RIPEMD160 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
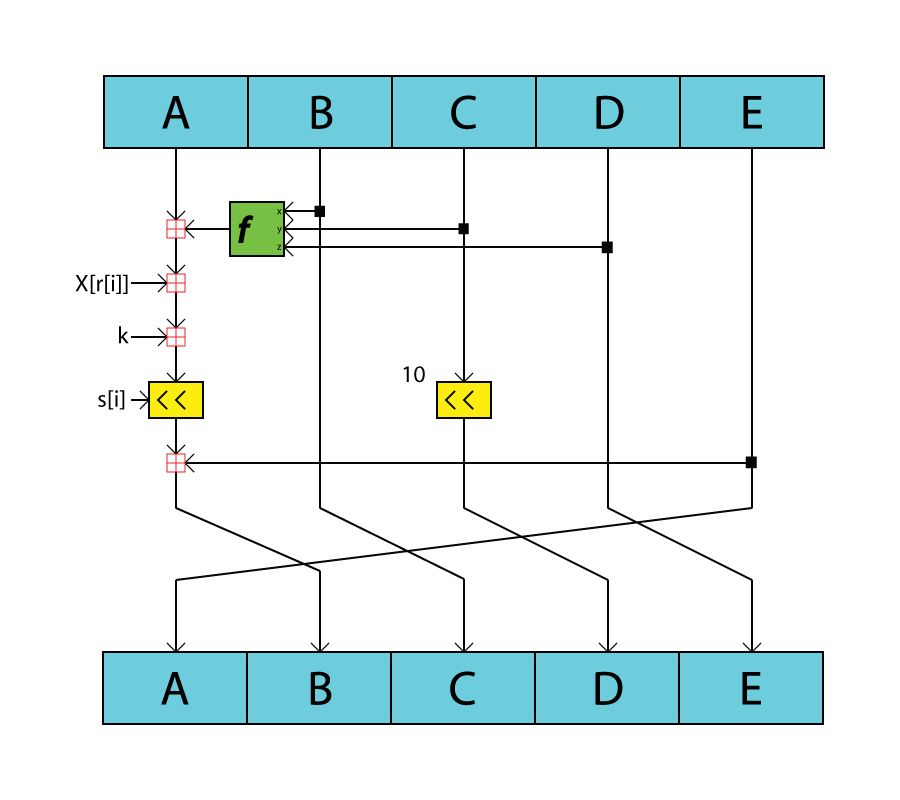 RIPEMD (RIPE Message Digest) is a family of
RIPEMD (RIPE Message Digest) is a family of
The hash function RIPEMD-160
RIPEMD-160 Ecrypt page
RIPEMD-128bit Algorithm
{{Cryptography navbox , hash Cryptographic hash functions
 RIPEMD (RIPE Message Digest) is a family of
RIPEMD (RIPE Message Digest) is a family of cryptographic hash function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map (mathematics), map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for a cryptography, cryptographic application: ...
s developed in 1992 (the original RIPEMD) and 1996 (other variants). There are five functions in the family: RIPEMD, RIPEMD-128, RIPEMD-160, RIPEMD-256, and RIPEMD-320, of which RIPEMD-160 is the most common.
The original RIPEMD, as well as RIPEMD-128, is not considered secure because 128-bit result is too small and also (for the original RIPEMD) because of design weaknesses. The 256- and 320-bit versions of RIPEMD provide the same level of security as RIPEMD-128 and RIPEMD-160, respectively; they are designed for applications where the security level is sufficient but longer hash result is necessary.
While RIPEMD functions are less popular than SHA-1
In cryptography, SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a hash function which takes an input and produces a 160-bit (20-byte) hash value known as a message digest – typically rendered as 40 hexadecimal digits. It was designed by the United States ...
and SHA-2
SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression ...
, they are used, among others, in Bitcoin
Bitcoin (abbreviation: BTC; Currency symbol, sign: ₿) is the first Decentralized application, decentralized cryptocurrency. Based on a free-market ideology, bitcoin was invented in 2008 when an unknown entity published a white paper under ...
and other cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership records ...
based on Bitcoin.
History
The original RIPEMD function was designed in the framework of the EU project RIPE ( RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation) in 1992. Its design was based on theMD4
The MD4 Message-Digest Algorithm is a cryptographic hash function developed by Ronald Rivest in 1990. The digest length is 128 bits. The algorithm has influenced later designs, such as the MD5, SHA-1 and RIPEMD algorithms. The initialism "MD" st ...
hash function. In 1996, in response to security weaknesses found in the original RIPEMD, Hans Dobbertin
Hans Dobbertin (17 April, 1952 – 2 February, 2006) was a German cryptographer who is best known for his work on cryptanalysis of the MD4, MD5, and original RIPEMD hash functions, and for his part in the design of the new version of the RIPEMD ...
, Antoon Bosselaers and Bart Preneel
Bart Preneel (born 15 October 1963 in Leuven, Belgium) is a Belgium, Belgian cryptographer and cryptanalyst. He is a professor at Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, in the COSIC group.
