receptor agonist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular
proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist.
Etymology
The word originates from the Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive."Types of agonists
Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such ashormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s and neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s) or exogenous agonists (such as drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonist is a substance that creates the same bodily responses but does not bind to the same receptor.
* An endogenous agonist for a particular receptor is a compound naturally produced by the body that binds to and activates that receptor. For example, the endogenous agonist for serotonin receptors is serotonin, and the endogenous agonist for dopamine receptors is dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
.
* Full agonists bind to and activate a receptor with the maximum response that an agonist can elicit at the receptor. One example of a drug that can act as a full agonist is isoproterenol, which mimics the action of adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
at β adrenoreceptors. Another example is morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
, which mimics the actions of endorphins at μ-opioid receptors throughout the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. However, a drug can act as a full agonist in some tissues and as a partial agonist in other tissues, depending upon the relative numbers of receptors and differences in receptor coupling.
* A co-agonist works with other co-agonists to produce the desired effect together. NMDA receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and predominantly Ca2+ ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other ...
activation requires the binding of both glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
, glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
and D-serine co-agonists. Calcium can also act as a co-agonist at the IP3 receptor.
* A selective agonist is selective for a specific type of receptor. E.g. buspirone
Buspirone, sold under the brand name Buspar among others, is an anxiolytic, a medication primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). It is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, 5-HT1A receptor partial ag ...
is a selective agonist for serotonin 5-HT1A.
* Partial agonist
In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given Receptor (biochemistry), receptor, but have only partial Intrinsic activity, efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered Ligand (bio ...
s (such as buspirone
Buspirone, sold under the brand name Buspar among others, is an anxiolytic, a medication primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). It is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, 5-HT1A receptor partial ag ...
, aripiprazole, buprenorphine, or norclozapine) also bind and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
at the receptor relative to a full agonist, even at maximal receptor occupancy. Agents like buprenorphine are used to treat opiate
An opiate is an alkaloid substance derived from opium (or poppy straw). It differs from the similar term ''opioid'' in that the latter is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain ( ...
dependence for this reason, as they produce milder effects on the opioid receptor with lower dependence and abuse potential.
* An inverse agonist is an agent that binds to the same receptor binding-site as an agonist for that receptor and inhibits the constitutive activity of the receptor. Inverse agonists exert the opposite pharmacological effect of a receptor agonist, not merely an absence of the agonist effect as seen with an antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.rimonabant.
* A superagonist is a term used by some to identify a compound that is capable of producing a greater response than the endogenous agonist for the target receptor. It might be argued that the endogenous agonist is simply a partial agonist in that tissue.
* An irreversible agonist is a type of agonist that binds permanently to a receptor through the formation of covalent bonds.
* A biased agonist is an agent that binds to a receptor without affecting the same signal transduction pathway. Oliceridine is a μ-opioid receptor agonist that has been described to be functionally selective towards G protein and away from β-arrestin2 pathways.
New findings that broaden the conventional definition of pharmacology demonstrate that
 For the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which is a G protein-coupled receptor(GPCR), the endogenous agonist is
For the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which is a G protein-coupled receptor(GPCR), the endogenous agonist is 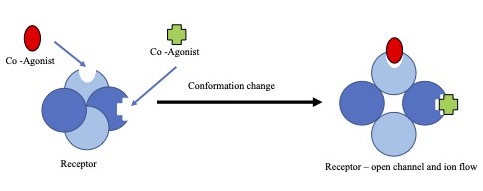 The
The
ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
s can concurrently behave as agonist ''and'' antagonists at the same receptor, depending on effector pathways or tissue type. Terms that describe this phenomenon are " functional selectivity", "protean agonism", or selective receptor modulators.
Mechanism of action
As mentioned above, agonists have the potential to bind in different locations and in different ways depending on the type of agonist and the type of receptor. The process of binding is unique to the receptor-agonist relationship, but binding induces a conformational change and activates the receptor. This conformational change is often the result of small changes in charge or changes inprotein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after Protein biosynthesis, synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of Amino acid, amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered protein tertiary structure, t ...
when the agonist is bound. Two examples that demonstrate this process are the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor and NMDA receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and predominantly Ca2+ ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other ...
and their respective agonists.
 For the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which is a G protein-coupled receptor(GPCR), the endogenous agonist is
For the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which is a G protein-coupled receptor(GPCR), the endogenous agonist is acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
. The binding of this neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
causes the conformational changes that propagate a signal into the cell. The conformational changes are the primary effect of the agonist, and are related to the agonist's binding affinity and agonist efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
. Other agonists that bind to this receptor will fall under one of the different categories of agonist mentioned above based on their specific binding affinity and efficacy.
 The
The NMDA receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and predominantly Ca2+ ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other ...
is an example of an alternate mechanism of action, as the NMDA receptor requires co-agonists for activation. Rather than simply requiring a single specific agonist, the NMDA receptor requires both the endogenous agonists, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
. These co-agonists are both required to induce the conformational change needed for the NMDA receptor to allow flow through the ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiol ...
, in this case calcium. An aspect demonstrated by the NMDA receptor is that the mechanism or response of agonists can be blocked by a variety of chemical and biological factors. NMDA receptors specifically are blocked by a magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
ion unless the cell is also experiencing depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell (biology), cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolar ...
.
These differences show that agonists have unique mechanisms of action depending on the receptor activated and the response needed. The goal and process remains generally consistent however, with the primary mechanism of action requiring the binding of the agonist and the subsequent changes in conformation to cause the desired response at the receptor. This response as discussed above can vary from allowing flow of ions to activating a GPCR and transmitting a signal into the cell.
Activity
Potency
Potency is the amount of agonist needed to elicit a desired response. The potency of an agonist is inversely related to its half maximal effective concentration (EC50) value. The EC50 can be measured for a given agonist by determining the concentration of agonist needed to elicit half of the maximum biological response of the agonist. The EC50 value is useful for comparing the potency of drugs with similar efficacies producing physiologically similar effects. The smaller the EC50 value, the greater the potency of the agonist, the lower the concentration of drug that is required to elicit the maximum biological response.Therapeutic index
Therapeutic index is a meaure of a drug's safety margin. When a drug is used therapeutically, it is important to understand the margin of safety that exists between the dose needed for the desired effect and the dose that produces unwanted and possibly dangerous side-effects (measured by the TD50, the dose that produces toxicity in 50% of individuals). This relationship, termed the therapeutic index, is defined as the ratio TD50: ED50. In general, the narrower this margin, the more likely it is that the drug will produce unwanted effects. The therapeutic index emphasizes the importance of the margin of safety, as distinct from the potency, in determining the usefulness of a drug.See also
* Allosteric modulator * Dose response curve * Excitatory postsynaptic potential * Functional selectivity * Intrinsic activity * Inverse agonist * Mixed agonist/antagonist *Receptor antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of rec ...
* Receptor theory
References