Random Pulse-width Modulation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Random pulse-width modulation (RPWM) is a 
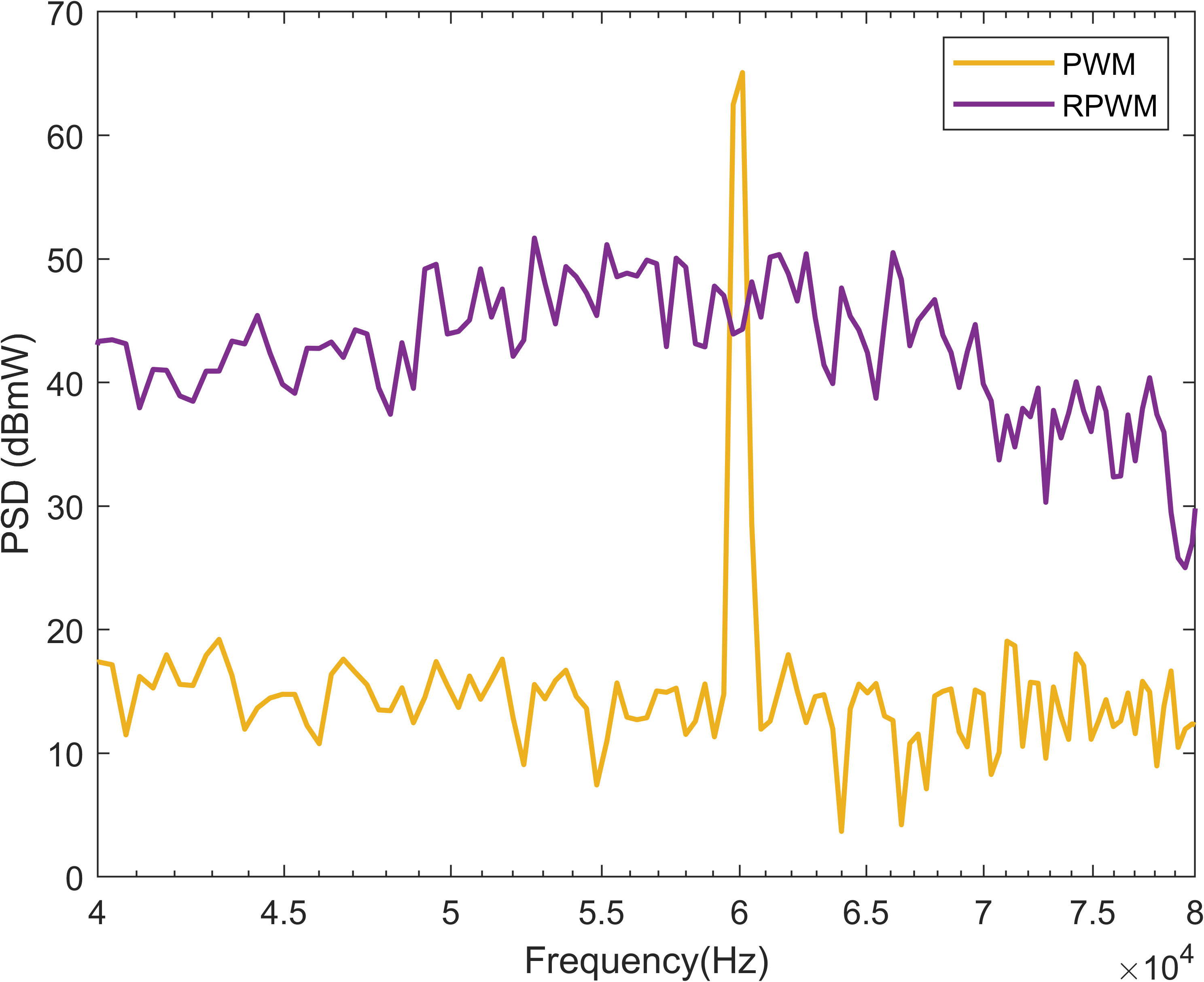
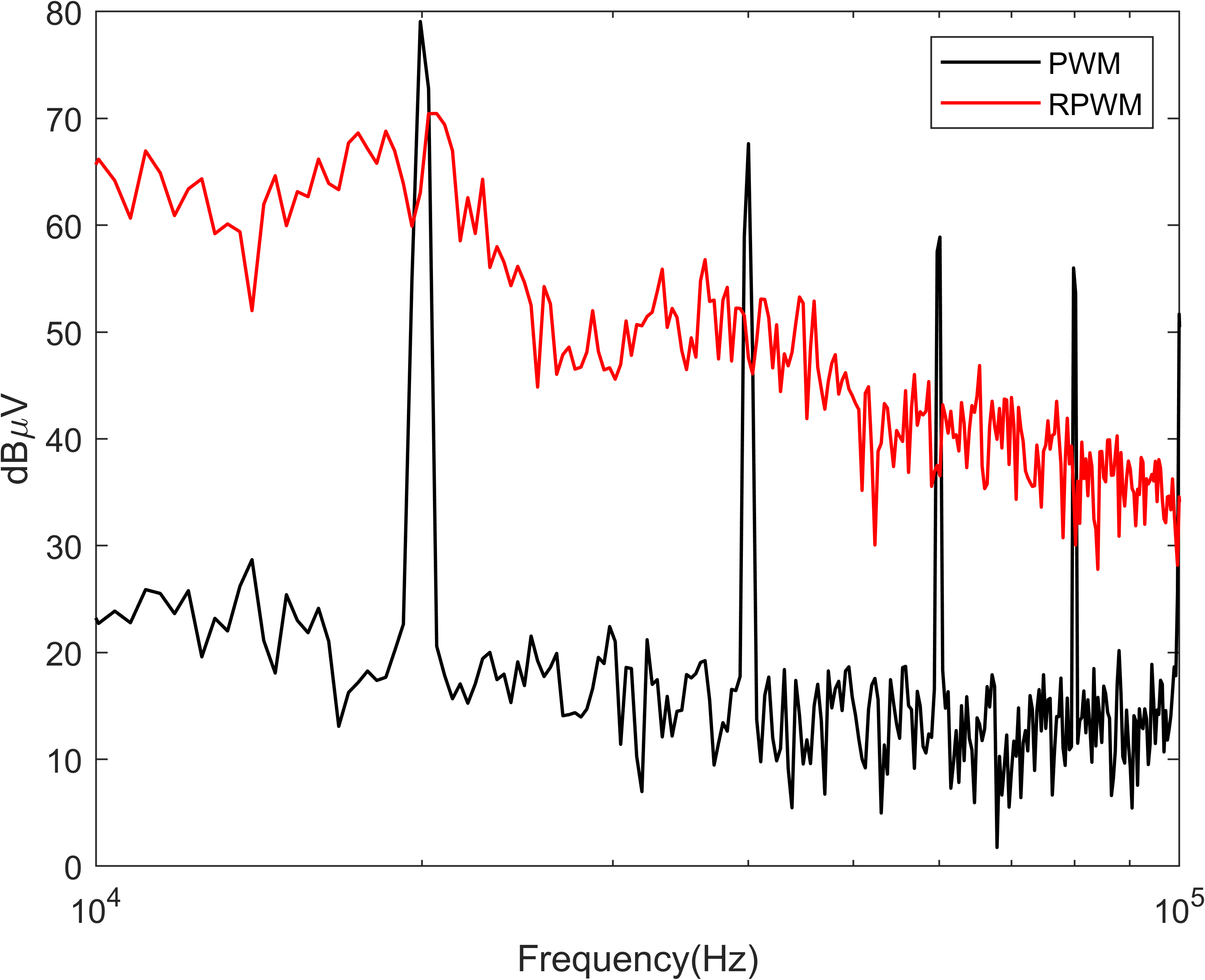
 The interference can be worsened when the switching frequency and the
The interference can be worsened when the switching frequency and the
modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
technique introduced for mitigating electromagnetic interference (EMI) of power converters by spreading the energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
of the noise signal over a wider bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
, so that there are no significant peaks of the noise. This is achieved by randomly varying the main parameters of the pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying peri ...
signal.

Description
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters have been widely used for filtering out the conducted emissions generated by power converters since their advent. However, when size is of great concern like inaircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
and automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
applications, one of the practical solutions to suppress conducted emissions is to use random pulse-width modulation (RPWM). In conventional pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying peri ...
(PWM) schemes, the harmonics
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st harm ...
power is concentrated on the deterministic or known frequencies with a significant magnitude, which leads to mechanical vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the oscill ...
, noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
, and EMI. However, by applying randomness
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of definite pattern or predictability in information. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. ...
to the conventional PWM scheme, the harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
power will spread out so that no harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
of significant magnitude exists, and peak harmonics
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st harm ...
at discrete frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
are significantly reduced.
In RPWM, one of the switching parameters of the PWM signal, such as switching frequency, pulse position and duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a for ...
are varied randomly in order to spread the energy of the PWM signal. Hence, depending on the parameter which is made random, RPWM can be classified as ''random frequency modulation'' (RFM), ''random pulse-position modulation'' (RPPM) and ''random duty-cycle modulation'' (RDCM).
The properties of RPWM can be investigated further by looking at the power spectral density
In signal processing, the power spectrum S_(f) of a continuous time signal x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components f composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into ...
(PSD). For conventional PWM, the PSD can be directly determined from the Fourier Series
A Fourier series () is an Series expansion, expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems ...
expansion of the PWM signal. However, the PSD of the RPWM signals can be described only by a probabilistic
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
level using the theory of stochastic process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Sto ...
es such as wide-sense stationary (WSS) random processes.

RFM
Among the different RPWM techniques, RFM (random frequency modulation) is the most common method of the three major types, used in many power converter topologies to pass the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) test. In this type of modulation, the switching frequency of the PWM signal is variedrandomly
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of definite pattern or predictability in information. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. In ...
in order to spread the emitted noise of the power converters in which it is applied. RFM is very easy to implement and it offers significant reduction of the noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
peaks compared to conventional PWM. However, application is limited to power converters which does not require fixed switching frequency for their normal operation. A greater degree of switching frequency variation can affect the proper functioning of the devices and components inside the power converter circuit.

RPPM
RPPM is also commonly deployed in power converters to pass the EMC compliance tests. Thismodulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
technique also offers significant reduction of the conducted emission and, consequentially, the radiated emission of power converters. However, compared to RFM, RPPM is less effective in EMI reduction. This is because the PSD of RPPM contains both the density and harmonic components, and the spectrum cannot be fully spread unlike that of RFM where the spectrum has only the density component. However, in this modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
scheme, both the switching frequency and the pulse width are fixed so that the converter components like inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
s and capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s can function properly.
RDCM
In RDCM, the pulse width or theduty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a for ...
of the PWM signal is varied randomly in order to spread the noise spectrum. This kind of modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
is less common compared to the previous ones. This is because RDCM is less effective at spreading the noise. Moreover, randomly varying the duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a for ...
may cause output voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
fluctuations and ripples. Besides, in some power converter topologies, the duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a for ...
variation is the primary means of controlling the input-output voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
s and currents
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (hy ...
using closed loop control systems. An example of this could be the drive for a brushed DC motor. Since the power to the motor is already being "chopped" at a specific frequency to vary the voltage and current, introducing randomization into the process could cause detriments to the system's performance.
In variable-frequency inverter systems
This type of modulation is becoming more common invariable-frequency drive
A variable-frequency drive (VFD, or adjustable-frequency drive, adjustable-speed drive, variable-speed drive, AC drive, micro drive, inverter drive, variable voltage variable frequency drive, or drive) is a type of AC motor, AC motor drive (sys ...
s of all sizes and applications. in consumer-sized VFDs that include it as a feature, it presents as a user-selectable parameter, often with several different operating levels. Some drives may also use more than one method at once. However, while the term "RPWM" is generally used to label this type of modulation in a technical sense, the technology does not yet have a label in the world of VFD parameter names. For example, Fuji Electric
, operating under the brand name FE, is a Japanese electrical equipment company, manufacturing pressure transmitters, flowmeters, gas analyzers, controllers, inverters, pumps, generators, ICs, motors, and power equipment.
