Republic Of Mainz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
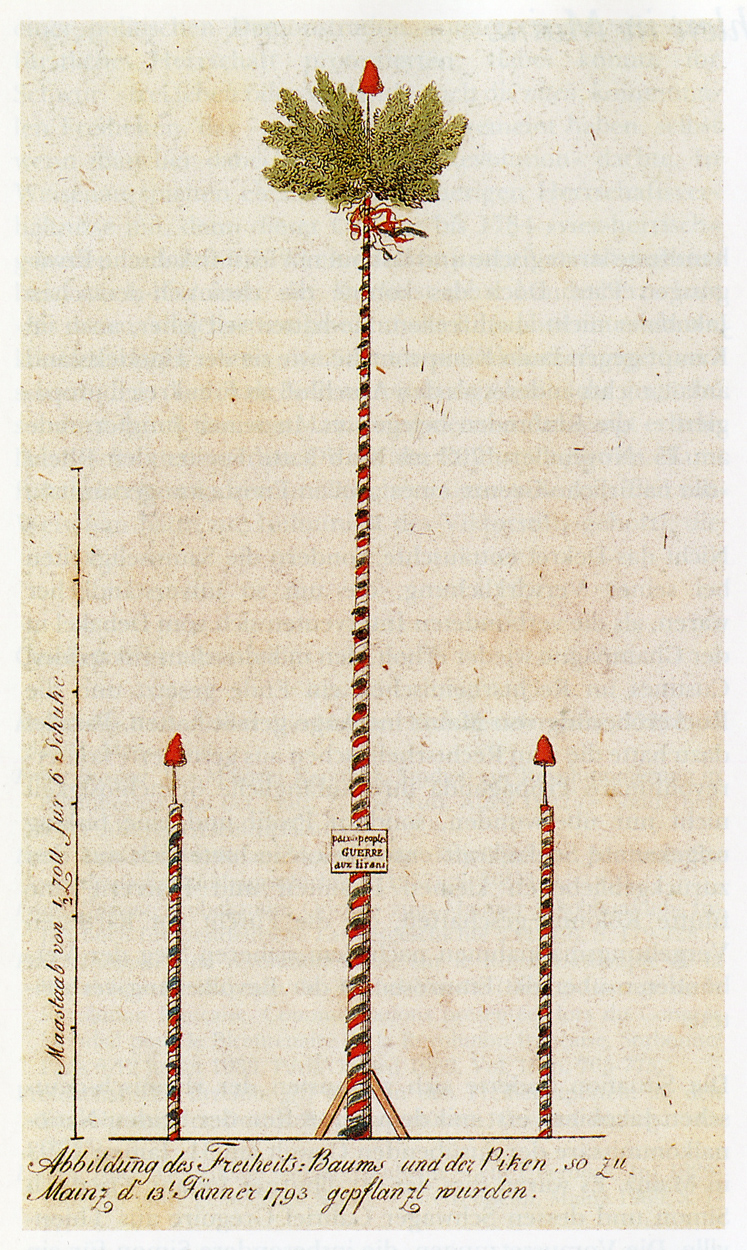 The Republic of Mainz was the first democratic state in the current German territoryThe short-lived republic is often ignored in identifying the "first German democracy", in favour of the
The Republic of Mainz was the first democratic state in the current German territoryThe short-lived republic is often ignored in identifying the "first German democracy", in favour of the

 The Republic of Mainz was the first democratic state in the current German territoryThe short-lived republic is often ignored in identifying the "first German democracy", in favour of the
The Republic of Mainz was the first democratic state in the current German territoryThe short-lived republic is often ignored in identifying the "first German democracy", in favour of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
; e.g. "the failure of the first German democracy after the First World War (the Weimar Republic)..." (Peter J. Burnell, ''Democracy Assistance: international co-operation for democratization'' 2000:131), or Ch. 3. 'The First Attempt at Democracy, 1918–1933', in Michael Balfour, ''West Germany: a contemporary history'', 1982:60 and was centered in Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
. A product of the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
, it lasted from March to July 1793.
Context
During theWar of the First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition () was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797, initially against the Constitutional Cabinet of Louis XVI, constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French First Republic, Frenc ...
against France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the Prussian and Austrian troops that had invaded France retreated after the Battle of Valmy, allowing the French revolutionary army to counterattack. The troops of General Custine entered the Palatinate in late September and occupied Mainz on 21 October 1792. The ruler of Mainz, Elector-Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
Friedrich Karl Joseph von Erthal, had fled the city.
Jacobin club
On the next day, 20 citizens of Mainz founded aJacobin
The Society of the Friends of the Constitution (), renamed the Society of the Jacobins, Friends of Freedom and Equality () after 1792 and commonly known as the Jacobin Club () or simply the Jacobins (; ), was the most influential political cl ...
club, the ' (). Together with their filial clubs founded later in Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ; ; ), historically known in English as Spires, is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in the western part of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the r ...
and Worms
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive catalogue and list of names of marine organisms.
Content
The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scien ...
, they promoted the Enlightenment and the French revolutionary ideals of ' in Germany, aiming for a German republic to be established following the French model. Most of the founding members of the Jacobin club were professors and students of the University of Mainz, together with the university librarian, Georg Forster
Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster (; 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German geography, geographer, natural history, naturalist, ethnology, ethnologist, travel literature, travel writer, journalist and revol ...
, some merchants and Mainz state officials. For some time the ecclesiastic was president of the club and editor of the ' ().
Founding
By order of the French National Convention, elections in the French-occupied territories west of theRhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
were held on 24 February 1793. 130 cities and towns sent their deputies to Mainz. The first democratically elected parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
on the territory of future Germany, called the ' (), met initially on 17 March 1793, in the Deutschhaus building in Mainz (today the seat of the Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are ...
state parliament). The convention declared the represented territory (which extended to Bingen in the west and to Landau
Landau (), officially Landau in der Pfalz (, ), is an autonomous (''kreisfrei'') town surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long ...
in the south) to be free and democratic, and disclaimed any ties to the empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
. The convention's president, Andreas Joseph Hofmann, proclaimed the Rhenish-German Free State () from the balcony of the Deutschhaus. On 21 March 1793, it was decided to seek the accession of the Free State to France and delegates (among them Georg Forster
Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster (; 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German geography, geographer, natural history, naturalist, ethnology, ethnologist, travel literature, travel writer, journalist and revol ...
and Adam Lux) were sent to Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
. The French National Convention granted the request on 30 March.
End
Soon after, Prussian troops retook all the French-occupied territory except for the heavily fortified city of Mainz itself. After a longsiege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
in which much of the city was destroyed, Prussian and Austrian troops conquered the city on 22 July 1793. The republic ended, and the Jacobins were persecuted until 1795 when Mainz came under French control again.
Notes
Further reading
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mainz, Republic Former states and territories of Rhineland-Palatinate Republic of Mainz States and territories disestablished in 1793