Radiolarians 1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are unicellular eukaryotes of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate
 In the diagram on the right, a Illustrates generalized radiolarian provinces and their relationship to water mass temperature (warm versus cool color shading) and circulation (gray arrows). Due to high-latitude water mass submergence under warm, stratified waters in lower latitudes, radiolarian species occupy habitats at multiple latitudes, and depths throughout the world oceans. Thus, marine sediments from the tropics reflect a composite of several vertically stacked faunal assemblages, some of which are contiguous with higher latitude surface assemblages. Sediments beneath polar waters include cosmopolitan deep-water radiolarians, as well as high-latitude endemic surface water species. Stars in (a) indicate the latitudes sampled, and the gray bars highlight the radiolarian assemblages included in each sedimentary composite. The horizontal purple bars indicate latitudes known for good radiolarian (silica) preservation, based on surface sediment composition. Material was copied from this source, which is available under
In the diagram on the right, a Illustrates generalized radiolarian provinces and their relationship to water mass temperature (warm versus cool color shading) and circulation (gray arrows). Due to high-latitude water mass submergence under warm, stratified waters in lower latitudes, radiolarian species occupy habitats at multiple latitudes, and depths throughout the world oceans. Thus, marine sediments from the tropics reflect a composite of several vertically stacked faunal assemblages, some of which are contiguous with higher latitude surface assemblages. Sediments beneath polar waters include cosmopolitan deep-water radiolarians, as well as high-latitude endemic surface water species. Stars in (a) indicate the latitudes sampled, and the gray bars highlight the radiolarian assemblages included in each sedimentary composite. The horizontal purple bars indicate latitudes known for good radiolarian (silica) preservation, based on surface sediment composition. Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Data show that some species were extirpated from high latitudes but persisted in the tropics during the late
File:Circogoniaicosahedra ekw.jpg, ''Circogonia icosahedra'', radiolarian species shaped like a
"Plankton - Animal plankton"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019.
File:Mikrofoto.de-Radiolarien 6.jpg, Like diatoms, radiolarians come in many shapes
File:Theocotylissa ficus Ehrenberg - Radiolarian (34638920262).jpg, Also like diatoms, radiolarian shells are usually made of silicate
File:Acantharian radiolarian Xiphacantha (Haeckel).jpg, However acantharian radiolarians have shells made from
File:Spherical radiolarian 2.jpg, Cutaway schematic diagram of a spherical radiolarian shell
File:Cladococcus abietinus.jpg, ''Cladococcus abietinus''
File:Cromyatractus tetracelyphus.jpg, ''Cromyatractus tetracelyphus'' with 2 spines
File:Circopus sexfurcus.jpg, ''Circopus sexfurcus'' with 6 spines
File:Circopurus octahedrus.jpg, ''Circopurus octahedrus'' with 6 spines and 8 faces
File:Circogonia icosahedra.jpg, ''Circogonia icosahedra'' with 12 spines and 20 faces
File:Circorrhegma dodecahedra.jpg, ''Circorrhegma dodecahedra'' with 20 (incompletely drawn) spines and 12 faces
File:Cannocapsa stethoscopium.jpg, ''Cannocapsa stethoscopium'' with 20 spines
The gallery shows images of the radiolarians as extracted from drawings made by the German zoologist and polymath
"Turing, Richards and Morphogenesis"
''
*
Radiolaria.org
*
Tree Of Life—Radiolaria
{{Authority control * Amoeboids Extant Cambrian first appearances Diaphoretickes subphyla Taxa named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
s, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm
Endoplasm, also known as entoplasm, generally refers to the inner (often granulated), dense part of a cell's cytoplasm. This is opposed to the ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm which is the outer (non-granulated) layer of the cytoplasm, which ...
and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
. They are found as zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
ic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbiont
An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), whi ...
s and are, therefore, considered mixotroph
A mixotroph is an organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than ...
s. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze
Siliceous ooze is a type of biogenic pelagic sediment located on the Abyssal, deep ocean floor. Siliceous oozes are the least common of the deep sea sediments, and make up approximately 15% of the ocean floor. Oozes are defined as sediments which ...
. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
found from the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
onwards.
