Pulpotomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a  There is another term also related to vital pulp therapy, '' apexogenesis''.
Apexogenesis is a treatment in preserving vital pulp tissue in the apical part of a root canal to allow the completion in formation of the root apex. This clinical procedure is essentially a deep pulpotomy, aimed to preserve the pulp in immature teeth that have deep pulpal inflammation. Examples include teeth with carious exposures and trauma in which treatment of the exposed pulp is delayed and it becomes necessary to extend farther into the canal to reach healthy tissue.
There is another term also related to vital pulp therapy, '' apexogenesis''.
Apexogenesis is a treatment in preserving vital pulp tissue in the apical part of a root canal to allow the completion in formation of the root apex. This clinical procedure is essentially a deep pulpotomy, aimed to preserve the pulp in immature teeth that have deep pulpal inflammation. Examples include teeth with carious exposures and trauma in which treatment of the exposed pulp is delayed and it becomes necessary to extend farther into the canal to reach healthy tissue.
Primary root overfilling rate with different techniques
{{Endodontology Dentistry procedures Endodontics
 Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a primary tooth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Fehrenbach, MJ and Popowics, T. (2026). ''Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy'', 6th edition, Elsevier, page 287–296. are ...
with extensive caries
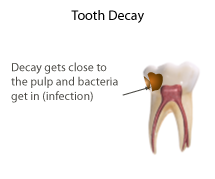
Tooth decay, also known as caries,The word 'caries' is a mass noun, and is not a plural of 'carie'.'' is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The resulting cavities may be a number of different colors, from yellow to black ...
but without evidence of root pathology. The minimally invasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definitio ...
, endodontic techniques of vital pulp therapy (VPT) are based on improved understanding of the capacity of pulp tissues to heal and regenerate plus the availability of advanced endodontic materials. During caries removal, this results in a carious or mechanical pulp exposure from the cavity. During pulpotomy, the inflamed/diseased pulp tissue is removed from the coronal pulp chamber of the tooth, leaving healthy pulp tissue which is dressed with a long-term clinically successful medicament that maintains the survival of the pulp and promotes repair. There are various types of medicament placed above the vital pulp such as Buckley's Solution of formocresol, ferric sulfate
Iron(III) sulfate or ferric sulfate (British English: sulphate instead of sulfate) is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of water of crystallization, hydrates are known, including the most commonly encount ...
, calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approxim ...
or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). MTA is a more recent material used for pulpotomies with a high rate of success, better than formocresol or ferric sulfate. It is also recommended to be the preferred pulpotomy agent in the future. After the coronal pulp chamber is filled, the tooth is restored with a filling material that seals the tooth from microleakage, such as a stainless steel crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
which is the most effective long-term restoration. However, if there is sufficient remaining supporting tooth structure, other filling materials such as amalgam or composite resin can provide a functional alternative when the primary tooth has a life span of two years or less. The medium- to long-term treatment outcomes of pulpotomy in symptomatic permanent teeth with caries, especially in young people, indicate that pulpotomy can be a potential alternative to root canal therapy (RCT).
 There is another term also related to vital pulp therapy, '' apexogenesis''.
Apexogenesis is a treatment in preserving vital pulp tissue in the apical part of a root canal to allow the completion in formation of the root apex. This clinical procedure is essentially a deep pulpotomy, aimed to preserve the pulp in immature teeth that have deep pulpal inflammation. Examples include teeth with carious exposures and trauma in which treatment of the exposed pulp is delayed and it becomes necessary to extend farther into the canal to reach healthy tissue.
There is another term also related to vital pulp therapy, '' apexogenesis''.
Apexogenesis is a treatment in preserving vital pulp tissue in the apical part of a root canal to allow the completion in formation of the root apex. This clinical procedure is essentially a deep pulpotomy, aimed to preserve the pulp in immature teeth that have deep pulpal inflammation. Examples include teeth with carious exposures and trauma in which treatment of the exposed pulp is delayed and it becomes necessary to extend farther into the canal to reach healthy tissue.
Objectives
In primary tooth
After the pulpotomy treatment, the radicular pulp should remain asymptomatic without any adverse clinical signs or symptoms such as sensitivity,pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
, or swelling. From the radiographs
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeu ...
