Q Cygni on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Q Cygni (Q Cyg), is a 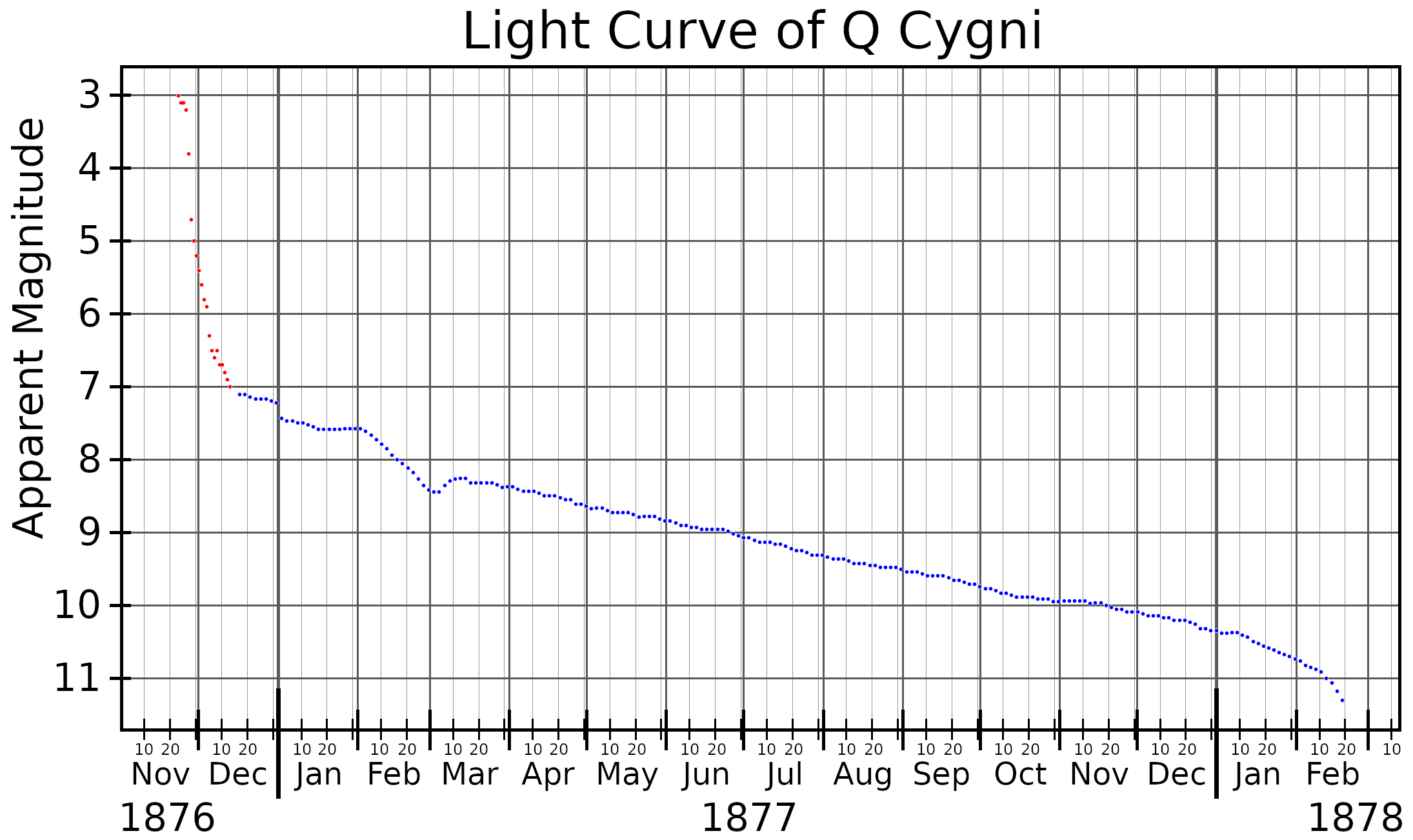
Stars of Cygnus
{{NGC objects:7000-7499 Cygnus (constellation) Novae 8296 J21414393+4250290 Durchmusterung objects NGC objects Cygni, Q
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
located in the constellation Cygnus. It is also known as Nova Cygni 1876, and has the designation NGC 7114, and HR 8296. Nova Cygni is located in the northwestern portion of Cygnus along the border with Lacerta
Lacerta is one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Its name is Latin for lizard. A small, faint constellation, it was defined in 1687 by the astronomer Johannes Hevelius. Its brightest stars form a "W" ...
.
One of the earliest nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white ...
e recorded, Q Cygni was discovered by astronomer Johann Friedrich Julius Schmidt
Johann Friedrich Julius Schmidt (25 October 1825 in Eutin, German Confederation, Germany – 7 February 1884 in Athens, Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece) was a German astronomer and geophysicist. He was the director of the National Observa ...
on November 24, 1876. The star had undergone a nova, brightening to about 3rd magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
and remaining as bright for four days.
The system is termed a cataclysmic variable
In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since those with an outburst brightness visible to ...
, composed of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
in close orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
with another star that orbit each other every 10 hours. The white dwarf is surrounded by an accretion disc
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is most frequently a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and ...
, which blazes much brighter than the star it circles. The system has been estimated to be 740 ± 11 parsecs distant. The secondary star has been estimated to be around 0.6 times as massive as the Sun, making it an orange dwarf of spectral type K5. Also known as a donor star, the secondary supplies mass to the white dwarf via its accretion disc.
A small nebulous disc was reported around the nova and this led to it being listed in the New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxy, galaxies, star cluste ...
as a possible planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The ...
. No nebulosity
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the ...
is visible in modern observations and the Revised New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxy, galaxies, star cluste ...
lists this as a "non-existent" object.

References
External links
Stars of Cygnus
{{NGC objects:7000-7499 Cygnus (constellation) Novae 8296 J21414393+4250290 Durchmusterung objects NGC objects Cygni, Q