Description
Radiolarians have many needle-likepseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and ...
s supported by bundles of microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
s, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
and most other organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s are in the endoplasm, while the ectoplasm is filled with frothy vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water ...
s and lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
droplets, keeping them buoyant. The radiolarian can often contain symbiotic
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biolo ...
algae, especially zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae (; zooxanthella) is a colloquial term for single-celled photosynthetic organisms that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including corals, jellyfish, demosponges, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthell ...
, which provide most of the cell's energy. Some of this organization is found among the heliozoa
Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes (protists) with stiff arms (Pseudopodia#Morphology, axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule- ...
, but those lack central capsules and only produce simple scales and spines.
Some radiolarians are known for their resemblance to regular polyhedra
A regular polyhedron is a polyhedron whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags. A regular polyhedron is highly symmetrical, being all of edge-transitive, vertex-transitive and face-transitive. In classical contexts, many different eq ...
, such as the icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons".
There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical tha ...
-shaped ''Circogonia icosahedra'' pictured below.
Taxonomy
The radiolarians belong to the supergroupRhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera ...
together with (amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and r ...
or flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and the ...
) Cercozoa
Cercozoa (now synonymised with Filosa) is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by phylogeny, molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or Ubiqu ...
and (shelled amoeboid) Foraminifera
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell bio ...
. Traditionally the radiolarians have been divided into four groups—Acantharea
The Acantharia are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine Plankton, microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several milli ...
, Nassellaria
Nassellaria is an order of Rhizaria belonging to the class Radiolaria. The organisms of this order are characterized by a skeleton cross link with a cone or ring.
Introduction
Nassellaria is an order of Radiolaria under the class Polycystina. ...
, Spumellaria
Spumellaria is an order of radiolarians in the class Polycystinea. They are ameboid protists appearing in abundance in the world's oceans, possessing a radially-symmetrical silica (opal) skeleton that has ensured their preservation in fossil re ...
and Phaeodarea
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They a ...
. Phaeodaria is however now considered to be a Cercozoan. Nassellaria and Spumellaria both produce siliceous skeletons and were therefore grouped together in the group Polycystina. Despite some initial suggestions to the contrary, this is also supported by molecular phylogenies. The Acantharea produce skeletons of strontium sulfate
Strontium sulfate (SrSO4) is the sulfate salt of strontium. It is a white crystalline powder and occurs in nature as the mineral celestine. It is poorly soluble in water to the extent of 1 part in 8,800. It is more soluble in dilute HCl and nitr ...
and is closely related to a peculiar genus, ''Sticholonche
''Sticholonche'' is a genus of radiolarians with a single species, ''Sticholonche zanclea'', found in open oceans at depths of 99–510 metres. It is generally considered a heliozoan, placed in its own order, called the Taxopodida. However it h ...
'' (Taxopodida
''Sticholonche'' is a genus of radiolarians with a single species, ''Sticholonche zanclea'', found in open oceans at depths of 99–510 metres. It is generally considered a heliozoan, placed in its own order, called the Taxopodida. However it h ...
), which lacks an internal skeleton and was for long time considered a heliozoa
Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes (protists) with stiff arms (Pseudopodia#Morphology, axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule- ...
n. The Radiolaria can therefore be divided into two major lineages: Polycystina (Spumellaria + Nassellaria) and Spasmaria (Acantharia + Taxopodida).
There are several higher-order groups that have been detected in molecular analyses of environmental data. Particularly, groups related to Acantharia and Spumellaria. These groups are so far completely unknown in terms of morphology and physiology and the radiolarian diversity is therefore likely to be much higher than what is currently known.
The relationship between the Foraminifera and Radiolaria is also debated. Molecular trees support their close relationship—a grouping termed Retaria. But whether they are sister lineages or whether the Foraminifera should be included within the Radiolaria is not known.
