Quest Joint Airlock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Quest'' Joint Airlock is the primary
 ''Quest'' was necessary because American suits (EMUs) will not fit through a Russian airlock hatch and have different components, fittings, and connections. The airlock is designed to contain equipment that can work with both types of spacesuits, however, it is currently only able to host American spacewalks because the equipment necessary to work with Russian space suits has not been launched yet, which required the Expedition 9 crew to take a circuitous route to a worksite because of problems with the American space suits.
It is sized to allow EVAs with two crew.
''Quest'' was necessary because American suits (EMUs) will not fit through a Russian airlock hatch and have different components, fittings, and connections. The airlock is designed to contain equipment that can work with both types of spacesuits, however, it is currently only able to host American spacewalks because the equipment necessary to work with Russian space suits has not been launched yet, which required the Expedition 9 crew to take a circuitous route to a worksite because of problems with the American space suits.
It is sized to allow EVAs with two crew.
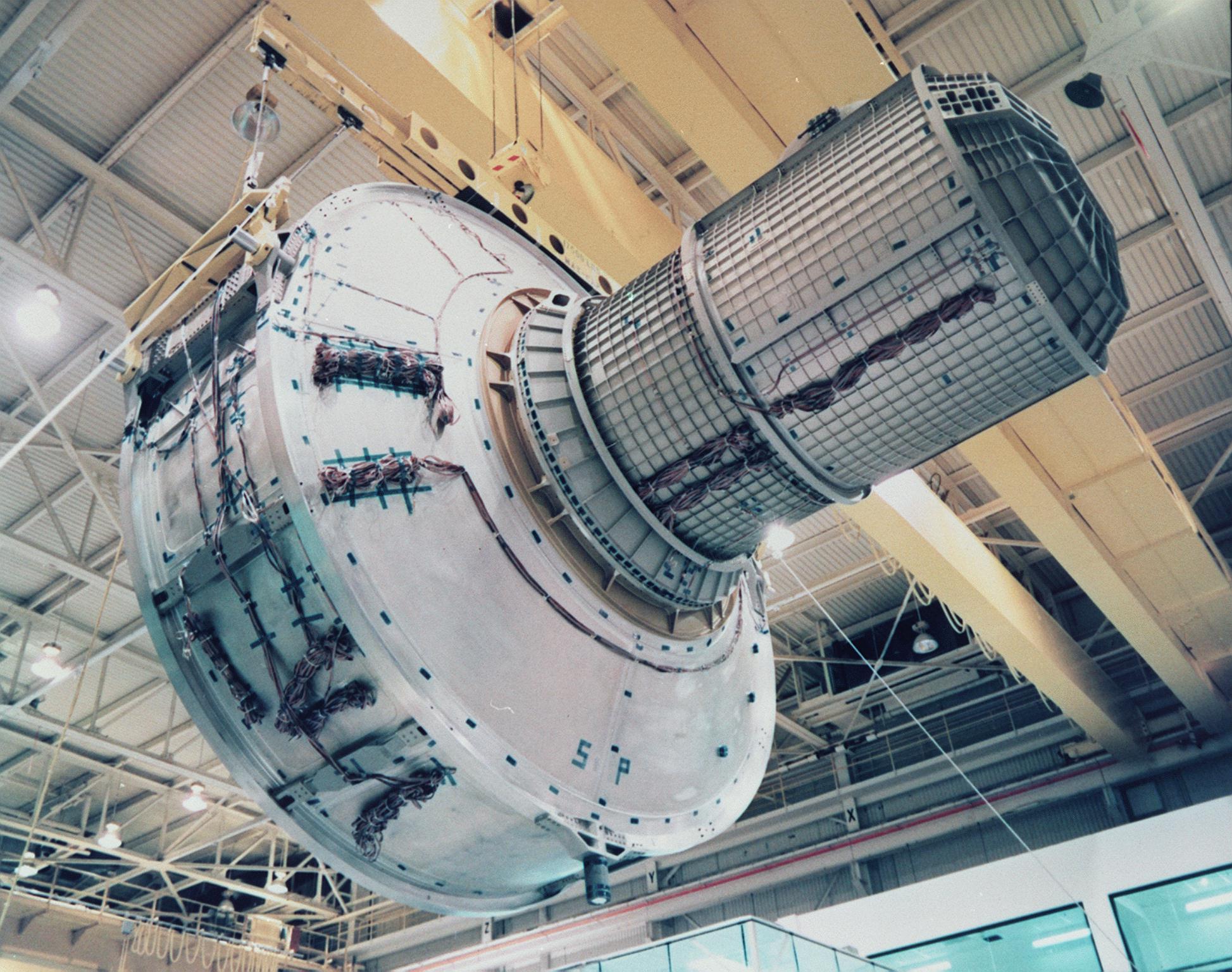
 The ''Quest'' Airlock consists of two segments, the "Equipment lock" that stores spacesuits and equipment, and the "Crew Lock" from which astronauts can exit into space. It was derived from the Space Shuttle airlock, although it was significantly modified to waste less atmospheric gas when used. It has mountings for four high-pressure gas tanks, two containing
The ''Quest'' Airlock consists of two segments, the "Equipment lock" that stores spacesuits and equipment, and the "Crew Lock" from which astronauts can exit into space. It was derived from the Space Shuttle airlock, although it was significantly modified to waste less atmospheric gas when used. It has mountings for four high-pressure gas tanks, two containing
 This module was
This module was
/ref>
EVA from ''Quest'' Airlock – Posted February 14, 2010
{{Orbital launches in 2001 Boeing spacecraft and space launch systems Components of the International Space Station Spacecraft launched in 2001
airlock
An airlock is a room or compartment which permits passage between environments of differing atmospheric pressure or composition, while minimizing the changing of pressure or composition between the differing environments.
An airlock consist ...
for the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
. ''Quest'' was designed to host spacewalks with both Extravehicular Mobility Unit
The Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) is an independent spacesuit that provides environmental protection, mobility, life support, and communications for astronauts performing extravehicular activity (EVA) in Geocentric orbit, Earth orbit. Introd ...
(EMU) spacesuit
A space suit (or spacesuit) is an environmental suit used for protection from the harsh Space environment, environment of outer space, mainly from its Vacuum (outer space), vacuum as a highly specialized pressure suit, but also its temperatu ...
s and Orlan space suits. The airlock was launched on STS-104 on July 14, 2001.
It was attached to the starboard CBM of the '' Unity'' during STS-104. The four external HP tanks were installed in pairs on two occasions.
Before ''Quest'' was attached, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n spacewalks using Orlan suits could only be done from the '' Zvezda'' service module, and American spacewalks using EMUs were only possible when a Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
was docked, allowing the astronauts to use the Shuttle's airlock, located in its payload bay. The arrival of ''Pirs'' docking compartment on September 16, 2001, provided another airlock from which Orlan spacewalks can be conducted.
Requirements
 ''Quest'' was necessary because American suits (EMUs) will not fit through a Russian airlock hatch and have different components, fittings, and connections. The airlock is designed to contain equipment that can work with both types of spacesuits, however, it is currently only able to host American spacewalks because the equipment necessary to work with Russian space suits has not been launched yet, which required the Expedition 9 crew to take a circuitous route to a worksite because of problems with the American space suits.
It is sized to allow EVAs with two crew.
''Quest'' was necessary because American suits (EMUs) will not fit through a Russian airlock hatch and have different components, fittings, and connections. The airlock is designed to contain equipment that can work with both types of spacesuits, however, it is currently only able to host American spacewalks because the equipment necessary to work with Russian space suits has not been launched yet, which required the Expedition 9 crew to take a circuitous route to a worksite because of problems with the American space suits.
It is sized to allow EVAs with two crew.
Early use
EMU EVAs were conducted from the ISS Joint Airlock in July 2001, February 2002, April 2002, and June 2002.Design
 The ''Quest'' Airlock consists of two segments, the "Equipment lock" that stores spacesuits and equipment, and the "Crew Lock" from which astronauts can exit into space. It was derived from the Space Shuttle airlock, although it was significantly modified to waste less atmospheric gas when used. It has mountings for four high-pressure gas tanks, two containing
The ''Quest'' Airlock consists of two segments, the "Equipment lock" that stores spacesuits and equipment, and the "Crew Lock" from which astronauts can exit into space. It was derived from the Space Shuttle airlock, although it was significantly modified to waste less atmospheric gas when used. It has mountings for four high-pressure gas tanks, two containing oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and two containing nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, which provides for atmospheric replenishment to the American side of the space station, most specifically for the gas lost after a hatch opening during a space walk.
Equipment lock segment
The larger equipment lock has storage space for EMU suits and equipment to check and maintain the EMUs. There is a Battery Charging Assembly, a Battery Stowage Assembly, a Fluid Pumping Unit (FPU) (to refill the EMU water tanks after each EVA), and much else.Crew lock segment
The hatch to space (EV hatch) has an inward opening airtight hard hatch, and an outwardly hinged thermal cover. The inner airtight hatch gets stowed at the end of the crew lock to allow ingress and egress. In the crew lock is the Umbilical Interface Assembly, able to support two US suits, or two Orlan-M suits, or one of each.Camp-out procedure
''Quest'' provides an environment where astronauts can "camp out" before a spacewalk in a reduced-nitrogen atmosphere to purge nitrogen from their bloodstream and avoiddecompression sickness
Decompression sickness (DCS; also called divers' disease, the bends, aerobullosis, and caisson disease) is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from Solution (chemistry), solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during D ...
in the low-pressure () pure-oxygen atmosphere of the spacesuit. In April 2006, Expedition 12 Commander Bill McArthur and Expedition 13 flight engineer Jeffrey Williams tested this new method of preparing for spacewalks by spending the night in the ''Quest'' Airlock. In the chamber, the pressure was reduced from the normal . Four hours into the Expedition 13 crew's sleep period, an error tone prompted mission controllers to cut short the activity, but the test was still deemed a success. American spacewalk activities thereafter have employed the "camp-out" pre-breathing technique.
The previous method of preparing for spacewalks involved breathing pure oxygen for several hours prior to an EVA to purge the body of nitrogen.
More recently astronauts have been using the In-Suit Light Exercise protocol rather than camp-out to prevent decompression sickness.
High-pressure gas tanks
Two oxygen and two nitrogen high-pressure gas tanks are attached externally to the equipment lock segment. These tanks (known as the High Pressure Gas Assembly.) provide a replenishable source of gas to the atmosphere control and supply system and oxygen for recharging the space suits (EMUs). Recharging the high-pressure tanks was accomplished by the Space Shuttle fleet until its retirement. When an orbiter was docked to the station's Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMA-2 or PMA-3), oxygen was routed through pressure lines from the PMAs to the ''Quest'' Airlock. The pumping of the oxygen from the docked spacecraft tanks into ''Quest''s high-pressure tank was accomplished by the Oxygen Recharge Compressor Assembly (ORCA). After the retirement of the Space Shuttle fleet, the Nitrogen Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) and spacecraft from theCommercial Crew Development
Development of the Commercial Crew Program (CCDev) began in the second round of the program, which was rescoped from a smaller technology development program for human spaceflight to a competitive development program that would produce the space ...
program will take over this task.
Construction
 This module was
This module was manufactured
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a ...
by Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
, under contract by NASA, at the Marshall Space Flight Center in 2000. It is made from aluminum and steel alloys.
The design for the crew airlock segment was derived from that of the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
's external airlock.''ISS Elements: Joint Airlock "Quest"''/ref>
Airlock specifications
*Material: aluminium and steel *Length: *Diameter: *Mass: *Volume: *Cost: $164 million, including tanksReferences
External links
EVA from ''Quest'' Airlock – Posted February 14, 2010
{{Orbital launches in 2001 Boeing spacecraft and space launch systems Components of the International Space Station Spacecraft launched in 2001