Quantum computational chemistry is an emerging field that exploits
quantum computing
A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of wave-particle duality, both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using s ...
to simulate chemical systems. Despite quantum mechanics' foundational role in understanding chemical behaviors, traditional computational approaches face significant challenges, largely due to the complexity and computational intensity of quantum mechanical equations. This complexity arises from the exponential growth of a quantum system's wave function with each added particle, making exact simulations on classical computers inefficient.
Efficient quantum algorithms for chemistry problems are expected to have run-times and resource requirements that scale polynomially with system size and desired accuracy. Experimental efforts have validated proof-of-principle chemistry calculations, though currently limited to small systems.
Brief History of Quantum Computational Chemistry
* 1929:
Dirac noted the inherent complexity of quantum mechanical equations, underscoring the difficulties in solving these equations using classical computation.
* 1982:
Feynman proposed using quantum hardware for simulations, addressing the inefficiency of classical computers in simulating quantum systems.
Common Methods in Quantum Computational Chemistry
While there are several common methods in
quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions ...
, the section below lists only a few examples.
Qubitization
Qubitization is a mathematical and algorithmic concept in quantum computing for the simulation of quantum systems via Hamiltonian dynamics. The core idea of qubitization is to encode the problem of Hamiltonian simulation in a way that is more efficiently processable by quantum algorithms.
Qubitization involves a transformation of the Hamiltonian operator, a central object in quantum mechanics representing the total energy of a system. In classical computational terms, a Hamiltonian can be thought of as a matrix describing the energy interactions within a quantum system. The goal of qubitization is to embed this Hamiltonian into a larger, unitary operator, which is a type of operator in quantum mechanics that preserves the norm of vectors upon which it acts.
Mathematically, the process of qubitization constructs a unitary operator
such that a specific projection of
is proportional to the Hamiltonian
of interest. This relationship can often be represented as
, where
is a specific quantum state and
is its
conjugate transpose
In mathematics, the conjugate transpose, also known as the Hermitian transpose, of an m \times n complex matrix \mathbf is an n \times m matrix obtained by transposing \mathbf and applying complex conjugation to each entry (the complex conjugate ...
. The efficiency of this method comes from the fact that the unitary operator
can be implemented on a quantum computer with fewer resources (like qubits and quantum gates) than would be required for directly simulating
A key feature of qubitization is in simulating Hamiltonian dynamics with high precision while reducing the quantum resource overhead. This efficiency is especially beneficial in quantum algorithms where the simulation of complex quantum systems is necessary, such as in quantum chemistry and materials science simulations. Qubitization also develops quantum algorithms for solving certain types of problems more efficiently than classical algorithms. For instance, it has implications for the Quantum Phase Estimation algorithm, which is fundamental in various quantum computing applications, including factoring and solving linear systems of equations.
Applications of qubitization in chemistry
= Gaussian orbital basis sets
=
In Gaussian orbital
basis sets, phase estimation algorithms have been optimized empirically from
to
where
is the number of basis sets. Advanced Hamiltonian simulation algorithms have further reduced the scaling, with the introduction of techniques like Taylor series methods and qubitization, providing more efficient algorithms with reduced computational requirements.
= Plane wave basis sets
=
Plane wave basis sets, suitable for periodic systems, have also seen advancements in algorithm efficiency, with improvements in product formula-based approaches and Taylor series methods.
Quantum phase estimation in chemistry
Overview
Phase estimation, as proposed by Kitaev in 1996, identifies the lowest energy eigenstate (
) and excited states (
) of a physical Hamiltonian, as detailed by Abrams and Lloyd in 1999. In quantum computational chemistry, this technique is employed to encode
fermionic Hamiltonians into a
qubit
In quantum computing, a qubit () or quantum bit is a basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classic binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical syste ...
framework.
Brief methodology
Initialization
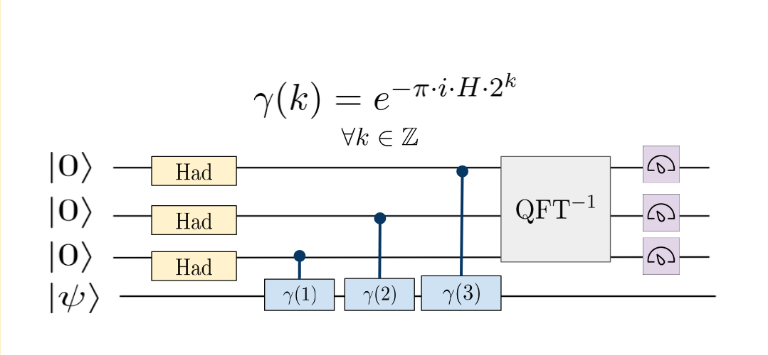
The qubit register is initialized in a state, which has a nonzero overlap with the Full Configuration Interaction (FCI) target eigenstate of the system. This state
is expressed as a sum over the energy eigenstates of the Hamiltonian,
, where
represents complex coefficients.
Application of Hadamard gates
Each
ancilla qubit undergoes a Hadamard gate application, placing the ancilla register in a superposed state. Subsequently, controlled gates, as shown above, modify this state.
Inverse quantum fourier transform
This transform is applied to the ancilla qubits, revealing the phase information that encodes the energy eigenvalues.
Measurement
The ancilla qubits are measured in the Z basis, collapsing the main register into the corresponding energy eigenstate
based on the probability
.
Requirements
The algorithm requires
ancilla qubits, with their number determined by the desired precision and success probability of the energy estimate. Obtaining a binary energy estimate precise to n bits with a success probability
necessitates.
ancilla qubits. This phase estimation has been validated experimentally across various quantum architectures.
Applications of QPEs in chemistry
Time evolution and error analysis
The total coherent
time evolution
Time evolution is the change of state brought about by the passage of time, applicable to systems with internal state (also called ''stateful systems''). In this formulation, ''time'' is not required to be a continuous parameter, but may be discr ...
required for the algorithm is approximately
. The total evolution time is related to the binary precision
, with an expected repeat of the procedure for accurate ground state estimation. Errors in the algorithm include errors in energy eigenvalue estimation (
), unitary evolutions (
), and circuit synthesis errors (
), which can be quantified using techniques like the
Solovay-Kitaev theorem.
The phase estimation algorithm can be enhanced or altered in several ways, such as using a single
ancilla qubit for sequential measurements, increasing efficiency, parallelization, or enhancing noise resilience in analytical chemistry. The algorithm can also be scaled using classically obtained knowledge about energy gaps between states.
Limitations
Effective
state preparation is needed, as a randomly chosen state would exponentially decrease the probability of collapsing to the desired ground state. Various methods for state preparation have been proposed, including classical approaches and quantum techniques like adiabatic state preparation.
Variational quantum eigensolver (VQE)
Overview
The variational quantum eigensolver is an algorithm in quantum computing, crucial for near-term quantum hardware. Initially proposed by Peruzzo et al. in 2014 and further developed by McClean et al. in 2016, VQE finds the lowest eigenvalue of Hamiltonians, particularly those in chemical systems. It employs the
variational method (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the variational method is one way of finding approximations to the lowest energy eigenstate or ground state, and some excited states. This allows calculating approximate wavefunctions such as molecular orbitals. The basis for ...
, which guarantees that the expectation value of the Hamiltonian for any parameterized trial wave function is at least the lowest energy eigenvalue of that Hamiltonian. VQE is a hybrid algorithm that utilizes both quantum and classical computers. The quantum computer prepares and measures the quantum state, while the classical computer processes these measurements and updates the system. This synergy allows VQE to overcome some limitations of purely quantum methods.
Applications of VQEs in chemistry
= 1-RDM and 2-RDM calculations
=
The reduced density matrices (1-RDM and 2-RDM) can be used to extrapolate the electronic structure of a system.
= Ground state energy extrapolation
=
In the Hamiltonian variational ansatz, the initial state
is prepared to represent the ground state of the molecular Hamiltonian without electron correlations. The evolution of this state under the Hamiltonian, split into commuting segments
, is given by the equation below.
where
are variational parameters optimized to minimize the energy, providing insights into the electronic structure of the molecule.
= Measurement scaling
=
McClean et al. (2016) and Romero et al. (2019) proposed a formula to estimate the number of measurements (
) required for energy precision. The formula is given by
, where
are coefficients of each Pauli string in the Hamiltonian. This leads to a scaling of
in a Gaussian orbital basis and
in a plane wave dual basis. Note that
is the number of basis functions in the chosen basis set.
= Fermionic level grouping
=
A method by Bonet-Monroig, Babbush, and O'Brien (2019) focuses on grouping terms at a
fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin (spin 1/2, spin , Spin (physics)#Higher spins, spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles i ...
ic level rather than a
qubit
In quantum computing, a qubit () or quantum bit is a basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classic binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical syste ...
level, leading to a measurement requirement of only
circuits with an additional gate depth of
.
= Limitations of VQE
=
While VQE's application in solving the electronic
Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after E ...
for small molecules has shown success, its scalability is hindered by two main challenges: the complexity of the quantum circuits required and the intricacies involved in the classical optimization process. These challenges are significantly influenced by the choice of the variational ansatz, which is used to construct the trial wave function. Modern quantum computers face limitations in running deep quantum circuits, especially when using the existing ansatzes for problems that exceed several qubits.
Jordan-Wigner encoding
Jordan-Wigner encoding is a method in quantum computing used for simulating fermionic systems like
molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding ...
s and
electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
interactions in quantum chemistry.
Overview
In quantum chemistry, electrons are modeled as
fermions
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin ( spin , spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles include all quarks and leptons and ...
with
antisymmetric wave functions. The Jordan-Wigner encoding maps these fermionic orbitals to qubits, preserving their antisymmetric nature. Mathematically, this is achieved by associating each fermionic creation
and annihilation
operator with corresponding qubit
operators
Operator may refer to:
Mathematics
* A symbol indicating a mathematical operation
* Logical operator or logical connective in mathematical logic
* Operator (mathematics), mapping that acts on elements of a space to produce elements of another ...
through the
Jordan-Wigner transformation:
Where
,
, and
are Pauli matrices acting on the
qubit.
Applications of Jordan-Wigner encoding in chemistry
= Electron hopping
=
Electron hopping between orbitals, central to chemical bonding and reactions, is represented by terms like
. Under Jordan-Wigner encoding, these transform as follows:
This transformation captures the quantum mechanical behavior of electron movement and interaction within molecules.
= Computational complexity in molecular systems
=
The complexity of simulating a molecular system using Jordan-Wigner encoding is influenced by the structure of the molecule and the nature of electron interactions. For a molecular system with
orbitals, the number of required qubits scales linearly with
, but the complexity of gate operations depends on the specific interactions being modeled.
Limitations of Jordan–Wigner encoding
The Jordan-Wigner transformation encodes fermionic operators into qubit operators, but it introduces non-local string operators that can make simulations inefficient. The FSWAP gate is used to mitigate this inefficiency by rearranging the ordering of fermions (or their qubit representations), thus simplifying the implementation of fermionic operations.
Fermionic SWAP (FSWAP) network
FSWAP networks rearrange qubits to efficiently simulate electron dynamics in molecules. These networks are essential for reducing the gate complexity in simulations, especially for
non-neighboring electron interactions.
When two fermionic modes (represented as qubits after the Jordan-Wigner transformation) are swapped, the FSWAP gate not only exchanges their states but also correctly updates the phase of the wavefunction to maintain fermionic
antisymmetry
In linguistics, antisymmetry, is a theory of syntax described in Richard S. Kayne's 1994 book ''The Antisymmetry of Syntax''. Building upon X-bar theory, it proposes a universal, fundamental word order for phrases (Branching (linguistics), branchin ...
. This is in contrast to the standard
SWAP gate, which does not account for the phase change required in the antisymmetric wavefunctions of fermions.
The use of FSWAP gates can significantly reduce the complexity of quantum circuits for simulating fermionic systems. By intelligently rearranging the fermions, the number of gates required to simulate certain fermionic operations can be reduced, leading to more efficient simulations. This is particularly useful in simulations where fermions need to be moved across large distances within the system, as it can avoid the need for long chains of operations that would otherwise be required.
References
Quantum chemistry
Further reading
*
*
{{subject bar, auto=y, d=y, portal=chemistry
 The qubit register is initialized in a state, which has a nonzero overlap with the Full Configuration Interaction (FCI) target eigenstate of the system. This state is expressed as a sum over the energy eigenstates of the Hamiltonian, , where represents complex coefficients.
The qubit register is initialized in a state, which has a nonzero overlap with the Full Configuration Interaction (FCI) target eigenstate of the system. This state is expressed as a sum over the energy eigenstates of the Hamiltonian, , where represents complex coefficients.