disease when the tumors are small, but cannot be controlled with local therapies alone.
* Intra-arterial chemotherapy – Chemotherapeutic drugs are administered locally by a thin catheter threaded through the groin, through the aorta, and the neck, directly into the optic vessels.
* Nanoparticulate chemotherapy – To reduce the adverse effects of systemic therapy, subconjuctival (local) injection of nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
carriers containing chemotherapeutic agents (carboplatin) has been developed, which has shown promising results in the treatment of retinoblastoma in animal models without adverse effects.
* Chemoreduction is a combined approach using chemotherapy to initially reduce the size of the tumor, and adjuvant focal treatments, such as transpupillary thermotherapy, to control the tumor.
Prognosis
In the developed world, retinoblastoma has one of the best cure rates of all childhood cancers (95-98%), with more than 90% of sufferers surviving into adulthood. In the UK, around 40 to 50 new cases are diagnosed each year. Good prognosis depends upon early presentation of the child in health facility. Late presentation is associated with a poor prognosis. Survivors of hereditary retinoblastoma have a higher risk of developing other cancers later in life. About 5% of cases require enucleation.Epidemiology
Retinoblastoma presents with cumulative lifetime incidence rate of one case of retinoblastoma per 18000 to 30000 live births worldwide. A higher incidence is noted in developing countries, which has been attributed to lower socioeconomic status and the presence of human papilloma virus sequences in the retinoblastoma tissue. Almost 80% of children with retinoblastoma are diagnosed before three years of age and diagnosis in children above six years of age is extremely rare. In the UK, bilateral cases usually present within 14 to 16 months, while diagnosis of unilateral cases peaks between 24 and 30 months.See also
* Eye cancer *Eye examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. ...
* Retinoblastoma protein
References
External links
Retinoblastoma information
from
MedlinePlus
MedlinePlus is an online information service produced by the United States National Library of Medicine. The service provides curated consumer health information in English and Spanish with select content in additional languages.
The site brings ...
*
RB1 Mutation Database
NCBI Genetic Testing Registry
{{Eye tumors Ocular neoplasia Rare diseases Nervous system neoplasia Hereditary cancers Small-blue-round-cell tumors Pediatric cancers