Biogeography
 In the diagram on the right, a Illustrates generalized radiolarian provinces and their relationship to water mass temperature (warm versus cool color shading) and circulation (gray arrows). Due to high-latitude water mass submergence under warm, stratified waters in lower latitudes, radiolarian species occupy habitats at multiple latitudes, and depths throughout the world oceans. Thus, marine sediments from the tropics reflect a composite of several vertically stacked faunal assemblages, some of which are contiguous with higher latitude surface assemblages. Sediments beneath polar waters include cosmopolitan deep-water radiolarians, as well as high-latitude endemic surface water species. Stars in (a) indicate the latitudes sampled, and the gray bars highlight the radiolarian assemblages included in each sedimentary composite. The horizontal purple bars indicate latitudes known for good radiolarian (silica) preservation, based on surface sediment composition. Material was copied from this source, which is available under
In the diagram on the right, a Illustrates generalized radiolarian provinces and their relationship to water mass temperature (warm versus cool color shading) and circulation (gray arrows). Due to high-latitude water mass submergence under warm, stratified waters in lower latitudes, radiolarian species occupy habitats at multiple latitudes, and depths throughout the world oceans. Thus, marine sediments from the tropics reflect a composite of several vertically stacked faunal assemblages, some of which are contiguous with higher latitude surface assemblages. Sediments beneath polar waters include cosmopolitan deep-water radiolarians, as well as high-latitude endemic surface water species. Stars in (a) indicate the latitudes sampled, and the gray bars highlight the radiolarian assemblages included in each sedimentary composite. The horizontal purple bars indicate latitudes known for good radiolarian (silica) preservation, based on surface sediment composition. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Data show that some species were extirpated from high latitudes but persisted in the tropics during the late
Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of th ...
, either by migration or range restriction (b). With predicted global warming, modern Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
species will not be able to use migration or range contraction to escape environmental stressors, because their preferred cold-water habitats are disappearing from the globe (c). However, tropical endemic species may expand their ranges toward midlatitudes. The color polygons in all three panels represent generalized radiolarian biogeographic provinces, as well as their relative water mass temperatures (cooler colors indicate cooler temperatures, and vice versa).
regular icosahedron
The regular icosahedron (or simply ''icosahedron'') is a convex polyhedron that can be constructed from pentagonal antiprism by attaching two pentagonal pyramids with Regular polygon, regular faces to each of its pentagonal faces, or by putting ...
File:Anthocyrtium hispidum Haeckel - Radiolarian (34986365113).jpg, ''Anthocyrtium hispidum Haeckel''
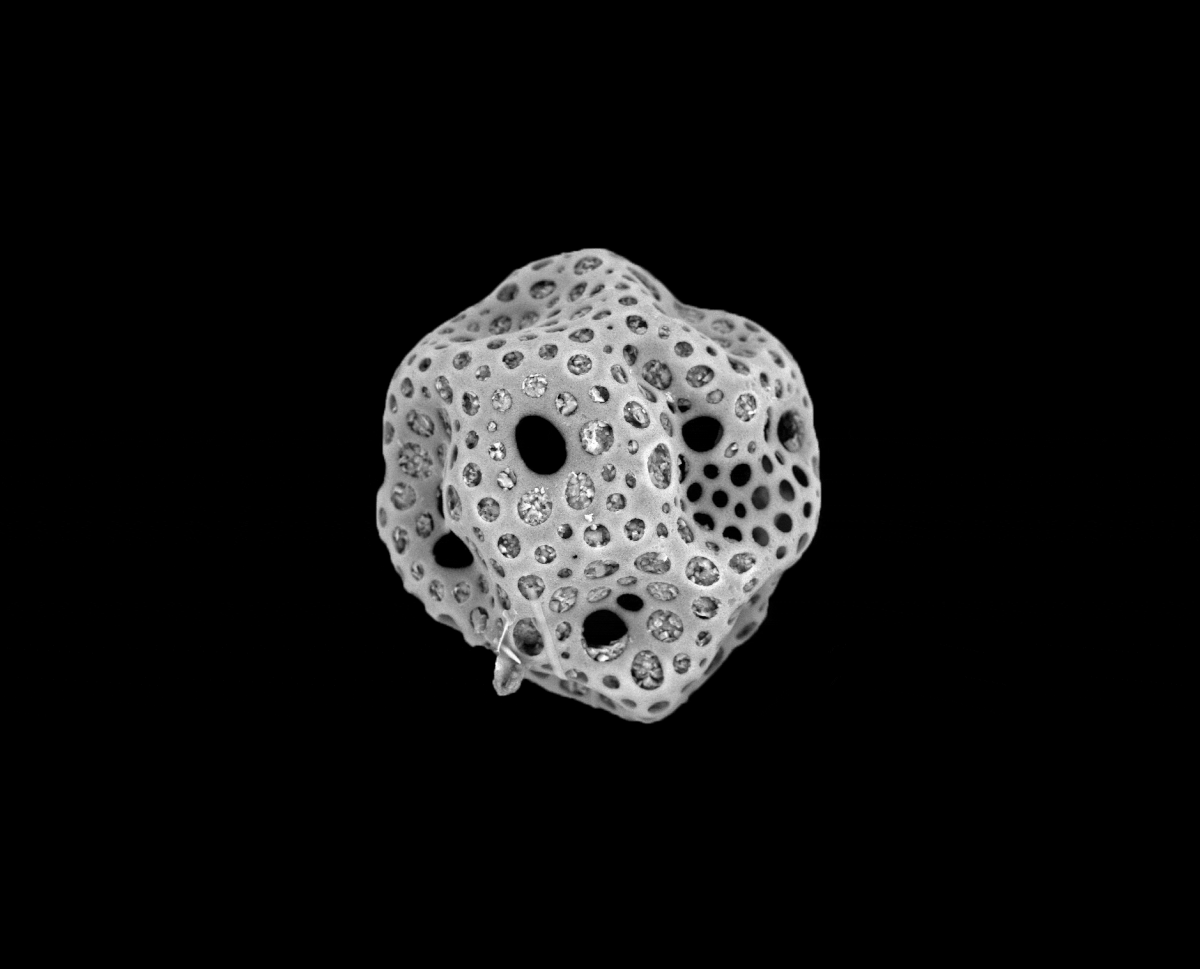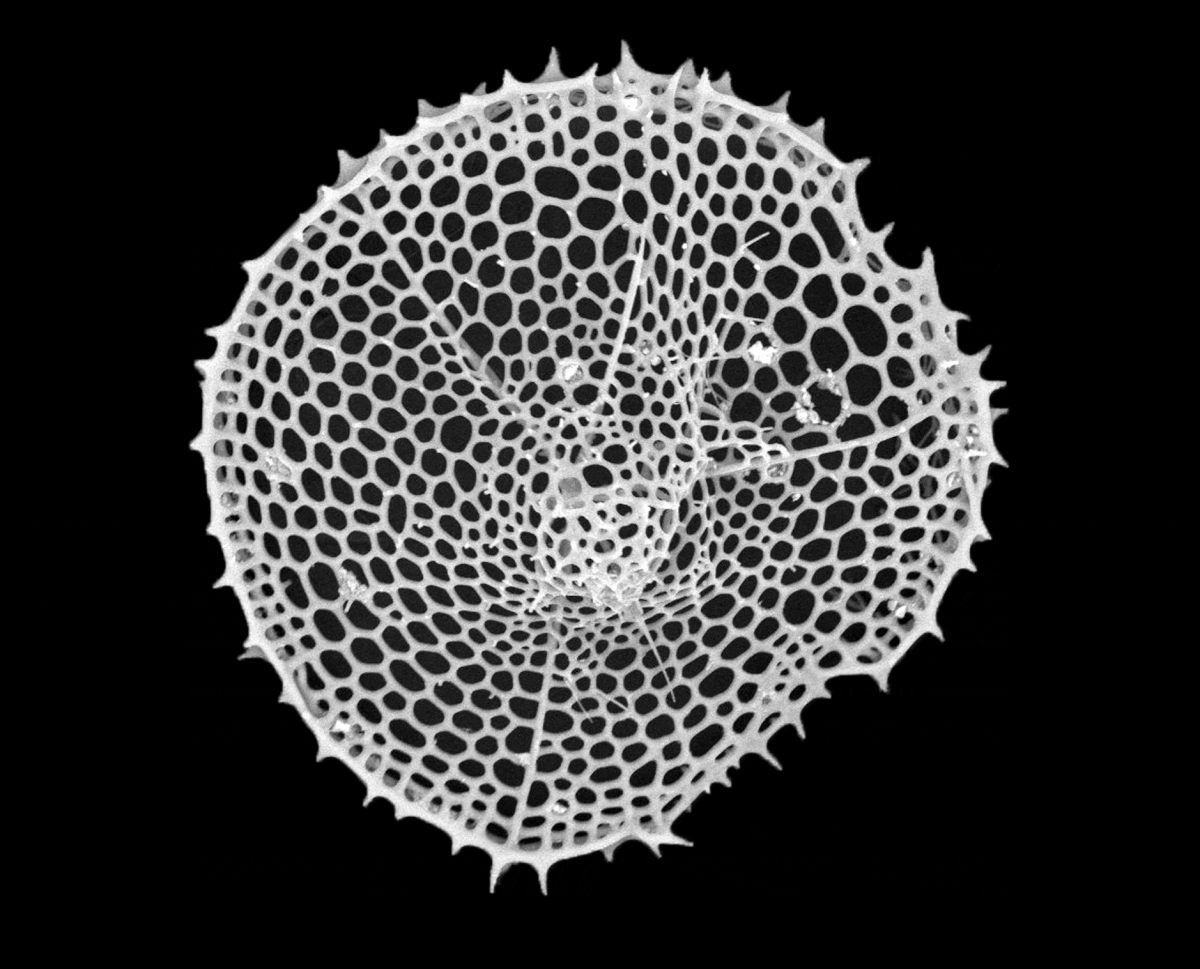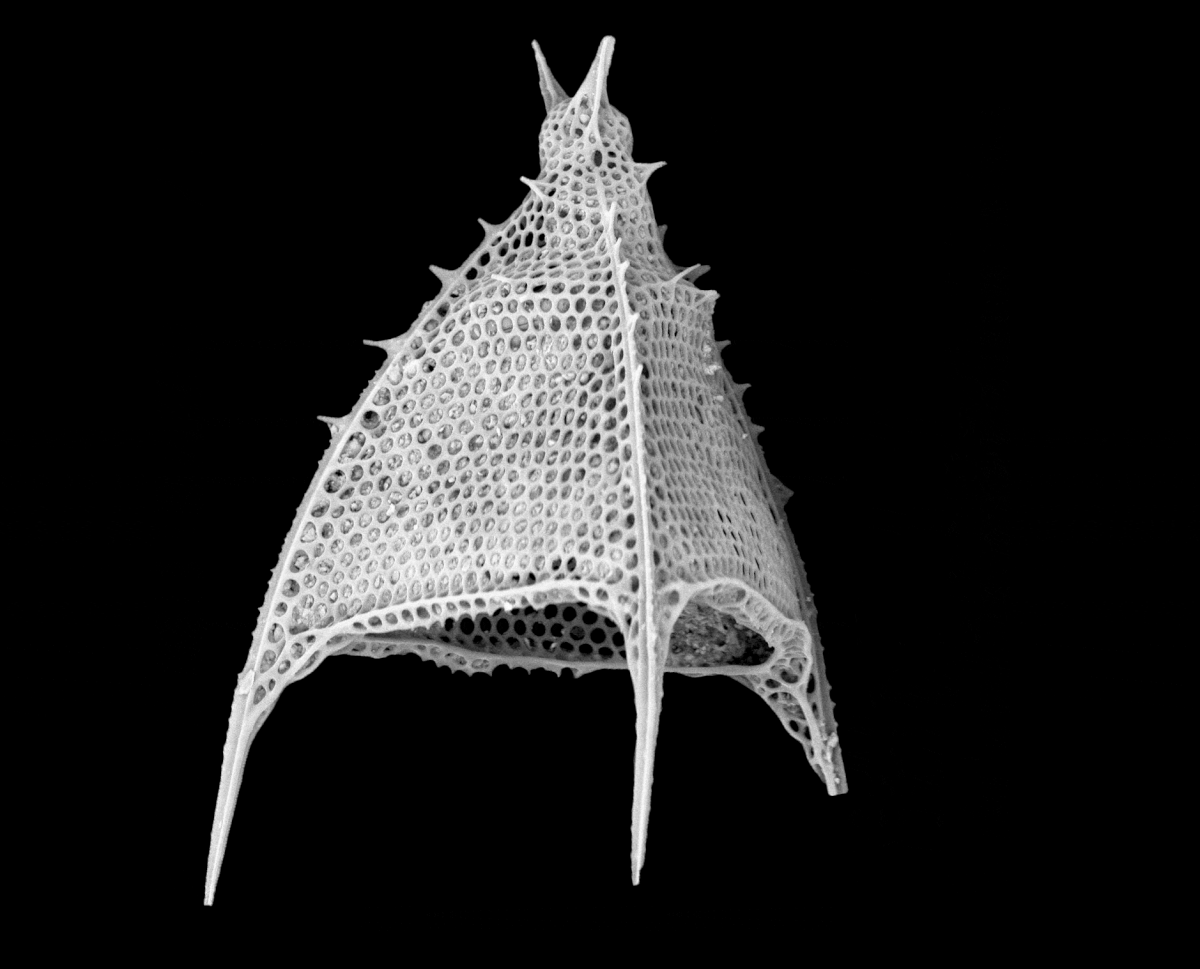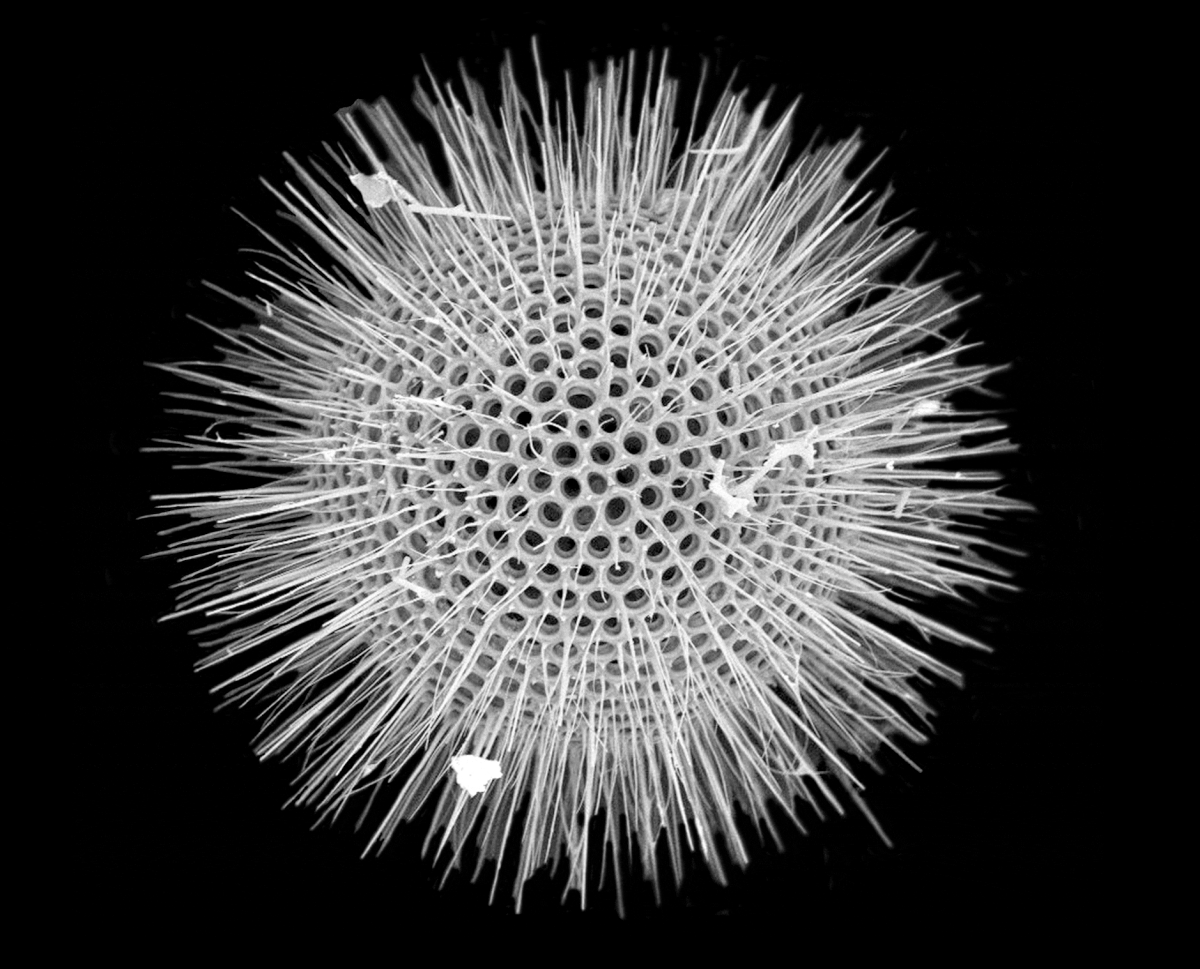
Radiolarian shells
Radiolarians are unicellular predatoryprotists
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants o ...