, there should be absence of postoperative evidence of pathologic root resorption
Resorption of the root of the tooth, or root resorption, is the progressive loss of dentin and cementum by the action of odontoclasts. Root resorption is a normal physiological process that occurs in the exfoliation of the primary dentition. How ...
. There should be absence of clinical signs of infection and inflammation and no harm to the succedaneous tooth. However, radiographs play a very important role, to check if pulpotomy can be done on the primary tooth. For example, aspects considered are the extension of caries in the primary tooth, and the development of the succedaneous permanent tooth.
In mature permanent tooth
The tooth should be asymptomatic. There should be no clinical signs and symptoms. From the radiographs, there should be absence of postoperative evidence of pathology.In immature tooth
Pulpotomy allows the continuation of root formation, leading to tooth end closure, preservation and maintenance of pulp vitality, stronger root structure and greater structural integrity.Indications
Primary teeth
Primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Work ...
/deciduous (baby) teeth in children have relatively large pulp spaces. Caries do not have to develop significantly before they reach the pulp chamber.
When the soft tissue in the pulp chamber is infected (has bacteria in it) or affected (is inflamed), it can be removed by a dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in provi ...
or dental therapist
A dental therapist is a member of the dental team who provides preventive and restorative dental care for children and adults. The precise role varies and is dependent on the therapist's education and the various dental regulations and guideline ...
under local anaesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sense, sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sen ...
. If the soft tissue in the canals is still healthy enough, a special medicated filling can be put into the chamber in an attempt to keep the remaining pulp (in the canals) alive. The process of removing the pulp from the chamber is the actual pulpotomy, though the word is often used for the entire process including placement of the medication. There are many medicaments that can be used to fill the pulp chamber, including zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) is a material created by the combination of zinc oxide and eugenol contained in clove oil. An acid–base reaction takes place with the formation of zinc eugenolate chelate. The reaction is catalysed by water and is accel ...
as well as mineral trioxide aggregate.
There are two types of pulpotomy techniques depending the extent of caries in a tooth and the symptoms it presents. A vital pulpotomy or a non-vital pulpotomy can be carried out. However, recent research shows that non-vital pulpotomies are rarely indicated due to their low success rates and it is therefore sometimes better to extract
An extract (essence) is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures or absolutes or dried and powdered.
The aromatic principles of ma ...
the tooth.
Afterwards the tooth is restored with a regular filling, either composite or amalgam, or a stainless steel crown. Due to the process of a pulpotomy causing the tooth to become slightly brittle, a stainless steel crown is normally indicated as the preferred choice of definitive restoration.
A pulpotomy can be done to both permanent and primary teeth.
Types
Primary teeth
The indication of this pulpotomy procedure is when pulp exposure occurs during caries removal in a primary tooth with a normal pulp or reversible pulpitis or after a traumatic pulp exposure. Then, the coronal tissue is amputated, and the remaining radicular tissue is judged to be vital withoutsuppuration
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during infections, regardless of cause. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collec ...
, pus, necrosis, or excessive bleeding which cannot be controlled by a moist cotton pellet (with saline) after several minutes, and there are no radiographic signs of infection or pathologic resorption.
Pulpotomy therapy can be classified according to the following treatment objectives: devitalization (mummification, cauterization), preservation (minimal devitalization, noninductive), or regeneration (inductive, reparative).
Devitalization
Multiple visits with application of formocresol in pulpotomy is used to fix the radicular pulp completely to reduce pulp infection. The radicular pulp was theoretically sterilized and devitalized, thereby reducing infection and internal resorption. Another form of nonchemical devitalization emerged: electrosurgical pulpotomy.Electrocautery
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, o ...
releases heat that denatures pulp and reduces bacterial contamination. Experimentally, electrosurgery has been shown to reduce pathologic root resorption and periapical pathology, and a series of pulpal effects including acute and chronic inflammation, swelling and diffuse necrosis. It is reported that this method has high success rate in pulpotomies.
However, this method may prove to be more diagnosis and technique sensitive, and it may not be suitable if apical root resorption has occurred.