He was the president of the International Association for Crypt ...
at the COSIC
The Computer Security and Industrial Cryptography research group, commonly called COSIC, is a research group at the Department of Electrical Engineering of KU Leuven, which is headed by Bart Preneel.
Research
Research and expertise in digital ...
research group at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven
KU Leuven (Katholieke Universiteit Leuven) is a Catholic research university in the city of Leuven, Belgium. Founded in 1425, it is the oldest university in Belgium and the oldest university in the Low Countries.
In addition to its main camp ...
in Leuven, Belgium
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the sub-municipalities of ...
published four strengthened variants: RIPEMD-128, RIPEMD-160, RIPEMD-256, and RIPEMD-320.
In August 2004, a collision was reported for the original RIPEMD. This does not apply to RIPEMD-160.
In 2019, the best collision attack for RIPEMD-160 could reach 34 rounds out of 80 rounds, which was published at CRYPTO 2019.
In February 2023, a collision attack for RIPEMD-160 was published at EUROCRYPT 2023, which could reach 36 rounds out of 80 rounds with time complexity of 264.5.
In December 2023, an improved collision attack was found based on the technique from the previous best collision attack, this improved collision attack could reach 40 rounds out of 80 round with a theoretical time complexity of 249.9.
RIPEMD-160 hashes
The 160-bit RIPEMD-160 hashes (also termed RIPE ''message digests'') are typically represented as 40-digithexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbo ...
numbers. The following demonstrates a 43-byte ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
input and the corresponding RIPEMD-160 hash:
RIPEMD-160("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy og") =
37f332f68db77bd9d7edd4969571ad671cf9dd3b
RIPEMD-160 behaves with the desired avalanche effect
In cryptography, the avalanche effect is the desirable property of cryptographic algorithms, typically block ciphers and cryptographic hash functions, wherein if an input is changed slightly (for example, flipping a single bit), the output changes ...
of cryptographic hash functions (small changes, e.g. changing to , result in a completely different hash):
RIPEMD-160("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy og") =
132072df690933835eb8b6ad0b77e7b6f14acad7
The hash of a zero-length string is:
RIPEMD-160("") =
9c1185a5c5e9fc54612808977ee8f548b2258d31
Implementations
Below is a list of cryptography libraries that support RIPEMD (specifically RIPEMD-160): * Botan *Bouncy Castle
Bounce or The Bounce may refer to:
* Deflection (physics), the event where an object collides with and bounces against a plane surface
Books
* Mr. Bounce, a character from the Mr. Men series of children's books
Broadcasting, film and TV
* '' ...
* Cryptlib
cryptlib is an open-source cross-platform software security toolkit library. It is distributed under the Sleepycat License, a free software license compatible with the GNU General Public License. Alternatively, cryptlib is available under a pro ...
* Crypto++
Crypto++ (also known as CryptoPP, libcrypto++, and libcryptopp) is a free and open-source C++ class library of cryptographic algorithms and schemes written by Wei Dai. Crypto++ has been widely used in academia, student projects, open-source, and ...
* Libgcrypt
Libgcrypt is a cryptography library developed as a separated module of GnuPG.
It can also be used independently of GnuPG, but depends on its error-reporting library Libgpg-error.
It provides functions for all fundamental cryptographic building b ...
* mbed TLS
Mbed TLS (previously PolarSSL) is an implementation of the Transport Layer Security, TLS and SSL protocols and the respective cryptographic algorithms and support code required. It is distributed under the Apache License version 2.0. Stated on t ...
* Nettle
Nettle refers to plants with stinging hairs, particularly those of the genus '' Urtica''. It can also refer to plants which resemble ''Urtica'' species in appearance but do not have stinging hairs. Plants called "nettle" include:
* ball nettle ...
* OpenSSL
OpenSSL is a software library for applications that provide secure communications over computer networks against eavesdropping, and identify the party at the other end. It is widely used by Internet servers, including the majority of HTTPS web ...
* wolfSSL
wolfSSL is a small, portable, embedded SSL/TLS library targeted for use by embedded systems developers. It is an open source implementation of TLS (SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and DTLS 1.0, 1.2, and 1.3) written in the C programming langu ...
See also
*Hash function security summary
This article summarizes publicly known attacks against cryptographic hash functions. Note that not all entries may be up to date. For a summary of other hash function parameters, see comparison of cryptographic hash functions.
Table color key
...
* Comparison of cryptographic hash functions
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of cryptographic hash functions. See the individual functions' articles for further information. This article is not all-inclusive or necessarily up-to-date. An overview of ...
*Comparison of cryptography libraries
The tables below compare cryptography libraries that deal with cryptography algorithms and have ''application programming interface'' (API) function calls to each of the supported features.
Cryptography libraries
FIPS 140
This table denote ...
* Topics in cryptography
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cryptography:
Cryptography (or cryptology) – practice and study of hiding information. Modern cryptography intersects the disciplines of mathematics, computer scie ...
References
External links
The hash function RIPEMD-160
RIPEMD-160 Ecrypt page
RIPEMD-128bit Algorithm
{{Cryptography navbox , hash Cryptographic hash functions