encased in elaborate globular shells (or "capsules"), usually made of silica and pierced with holes. Their name comes from the Latin for "radius". They catch prey by extending parts of their body through the holes. As with the silica frustules of diatoms, radiolarian shells can sink to the ocean floor when radiolarians die and become preserved as part of the ocean sediment. These remains, as microfossils
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, ...
, provide valuable information about past oceanic conditions.Wassilieff, Maggy (2006"Plankton - Animal plankton"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019.
strontium sulfate
Strontium sulfate (SrSO4) is the sulfate salt of strontium. It is a white crystalline powder and occurs in nature as the mineral celestine. It is poorly soluble in water to the extent of 1 part in 8,800. It is more soluble in dilute HCl and nitr ...
crystals

Diversity and morphogenesis
Bernard Richards, worked under the supervision ofAlan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer ...
(1912–1954) at Manchester as one of Turing's last students, helping to validate Turing’s theory of morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
.
"Turing was keen to take forward the work that D’Arcy Thompson
Sir D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson CB FRS FRSE (2 May 1860 – 21 June 1948) was a Scottish biologist, mathematician and classics scholar. He was a pioneer of mathematical and theoretical biology, travelled on expeditions to the Bering Strait a ...
had published in On Growth and Form
''On Growth and Form'' is a book by the Scottish mathematical biology, mathematical biologist D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson (1860–1948). The book is long – 793 pages in the first edition of 1917, 1116 pages in the second edition of 1942.
The ...
in 1917".
Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; ; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, natural history, naturalist, eugenics, eugenicist, Philosophy, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biology, marine biologist and artist ...
in 1887.
*
* Richards, Bernard (2005-2006"Turing, Richards and Morphogenesis"
''
The Rutherford Journal
Brian Jack Copeland (born 1950) is Professor of Philosophy at the University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, and author of books on the computing pioneer Alan Turing.
Education
Copeland was educated at the University of Oxford, obta ...
'', Volume 1.
Fossil record
The earliest known radiolaria date to the very start of theCambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
period, appearing in the same beds as the first small shelly fauna
The small shelly fauna, small shelly fossils (SSF), or early skeletal fossils (ESF) are mineralized fossils, many only a few millimetres long, with a nearly continuous record from the latest stages of the Ediacaran to the end of the Early Cambri ...
—they may even be terminal Precambrian in age. They have significant differences from later radiolaria, with a different silica lattice structure and few, if any, spikes on the test
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film) ...
. About ninety percent of known radiolarian species are extinct. The skeletons, or tests, of ancient radiolarians are used in geological dating
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is pr ...
, including for oil exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for hydrocarbon deposits, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.
Exploration methods
V ...
and determination of ancient climates.
Some common radiolarian fossils include '' Actinomma'', '' Heliosphaera'' and '' Hexadoridium''.
See also
*Radiolarite
Radiolarite is a Siliceous ooze, siliceous, comparatively hard, fine-grained, chert-like, and homogeneous sedimentary rock that is composed predominantly of the microscopic remains of radiolarians. This term is also used for Friability, indurat ...
References
* * * *External links
*Radiolarians*
Radiolaria.org
*
{{Authority control * Amoeboids Extant Cambrian first appearances Diaphoretickes subphyla Taxa named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith