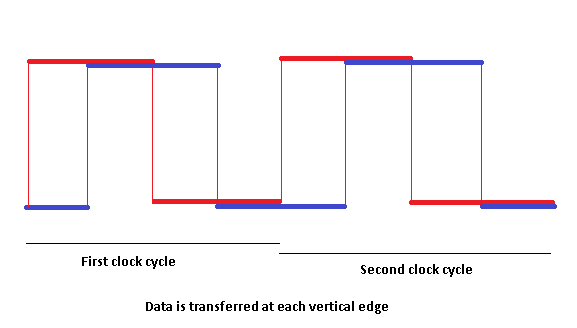
 Quad data rate (QDR, or quad pumping) is a communication signaling technique wherein data are transmitted at four points in the clock cycle: on the rising and falling edges, and at two intermediate points between them. The intermediate points are defined by a second clock that is 90° out of phase from the first. The effect is to deliver four bits of data per signal line per clock cycle.
In a quad data rate system, the data lines operate at twice the frequency of the clock signal. This is in contrast to double data rate systems, in which the clock and data lines operate at the same frequency.
Quad data rate technology was introduced by
Quad data rate (QDR, or quad pumping) is a communication signaling technique wherein data are transmitted at four points in the clock cycle: on the rising and falling edges, and at two intermediate points between them. The intermediate points are defined by a second clock that is 90° out of phase from the first. The effect is to deliver four bits of data per signal line per clock cycle.
In a quad data rate system, the data lines operate at twice the frequency of the clock signal. This is in contrast to double data rate systems, in which the clock and data lines operate at the same frequency.
Quad data rate technology was introduced by Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
in its Willamette-core Pentium 4 processor, and was subsequently employed in its Atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
, Pentium 4, Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed comp ...
, Pentium D and Core 2 processor ranges. This technology has allowed Intel to produce chipsets and processors
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, an ...
that can communicate with each other at data rates expected of the traditional front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
(FSB) technology running from 400 MT/s to 1600 MT/s, while maintaining a lower and thus more stable actual clock frequency of 100 MHz to 400 MHz.
Background
The reasons for operating in QDR rather than DDR are very different than those cited for operating in DDR rather than single data rate. Going to DDR allowed manufacturers of memory to send data at the same rate as the clock (one data-line transition for every clock-line transition), while SDR could only send data at half the rate of the clock (one data-line transition for every clock-line rising edge). A native implementation of QDR would result in the data rate being higher than the clock rate, negating any simple electrical advantage. The advantages for QDR arise when dealing with bus contention. On a modern computer, there may be several CPUs and several I/O devices, all competing for accesses to the memory. To handle this contention properly, modern systems aim to enable signals to propagate between all connected components within a single clock cycle, while setting a firm limit on the maximum clock rate. However, once the contention has been dealt with, the data transfer can be treated as a simple point-to-point unidirectional transfer. In such a simple transfer, it is no longer essential for signals to fully propagate within a cycle; they merely need to arrive coherently, marshaled by a special signal called "strobe". This reduced requirement on signal integrity allows the QDR data transfer to occur at twice the speed of the clock, as opposed to at the same speed as the clock as in DDR.See also
*Double data rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in ...
* Pumping (computer systems)
* GDDR5X
References
Digital electronics {{Compu-hardware-stub