Preservation
Zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) is a material created by the combination of zinc oxide and eugenol contained in clove oil. An acid–base reaction takes place with the formation of zinc eugenolate chelate. The reaction is catalysed by water and is accel ...
(ZOE) was the first agent to be used for preservation. In recent years, glutaraldehyde
Glutaraldehyde is an organic compound with the formula . The molecule consists of a five carbon chain doubly terminated with formyl (CHO) groups. It is usually used as a solution in water, and such solutions exists as a collection of hydrates, ...
has been proposed as an alternative to formocresol based on: its superior fixative properties and low toxicity. A nonaldehyde chemical, ferric sulfate, has received some attention recently as a pulpotomy agent. It minimizes the chances for inflammation and internal resorption. This category of pulp therapy is still in flux, although major changes in the future are not likely.
Regeneration
The ideal pulpotomy treatment should leave the radicular pulp alive and healthy. In this case, the tooth should be filled with noxious restorative materials within, thereby diminishing the chances of internal resorption, as well as formation of reparative dentin.Calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approxim ...
was the first agent used in pulpotomies that demonstrated any capacity to induce regeneration of dentin. However, the success rate is not very high. Recent advances in the field of bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
and dentin formation have opened new vistas for pulp therapy, which is a factor called bone morphogenetic protein
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Professor Marshall Urist and Professor Hari Reddi discovered their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now ...
(BMP). It has bone-inductive properties, that can predictably induce bone for use in the fields of orthopedic, oral, and periodontal surgery. Most importantly for dentistry, these osteogenic proteins hold promise for pulp therapy.
Young permanent teeth
Partial pulpotomy for carious exposures
Partial pulpotomy is also indicated in youngpermanent teeth
Permanent teeth or adult teeth are the second set of teeth formed in diphyodont mammals. In humans and old world simians, there are thirty-two permanent teeth, consisting of six maxillary and six mandibular molars, four maxillary and four mandib ...
with pulp exposure due to caries, provided that the bleeding can be controlled within several minutes. It is a procedure in which the inflamed pulp tissue beneath an exposure is removed to a depth of 1 to 3mm or deeper to reach the level of healthy pulp tissue. Pulpal bleeding can be controlled by irrigation of sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite is an alkaline inorganic chemical compound with the formula (also written as NaClO). It is commonly known in a dilute aqueous solution as bleach or chlorine bleach. It is the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid, consisting of ...
or chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and ...
. The site is then covered with a pulpal medicament, calcium hydroxide or MTA, followed by a final restoration that provides a complete seal to prevent any leakage and bacterial contamination following the restoration.
After the procedure, the remaining pulp should remain vital and the patient should be free of any adverse clinical signs or symptoms such as sensitivity, pain or swelling. Immature teeth should continue normal development and apexogenesis.
Partial pulpotomy for traumatic exposures
Tooth crown fractures are one of the most common dental injuries and the pulp is exposed in approximately 25% of all crown fractures. Maintaining vitality of the pulp tissue in an immature tooth is important to allow continued growth of the tooth. Partial pulpotomy due to a traumatic exposure is also known as Cvek pulpotomy. The procedure involves removal of of inflamed pulp tissue beneath an exposure to reach the level of healthy pulp tissue. The surface of the remaining pulp is then irrigated with bacteriocidal irrigants such as sodium hypochlorite or chlorhexidine until bleeding has ceased. The site is then covered with a pulpal medicament, either calcium hydroxide or MTA. The remaining cavity is then restored with a material that provides a complete seal to prevent any leakage and bacterial contamination following the restoration. The remaining pulp tissue should continue to be vital after partial pulpotomy and teeth with immature roots should show continued normal development and apexogenesis. There should be no signs of pain, swelling, or sensitivity after the procedure. Cvek et al reported that partial pulpotomies after a traumatic exposure had a success rate of 96%.Medicaments
Pulpotomy is a vital pulp therapy; medicaments that can promote healing and preserve the vitality of the tooth should be placed after removal of the inflamed pulp. In primary teeth medicaments such as formocresol, mineral trioxide aggregate, zinc oxide eugenol andcalcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approxim ...
can be used in pulpotomy. Formocresol use has been questioned due to toxicity concerns. Ferric sulfate
Iron(III) sulfate or ferric sulfate (British English: sulphate instead of sulfate) is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of water of crystallization, hydrates are known, including the most commonly encount ...
, sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite is an alkaline inorganic chemical compound with the formula (also written as NaClO). It is commonly known in a dilute aqueous solution as bleach or chlorine bleach. It is the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid, consisting of ...
or a local anaesthetic solution containing a vasoconstrictor agent can be used to arrest any bleeding from the pulp prior to the placement of medicament. Calcium enriched mixtures have been used in permanent molar teeth with irreversible pulpitis showing positive outcomes.
Ferric sulfate
Ferric sulfate is used to arrest pulpal bleeding by forming a sealing membrane through the agglutination of the blood proteins with ferric and sulfate ions. This metal-protein clot at the surface of the pulp may act as a barrier to external irritants. The physiological clot formation is thought to be able to minimize inflammation and internal resorption compared to calcium hydroxide. Most importantly, ferric sulfate causes minimal devitalization and subsequent preservation of the pulp tissue. Ferric sulphate has been shown to have close to a 100% clinical success compared to formocresol (77%) with one-year follow-up.Formocresol
Formocresol has been used in pulpotomy procedures of the primary teeth since 80 years. Formocresol is both a bactericidal and devitalizing agent. It kills bacteria and converts the pulp tissue into inert compounds. This action fastens the vital pulp, maintaining them inert and conserves the primary tooth until it falls off physiologically. However, formaldehyde, a primary component in formocresol has raised concerns regarding its safe of use. Formaldehyde is a hazardous substance and has perceived the need to reevaluate the use of formocresol.Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE)
After pulpal bleeding is arrested, a suitable base such as zinc oxide eugenol is placed to seal the tooth from microleakage. ZOE is a nontoxic material for pulpal cells and possess antimicrobial as well as anti-inflammatory properties. In addition, it also has local anesthetic or soothing effect on the dental pulp.Calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 is conventionally used as a pulpotomy agent of the permanent teeth but with less long-term success. Calcium hydroxide is a highly alkaline (pH 12) material that has bactericidal effect and has the potential to enhance reparative dentin (dentin bridge) formation. However, it also leads to superficial necrosis of the pulp tissue in contact with the medication and has been shown to be toxic to cells in tissue culture. Therefore, in spite being a popular vital pulp therapy material, its use as a pulpotomy agent remains controversial.Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA)
MTA is a more recent material that consists of tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, tricalcium aluminate, tetracalcium aluminoferrite, bismuth oxide and calcium sulfate. MTA is known to have excellent physical characteristics, biocompatibility and has the ability to stimulate cytokine release from pulpal fibroblast, which can stimulate hard tissue formation. It has better structural integrity and forms a thicker, more localized dentinal bridge. MTA results in a more predictable dentin bridge formation and pulpal health. MTA has a high rate of success and has been shown to perform equal or better than formocresol or ferric sulfate. However, the cost, availability and difficulty in handling this material remains its current drawback.Alternative pulpotomy techniques
Electro-surgery pulpotomy
Electro-surgical pulpotomy is a method of cutting and coagulating soft tissues by means of high frequency radio waves. It can control bleeding without chemical coagulation and is antibacterial. Electrosurgical pulpotomy has a success rate of 70 to 94%. However, it is considered as a sensitive technique.Laser pulpotomy
The carbon-dioxide laser emits an infrared beam that has an affinity for water, and is capable of producing well-localized cautery to soft tissue. Tissue is removed byablation
Ablation ( – removal) is the removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosion, erosive processes, or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, including spacecraft material for as ...
through conversion of the laser beam to heat. The carbon-dioxide laser appears to be a promising alternative for pulpotomy therapy.
Clinical significance
Conserving the vitality of pulp tissues appears to be a less painful alternative to root canal treatment (RCT) for younger patients. The high success rate reported for pulpotomy suggests that this procedure offers hope as an alternative to root canal treatment in teeth with a diagnosis of irreversible pulpitis.See also
* PulpectomyReferences
External links
Primary root overfilling rate with different techniques
{{Endodontology Dentistry procedures Endodontics