R Foundation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
R is a

> install.packages("tidyverse")
To load the functions, data, and documentation of a package, one calls the
> # The package name can be enclosed in quotes
> library("tidyverse")
> # But the package name can also be used without quotes
> library(tidyverse)
The
Task Views
area lists packages that are relevant for specific topics; sample topics include
website
* Directions in Statistical Computing (DSC)
website
* R-Ladies: an organization to promote gender diversity in the R community
website
* SatRdays: R-focused conferences held on Saturdays
website
* R Conference
website
* posit::conf (formerly known as rstudio::conf)
website
On social media sites such as Twitter, the hashtag
> print("Hello, World!")
[1] "Hello, World!" Here is an alternative version, which uses the
> cat("Hello, World!")
Hello, World!
> x <- 1:6 # Create a numeric vector in the current environment
> y <- x^2 # Similarly, create a vector based on the values in x.
> print(y) # Print the vector’s contents.
[1] 1 4 9 16 25 36
> z <- x + y # Create a new vector that is the sum of x and y
> z # Return the contents of z to the current environment.
[1] 2 6 12 20 30 42
> z_matrix <- matrix(z, nrow = 3) # Create a new matrix that transforms the vector z into a 3x2 matrix object
> z_matrix
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 2 20
[2,] 6 30
[3,] 12 42
> 2 * t(z_matrix) - 2 # Transpose the matrix; multiply every element by 2; subtract 2 from each element in the matrix; and then return the results to the terminal.
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 2 10 22
[2,] 38 58 82
> new_df <- data.frame(t(z_matrix), row.names = c("A", "B")) # Create a new dataframe object that contains the data from a transposed z_matrix, with row names 'A' and 'B'
> names(new_df) <- c("X", "Y", "Z") # Set the column names of the new_df dataframe as X, Y, and Z.
> print(new_df) # Print the current results.
X Y Z
A 2 6 12
B 20 30 42
> new_df$Z # Output the Z column
[1] 12 42
> new_df$Z new_df['Z'] && new_df[3] new_df$Z # The dataframe column Z can be accessed using the syntax $Z, ['Z'], or [3], and the values are the same.
[1] TRUE
> attributes(new_df) # Print information about attributes of the new_df dataframe
$names
[1] "X" "Y" "Z"
$row.names
[1] "A" "B"
$class
[1] "data.frame"
> attributes(new_df)$row.names <- c("one", "two") # Access and then change the row.names attribute; this can also be done using the rownames() function
> new_df
X Y Z
one 2 6 12
two 20 30 42
# The function's input parameters are x and y.
# The function, named f, returns a linear combination of x and y.
f <- function(x, y)
# As an alternative, the last statement executed in a function is returned implicitly.
f <- function(x, y) 3 * x + 4 * y
The following is some output from using the function defined above:
> f(1, 2) # 3 * 1 + 4 * 2 = 3 + 8
[1] 11
> f(c(1, 2, 3), c(5, 3, 4)) # Element-wise calculation
[1] 23 18 25
> f(1:3, 4) # Equivalent to f(c(1, 2, 3), c(4, 4, 4))
[1] 19 22 25
It is possible to define functions to be used as Infix notation, infix operators by using the special syntax
> `%sumx2y2%` <- function(e1, e2)
> 1:3 %sumx2y2% -(1:3)
[1] 2 8 18
Since R version 4.1.0, functions can be written in a short notation, which is useful for passing anonymous functions to higher-order functions:
> sapply(1:5, \(i) i^2) # here \(i) is the same as function(i)
[1] 1 4 9 16 25
> nrow(subset(mtcars, cyl 4)) # Nested without the pipe character
[1] 11
> mtcars , > subset(cyl 4) , > nrow() # Using the pipe character
[1] 11
Another alternative to nested functions is the use of intermediate objects, rather than the pipe operator:
> mtcars_subset_rows <- subset(mtcars, cyl 4)
> num_mtcars_subset <- nrow(mtcars_subset_rows)
> print(num_mtcars_subset)
[1] 11
While the pipe operator can produce code that is easier to read, it is advisable to chain together at most 10-15 lines of code using this operator, as well as to chunk code into Task (project management), sub-tasks that are saved into objects having meaningful names.
