Red (programming Language) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Red is a 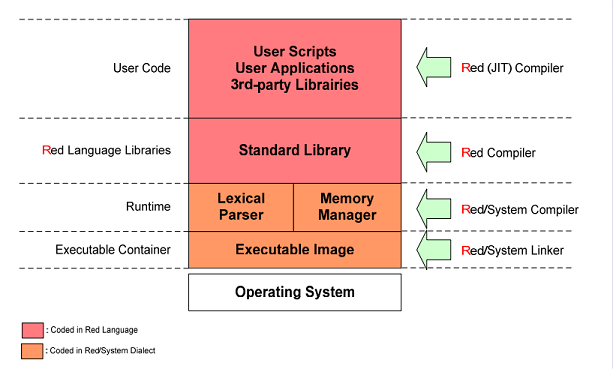
''red-lang.org'', September 14, 2011. Rakočević is a long-time Rebol developer known as the creator of the Cheyenne HTTP server.
''red-lang.org'', March 2020. — Live coded diagramming * SmartXML«SmartXML»
''redata.dev''. — XML parsing tool.
Red itle: "Simple hello world script"print "Hello, World!"
Red itle: "A factorial script" ; Note: The title is optional.
factorial: func x [integer! ; Giving the type of an argument in Red is optional
">nteger!.html" ;"title=" x [integer!"> x [integer! ; Giving the type of an argument in Red is optional
either x = 0 [1][x * factorial x - 1]
]
The following is the same factorial example in Red/System (in this very simple case, the source code is very similar to Red's version):
Red/System itle: "A factorial script"
factorial: func x [integer! ; This is compulsory in Red/System
return: [integer!">nteger!.html" ;"title=" x [integer!"> x [integer! ; This is compulsory in Red/System
return: [integer! ; This is compulsory in Red/System
][
either x = 0 [1][x * factorial x - 1]
]
Latest builds from official website
*
Redprogramming.com
{{Programming languages Programming languages Systems programming languages Extensible syntax programming languages Domain-specific programming languages High-level programming languages Homoiconic programming languages Procedural programming languages Functional languages Cross-platform free software Cross-platform software Free and open source compilers Free and open source interpreters Software using the BSD license Software using the Boost license Programming languages created in 2011 2011 software
programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
designed to overcome the limitations of the programming language Rebol. Red was introduced in 2011 by Nenad Rakočević, and is both an imperative and functional programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarat ...
language. Its syntax and general usage overlaps that of the interpreted Rebol language.
The implementation choices of Red intend to create a full stack programming language: Red can be used for extremely high-level programming (DSL
Digital subscriber line (DSL; originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric di ...
s and GUIs) as well as low-level programming (operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s and device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
s). Key to the approach is that the language has two parts: ''Red/System'' and ''Red''.
* ''Red/System'' is similar to C, but packaged into a Rebol lexical structure for example, one would write instead of .
* ''Red'' is a homoiconic language, which is capable of meta-programming with Rebol-like semantics. Red's runtime library is written in Red/System, and uses a hybrid approach: it compiles what it can deduce statically and uses an embedded interpreter
Interpreting is translation from a spoken or signed language into another language, usually in real time to facilitate live communication. It is distinguished from the translation of a written text, which can be more deliberative and make use o ...
otherwise. The project roadmap includes a just-in-time compiler
In computing, just-in-time (JIT) compilation (also dynamic translation or run-time compilations) is compiler, compilation (of Source code, computer code) during execution of a program (at run time (program lifecycle phase), run time) rather than b ...
for cases in between, but this has not yet been implemented.
Red seeks to remain independent of any other toolchain
A toolchain is a set of software development tools used to build and otherwise develop software. Often, the tools are executed sequentially and form a pipeline such that the output of one tool is the input for the next. Sometimes the term is us ...
; it does its own code generation. It is therefore possible to cross-compile
A cross compiler is a compiler capable of creating executable code for a platform other than the one on which the compiler is running. For example, a compiler that runs on a PC but generates code that runs on Android devices is a cross compil ...
Red programs from any platform it supports to any other, via a command-line switch. Both Red and Red/System are distributed as open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
under the modified BSD license
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD licen ...
. The runtime library is distributed under the more permissive Boost Software License
Boost is a set of library (computing), libraries for the C++ programming language that provides support for tasks and structures such as linear algebra, pseudorandom number generator, pseudorandom number generation, multithreading, image proces ...
.
As of version 0.6.4 Red includes a garbage collector "the Simple GC".
Introduction
Red was introduced in theNetherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
in February 2011 at the ''Rebol & Boron conference'' by its author Nenad Rakočević. In September 2011, the Red programming language was presented to a larger audience during the Software Freedom Day
Software Freedom Day (SFD) is an annual list of minor secular observances#September, worldwide celebration of Free Software organized by the Digital Freedom Foundation (DFF). SFD is a public education effort with the aim of awareness raising, i ...
2011.« Red Programming Language: Red at Software Freedom Day 2011 »''red-lang.org'', September 14, 2011. Rakočević is a long-time Rebol developer known as the creator of the Cheyenne HTTP server.
Features
Red's syntax and semantics are very close to those of Rebol. Like Rebol, it strongly supportsmetaprogramming
Metaprogramming is a computer programming technique in which computer programs have the ability to treat other programs as their data. It means that a program can be designed to read, generate, analyse, or transform other programs, and even modi ...
and domain-specific languages ( DSLs) and is therefore a highly efficient tool for dialecting (creating embedded DSLs). Red includes a dialect called Red/System, a C-level language which provides system programming facilities. Red is easy to integrate with other tools and languages as a DLL (libRed) and very lightweight (around 1 MB). It is also able to cross-compile to various platforms (see Cross Compilation section below) and create packages for platforms that require them (e.g., .APK on Android). Red also includes a fully reactive cross-platform GUI system based on an underlying reactive dataflow engine, a 2D drawing dialect comparable to SVG, compile-time and runtime macro support, and more than 40 standard datatypes.
Goals
The following is the list of Red's Goals as presented on theSoftware Freedom Day
Software Freedom Day (SFD) is an annual list of minor secular observances#September, worldwide celebration of Free Software organized by the Digital Freedom Foundation (DFF). SFD is a public education effort with the aim of awareness raising, i ...
2011:
* Simplicity ("An IDE should not be necessary to write code.")
* Compactness ("Being highly expressive maximizes productivity.")
* Speed ("If too slow, it cannot be general-purpose enough.")
* Be "Green", Have a Small Footprint ("Because resources are not limitless.")
* Ubiquity ("Spread everywhere.")
* Portability, Write once run everywhere ("That's the least expected from a programming language.")
* Flexibility ("Not best but good fit for any task!")
Commercial applications
The following commercial applications are currently developed on Red: * DiaGrammar«DiaGrammar»''red-lang.org'', March 2020. — Live coded diagramming * SmartXML«SmartXML»
''redata.dev''. — XML parsing tool.
Development
Red's development is planned to be done in two phases: # Initial phase: Red and Red/System compilers written in Rebol 2 # Bootstrap phase: Red and Red/System compilers complemented by a Red JIT-compiler, all written in RedCross compilation
Red currently supports the following cross-compilation targets: *MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
: Windows, x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
, console (and GUI) applications
* Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
: Windows, x86, GUI applications
* Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
: Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, x86
* Linux-ARM: Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, ARMv5, armel (soft-float)
* Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi ( ) is a series of small single-board computers (SBCs) developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in collaboration with Broadcom Inc., Broadcom. To commercialize the product and support its growing demand, the ...
: Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, ARMv5, armhf
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for computer processors. Arm Holdings develops the ISAs and lice ...
(hard-float)
* FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
: x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
* Darwin: OS X
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
Intel, console (and GUI) applications
* Android: Android, ARMv5
* Android-x86: Android, x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
(Note: Presently, Red applications are 32-bit, but it is planned to switch to 64-bit in the future.)
Hello World!
The"Hello, World!" program
A "Hello, World!" program is usually a simple computer program that emits (or displays) to the screen (often the Console application, console) a message similar to "Hello, World!". A small piece of code in most general-purpose programming languag ...
in Red:
Factorial example
IMPORTANT: These are intended as syntax examples. Until Red has64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
support, the integer example will overflow a 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
integer very quickly. Changing that to `float!` will go farther, but these are merely to show the syntax of the language.
The following is a factorial example in Red:
See also
* Comparison of programming languages * History of programming languages * List of programming languages *List of programming languages by type
This is a list of notable programming languages, grouped by type.
The groupings are overlapping; not mutually exclusive. A language can be listed in multiple groupings.
Agent-oriented programming languages
Agent-oriented programming allows ...
References
Further reading
*External links
*Latest builds from official website
*
Redprogramming.com
{{Programming languages Programming languages Systems programming languages Extensible syntax programming languages Domain-specific programming languages High-level programming languages Homoiconic programming languages Procedural programming languages Functional languages Cross-platform free software Cross-platform software Free and open source compilers Free and open source interpreters Software using the BSD license Software using the Boost license Programming languages created in 2011 2011 software