History
Fuji Electric ...
labels its noise-reduction parameter as "motor tone", while both Mitsubishi Electric
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational electronics and electrical equipment manufacturing company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. The company was established in 1921 as a spin-off from the electrical machinery manufacturing d ...
and Teco Westinghouse label it as "soft PWM". The use of the term "soft PWM" could potentially cause confusion to those not familiar with this technique, as zero crossing control is sometimes labeled as "soft switching".
A term that could be potentially used as a standard label could be "scrambled PWM" or "carrier scrambling", as the word "scramble" in this sense is nonspecific to the method of RPWM used, yet informs the user that there is indeed a specialized process occurring which affects the shape and properties of the output waveform. In addition, the word has a home in the telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
field, where a scrambler
In telecommunications, a scrambler is a device that transposes or inverts signals or otherwise encodes a message at the sender's side to make the message unintelligible at a receiver not equipped with an appropriately set descrambling device. Wher ...
is any device (typically analog) that is used to encode a signal so that it will be unintelligible if intercepted before it can reach the intended recipient without an appropriately tuned de-scrambler. That is to say that "scramble" would not be out of place if used to label RPWM in a more general sense.
Regardless of the label, upon observation of the manual in consumer-sized VFDs that include it, the focus of the parameter description does appear to be on acoustic noise reduction, rather than EMI reduction and motor health.
In modern rail traction converters, this method presents in a change in the sound that the motors emit when driven by inverters which utilize it. As opposed to the normally steady, carrier-based whine of a classic SPWM convertor, the sound is more of a hiss, akin to white noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, i ...
. Because rail traction convertors operate at such high power levels, EMI is more readily created in such systems. In these applications RPWM is highly beneficial to the motor's health and the level of emitted EMI.
Coexistence issue
RPWM techniques are very effective in reducing the EMI of power converters. However, when power converters with this special type ofmodulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
coexist with communication systems
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Commun ...
, there may be a severe electromagnetic interference conflict between the power system and the communication system
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Communic ...
. This detrimental effect can be observed in power line communication
Power-line communication (PLC) is the carrying of data on a conductor (the ''power-line carrier'') that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers.
A wide range of power-line comm ...
(PLC) systems, where both power converters and communication systems
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Commun ...
coexist. Indeed, recent studies have confirmed that RPWM applied to power converters to minimize conducted emissions can detrimentally interfere with the PLC system.
 The interference can be worsened when the switching frequency and the
The interference can be worsened when the switching frequency and the bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
of the PLC system overlaps with that of the power system. Most power converters use a switching frequency that is below 150 kHz, which is in the low frequency electromagnetic compatibility range. This could cause coexistence issues mainly in narrow band PLC systems, (specialized PLC protocols which are being used for smart grid
The smart grid is an enhancement of the 20th century electrical grid, using two-way communications and distributed so-called intelligent devices. Two-way flows of electricity and information could improve the delivery network. Research is main ...
application, such as Prime PLC and G3-PLC, in frequencies below 150 kHz.) In conventional PWM, the noise from power converter overlaps with the PLC frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
band at discrete multiples of the switching frequency only. This results in less interference to the PLC system. However, In RPWM, the noise is more evenly distributed and both the PLC and the noise from power converter shares wider bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
. This creates more disturbance to the PLC system. Therefore, it is advisable to carefully observe the properties of any coexisting systems in order to choose a switching frequency for randomly modulated power converters that does not overlap with that of a coexisting PLC system.
See also
* Conducted emissions * Electromagnetic compatibility * Electromagnetic interference *Power-line communication
Power-line communication (PLC) is the carrying of data on a conductor (the ''power-line carrier'') that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers.
A wide range of power-line comm ...
* Spread spectrum
In telecommunications, especially radio communication, spread spectrum are techniques by which a signal (electrical engineering), signal (e.g., an electrical, electromagnetic, or acoustic) generated with a particular Bandwidth (signal processi ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
* https://www.analog.com/en/technical-articles/spread-spectrum-frequency-modulation-reduces-emi.html * https://www.analog.com/en/technical-articles/easy-to-use-spread-spectrum-clock-generator-reduces-emi-and-more.html Signal processing