The following is an example having fewer than 10 lines, which some readers may find difficult to grasp in the absence of intermediate named steps:(\(x, n = 42, key = c(letters, LETTERS, " ", ":", ")"))
strsplit(x, "")1 , >
(Vectorize(\(chr) which(chr key) - 1))() , >
(`+`)(n) , >
(`%%`)(length(key)) , >
(\(i) key[i + 1])() , >
paste(collapse = "")
)("duvFkvFksnvEyLkHAErnqnoyr") The following is a version of the preceding code that is easier to read:
default_key <- c(letters, LETTERS, " ", ":", ")")
f <- function(x, n = 42, key = default_key)
f("duvFkvFksnvEyLkHAErnqnoyr")
> data <- c("a", "b", "c", "a", NA)
> summary(data)
Length Class Mode
5 character character
> summary(as.factor(data))
a b c NA's
2 1 1 1
 The R language has built-in support for data modeling and graphics. The following example shows how R can generate and plot a linear model with residuals.
The R language has built-in support for data modeling and graphics. The following example shows how R can generate and plot a linear model with residuals.
# Create x and y values
x <- 1:6
y <- x^2
# Linear regression model: y = A + B * x
model <- lm(y ~ x)
# Display an in-depth summary of the model
summary(model)
# Create a 2-by-2 layout for figures
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
# Output diagnostic plots of the model
plot(model)
The output from the
Residuals:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
3.3333 -0.6667 -2.6667 -2.6667 -0.6667 3.3333
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>, t, )
(Intercept) -9.3333 2.8441 -3.282 0.030453 *
x 7.0000 0.7303 9.585 0.000662 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3.055 on 4 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9583, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9478
F-statistic: 91.88 on 1 and 4 DF, p-value: 0.000662
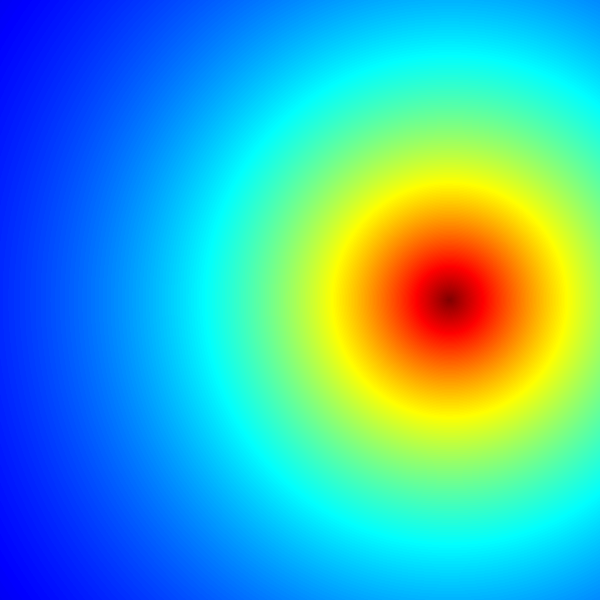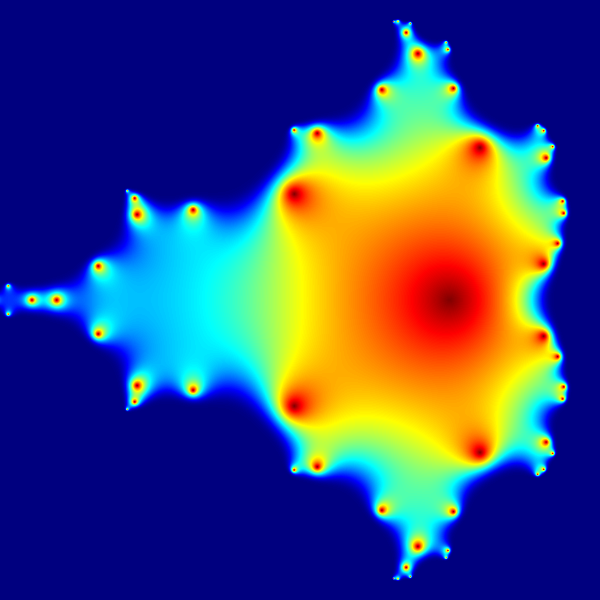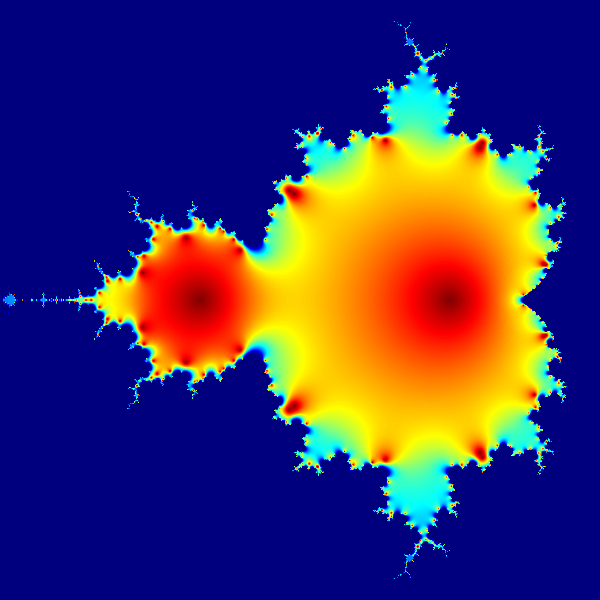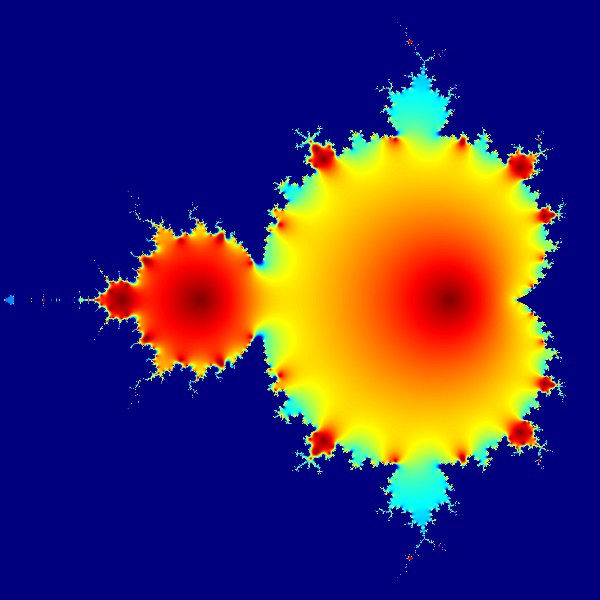 This example of a Mandelbrot set highlights the use of complex numbers. It models the first 20 iterations of the equation
This example of a Mandelbrot set highlights the use of complex numbers. It models the first 20 iterations of the equation
install.packages("caTools")
The sample code is as follows:
library(caTools)
jet.colors <-
colorRampPalette(
c("green", "pink", "#007FFF", "cyan", "#7FFF7F",
"white", "#FF7F00", "red", "#7F0000"))
dx <- 1500 # define width
dy <- 1400 # define height
C <-
complex(
real = rep(seq(-2.2, 1.0, length.out = dx), each = dy),
imag = rep(seq(-1.2, 1.2, length.out = dy), times = dx)
)
# reshape as matrix of complex numbers
C <- matrix(C, dy, dx)
# initialize output 3D array
X <- array(0, c(dy, dx, 20))
Z <- 0
# loop with 20 iterations
for (k in 1:20)
write.gif(
X,
"Mandelbrot.gif",
col = jet.colors,
delay = 100)
 All R version releases from 2.14.0 onward have Code name, codenames that make reference to Peanuts comics and films.
In 2018, core R developer Peter Dalgaard presented a history of R releases since 1997. Some notable early releases before the named releases include the following:
* Version 1.0.0, released on 29 February 2000, a Leap days, leap day
* Version 2.0.0, released on 4 October 2004, "which at least had a nice ring to it"
The idea of naming R version releases was inspired by the naming system for Debian version history, Debian and Ubuntu version history, Ubuntu versions. Dalgaard noted an additional reason for the use of Peanuts references in R codenames—the humorous observation that "everyone in statistics is a P-value, P-nut."
All R version releases from 2.14.0 onward have Code name, codenames that make reference to Peanuts comics and films.
In 2018, core R developer Peter Dalgaard presented a history of R releases since 1997. Some notable early releases before the named releases include the following:
* Version 1.0.0, released on 29 February 2000, a Leap days, leap day
* Version 2.0.0, released on 4 October 2004, "which at least had a nice ring to it"
The idea of naming R version releases was inspired by the naming system for Debian version history, Debian and Ubuntu version history, Ubuntu versions. Dalgaard noted an additional reason for the use of Peanuts references in R codenames—the humorous observation that "everyone in statistics is a P-value, P-nut."
StatET plugin
** Microsoft Visual Studio, Visual Studio via R Tools for Visual Studio. * Source-code editor, Source-code editors: ** Emacs Speaks Statistics, Emacs ** Vim (text editor), Vim via th
Nvim-R plugin
** Kate (text editor), Kate ** LyX via Sweave ** WinEdt
website
**
website
* Other scripting languages: ** Python (programming language), Python
website
** Perl
website
** Ruby (programming language), Ruby
source code
** F Sharp (programming language), F#
website
** Julia (programming language), Julia
source code
. * General-purpose programming languages: ** Java (programming language), Java via th
Rserve socket server
** C Sharp (programming language), .NET C#
website
Statistical frameworks that use R in the background include Jamovi and JASP.
pretty quick R
(pqR), by Radford M. Neal, which attempts to improve memory management. * Renjin for the Java virtual machine, Java Virtual Machine.
CXXR
and Riposte written in C++. * Oracle Corporation, Oracle's]
FastR
built o
GraalVM
* TIBCO Software, TIBCO Enterprise Runtime for R (TERR) to integrate with Spotfire. (The company also created S-PLUS, S-Plus, an implementation of the S language.) Microsoft R Open (MRO) was an R implementation. As of 30 June 2021, Microsoft began to phase out MRO in favor of the CRAN distribution.
R Technical Papers
Big Book of R
curated list of R-related programming books
partially annotated curated list of books relating to R or S. {{Authority control R (programming language), Array programming languages Cross-platform free software Data mining and machine learning software Data-centric programming languages Dynamically typed programming languages Free plotting software Free statistical software Functional languages GNU Project software Literate programming Numerical analysis software for Linux Numerical analysis software for macOS Numerical analysis software for Windows Programming languages created in 1993 Science software Statistical programming languages Articles with example R code
programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
for statistical computing
Computational statistics, or statistical computing, is the study which is the intersection of statistics and computer science, and refers to the statistical methods that are enabled by using computational methods. It is the area of computational ...
and data visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating Graphics, graphic or visual Representation (arts), representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and i ...
. It has been widely adopted in the fields of data mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and ...
, bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, ...
, data analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, Data cleansing, cleansing, Data transformation, transforming, and Data modeling, modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Da ...
, and data science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, stru ...
.
The core R language is extended by a large number of software packages, which contain reusable code, documentation, and sample data. Some of the most popular R packages are in the tidyverse
The tidyverse is a collection of open source packages for the R programming language introduced by Hadley Wickham and his team that "share an underlying design philosophy, grammar, and data structures" of tidy data. Characteristic features of t ...
collection, which enhances functionality for visualizing, transforming, and modelling data, as well as improves the ease of programming (according to the authors and users).
R is free and open-source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term encompassing free ...
distributed under the GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first ...
. The language is implemented primarily in C, Fortran, and R itself. Precompiled executable
In computer science, executable code, an executable file, or an executable program, sometimes simply referred to as an executable or binary, causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instruction (computer science), in ...
s are available for the major operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s (including Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, MacOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
, and Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
).
Its core is an interpreted language
In computer science, an interpreter is a computer program that directly executes instructions written in a programming or scripting language, without requiring them previously to have been compiled into a machine language program. An inter ...
with a native command line interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternati ...
. In addition, multiple third-party
Third party may refer to:
Business
* Third-party source, a supplier company not owned by the buyer or seller
* Third-party beneficiary, a person who could sue on a contract, despite not being an active party
* Third-party insurance, such as a veh ...
applications are available as graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
s; such applications include RStudio
RStudio IDE (or RStudio) is an integrated development environment for R, a programming language for statistical computing and graphics. It's available in two formats: RStudio Desktop is a regular desktop application while RStudio Server runs ...
(an integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
) and Jupyter
Project Jupyter (pronounced "Jupiter") is a project to develop open-source software, open standards, and services for interactive computing across multiple programming languages.
It was spun off from IPython in 2014 by Fernando Pérez and Brian ...
(a notebook interface
A notebook interface or computational notebook is a virtual notebook environment used for literate programming, a method of writing computer programs. Some notebooks are WYSIWYG environments including executable calculations embedded in formatte ...
).
History
R was started by professorsRoss Ihaka
George Ross Ihaka (born 1954) is a Māori people, Māori New Zealander statistician who was an associate professor of statistics at the University of Auckland until his retirement in 2017. Alongside Robert Gentleman (statistician), Robert Gentle ...
and Robert Gentleman as a programming language to teach introductory statistics at the University of Auckland
The University of Auckland (; Māori: ''Waipapa Taumata Rau'') is a public research university based in Auckland, New Zealand. The institution was established in 1883 as a constituent college of the University of New Zealand. Initially loc ...
. The language was inspired by the S programming language
S is a statistical programming language developed primarily by John Chambers and (in earlier versions) Rick Becker, Trevor Hastie, William Cleveland and Allan Wilks of Bell Laboratories. The aim of the language, as expressed by John Chambers, i ...
, with most S programs able to run unaltered in R. The language was also inspired by Scheme's lexical scoping
In computer programming, the scope of a name binding (an association of a name to an entity, such as a variable) is the part of a program where the name binding is valid; that is, where the name can be used to refer to the entity. In other parts ...
, allowing for local variable
In computer science, a local variable is a variable that is given ''local scope''. A local variable reference in the function or block in which it is declared overrides the same variable name in the larger scope. In programming languages with ...
s.
The name of the language, R, comes from being both an S language successor and the shared first letter of the authors, Ross and Robert. In August 1993, Ihaka and Gentleman posted a binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical op ...
file of R on StatLib — a data archive website. At the same time, they announced the posting on the ''s-news'' mailing list. On 5 December 1997, R became a GNU project
The GNU Project ( ) is a free software, mass collaboration project announced by Richard Stallman on September 27, 1983. Its goal is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and Computer hardware, computing dev ...
when version 0.60 was released. On 29 February 2000, the 1.0 version was released.
Packages
R package
R packages are extensions to the R statistical programming language. R packages contain code, data, and documentation in a standardised collection format that can be installed by users of R, typically via a centralised software repository such a ...
s are collections of functions, documentation, and data that expand R. For example, packages can add reporting features (using packages such as RMarkdown
RStudio IDE (or RStudio) is an integrated development environment for R, a programming language for statistical computing and graphics. It's available in two formats: RStudio Desktop is a regular desktop application while RStudio Server runs ...
, Quarto, knitr
knitr is a software engine for dynamic report generation with R. It is a package in the programming language R that enables integration of R code into LaTeX, LyX, HTML, Markdown, AsciiDoc, and reStructuredText documents. The purpose of knitr is ...
, and Sweave) and support for various statistical techniques (such as linear
In mathematics, the term ''linear'' is used in two distinct senses for two different properties:
* linearity of a '' function'' (or '' mapping'');
* linearity of a '' polynomial''.
An example of a linear function is the function defined by f(x) ...
, generalized linear and nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathe ...
modeling, classical statistical tests
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data provide sufficient evidence to reject a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic. T ...
, spatial analysis, time-series analysis
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Ex ...
, and clustering). Ease of package installation and use have contributed to the language's adoption in data science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, stru ...
.
Immediately available when starting R after installation, base packages provide the fundamental and necessary syntax and commands for programming, computing, graphics production, basic arithmetic
Elementary arithmetic is a branch of mathematics involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Due to its low level of abstraction, broad range of application, and position as the foundation of all mathematics, elementary arithm ...
, and statistical functionality.
An example is the tidyverse
The tidyverse is a collection of open source packages for the R programming language introduced by Hadley Wickham and his team that "share an underlying design philosophy, grammar, and data structures" of tidy data. Characteristic features of t ...
collection of R packages, which bundles several subsidiary packages to provide a common API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
. The collection specializes in tasks related to accessing and processing " tidy data", which are data contained in a two-dimensional
A two-dimensional space is a mathematical space with two dimensions, meaning points have two degrees of freedom: their locations can be locally described with two coordinates or they can move in two independent directions. Common two-dimension ...
table with a single row for each observation
Observation in the natural sciences is an act or instance of noticing or perceiving and the acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the percep ...
and a single column for each variable.
Installing a package occurs only once. For example, to install the tidyverse collection:
library() function. To load the tidyverse collection, one can execute the following code:
Comprehensive R Archive Network
R packages are extensions to the R statistical programming language. R packages contain code, data, and documentation in a standardised collection format that can be installed by users of R, typically via a centralised software repository such as ...
(CRAN) was founded in 1997 by Kurt Hornik and Friedrich Leisch to host R's source code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
, executable files, documentation, and user-created packages. CRAN's name and scope mimic the Comprehensive TeX Archive Network (CTAN) and the Comprehensive Perl Archive Network
The Comprehensive Perl Archive Network (CPAN) is a software repository of over 220,000 software modules and accompanying documentation for 45,500 distributions, written in the Perl programming language by over 14,500 contributors. ''CPAN'' can de ...
(CPAN). CRAN originally had only three mirror sites and twelve contributed packages. , it has 99 mirrors and 21,513 contributed packages. Packages are also available in repositories such as R-Forge, Omegahat, and GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug trackin ...
.
To provide guidance on the CRAN web site, itTask Views
area lists packages that are relevant for specific topics; sample topics include
causal inference
Causal inference is the process of determining the independent, actual effect of a particular phenomenon that is a component of a larger system. The main difference between causal inference and inference of association is that causal inference an ...
, finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, high-performance computing
High-performance computing (HPC) is the use of supercomputers and computer clusters to solve advanced computation problems.
Overview
HPC integrates systems administration (including network and security knowledge) and parallel programming into ...
, machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
, meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
, social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
s, and spatial statistics
Spatial statistics is a field of applied statistics dealing with spatial data.
It involves stochastic processes (random fields, point processes), sampling, smoothing and interpolation, regional ( areal unit) and lattice ( gridded) data, poin ...
.
The Bioconductor
Bioconductor is a free, open source and open development software project for the analysis and comprehension of genomic data generated by wet lab experiments in molecular biology.
Bioconductor is based primarily on the statistical R programming ...
project provides packages for genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, ...
data analysis, complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA that was reverse transcribed (via reverse transcriptase) from an RNA (e.g., messenger RNA or microRNA). cDNA exists in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms and in both natural and engin ...
, microarray
A microarray is a multiplex (assay), multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of biological interactions. It is a two-dimensional array on a Substrate (materials science), solid substrate—usu ...
, and high-throughput sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
methods.
Community
There are three main groups that help support R software development: * The R Core Team was founded in 1997 to maintain the Rsource code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
.
* The R Foundation for Statistical Computing was founded in April 2003 to provide financial support.
* The R Consortium is a Linux Foundation
The Linux Foundation (LF) is a non-profit organization established in 2000 to support Linux development and open-source software projects.
Background
The Linux Foundation started as Open Source Development Labs in 2000 to standardize and prom ...
project to develop R infrastructure.
''The R Journal
''The R Journal'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal published by The R Foundation since 2009. It publishes research articles in statistical computing that are of interest to users of the R programming language. The journal includes ...
'' is an open access
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which nominally copyrightable publications are delivered to readers free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 de ...
, academic journal that features short to medium-length articles on the use and development of R. The journal includes articles on packages, programming tips, CRAN news, and foundation news.
The R community hosts many conferences and in-person meetups. These groups include:
* UseR!: an annual international R user conferencewebsite
* Directions in Statistical Computing (DSC)
website
* R-Ladies: an organization to promote gender diversity in the R community
website
* SatRdays: R-focused conferences held on Saturdays
website
* R Conference
website
* posit::conf (formerly known as rstudio::conf)
website
On social media sites such as Twitter, the hashtag
#rstats can be used to follow new developments in the R community.
Examples
Hello, World!
The following is a "Hello, World!" program:cat() function:Basic syntax
The following examples illustrate the basic programming language syntax, syntax of the language and use of the command-line interface. In R, the generally preferred Assignment (computer science), assignment operator is an arrow made from two characters<-, although = can be used in some cases.
Structure of a function
R is able to create Function (computer programming), functions that add new functionality for code reuse. Object (computer science), Objects created within the body of the function (which are enclosed by curly brackets) remain Local variable, accessible only from within the function, and any data type may be returned. In R, almost all functions and all user-defined functions are closure (computer programming), closures. The following is an example of creating a function to perform an arithmetic calculation:`%name%`, where "name" is the function variable name:
Native pipe operator
In R version 4.1.0, a native Pipeline (computing), pipe operator,, >, was introduced. This operator allows users to chain functions together, rather than using nested function calls.
Object-oriented programming
The R language has native support for object-oriented programming. There are two native Application framework, frameworks, the so-called S3 and S4 systems. The former, being more informal, supports single dispatch on the first argument, and objects are assigned to a class simply by setting a "class" attribute in each object. The latter is a system like the CLOS, Common Lisp Object System (CLOS), with formal classes (also derived from S (programming language)#S4, S) and generic methods, which supports multiple dispatch and multiple inheritance In the example below,summary() is a generic function that dispatches to different methods depending on whether its Argument of a function, argument is a numeric Vector (mathematics and physics), vector or a ''factor'':
Modeling and plotting
summary() function in the preceding code block is as follows:
Mandelbrot set
 This example of a Mandelbrot set highlights the use of complex numbers. It models the first 20 iterations of the equation
This example of a Mandelbrot set highlights the use of complex numbers. It models the first 20 iterations of the equation z = z2 + c, where c represents different Complex number, complex constants.
To run this sample code, it is necessary to first install the package that provides the write.gif() function:
Version names
 All R version releases from 2.14.0 onward have Code name, codenames that make reference to Peanuts comics and films.
In 2018, core R developer Peter Dalgaard presented a history of R releases since 1997. Some notable early releases before the named releases include the following:
* Version 1.0.0, released on 29 February 2000, a Leap days, leap day
* Version 2.0.0, released on 4 October 2004, "which at least had a nice ring to it"
The idea of naming R version releases was inspired by the naming system for Debian version history, Debian and Ubuntu version history, Ubuntu versions. Dalgaard noted an additional reason for the use of Peanuts references in R codenames—the humorous observation that "everyone in statistics is a P-value, P-nut."
