Rana Esculenta on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The edible frog (''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'') is a species of common European frog, also known as the common water frog or green frog (however, this latter term is also used for the North American species '' Rana clamitans'').
It is used for food, particularly in France for the delicacy frog legs. Females are between 5 and 9 cm long, males between 6 and 11 cm.
This widespread and common frog has many common names, including European dark-spotted frog, European black-spotted pond frog, and European black-spotted frog.
The edible frog (''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'') is a species of common European frog, also known as the common water frog or green frog (however, this latter term is also used for the North American species '' Rana clamitans'').
It is used for food, particularly in France for the delicacy frog legs. Females are between 5 and 9 cm long, males between 6 and 11 cm.
This widespread and common frog has many common names, including European dark-spotted frog, European black-spotted pond frog, and European black-spotted frog.
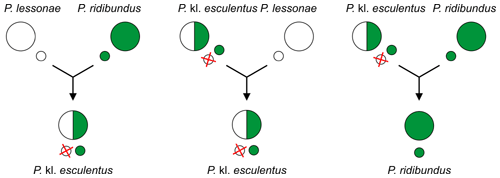 Because this hybrid requires another taxon as a sexual host to reproduce, usually one of the parental species, it is a klepton. Hence the addition of the "kl." (for ''klepton'') in the species name.
There are also known all-hybrid populations, where
Because this hybrid requires another taxon as a sexual host to reproduce, usually one of the parental species, it is a klepton. Hence the addition of the "kl." (for ''klepton'') in the species name.
There are also known all-hybrid populations, where
File:Rana-esculenta_swimming_331.jpg, Swimming frog
File:Rana-esculenta_mating_325.jpg, Attempted copulation between two males
File:Teichfrosch isst teichfrosch.JPG, Example of cannibalism
File:Waterfrog head.jpg, Close-up of head
File:Rana_esculenta_on_nymphaea_front_view.JPG, Head close-up, another perspective
File:Veekonn.JPG, Edible frog on a human arm
File:Pelophylax esculentus 002.jpg, Edible frog in pond habitat
File:Edible frog (Pelophylax esculentus).jpg, Edible frog in a swamp
ArchéoZooThèque : Edible frog skeleton drawing
Species account on HerpFrance.com
Video: Pool frogs and hybrid green frogs
on YouTube. Mixed mating of pool frog and edible frog; pool frog are grass green and smaller. {{Taxonbar, from=Q31694 Amphibia hybrids Amphibians of Europe Pelophylax Amphibians described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
 The edible frog (''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'') is a species of common European frog, also known as the common water frog or green frog (however, this latter term is also used for the North American species '' Rana clamitans'').
It is used for food, particularly in France for the delicacy frog legs. Females are between 5 and 9 cm long, males between 6 and 11 cm.
This widespread and common frog has many common names, including European dark-spotted frog, European black-spotted pond frog, and European black-spotted frog.
The edible frog (''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'') is a species of common European frog, also known as the common water frog or green frog (however, this latter term is also used for the North American species '' Rana clamitans'').
It is used for food, particularly in France for the delicacy frog legs. Females are between 5 and 9 cm long, males between 6 and 11 cm.
This widespread and common frog has many common names, including European dark-spotted frog, European black-spotted pond frog, and European black-spotted frog.
Distribution
''Pelophylax esculentus'' is endemic to Europe. It naturally occurs from the northern half of France to western Russia, and from Estonia and Denmark to Bulgaria and northern Italy. The edible frog is introduced in Spain, Norway and the United Kingdom. The natural range is nearly identical to that of '' P. lessonae''.Hybridogenesis
''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'' is the fertile hybrid of thepool frog
The pool frog (''Pelophylax lessonae'') is a European frog in the family Ranidae. Its specific name was chosen by the Italian herpetologist Lorenzo Camerano in 1882, in order to honour his master Michele Lessona.
Description
The pool frog ...
(''Pelophylax lessonae'') and the marsh frog
The marsh frog (''Pelophylax ridibundus'') is a species of water frog native to Europe and parts of western Asia.
Description
The marsh frog is the largest type of frog in most of its range, with males growing to a size around 100 mm (3.9 ...
(''Pelophylax ridibundus''). It reproduces by hybridogenesis (hemiclonally).
Hybridogenesis implies that during gametogenesis hybrids (of RL genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
) exclude one parental genome (L or R) and produce gametes with an unrecombined genome of the other parental species (R or L, respectively), instead of containing mixed recombined parental genomes. The hybrid populations are usually propagated by mating ( backcrosses) with a sympatric
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species sh ...
parental species – ''P. lessonae'' (LL) or ''P. ridibundus'' (RR) – providing the second, discarded parental genome (L or R respectively). Hybridogenesis is thus a hemiclonal mode of reproduction; half of the genome is transmitted to the next generation clonally, unrecombined (intact); the other half sexually, recombined.
For example, in the most widespread so called L–E system, edible frogs ''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'' (RE) produce gametes of the marsh frog ''P. ridibundus'' (R) and mate with coexisting pool frogs ''Pelophylax lessonae'' (L gametes) – see below in the middle.
 Because this hybrid requires another taxon as a sexual host to reproduce, usually one of the parental species, it is a klepton. Hence the addition of the "kl." (for ''klepton'') in the species name.
There are also known all-hybrid populations, where
Because this hybrid requires another taxon as a sexual host to reproduce, usually one of the parental species, it is a klepton. Hence the addition of the "kl." (for ''klepton'') in the species name.
There are also known all-hybrid populations, where diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively ...
hybrids (LR) coexist with triploid (LLR or LRR) hybrids, providing L or R genomes respectively. In this situation, diploid hybrids (LR) generate not only haploid R or L gametes, but also the diploid gametes (RL) needed to recreate triploids.
References
External links
ArchéoZooThèque : Edible frog skeleton drawing
Species account on HerpFrance.com
Video: Pool frogs and hybrid green frogs
on YouTube. Mixed mating of pool frog and edible frog; pool frog are grass green and smaller. {{Taxonbar, from=Q31694 Amphibia hybrids Amphibians of Europe Pelophylax Amphibians described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus