Radome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A radome (a
A radome (a
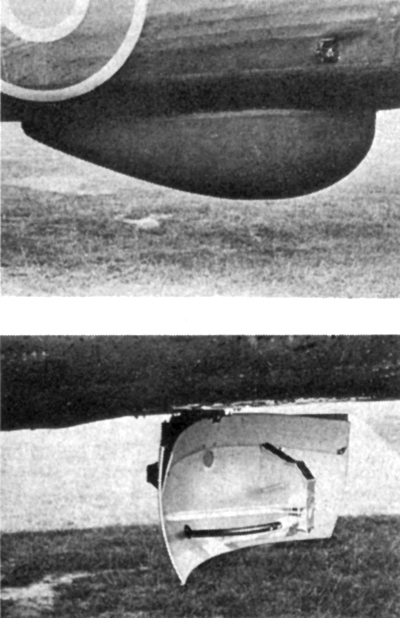 A radome is often used to prevent ice and
A radome is often used to prevent ice and
radomes.org/museum
for Baker AFS/821st Radar Squadron.
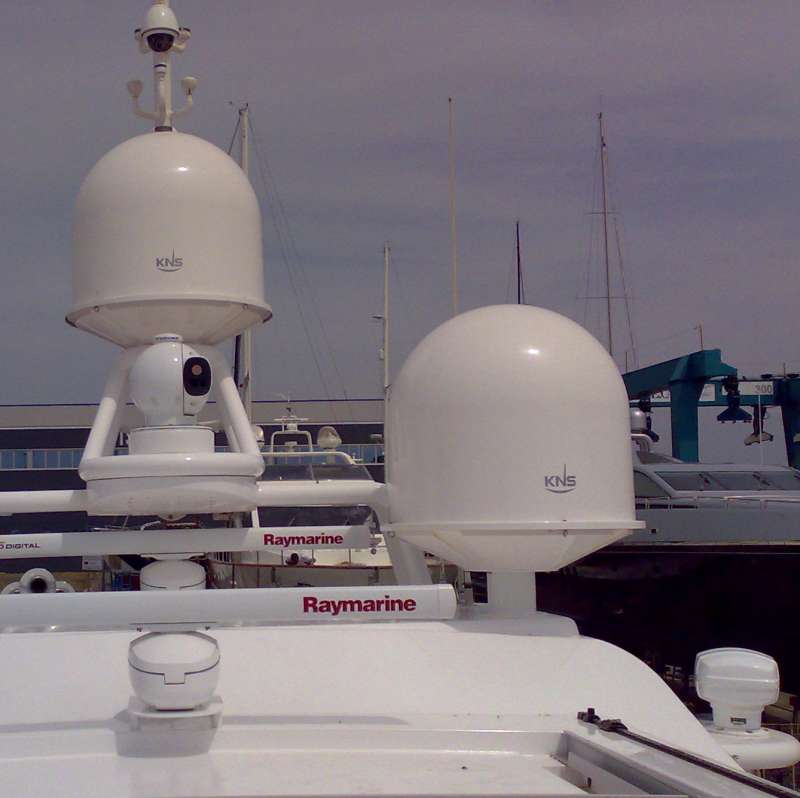 For maritime
For maritime
Photograph of Mount Hebo while active
overlooking Pacific Ocean ''(link no longer works)'' {{commons category, Radomes Radar Domes Antennas (radio) British inventions

 A radome (a
A radome (a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
of "radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
" and "dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
") is a structural, weatherproof enclosure that protects a radar antenna. The radome is constructed of material transparent to radio waves. Radomes protect the antenna from weather and conceal antenna electronic equipment from view. They also protect nearby personnel from being accidentally struck by quickly rotating antennas.
Radomes can be constructed in several shapes spherical, geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the locally shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a conn ...
, planar, etc. depending on the particular application, using various construction materials such as fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-coated fabric, and others.
In addition to radar protection, radomes on aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
platforms also act as fairings that streamline the antenna system, thus reducing drag. When found on fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using aerodynamic lift. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft (in which a rotor mounted on a spinning shaft generate ...
with forward-looking radar, as are commonly used for object or weather detection, the nose cone
A nose cone is the conically shaped forwardmost section of a rocket, guided missile or aircraft, designed to modulate oncoming fluid dynamics, airflow behaviors and minimize aerodynamic drag. Nose cones are also designed for submerged wat ...
s often additionally serve as radomes. On airborne early warning and control
An airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system is an airborne radar early warning system designed to detect aircraft, ships, vehicles, missiles and other incoming projectiles at long ranges, as well as performing command and control of the ...
(AEW&C) aircraft (e.g. the American E-3 Sentry), a discus-shaped rotating radome, often called a "rotodome", is mounted on the top of the fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French language, French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds Aircrew, crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an Aircraft engine, engine as wel ...
for 360-degree scanning coverage. Some newer AEW&C configurations instead use three 120-degree phased array
In antenna (radio), antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled Antenna array, array of antennas which creates a radio beam, beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point ...
modules inside a stationary radome, examples being the Chinese KJ-2000 and Indian DRDO AEW&Cs. On fixed-wing and rotary-wing
A rotary-wing aircraft, rotorwing aircraft or rotorcraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotor wing, rotary wings that spin around a vertical mast to generate lift (force), lift. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapt ...
aircraft using microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
for beyond-line-of-sight communication, radomes often appear as bulged "blisters" on the fuselage.
