Recursive Partitioning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
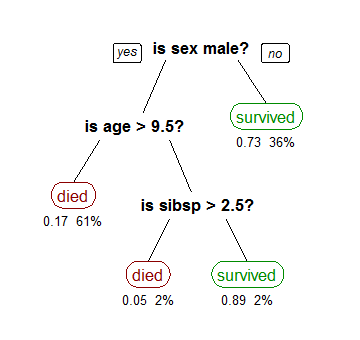 Recursive partitioning is a
Recursive partitioning is a
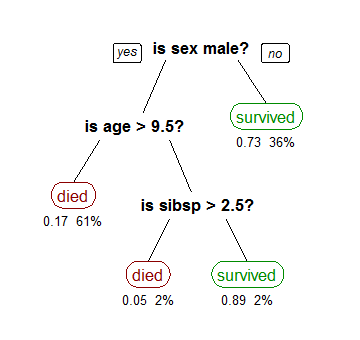 Recursive partitioning is a
Recursive partitioning is a statistical
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
method for multivariable analysis
Multivariate statistics is a subdivision of statistics encompassing the simultaneous observation and analysis of more than one outcome variable, i.e., ''multivariate random variables''.
Multivariate statistics concerns understanding the differe ...
. Recursive partitioning creates a decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event ou ...
that strives to correctly classify members of the population by splitting it into sub-populations based on several dichotomous independent variable
A variable is considered dependent if it depends on (or is hypothesized to depend on) an independent variable. Dependent variables are studied under the supposition or demand that they depend, by some law or rule (e.g., by a mathematical function ...
s. The process is termed recursive
Recursion occurs when the definition of a concept or process depends on a simpler or previous version of itself. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in m ...
because each sub-population may in turn be split an indefinite number of times until the splitting process terminates after a particular stopping criterion is reached.
Recursive partitioning methods have been developed since the 1980s. Well known methods of recursive partitioning include Ross Quinlan's ID3 algorithm
In decision tree learning, ID3 (Iterative Dichotomiser 3) is an algorithm invented by Ross QuinlanQuinlan, J. R. 1986. Induction of Decision Trees. Mach. Learn. 1, 1 (Mar. 1986), 81–106 used to generate a decision tree from a dataset. ID3 is th ...
and its successors, C4.5
C4.5 is an algorithm used to generate a decision tree developed by Ross Quinlan. C4.5 is an extension of Quinlan's earlier ID3 algorithm. The decision trees generated by C4.5 can be used for classification, and for this reason, C4.5 is often refer ...
and C5.0 and Classification and Regression Trees (CART). Ensemble learning
In statistics and machine learning, ensemble methods use multiple learning algorithms to obtain better predictive performance than could be obtained from any of the constituent learning algorithms alone.
Unlike a statistical ensemble in statist ...
methods such as Random Forest
Random forests or random decision forests is an ensemble learning method for statistical classification, classification, regression analysis, regression and other tasks that works by creating a multitude of decision tree learning, decision trees ...
s help to overcome a common criticism of these methods – their vulnerability to overfitting
In mathematical modeling, overfitting is "the production of an analysis that corresponds too closely or exactly to a particular set of data, and may therefore fail to fit to additional data or predict future observations reliably". An overfi ...
of the data – by employing different algorithms and combining their output in some way.
This article focuses on recursive partitioning for medical diagnostic
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
tests,
but the technique has far wider applications.
See decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event ou ...
.
As compared to regression analysis, which creates a formula that health care providers can use to calculate the probability that a patient has a disease, recursive partition creates a rule such as 'If a patient has finding x, y, or z they probably have disease q'.
A variation is 'Cox linear recursive partitioning'.
Advantages and disadvantages
Compared to other multivariable methods, recursive partitioning has advantages and disadvantages. * Advantages are: ** Generates clinically more intuitive models that do not require the user to perform calculations. ** Allows varying prioritizing of misclassifications in order to create a decision rule that has more sensitivity or specificity. ** May be more accurate. * Disadvantages are: ** Does not work well for continuous variables ** May overfit data.Examples
Examples are available of using recursive partitioning in research of diagnostic tests. Goldman used recursive partitioning to prioritize sensitivity in the diagnosis ofmyocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
among patients with chest pain in the emergency room.
See also
*Decision tree learning
Decision tree learning is a supervised learning approach used in statistics, data mining and machine learning. In this formalism, a classification or regression decision tree is used as a predictive model to draw conclusions about a set of obser ...
References
{{reflist Statistical classification Biostatistics