Reformatory Branch Rail Trail on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lexington and West Cambridge Railroad was a railroad company chartered in 1845 and opened in 1846 that operated in eastern
 A single track line was constructed in 1845–46, connecting Lexington Center to the
A single track line was constructed in 1845–46, connecting Lexington Center to the 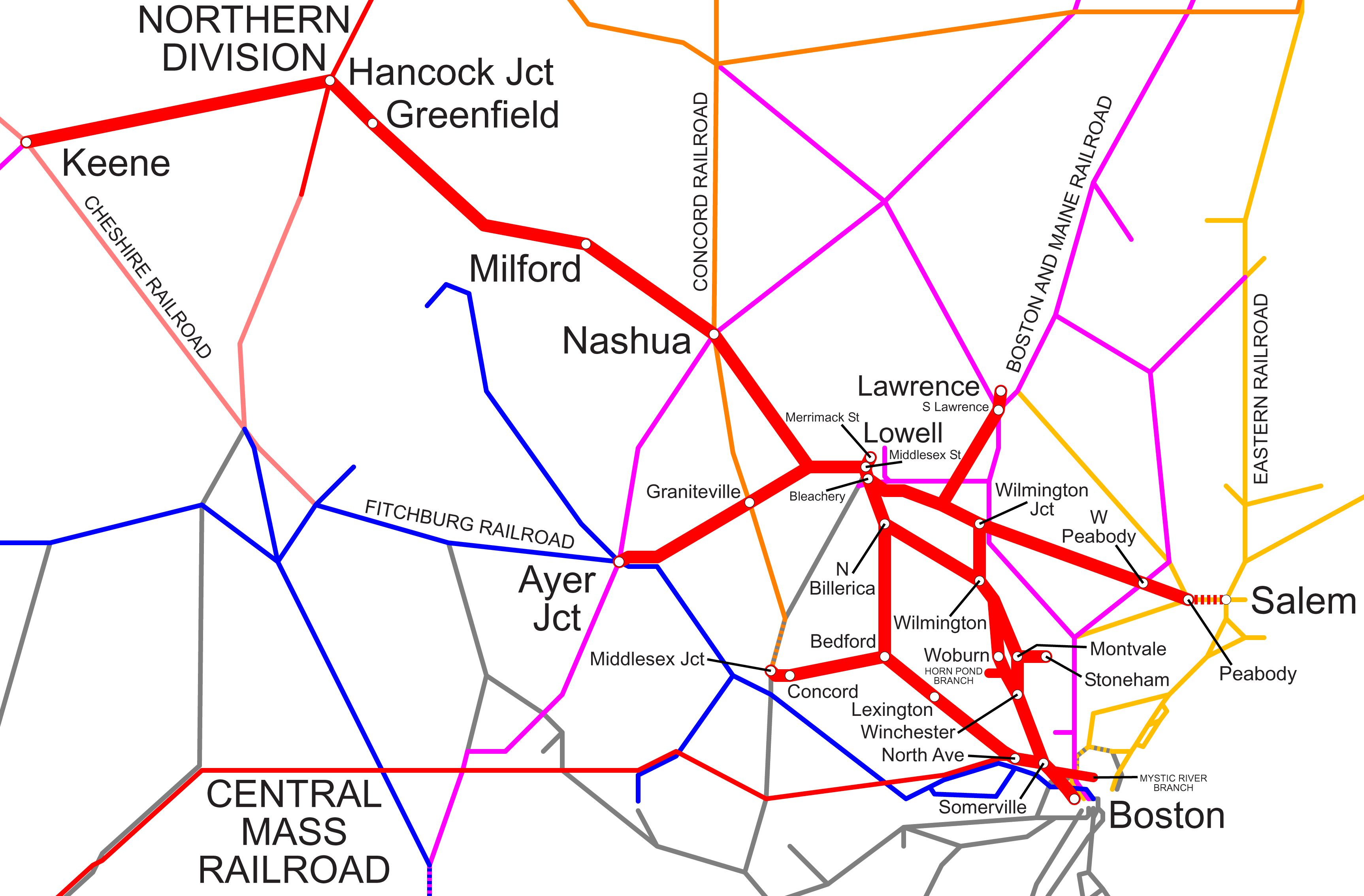 The
The
Accessed 2010-04-18 Double width bridge abutments can be found in Arlington. The branch eventually ended service, as it had begun, as a single track line. Grade crossings from Grove Street in Arlington Center to Park Avenue at Arlington Heights were eliminated in 1900, with modifications to Arlington Heights and Brattles stations. Around the turn of the 20th century, there were 19 daily round trips through Arlington. In January 1926, the B&M proposed to cut 7 of the 10 remaining round trips; all service to Lake Street, North Cambridge, West Somerville, and Somerville Highlands was to end. The B&M reached an agreement with a committee representing several municipalities in March, and with Somerville in April. Five daily round trips (six on Saturdays) were kept, including one round trip to Lowell; some service was maintained to the four stations. This schedule took effect on April 26, at which time two trains were given names - the ''Patriot'' and the ''Paul Revere Express''. Later that year, the B&M began reconstruction of the original route between East Arlington and the Fitchburg mainline as part of reconstruction of its Boston terminal area. On April 24, 1927, passenger service was rerouted over the rebuilt line; the Fitchburg Cutoff became freight-only, with North Cambridge, West Somerville, and Somerville Highlands stations closed. On April 24, 1926, the state approved discontinuance of passenger service on the Reformatory Branch. On February 5, 1927, the remaining freight service was abandoned on the short segment between Concord station and Reformatory station. On December 31, 1931, passenger service on the outer Lexington Branch from Bedford and North Billerica was discontinued. Remaining services were converted from steam to diesel trains in 1956. In 1958, all four stations in Arlington were closed as part of massive B&M service cuts; ridership was low because bus service on Massachusetts Avenue was more frequent and often faster. By popular request, was reopened in October 1965, and in March 1968. In 1962, the Boston and Maine abandoned both segments north and west of Bedford. It was noted at the time that the Bedford-Concord section had only seen 19 trains in 19 years. The town of Bedford purchased the rights of way within its boundaries in 1963. By 1965, the