All R version releases from 2.14.0 onward have Code name, codenames that make reference to Peanuts comics and films.
In 2018, core R developer Peter Dalgaard presented a history of R releases since 1997. Some notable early releases before the named releases include the following:
* Version 1.0.0, released on 29 February 2000, a Leap days, leap day
* Version 2.0.0, released on 4 October 2004, "which at least had a nice ring to it"
The idea of naming R version releases was inspired by the naming system for Debian version history, Debian and Ubuntu version history, Ubuntu versions. Dalgaard noted an additional reason for the use of Peanuts references in R codenames—the humorous observation that "everyone in statistics is a P-value, P-nut."
Interfaces
R is installed with a Command-line interface, command line console by default, but there are multiple ways to interface with the language: * Integrated development environment, Integrated development environment (IDE): ** R.app (OSX/macOS only) ** Rattle GUI ** R Commander ** RKWard **RStudio
RStudio IDE (or RStudio) is an integrated development environment for R, a programming language for statistical computing and graphics. It's available in two formats: RStudio Desktop is a regular desktop application while RStudio Server runs ...
** Tinn-R
* General-purpose IDEs:
** Eclipse (software), Eclipse via thStatET plugin
** Microsoft Visual Studio, Visual Studio via R Tools for Visual Studio. * Source-code editor, Source-code editors: ** Emacs Speaks Statistics, Emacs ** Vim (text editor), Vim via th
Nvim-R plugin
** Kate (text editor), Kate ** LyX via Sweave ** WinEdt
website
**
Jupyter
Project Jupyter (pronounced "Jupiter") is a project to develop open-source software, open standards, and services for interactive computing across multiple programming languages.
It was spun off from IPython in 2014 by Fernando Pérez and Brian ...
website
* Other scripting languages: ** Python (programming language), Python
website
** Perl
website
** Ruby (programming language), Ruby
source code
** F Sharp (programming language), F#
website
** Julia (programming language), Julia
source code
. * General-purpose programming languages: ** Java (programming language), Java via th
Rserve socket server
** C Sharp (programming language), .NET C#
website
Statistical frameworks that use R in the background include Jamovi and JASP.
Implementations
The main R implementation is written primarily in C, Fortran, and R itself. Other implementations include the following:pretty quick R
(pqR), by Radford M. Neal, which attempts to improve memory management. * Renjin for the Java virtual machine, Java Virtual Machine.
CXXR
and Riposte written in C++. * Oracle Corporation, Oracle's]
FastR
built o
GraalVM
* TIBCO Software, TIBCO Enterprise Runtime for R (TERR) to integrate with Spotfire. (The company also created S-PLUS, S-Plus, an implementation of the S language.) Microsoft R Open (MRO) was an R implementation. As of 30 June 2021, Microsoft began to phase out MRO in favor of the CRAN distribution.
Commercial support
Although R is an open-source project, some companies provide commercial support: * Oracle Corporation, Oracle provides commercial support for its Oracle Big Data Appliance, Big Data Appliance, which integrates R into its other products. * IBM provides commercial support for execution of R within Hadoop.See also
* Comparison of numerical-analysis software * Comparison of statistical packages * List of numerical-analysis software * List of statistical software * RmetricsNotes
References
Further reading
* *External links
R Technical Papers
Big Book of R
curated list of R-related programming books
partially annotated curated list of books relating to R or S. {{Authority control R (programming language), Array programming languages Cross-platform free software Data mining and machine learning software Data-centric programming languages Dynamically typed programming languages Free plotting software Free statistical software Functional languages GNU Project software Literate programming Numerical analysis software for Linux Numerical analysis software for macOS Numerical analysis software for Windows Programming languages created in 1993 Science software Statistical programming languages Articles with example R code