The use of radomes dates back as far as 1941.
The air supported radome built by Walter Bird in 1948 at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory is the first pneumatic construction built in history.
Use
 A radome is often used to prevent ice and
A radome is often used to prevent ice and freezing rain
Freezing rain is rain maintained at temperatures below melting point, freezing by the ambient air mass that causes freezing on contact with surfaces. Unlike rain and snow mixed, a mixture of rain and snow or ice pellets, freezing rain is made en ...
from accumulating on antennas. In the case of a spinning radar parabolic antenna
A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or p ...
, the radome also protects the antenna from debris and rotational irregularities due to wind. Its shape is easily identified by its hardshell, which has strong properties against being damaged.
Stationary antennas
For stationary antennas, excessive amounts of ice can de- tune the antenna to the point where its impedance at the inputfrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
rises drastically, causing the voltage standing wave ratio
In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the tra ...
(VSWR) to rise as well. This reflected power goes back to the transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
, where it can cause overheating. A foldback circuit can act to prevent this; however, one drawback of its use is that it causes the station's output power to drop dramatically, reducing its range. A radome avoids that by covering the antenna's exposed parts with a sturdy, weatherproof material, typically fiberglass, keeping debris or ice away from the antenna, thus preventing any serious issues. One of the main driving forces behind the development of fiberglass as a structural material was the need during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
for radomes. Gordon, J.E., The New Science of Strong Materials: 2nd Edition, Pelican, 1976. When considering structural load, the use of a radome greatly reduces wind load in both normal and iced conditions. Many tower sites require or prefer the use of radomes for wind loading benefits and for protection from falling ice or debris.
Where radomes might be considered unsightly if near the ground, electric antenna heaters could be used instead. Usually running on direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
, the heaters do not interfere physically or electrically with the alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
of the radio transmission.
Radar dishes
For radar dishes, a single, large, ball-shaped dome also protects the rotational mechanism and the sensitiveelectronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, and is heated in colder climates to prevent icing.
The RAF Menwith Hill
Royal Air Force Menwith Hill (RAF Menwith Hill) is a Royal Air Force List of Royal Air Force stations, station near Harrogate, North Yorkshire, England, which provides communications and intelligence support services to the United Kingdom and th ...
electronic surveillance base, which includes over 30 radomes, is widely believed to regularly intercept satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
communications. At Menwith Hill, the radome enclosures prevent observers from seeing the direction of the antennas, and therefore which satellites are being targeted. Similarly, radomes prevent observation of antennas used in ECHELON
Echelon may refer to:
* A level formation
** A level or rank in an organization, profession, or society
** A military sub-subunit smaller than a company but larger than a platoon
** Echelon formation, a step-like arrangement of units
* ECHELO ...
facilities.
The United States Air Force Aerospace Defense Command operated and maintained dozens of air defense radar stations in the contiguous United States and Alaska during the Cold War. Most of the radars used at these ground stations were protected by rigid or inflatable radomes. The radomes were typically at least in diameter and the radomes were attached to standardized radar tower buildings that housed the radar transmitter, receiver and antenna. Some of these radomes were very large. The CW-620 was a space frame rigid radome with a maximum diameter of , and a height of . This radome consisted of 590 panels, and was designed for winds up to . The total radome weight was with a surface area of . The CW-620 radome was designed and constructed by Sperry-Rand Corporation for the Columbus Division of North American Aviation. This radome was originally used for the FPS-35 search radar at Baker Air Force Station, Oregon. When Baker AFS was closed the radome was moved to provide a high-school gymnasium in Payette, Idaho. Pictures and documents are available online aradomes.org/museum
for Baker AFS/821st Radar Squadron.
Maritime satellites
 For maritime
For maritime satellite communications
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. ...
service, radomes are widely used to protect dish antennas which are continually tracking fixed satellites while the ship experiences pitch, roll and yaw movements. Large cruise ships and oil tankers may have radomes over 3m in diameter covering antennas for broadband transmissions for television, voice, data, and the Internet, while recent developments allow similar services from smaller installations such as the 85 cm motorised dish used in the SES Broadband for Maritime
SES Broadband for Maritime is a two-way satellite broadband Internet service for use on private boats and commercial ships throughout European waters.
SES Broadband for Maritime provides high-speed Internet access (at up to 2 Mbit/s downlink ...
system. Small private yachts may use radomes as small as 26cm in diameter for voice and low-speed data.
Alternatives
Anactive electronically scanned array
An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled antenna array in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the a ...
radar has no moving antenna and so a radome is not necessary. An example of this is the pyramid which replaced the golfball-style radome installations at RAF Fylingdales
Royal Air Force Fylingdales (RAF Fylingdales) is a Royal Air Force List of Royal Air Force stations, station on Snod Hill in the North York Moors, England. Its motto is ''Vigilamus'' ("We are watching"). It is a radar Military base, base and i ...
.
Notes
External links
Photograph of Mount Hebo while active
overlooking Pacific Ocean ''(link no longer works)'' {{commons category, Radomes Radar Domes Antennas (radio) British inventions