Qitai Radio Telescope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Xinjiang Qitai 120m Radio Telescope (QTT) is a planned
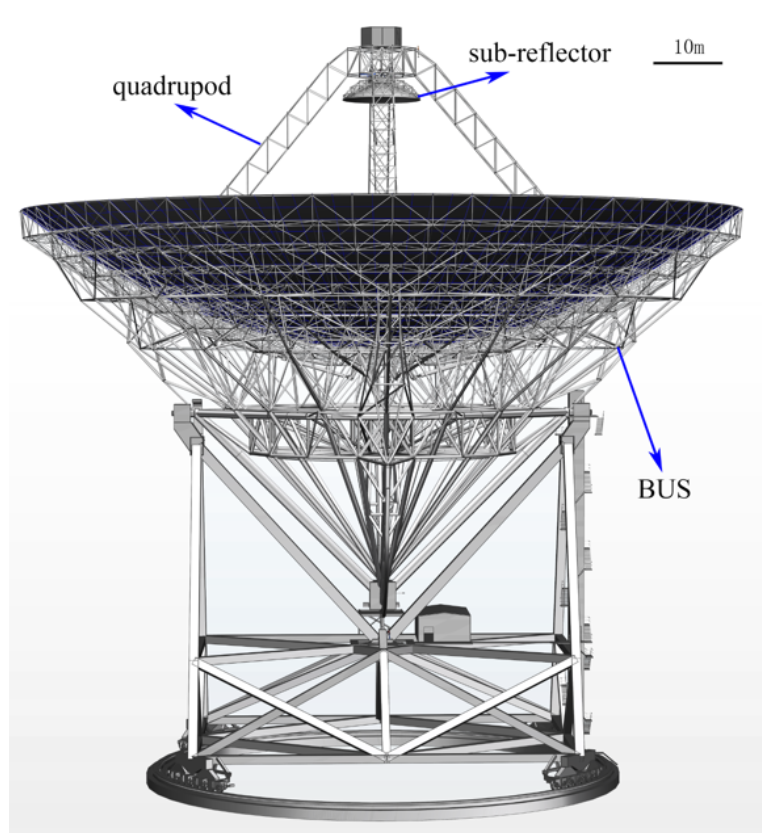 The QTT is a Gregorian parabolic antenna with an active main surface to correct the deformation caused by
The QTT is a Gregorian parabolic antenna with an active main surface to correct the deformation caused by
radio telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna (radio), antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the r ...
to be built in Qitai County in Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. Upon completion, which is scheduled for 2028, it will be the world's largest fully steerable single-dish radio telescope. It is intended to operate at 150 MHz to 115 GHz. The construction of the antenna project is under the leadership of the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS; ) is the national academy for natural sciences and the highest consultancy for science and technology of the People's Republic of China. It is the world's largest research organization, with 106 research i ...
.
The fully steerable dish of the QTT will allow it to observe 75% of the stars in the sky at any given time. The QTT and the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), also located in China, can both observe frequencies in the " water hole" that has traditionally been favored by scientists engaged in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence ( SETI), meaning that each observatory could provide follow-up observations of putative signals from extraterrestrials detected in this quiet part of the radio spectrum at the other observatory.
The radio telescope site selection team considered 48 candidate locations throughout Xinjiang. The chosen site for the facility is in the foothills of the Tian Shan mountains, near Shihezi village, Banjiegou Town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city.
The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ...
, about 46 km (straight-line distance) south-south-east of the Qitai county seat (Qitai Town). The mountain ridges surrounding the site are supposed to provide some protection from electromagnetic noise. The authorities propose designating a radio quiet zone (a 10 km by 15 km rectangle, much smaller than the United States National Radio Quiet Zone) around the future facility. A paper from October 2023 stated that a radio quiet zone with a radius of 30 km will be established. The zone will have a core zone (2.5x4 km), restricted zone (10x15 km) and coordination zone (r=30 km) with reducing control levels.
China started to build the QTT in September 2022 and it will take six years to complete the telescope.
Antenna
 The QTT is a Gregorian parabolic antenna with an active main surface to correct the deformation caused by
The QTT is a Gregorian parabolic antenna with an active main surface to correct the deformation caused by gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
. The antenna has an azimuth-elevation structure on a wheel-and-track mount. The back of the antenna has design similarities to the umbrella-like structure of the Eiffelsberg telescope. To reduce dead load and thermal deformation, the sub-reflector will use carbon fiber-reinforced plastic. The telescope can switch between Gregorian and primary focus. For the primary focus it uses the prime focus platform (PEP). The PEP is aligned to one of the quadruple legs in stow mode and it is moved horizontally over the sub-reflector in primary operation mode. The PEP contains receivers and auxiliary equipment. To access the telescope an elevator, stairs, catwalks, platforms and a crane is part of the antenna.
Receivers
The QTT will containbroadband
In telecommunications, broadband or high speed is the wide-bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth data transmission that exploits signals at a wide spread of frequencies or several different simultaneous frequencies, and is used in fast Inter ...
, ultra wide-band (UWB), multi-beam and phased array feeds (PAF) low-noise cryogenic receivers from 40 cm to 3 mm bands, all linearly polarized. Currently only 40 cm to 1.3 cm receivers are planned.
Goals
The main goals of the QTT include imaging ofpulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be obse ...
s, stellar formation, and the large-scale radio structure of the universe. Other goals are the use of Pulsar Timing Arrays to detect nanoHertz gravitational waves, to be part of Very Long Baseline Interferometry, to study the interstellar medium, to study galaxies and black holes, to study dark matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relat ...
and to carry out astrometry.
Similar fully steerable telescopes
* Green Bank Telescope, the current largest fully steerable parabolic dish wideband radio telescope, of similar capabilities and 110m x 100m elliptical aperture * Effelsberg 100-m Radio Telescope *The three NASA Deep Space Network stations each sport a fully steerable 70m dish telescope, and the counterpart Soviet Deep Space Network likewise uses the comparable 70m aperture RT-70 lineSee also
* List of radio telescopesReferences
{{Portal bar, China, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System, Education, Science Chinese telescopes Radio telescopes Buildings and structures in Xinjiang Proposed buildings and structures in China Proposed telescopes Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture