REM Atonia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of
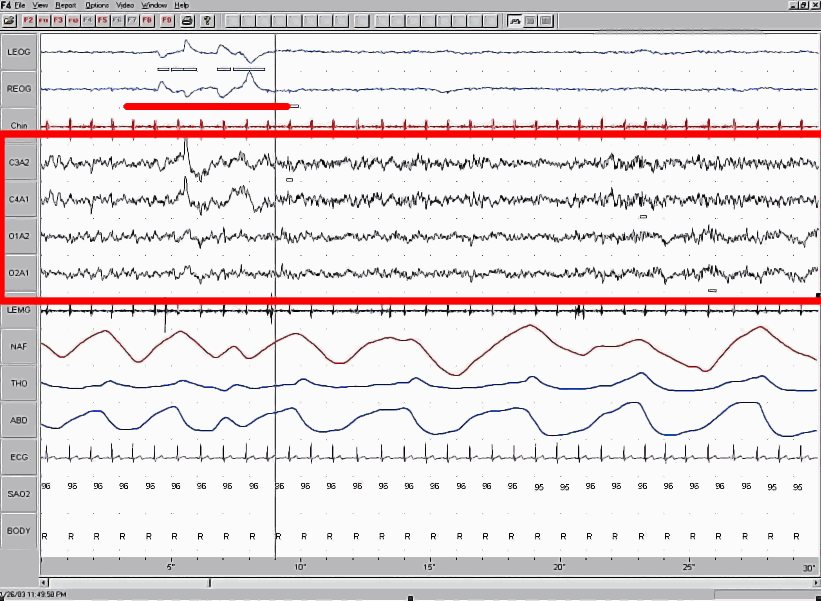 REM sleep is called "paradoxical" because of its similarities to
REM sleep is called "paradoxical" because of its similarities to
 In the '' ultradian sleep cycle'', an organism alternates between deep sleep (slow, large, synchronized brain waves) and paradoxical sleep (faster, desynchronized waves). Sleep happens in the context of the larger
In the '' ultradian sleep cycle'', an organism alternates between deep sleep (slow, large, synchronized brain waves) and paradoxical sleep (faster, desynchronized waves). Sleep happens in the context of the larger
PBS' NOVA episode "What Are Dreams?" Video and Transcript
LSDBase
– an open sleep research database with images of REM sleep recordings. {{DEFAULTSORT:Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Dream Sleep physiology Neurophysiology Articles containing video clips
 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain Sensory nervous system, sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with th ...
in mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
(including human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s) and birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
, accompanied by low muscle tone
In physiology, medicine, and anatomy, muscle tone (residual muscle tension or tonus) is the continuous and passive partial contraction of the muscles, or the muscle's resistance to passive stretch during resting state.O’Sullivan, S. B. (2007) ...
throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream
A dream is a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensation (psychology), sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. Humans spend about two hours dreaming per night, and each dream lasts around ...
vividly. The core body and brain temperatures increase during REM sleep and skin temperature decreases to lowest values.
The REM phase is also known as paradoxical sleep (PS) and sometimes desynchronized sleep or dreamy sleep, because of physiological similarities to waking states including rapid, low-voltage desynchronized brain waves. Electrical and chemical activity regulating this phase seem to originate in the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
, and is characterized most notably by an abundance of the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
, combined with a nearly complete absence of monoamine
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
All monoamines are ...
neurotransmitters histamine, serotonin and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
. Experiences of REM sleep are not transferred to permanent memory due to absence of norepinephrine.
REM sleep is physiologically different from the other phases of sleep, which are collectively referred to as non-REM sleep (NREM sleep, NREMS, synchronized sleep). The absence of visual and auditory stimulation (sensory deprivation
Sensory deprivation or perceptual isolation is the deliberate reduction or removal of stimuli from one or more of the senses. Simple devices such as blindfolds or hoods and earmuffs can cut off sight and hearing, while more complex devices can ...
) during REM sleep can cause hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ...
s. REM and non-REM sleep alternate within one sleep cycle, which lasts about 90 minutes in adult humans. As sleep cycles continue, they shift towards a higher proportion of REM sleep. The transition to REM sleep brings marked physical changes, beginning with electrical bursts called "ponto-geniculo-occipital waves" ( PGO waves) originating in the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
. REM sleep occurs 4 times in a 7-hour sleep. Organisms in REM sleep suspend central homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
, allowing large fluctuations in respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
, thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
and circulation which do not occur in any other modes of sleeping or waking. The body abruptly loses muscle tone, a state known as REM atonia.
In 1953, Professor Nathaniel Kleitman
Nathaniel Kleitman (April 26, 1895 – August 13, 1999) was an American physiologist and sleep researcher who served as Professor Emeritus in Physiology at the University of Chicago. He is recognized as the father of modern sleep research, a ...
and his student Eugene Aserinsky
Eugene Aserinsky (May 6, 1921 – July 22, 1998), a pioneer in sleep research, was a graduate student at the University of Chicago in 1953 when he discovered REM sleep. He was the son of a dentist of Russian–Jewish descent.