Map of historical railroads North and West of Boston
The Lexington and West Cambridge R/R is shown in red. {{DEFAULTSORT:Lexington West Cambridge Railroad Defunct Massachusetts railroads Predecessors of the Boston and Maine Railroad Railway companies established in 1845 Railway companies disestablished in 1867 American companies established in 1845 American companies disestablished in 1867
Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
. It and its successors provided passenger service until 1977 and freight service until 1980 or early 1981.
History
Fitchburg Railroad
The Fitchburg Railroad is a former railroad company, which built a railroad line across northern Massachusetts, United States, leading to and through the Hoosac Tunnel. The Fitchburg was leased to the Boston and Maine Railroad in 1900. The main l ...
(now the MBTA
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
Fitchburg Line
The Fitchburg Line is a branch of the MBTA Commuter Rail system which runs from Boston's North Station to Wachusett station in Fitchburg, Massachusetts. The line is along the tracks of the former Fitchburg Railroad, which was built across nort ...
) in West Cambridge (near the site of the modern Alewife Station). When the separate ''town'' of West Cambridge changed its name to Arlington in 1867, the railroad was also renamed, as the Lexington and Arlington Railroad.
 The
The Boston and Lowell Railroad
The Boston and Lowell Railroad was a railroad that operated in Massachusetts in the United States. It was one of the first railroads in North America and the first major one in the state. The line later operated as part of the Boston and Maine R ...
purchased the line in 1870 and built a new connection (most of which would constitute a major portion of the later Fitchburg Cutoff) to their main line at Somerville Junction
Magoun Square station is a light rail station on the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Green Line (MBTA), Green Line located at Lowell Street south of Magoun Square in Somerville, Massachusetts. The accessible station has a sin ...
. The connection, from what is now the Magnolia Field-Varnum Street area in Arlington, ran through North Cambridge and West Somerville (Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts, United States, where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is of ...
); a station was located at Somerville Junction, commemorated by a park near what are now Centre and Woodbine Streets. The Boston and Lowell created a subsidiary, the Middlesex Central Railroad, to build an extension from Lexington to Bedford
Bedford is a market town in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 Census, the population was 106,940. Bedford is the county town of Bedfordshire and seat of the Borough of Bedford local government district.
Bedford was founded at a ford (crossin ...
and then Concord Center (Lowell Road), which opened in 1873. The Lowell Road station was adjacent to today's Minuteman National Historical Park. A extension from Concord Center to Concord Prison (Reformatory Station on Elm Street) would give the name Reformatory Branch to the Bedford-Concord segment in 1879. The branch continued another half mile further west to a junction (called "Concord Junction" or "Middlesex Junction" per different sources) with the Nashua, Acton & Boston Railroad and other rail lines.
The independent Billerica and Bedford Railroad built a connecting narrow-gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curv ...
line in 1877, but went bankrupt the next year. In 1885, the Middlesex Central purchased the right-of-way and used it to build a standard-gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
extension to from Bedford. The North Billerica–Boston segment was known as the Lexington Branch. In 1888, Willow Street station and Somerville Highlands station (at Cedar Street) were consolidated at Highland Road, retaining the Somerville Highlands name.
The Boston and Maine Railroad
The Boston and Maine Railroad was a United States, U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. It was chartered in 1835, and became part of what was the Pan Am Railways network in 1983 (most of which was purchased by CSX in 2022).
At the e ...
purchased all of the Boston and Lowell in 1887. Double-tracking from Somerville Junction to Lexington was instituted just prior to the B&M era, in 1885–86, and discontinued in 1927.Archival researchAccessed 2010-04-18 Double width bridge abutments can be found in Arlington. The branch eventually ended service, as it had begun, as a single track line. Grade crossings from Grove Street in Arlington Center to Park Avenue at Arlington Heights were eliminated in 1900, with modifications to Arlington Heights and Brattles stations. Around the turn of the 20th century, there were 19 daily round trips through Arlington. In January 1926, the B&M proposed to cut 7 of the 10 remaining round trips; all service to Lake Street, North Cambridge, West Somerville, and Somerville Highlands was to end. The B&M reached an agreement with a committee representing several municipalities in March, and with Somerville in April. Five daily round trips (six on Saturdays) were kept, including one round trip to Lowell; some service was maintained to the four stations. This schedule took effect on April 26, at which time two trains were given names - the ''Patriot'' and the ''Paul Revere Express''. Later that year, the B&M began reconstruction of the original route between East Arlington and the Fitchburg mainline as part of reconstruction of its Boston terminal area. On April 24, 1927, passenger service was rerouted over the rebuilt line; the Fitchburg Cutoff became freight-only, with North Cambridge, West Somerville, and Somerville Highlands stations closed. On April 24, 1926, the state approved discontinuance of passenger service on the Reformatory Branch. On February 5, 1927, the remaining freight service was abandoned on the short segment between Concord station and Reformatory station. On December 31, 1931, passenger service on the outer Lexington Branch from Bedford and North Billerica was discontinued. Remaining services were converted from steam to diesel trains in 1956. In 1958, all four stations in Arlington were closed as part of massive B&M service cuts; ridership was low because bus service on Massachusetts Avenue was more frequent and often faster. By popular request, was reopened in October 1965, and in March 1968. In 1962, the Boston and Maine abandoned both segments north and west of Bedford. It was noted at the time that the Bedford-Concord section had only seen 19 trains in 19 years. The town of Bedford purchased the rights of way within its boundaries in 1963. By 1965, the
Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
was subsidizing a single daily passenger train (using Budd Rail Diesel Car
The Budd Rail Diesel Car (RDC), also known as the Budd car or Buddliner, is a self-propelled diesel multiple unit (DMU) railcar. Between 1949 and 1962, 398 RDCs were built by the Budd Company of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The cars ...
s) between Boston and Bedford. On December 26, 1976, the MBTA purchased the rights of way and passenger equipment from the Boston and Maine (which retained freight trackage rights). Operation of MBTA Commuter Rail
The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's (MBTA's) transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over of track on 12 lines to 142 stations. It ...
was contracted at that time to the Boston and Maine, and later was awarded to other private companies. Beginning on January 10, 1977, a snowstorm blocked the line for a few days, after which the MBTA announced it would not resume passenger service.
The B&M filed for abandonment of the branch in March 1979; hearings were held a year later. The Interstate Commerce Commission
The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) was a regulatory agency in the United States created by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887. The agency's original purpose was to regulate railroads (and later Trucking industry in the United States, truc ...
soon gave permission for the B&M to stop running freights on the line. Common power on the branch at that time was SW # 1227. The last freight train to ply the line was hauled by a GP9, with 23 cars. According to one source the final trip was in 1980, and the same year the tracks were severed from the main line. Another source gives the date of the final run as January 31, 1981.
In 1980, a federal judge ruled that the Lexington Branch must be restored after construction of the parking garage at Alewife station over the right-of-way. In 1981, the MBTA entered into an agreement with the Town of Arlington to advocate that the Lexington Branch be abandoned. In return for the MBTA's support for converting the railroad to a bikeway, Arlington allowed the MBTA to use some of its land as a construction staging area for the Red Line extension project.
Route maps
Rail trails
The right-of-way was railbanked in 1991. Although the rails were removed, trackage can be relaid without objection if the MBTA should find it necessary. The Minuteman Bikeway opened between Alewife and Bedford in 1993. A former Boston and Maine Rail Diesel Car (RDC) of the type used on the line was purchased and is on display at the western end of the trail at Bedford Depot Park. The Alewife Linear Park (portions of which are also known as the Somerville Community Path and the Cambridge Linear Park) follows the right-of-way used by the Lexington Branch from 1870 to 1927, from Somerville nearly to Alewife. One of the main access points to the Linear Park is situated where the park crosses Massachusetts Avenue, at the intersection with Cedar Street, adjacent to which the North Cambridge station was located. The Bedford Narrow Gauge Rail Trail connects at Bedford Depot and heads north toward Billerica, passing Fawn Lake (also known as Hayden Pond). The current connection is indirect; the Minuteman ends at South Road, but the Narrow Gauge begins at Loomis Street just east of Hartford Street. The Bedford DPW is planning a more direct, sidewalk connection. It is named after the Billerica and Bedford Railroad, even though a standard-gauge railroad succeeded it. A historical recreation of the narrow-gauge predecessor has been installed near Loomis Street. The trail is paved only from Loomis Street to Great Road; after that it is improved with stone dust. The public portion of the trail ends after five miles (8 km) at the Bedford/Billerica town line (marked with a pair of gates in the middle of the woods), after which it becomes sandy (requiring a mountain bike or walking on foot) and continues on private property. The Bedford section of the trail was originally constructed (with stone dust) in 1998. The Reformatory Branch Rail Trail follows the old right-of-way from Railroad Avenue at Bedford Depot Park to Concord, though the bridges over theSudbury River
The Sudbury River is a tributary of the Concord River in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, in the United States.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011
Origin ...
and Assabet River
The Assabet River is a small, long river located about west of Boston, Massachusetts, United States.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed October 3, 2011 The Assabet rises ...
near Egg Rock no longer exist. The unimproved dirt hiking trail passes the Great Meadows National Wildlife Refuge. From Railroad Avenue, it is to Lowell Road in Concord, and then another on the other side of the river to the Concord State Prison.
The Narrow Gauge and Reformatory Branch Rail Trails are part of the Bay Circuit Trail and Greenway.
References and notes
External links
*Map of historical railroads North and West of Boston
The Lexington and West Cambridge R/R is shown in red. {{DEFAULTSORT:Lexington West Cambridge Railroad Defunct Massachusetts railroads Predecessors of the Boston and Maine Railroad Railway companies established in 1845 Railway companies disestablished in 1867 American companies established in 1845 American companies disestablished in 1867