He made the disc ...
defined rapid eye movement and linked it to dreams. REM sleep was further described by researchers, including William Dement
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is ...
and Michel Jouvet
Michel Valentin Marcel Jouvet (16 November 1925 – 3 October 2017) was a French neuroscientist and medical researcher.
His works, and those of his team, have brought about the discovery of paradoxical sleep (a term he coined) and to its in ...
. Many experiments have involved awakening test subjects whenever they begin to enter the REM phase, thereby producing a state known as REM deprivation. Subjects allowed to sleep normally again usually experience a modest REM rebound
REM rebound is the lengthening and increasing frequency and depth of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep which occurs after periods of sleep deprivation. When people have been prevented from experiencing REM, they take less time than usual to attain t ...
. Techniques of neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the specialty (medicine), medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system ...
, chemical injection, electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in ...
, positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
, and reports of dreamers upon waking have all been used to study this phase of sleep.
Physiology
Electrical activity in the brain
 REM sleep is called "paradoxical" because of its similarities to
REM sleep is called "paradoxical" because of its similarities to wakefulness
Wakefulness is a daily recurring brain state and state of consciousness in which an individual is conscious and engages in coherent cognition, cognitive and behavioral responses to the external world.
Being awake is the opposite of being asleep, ...
. Although the body is paralyzed, the brain acts as if it is somewhat awake, with cerebral neurons firing with the same overall intensity as in wakefulness. Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in ...
during REM sleep reveals fast, low amplitude, desynchronized neural oscillation
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by ...
(brainwaves) that resemble the pattern seen during wakefulness, which differ from the slow δ (delta) waves pattern of NREM deep sleep. An important element of this contrast is the 3–10 Hz theta rhythm in the hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
and 40–60 Hz gamma waves in the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
; patterns of EEG activity similar to these rhythms are also observed during wakefulness. The cortical and thalamic
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the ...
neurons in the waking and REM sleeping brain are more depolarized (fire more readily) than in the NREM deep sleeping brain. Human theta wave activity predominates during REM sleep in both the hippocampus and the cortex.
During REM sleep, electrical connectivity among different parts of the brain manifests differently than during wakefulness. Frontal and posterior areas are less coherent
Coherence is, in general, a state or situation in which all the parts or ideas fit together well so that they form a united whole.
More specifically, coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics ...
in most frequencies, a fact which has been cited in relation to the chaotic experience of dreaming. However, the posterior areas are more coherent with each other; as are the right and left hemispheres of the brain, especially during lucid dream
In the psychology subfield of oneirology, a lucid dream is a type of dream wherein the dreamer realizes that they are dreaming during their dream. The capacity to have lucid dreams is a trainable cognitive skill. During a lucid dream, the dreamer ...
s.
Brain energy use in REM sleep, as measured by oxygen and glucose metabolism, equals or exceeds energy use in waking. The rate in non-REM sleep is 11–40% lower.
Brain stem
Neural activity during REM sleep seems to originate in thebrain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
, especially the pontine tegmentum
The pontine tegmentum, or dorsal pons, is the dorsal part of the pons located within the brainstem. The ventral part or ventral pons is known as the basilar part of the pons, or basilar pons. Along with the dorsal surface of the medulla oblonga ...
and locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular ...
. REM sleep is punctuated and immediately preceded by PGO (ponto-geniculo-occipital) waves, bursts of electrical activity originating in the brain stem. (PGO waves have long been measured directly in cats but not in humans because of constraints on experimentation; however, comparable effects have been observed in humans during "phasic" events which occur during REM sleep, and the existence of similar PGO waves is thus inferred.) These waves occur in clusters about every 6 seconds for 1–2 minutes during the transition from deep to paradoxical sleep. They exhibit their highest amplitude upon moving into the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
and are a cause of the "rapid eye movements" in paradoxical sleep. Other muscles may also contract under the influence of these waves.
Forebrain
Research in the 1990s usingpositron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
(PET) confirmed the role of the brain stem and suggested that, within the forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions.
Ve ...
, the limbic
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''P ...
and paralimbic systems showed more activation than other areas. The areas activated during REM sleep are approximately inverse to those activated during non-REM sleep and display greater activity than in quiet waking. The "anterior paralimbic REM activation area" (APRA) includes areas linked with emotion
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is ...
, memory, fear and sex, and may thus relate to the experience of dreaming during REMS. More recent PET research has indicated that the distribution of brain activity during REM sleep varies in correspondence with the type of activity seen in the prior period of wakefulness.
The superior frontal gyrus
In neuroanatomy, the superior frontal gyrus (SFG, also marginal gyrus) is a gyrus – a ridge on the brain's cerebral cortex – which makes up about one third of the frontal lobe. It is bounded laterally by the superior frontal sulcus.
The su ...
, medial frontal areas, intraparietal sulcus
The intraparietal sulcus (IPS) is located on the lateral surface of the parietal lobe, and consists of an oblique and a horizontal portion. The IPS contains a series of functionally distinct subregions that have been intensively investigated usin ...
, and superior parietal cortex, areas involved in sophisticated mental activity, show equal activity in REM sleep as in wakefulness. The amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is c ...
is also active during REM sleep and may participate in generating the PGO waves, and experimental suppression of the amygdala results in less REM sleep. The amygdala may also regulate cardiac function in lieu of the less active insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere ...
.
Chemicals in the brain
Compared to slow-wave sleep, both waking and paradoxical sleep involve higher use of the neurotransmitteracetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
, which may cause the faster brainwaves. The monoamine
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
All monoamines are ...
neurotransmitters norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
and histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
are completely unavailable. Injections of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level an ...
, which effectively increases available acetylcholine, have been found to induce paradoxical sleep in humans and other animals already in slow-wave sleep. Carbachol
Carbachol, also known as carbamylcholine and sold under the brand name Miostat among others, is a cholinomimetic drug that binds and activates acetylcholine receptors. Thus it is classified as a cholinergic agonist. It is primarily used for v ...
, which mimics the effect of acetylcholine on neurons, has a similar influence. In waking humans, the same injections produce paradoxical sleep only if the monoamine neurotransmitters have already been depleted..
Two other neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotransmitters are rele ...
, orexin
Orexin (), also known as hypocretin, is a neuropeptide that regulates arousal, wakefulness, and appetite. It exists in the forms of orexin-A and orexin-B. The most common form of narcolepsy, type 1, in which the individual experiences brief loss ...
and gamma-Aminobutyric acid
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
(GABA), seem to promote wakefulness, diminish during deep sleep, and inhibit paradoxical sleep.
Unlike the abrupt transitions in electrical patterns, the chemical changes in the brain show continuous periodic oscillation.
Models of REM regulation
According to theactivation-synthesis hypothesis
The activation-synthesis hypothesis, proposed by Harvard University psychiatrists Allan Hobson, John Allan Hobson and Robert McCarley, is a neurobiological theory of dreams first published in the American Journal of Psychiatry in December 1977. Th ...
proposed by Robert McCarley and Allan Hobson in 1975–1977, control over REM sleep involves pathways of "REM-on" and "REM-off" neurons in the brain stem. REM-on neurons are primarily cholinergic (i.e., involve acetylcholine); REM-off neurons activate serotonin and noradrenaline, which among other functions suppress the REM-on neurons. McCarley and Hobson suggested that the REM-on neurons actually stimulate REM-off neurons, thereby serving as the mechanism for the cycling between REM and non-REM sleep. They used Lotka–Volterra equations to describe this cyclical inverse relationship. Kayuza Sakai and Michel Jouvet advanced a similar model in 1981. Whereas acetylcholine manifests in the cortex equally during wakefulness and REM, it appears in higher concentrations in the brain stem during REM. The withdrawal of orexin and GABA may cause the absence of the other excitatory neurotransmitters; researchers in recent years increasingly include GABA regulation in their models.
Eye movements
Most of theeye movements
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of i ...
in "rapid eye movement" sleep are in fact less rapid than those normally exhibited by waking humans. They are also shorter in duration and more likely to loop back to their starting point. About seven such loops take place over one minute of REM sleep. In slow-wave sleep, the eyes can drift apart; however, the eyes of the paradoxical sleeper move in tandem. These eye movements follow the ponto-geniculo-occipital waves originating in the brain stem. The eye movements themselves may relate to the sense of vision experienced in the dream, but a direct relationship remains to be clearly established. Congenitally blind people, who do not typically have visual imagery in their dreams, still move their eyes in REM sleep. An alternative explanation suggests that the functional purpose of REM sleep is for procedural memory processing, and the rapid eye movement is only a side effect of the brain processing the eye-related procedural memory.
Circulation, respiration, and thermoregulation
Generally speaking, the body suspendshomeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
during paradoxical sleep. Heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
, cardiac pressure, cardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: tha ...
, arterial pressure, and breathing rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is me ...
quickly become irregular when the body moves into REM sleep. In general, respiratory reflexes such as response to hypoxia diminish. Overall, the brain exerts less control over breathing; electrical stimulation of respiration-linked brain areas does not influence the lungs, as it does during non-REM sleep and in waking.
Erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
s of the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
(nocturnal penile tumescence
Nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT) is a spontaneous erection of the penis during sleep or when waking up. Along with nocturnal clitoral tumescence, it is also known as sleep-related erection. Colloquially, the term morning wood, or less commonly, ...
or NPT) normally accompany REM sleep in rats and humans. If a male has erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
(ED) while awake, but has NPT episodes during REM, it would suggest that the ED is from a psychological rather than a physiological cause. In females, erection of the clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. Th ...
( nocturnal clitoral tumescence or NCT) causes enlargement, with accompanying vaginal blood flow and transudation (i.e. lubrication). During a normal night of sleep, the penis and clitoris may be erect for a total time of from one hour to as long as three and a half hours during REM.
Body temperature is not well regulated during REM sleep, and thus organisms become more sensitive to temperatures outside their thermoneutral zone. Cats and other small furry mammals will shiver and breathe faster to regulate temperature during NREMS—but not during REMS. With the loss of muscle tone, animals lose the ability to regulate temperature through body movement. (However, even cats with pontine lesions preventing muscle atonia during REM did not regulate their temperature by shivering.) Neurons that typically activate in response to cold temperatures—triggers for neural thermoregulation—simply do not fire during REM sleep, as they do in NREM sleep and waking.
Consequently, hot or cold environmental temperatures can reduce the proportion of REM sleep, as well as amount of total sleep. In other words, if at the end of a phase of deep sleep, the organism's thermal indicators fall outside of a certain range, it will not enter paradoxical sleep lest deregulation allow temperature to drift further from the desirable value. This mechanism can be 'fooled' by artificially warming the brain.
Muscle
REM atonia, an almost complete paralysis of the body, is accomplished through the inhibition ofmotor neurons
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or ...
. When the body shifts into REM sleep, motor neurons throughout the body undergo a process called hyperpolarization: their already-negative membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. It equals the interior potential minus the exterior potential. This is th ...
decreases by another 2–10 millivolts, thereby raising the threshold which a stimulus must overcome to excite them. Muscle inhibition may result from unavailability of monoamine neurotransmitters (restraining the abundance of acetylcholine in the brainstem) and perhaps from mechanisms used in waking muscle inhibition. The medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
, located between pons and spine, seems to have the capacity for organism-wide muscle inhibition. Some localized twitching and reflexes can still occur. Pupils contract.
Lack of REM atonia causes REM behavior disorder
Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder or REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a sleep disorder in which people act out their dreams. It involves abnormal behavior during the sleep phase with Rapid eye movement sleep, rapid eye movement (RE ...
, where those affected physically act out their dreams, or conversely "dream out their acts", under an alternative theory on the relationship between muscle impulses during REM and associated mental imagery (which would also apply to people without the condition, except that commands to their muscles are suppressed). This is different from conventional sleepwalking
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism or noctambulism, is a phenomenon of combined sleep and wakefulness. It is classified as a sleep disorder belonging to the parasomnia family. It occurs during the slow wave stage of sleep, in a state of ...
, which takes place during slow-wave sleep, not REM. Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that impairs the ability to regulate sleep–wake cycles, and specifically impacts REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. The symptoms of narcolepsy include excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep-r ...
, by contrast, seems to involve excessive and unwanted REM atonia: cataplexy
Cataplexy is a sudden and transient episode of muscle weakness accompanied by full conscious awareness, typically triggered by emotions such as laughing, crying, or terror. Cataplexy is the first symptom to appear in about 10% of cases of narcol ...
and excessive daytime sleepiness while awake, hypnagogic hallucinations before entering slow-wave sleep, or sleep paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a state, during waking up or falling asleep, in which a person is conscious but in a complete state of full-body paralysis. During an episode, the person may hallucinate (hear, feel, or see things that are not there), wh ...
while waking. Other psychiatric disorders including depression have been linked to disproportionate REM sleep. Patients with suspected sleep disorders are typically evaluated by polysomnogram.
Lesions of the pons to prevent atonia have induced functional "REM behavior disorder" in animals.
Psychology
Dreaming
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) has since its discovery been closely associated withdream
A dream is a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensation (psychology), sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. Humans spend about two hours dreaming per night, and each dream lasts around ...
ing. Waking up sleepers during a REM phase is a common experimental method for obtaining dream reports; 80% of people can give some kind of dream report under these circumstances. Sleepers awakened from REM tend to give longer, more narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether non-fictional (memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travel literature, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller ...
descriptions of the dreams they were experiencing, and to estimate the duration of their dreams as longer. Lucid dream
In the psychology subfield of oneirology, a lucid dream is a type of dream wherein the dreamer realizes that they are dreaming during their dream. The capacity to have lucid dreams is a trainable cognitive skill. During a lucid dream, the dreamer ...
s are reported far more often in REM sleep. (In fact these could be considered a hybrid state combining essential elements of REM sleep and waking consciousness.) The mental events which occur during REM most commonly have dream hallmarks including narrative structure, convincingness (e.g., experiential resemblance to waking life), and incorporation of instinctual themes. Sometimes, they include elements of the dreamer's recent experience taken directly from episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred ...
. By one estimate, 80% of dreams occur during REM.
Hobson and McCarley proposed that the PGO waves characteristic of "phasic" REM might supply the visual cortex and forebrain with electrical excitement which amplifies the hallucinatory aspects of dreaming. However, people woken up during sleep do not report significantly more bizarre dreams during phasic REMS, compared to tonic REMS. Another possible relationship between the two phenomena could be that the higher threshold for sensory interruption during REM sleep allows the brain to travel further along unrealistic and peculiar trains of thought.
Some dreaming can take place during non-REM sleep. "Light sleepers" can experience dreaming during stage 2 non-REM sleep, whereas "deep sleepers", upon awakening in the same stage, are more likely to report "thinking" but not "dreaming". Certain scientific efforts to assess the uniquely bizarre nature of dreams experienced while asleep were forced to conclude that waking thought could be just as bizarre, especially in conditions of sensory deprivation
Sensory deprivation or perceptual isolation is the deliberate reduction or removal of stimuli from one or more of the senses. Simple devices such as blindfolds or hoods and earmuffs can cut off sight and hearing, while more complex devices can ...
. Because of non-REM dreaming, some sleep researchers have strenuously contested the importance of connecting dreaming to the REM sleep phase. The prospect that well-known neurological aspects of REM do not themselves cause dreaming suggests the need to re-examine the neurobiology of dreaming ''per se''. Some researchers (Dement, Hobson, Jouvet, for example) tend to resist the idea of disconnecting dreaming from REM sleep.
Effects of SSRIs
Previous research has shown thatselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs primarily work by blo ...
s (SSRIs) have an important effect on REM sleep neurobiology and dreaming. A study at Harvard Medical School in 2000 tested the effects of paroxetine
Paroxetine ( ), sold under the brand name Paxil among others, is an Antidepressant, antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, o ...
and fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine, sold under the brand name Luvox among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and, perhaps more-especially, obsessive–compu ...
on healthy young adult male and females for 31 days: a drug-free baseline week, 19 days on either paroxetine or fluvoxamine with morning and evening doses, and 5 days of absolute discontinuation. Results showed that SSRI treatment decreased the average amount of dream recall frequency in comparison to baseline measurements as a result of serotonergic REM suppression. Fluvoxamine increased the length of dream reporting, bizarreness of dreams as well as the intensity of REM sleep. These effects were the greatest during acute discontinuation compared to treatment and baseline days. However, the ''subjective'' intensity of dreaming increased and the proclivity to enter REM sleep was decreased during SSRI treatment compared to baseline and discontinuation days.
Creativity
After waking from REM sleep, the mind seems "hyperassociative"—more receptive to semantic priming effects. People awakened from REM have performed better on tasks likeanagram
An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once. For example, the word ''anagram'' itself can be rearranged into the phrase "nag a ram"; which ...
s and creative problem solving.
Sleep aids the process by which creativity
Creativity is the ability to form novel and valuable Idea, ideas or works using one's imagination. Products of creativity may be intangible (e.g. an idea, scientific theory, Literature, literary work, musical composition, or joke), or a physica ...
forms associative elements into new combinations that are useful or meet some requirement. This occurs in REM sleep rather than in NREM sleep. Rather than being due to memory processes, this has been attributed to changes during REM sleep in cholinergic
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word " choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cation ...
and noradrenergic neuromodulation
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a sec ...
. High levels of acetylcholine in the hippocampus suppress feedback from hippocampus to the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
, while lower levels of acetylcholine and norepinephrine in the neocortex encourage the uncontrolled spread of associational activity within neocortical areas. This is in contrast to waking consciousness, where higher levels of norepinephrine and acetylcholine inhibit recurrent connections in the neocortex. REM sleep through this process adds creativity by allowing "neocortical structures to reorganise associative hierarchies, in which information from the hippocampus would be reinterpreted in relation to previous semantic representations or nodes."
Timing
circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
, which influences sleepiness and physiological factors based on timekeepers within the body. Sleep can be distributed throughout the day or clustered during one part of the rhythm: in nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
animals, during the day, and in diurnal animals, at night. The organism returns to homeostatic regulation almost immediately after REM sleep ends.
During a night of sleep, humans usually experience about four or five periods of REM sleep; they are shorter (~15 min) at the beginning of the night and longer (~25 min) toward the end. Many animals and some people tend to wake, or experience a period of very light sleep, for a short time immediately after a bout of REM. The relative amount of REM sleep varies considerably with age. A newborn baby spends more than 80% of total sleep time in REM.
REM sleep typically occupies 20–25% of total sleep in adult humans: about 90–120 minutes of a night's sleep. The first REM episode occurs about 70 minutes after falling asleep. Cycles of about 90 minutes each follow, with each cycle including a larger proportion of REM sleep. (The increased REM sleep later in the night is connected with the circadian rhythm and occurs even in people who did not sleep in the first part of the night.)
In the weeks after a human baby is born, as its nervous system matures, neural patterns in sleep begin to show a rhythm of REM and non-REM sleep. (In faster-developing mammals, this process occurs in utero.) Infants spend more time in REM sleep than adults. The proportion of REM sleep then decreases significantly in childhood. Older people tend to sleep less overall, but sleep in REM for about the same absolute time (and therefore spend a greater proportion of sleep in REM).
Rapid eye movement sleep can be subclassified into tonic and phasic modes. Tonic REM is characterized by theta rhythms in the brain; phasic REM is characterized by PGO waves and actual "rapid" eye movements. Processing of external stimuli is heavily inhibited during phasic REM, and recent evidence suggests that sleepers are more difficult to arouse from phasic REM than in slow-wave sleep.
Deprivation effects
Selective REMS deprivation causes a significant increase in the number of attempts to go into REM stage while asleep. On recovery nights, an individual will usually move to stage 3 and REM sleep more quickly and experience aREM rebound
REM rebound is the lengthening and increasing frequency and depth of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep which occurs after periods of sleep deprivation. When people have been prevented from experiencing REM, they take less time than usual to attain t ...
, which refers to an increase in the time spent in REM stage over normal levels. These findings are consistent with the idea that REM sleep is biologically necessary. However, the "rebound" REM sleep usually does not last fully as long as the estimated length of the missed REM periods.
After the deprivation is complete, mild psychological disturbances, such as anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, irritability
Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimul ...
, hallucinations
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ...
, and difficulty concentrating may develop and appetite
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to reg ...
may increase. There are also positive consequences of REM deprivation. Some symptoms of depression are found to be suppressed by REM deprivation; aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In h ...
may increase, and eating behavior may get disrupted. Higher norepinepherine is a possible cause of these results. Whether and how long-term REM deprivation has psychological effects remains a matter of controversy. Several reports have indicated that REM deprivation increases aggression and sexual behavior
Human sexual activity, human sexual practice or human sexual behaviour is the manner in which humans experience and express their sexuality. People engage in a variety of sexual acts, ranging from activities done alone (e.g., masturbation) t ...
in laboratory test animals. Rats deprived of paradoxical sleep die in 4–6 weeks (twice the time before death in case of total sleep deprivation). Mean body temperature falls continually during this period.
It has been suggested that acute REM sleep deprivation can improve certain types of depression—when depression appears to be related to an imbalance of certain neurotransmitters. Although sleep deprivation in general annoys most of the population, it has repeatedly been shown to alleviate depression, albeit temporarily. More than half the individuals who experience this relief report it to be rendered ineffective after sleeping the following night. Thus, researchers have devised methods such as altering the sleep schedule for a span of days following a REM deprivation period and combining sleep-schedule alterations with pharmacotherapy to prolong this effect. Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s (including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs primarily work by blo ...
s, tricyclics, and monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressa ...
s) and stimulants (such as amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
, methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
and cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
) interfere with REM sleep by stimulating the monoamine neurotransmitters which must be suppressed for REM sleep to occur. Administered at therapeutic doses, these drugs may stop REM sleep entirely for weeks or months. Withdrawal causes a REM rebound. Sleep deprivation stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis much as antidepressants do, but whether this effect is driven by REM sleep in particular is unknown.
In other animals
Although it manifests differently in different animals, REM sleep or something like it occurs in all landmammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
—as well as in birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
. The primary criteria used to identify REM are the change in electrical activity, measured by EEG, and loss of muscle tone, interspersed with bouts of twitching in phasic REM.
The amount of REM sleep and cycling varies among animals; predators experience more REM sleep than prey. Larger animals also tend to stay in REM for longer, possibly because higher thermal inertia
Thermal inertia is a term commonly used to describe the observed delays in a body's temperature response during heat transfers. The phenomenon exists because of a body's ability to both store and transport heat relative to its environment. Sinc ...
of their brains and bodies allows them to tolerate longer suspension of thermoregulation. The period (full cycle of REM and non-REM) lasts for about 90 minutes in humans, 22 minutes in cats, and 12 minutes in rats. In utero, mammals spend more than half (50–80%) of a 24-hour day in REM sleep.
Sleeping reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s do not seem to have PGO waves or the localized brain activation seen in mammalian REM. However, they do exhibit sleep cycles with phases of REM-like electrical activity measurable by EEG. A recent study found periodic eye movements in the central bearded dragon
The central bearded dragon (''Pogona vitticeps''), also known as the inland bearded dragon, is a species of Agamidae, agamid lizard found in a wide range of arid to semiarid regions of eastern and central Australia.
Taxonomy
''Pogona vitticeps' ...
of Australia, leading its authors to speculate that the common ancestor of amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tet ...
s may therefore have manifested some precursor to REMS.
Observations of jumping spiders in their nocturnal resting position also suggest a REM sleep-like state characterized by bouts of twitching and retinal movements and hints of muscle atonia (legs curling up as a result of pressure loss caused by muscle atonia in the prosoma).
Sleep deprivation experiments on non-human animals can be set up differently than those on humans. The "flower pot" method involves placing a laboratory animal above water on a platform so small that it falls off upon losing muscle tone. The naturally rude awakening which results may elicit changes in the organism which necessarily exceed the simple absence of a sleep phase. This method also stops working after about 3 days as the subjects (typically rats) lose their will to avoid the water. Another method involves computer monitoring of brain waves, complete with automatic mechanized shaking of the cage when the test animal drifts into REM sleep.
Possible functions
Some researchers argue that the perpetuation of a complex brain process such as REM sleep indicates that it serves an important function for the survival of mammalian and avian species. It fulfills important physiological needs vital for survival to the extent that prolonged REM sleep deprivation leads to death in experimental animals. In both humans and experimental animals, REM sleep loss leads to several behavioral and physiological abnormalities. Loss of REM sleep has been noticed during various natural and experimental infections. Survivability of the experimental animals decreases when REM sleep is totally attenuated during infection; this leads to the possibility that the quality and quantity of REM sleep is generally essential for normal body physiology. Further, the existence of a "REM rebound" effect suggests the possibility of a biological need for REM sleep. While the precise function of REM sleep is not well understood, several theories have been proposed.Memory
Sleep in general aids memory. REM sleep may favor the preservation of certain types ofmemories
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is Encoding (memory), encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future Action (philosophy), action. I ...
: specifically, procedural memory
Procedural memory is a type of implicit memory ( unconscious, long-term memory) which aids the performance of particular types of tasks without conscious awareness of these previous experiences.
Procedural memory guides the processes we perform ...
, spatial memory
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Sp ...
, and emotional memory
Emotion can have a powerful effect on humans and animals. Numerous studies have shown that the most vivid autobiographical memories tend to be of emotional events, which are likely to be recalled more often and with more clarity and detail tha ...
. In rats, REM sleep increases following intensive learning, especially several hours after, and sometimes for multiple nights. Experimental REM sleep deprivation has sometimes inhibited memory consolidation
Memory consolidation is a category of processes that stabilize a memory trace after its initial acquisition. A memory trace is a change in the nervous system caused by memorizing something. Consolidation is distinguished into two specific processe ...
, especially regarding complex processes (e.g., how to escape from an elaborate maze). In humans, the best evidence for REM's improvement of memory pertains to learning of procedures—new ways of moving the body (such as trampoline jumping), and new techniques of problem solving. REM deprivation seemed to impair declarative (i.e., factual) memory only in more complex cases, such as memories of longer stories. REM sleep apparently counteracts attempts to suppress certain thoughts.
According to the ''dual-process hypothesis'' of sleep and memory, the two major phases of sleep correspond to different types of memory. "Night half" studies have tested this hypothesis with memory tasks either begun before sleep and assessed in the middle of the night, or begun in the middle of the night and assessed in the morning. Slow-wave sleep, part of non-REM sleep, appears to be important for declarative memory
Explicit memory (or declarative memory) is one of the two main types of Long-term memory, long-term human memory, the other of which is implicit memory. Explicit memory is the Consciousness, conscious, intentional Recall (memory), recollection of f ...
. Artificial enhancement of the non-REM sleep improves the next-day recall of memorized pairs of words. Tucker et al. demonstrated that a daytime nap containing solely non-REM sleep enhances declarative memory
Explicit memory (or declarative memory) is one of the two main types of Long-term memory, long-term human memory, the other of which is implicit memory. Explicit memory is the Consciousness, conscious, intentional Recall (memory), recollection of f ...
—but not procedural memory
Procedural memory is a type of implicit memory ( unconscious, long-term memory) which aids the performance of particular types of tasks without conscious awareness of these previous experiences.
Procedural memory guides the processes we perform ...
. According to the ''sequential hypothesis'', the two types of sleep work together to consolidate memory.
Sleep researcher Jerome Siegel has observed that extreme REM deprivation does not significantly interfere with memory. One case study of an individual who had little or no REM sleep due to a shrapnel injury to the brainstem did not find the individual's memory to be impaired. Antidepressants, which suppress REM sleep, show no evidence of impairing memory and may improve it.
Graeme Mitchison and Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid doub ...
proposed in 1983 that by virtue of its inherent spontaneous activity, the function of REM sleep "is to remove certain undesirable modes of interaction in networks of cells in the cerebral cortex"—a process they characterize as " unlearning". As a result, those memories which are relevant (whose underlying neuronal substrate is strong enough to withstand such spontaneous, chaotic activation) are further strengthened, whilst weaker, transient, "noise" memory traces disintegrate. Memory consolidation during paradoxical sleep is specifically correlated with the periods of rapid eye movement, which do not occur continuously. One explanation for this correlation is that the PGO electrical waves, which precede the eye movements, also influence memory. REM sleep could provide a unique opportunity for "unlearning" to occur in the basic neural networks involved in homeostasis, which are protected from this "synaptic downscaling" effect during deep sleep.
Neural ontogeny
REM sleep prevails most after birth, and diminishes with age. According to the "ontogenetic hypothesis", REM (also known inneonate
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
s as ''active sleep'') aids the developing brain by providing the neural stimulation that newborns need to form mature neural connections. Sleep deprivation studies have shown that deprivation early in life can result in behavioral problems, permanent sleep disruption, and decreased brain mass. The strongest evidence for the ontogenetic hypothesis comes from experiments on REM deprivation, and from the development of the visual system in the lateral geniculate nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, Anatomical ter ...
and primary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
.
Defensive immobilization
Ioannis Tsoukalas of Stockholm University has hypothesized that REM sleep is an evolutionary transformation of a well-known defensive mechanism, thetonic immobility
Apparent death is a behavior in which animals take on the appearance of being dead. It is an immobile state most often triggered by a predatory attack and can be found in a wide range of animals from insects and crustaceans to mammals, birds, r ...
reflex. This reflex, also known as animal hypnosis or death feigning, functions as the last line of defense against an attacking predator and consists of the total immobilization of the animal so that it appears dead. Tsoukalas argues that the neurophysiology and phenomenology of this reaction shows striking similarities to REM sleep; for example, both reactions exhibit brainstem control, cholinergic neurotransmission, paralysis, hippocampal theta rhythm
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are c ...
, and thermoregulatory changes.
Shift of gaze
According to "scanning hypothesis", the directional properties of REM sleep are related to a shift of gaze in dream imagery. Against this hypothesis is that such eye movements occur in those born blind and infetuses
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a ...
in spite of lack of vision. Also, binocular REMs are non-conjugated (i.e., the two eyes do not point in the same direction at a time) and so lack a fixation point. In support of this theory, research finds that in goal-oriented dreams, eye gaze is directed towards the dream action, determined from correlations in the eye and body movements of REM sleep behavior disorder patients who enact their dreams.
Oxygen supply to cornea
Dr.David M. Maurice
David Myer Maurice (3 April 1922 in London – 20 July 2002 in Manhattan) was a British ophthalmologist, noted for his contributions to the development of the specular microscope used for examination of the cornea.
Biography
Maurice was educated a ...
, an eye specialist and former adjunct professor at Columbia University, proposed that REM sleep was associated with oxygen supply to the cornea, and that aqueous humor
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to blood plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the po ...
, the liquid between cornea and iris, was stagnant if not stirred. Among the supportive evidence, he calculated that if aqueous humor was stagnant, oxygen from the iris had to reach the cornea by diffusion through aqueous humor, which was not sufficient. According to the theory, when the organism is awake, eye movement (or cool environmental temperature) enables the aqueous humor to circulate. When the organism is sleeping, REM provides the much needed stir to aqueous humor. This theory is consistent with the observation that fetuses, as well as eye-sealed newborn animals, spend much time in REM sleep, and that during a normal sleep, a person's REM sleep episodes become progressively longer deeper into the night. However, owls experience REM sleep, but do not move their head more than in non-REM sleep; see Fig. S1 and it is well known that owls' eyes are nearly immobile.
Other theories
Another theory suggests that monoamine shutdown is required so that themonoamine receptor
A monoamine receptor is a receptor for the monoamine neurotransmitters and/or trace amines, endogenous small-molecule signaling molecules with a monoamine structure. The monoamine receptors are almost all G protein-coupled receptors, with the se ...
s in the brain can recover to regain full sensitivity.
The ''sentinel hypothesis'' of REM sleep was put forward by Frederick Snyder in 1966. It is based upon the observation that REM sleep in several mammals (the rat, the hedgehog, the rabbit, and the rhesus monkey) is followed by a brief awakening. This does not occur for either cats or humans, although humans are more likely to wake from REM sleep than from NREM sleep. Snyder hypothesized that REM sleep activates an animal periodically, to scan the environment for possible predators. This hypothesis does not explain the muscle paralysis of REM sleep; however, a logical analysis might suggest that the muscle paralysis exists to prevent the animal from fully waking up unnecessarily, and allowing it to return easily to deeper sleep.
Jim Horne, a sleep researcher at Loughborough University
Loughborough University (abbreviated as ''Lough'' or ''Lboro'' for Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a public university, public research university in the market town of Loughborough, Leicestershire, England. It has been a university sinc ...
, has suggested that REM in modern humans compensates for the reduced need for wakeful food foraging
Foraging is searching for wild food resources. It affects an animal's fitness because it plays an important role in an animal's ability to survive and reproduce. Foraging theory is a branch of behavioral ecology that studies the foraging behavi ...
.
Other theories are that REM sleep warms the brain, stimulates and stabilizes the neural circuits that have not been activated during waking, or creates internal stimulation to aid development of the CNS; while some argue that REM lacks any purpose, and simply results from random brain activation.
Furthermore, eye movements are also theorized to play a role in certain psychotherapies such as eye movement desensitization and reprocessing
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is a form of psychotherapy designed to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It was devised by Francine Shapiro in 1987.
EMDR involves talking about traumatic memories while engagin ...
(EMDR).
See also
*Neuroscience of sleep
The neuroscience of sleep is the study of the neuroscience, neuroscientific and Physiology, physiological basis of the nature of sleep and its functions. Traditionally, sleep has been studied as part of psychology and medicine. The study of sleep ...
* Pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN)
*Sleep and learning
Multiple hypotheses explain the possible connections between sleep and learning in humans. Research indicates that sleep does more than allow the brain to rest; it may also aid the consolidation of long-term memories.
REM sleep and slow-wave slee ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
PBS' NOVA episode "What Are Dreams?" Video and Transcript
LSDBase
– an open sleep research database with images of REM sleep recordings. {{DEFAULTSORT:Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Dream Sleep physiology Neurophysiology Articles containing video clips