Pseudo-LRU on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pseudo-LRU or PLRU is a family of
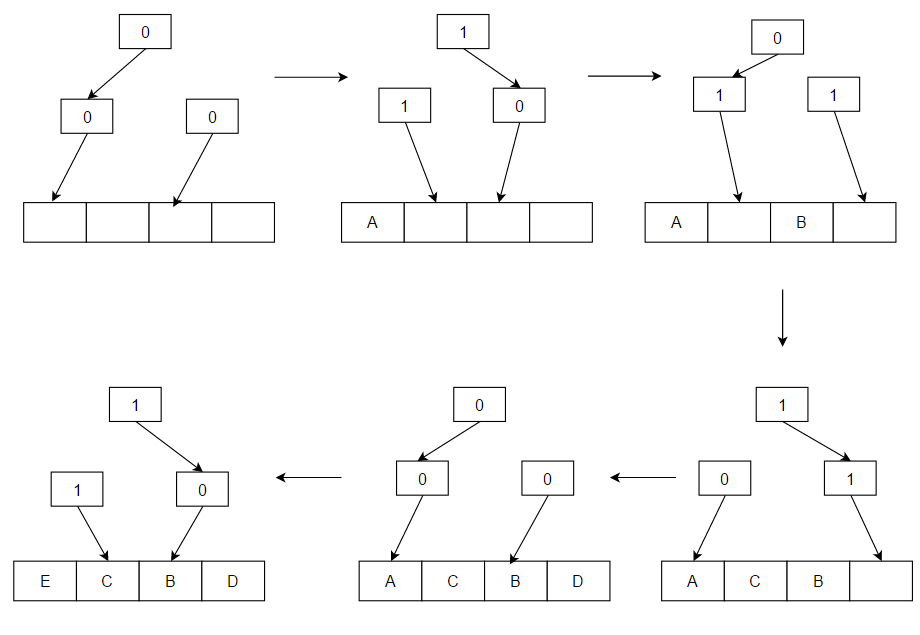 This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction, B would be chosen instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction, B would be chosen instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
Automatic Generation of Models of Microarchitectures
/ref>
cache algorithms
In computing, cache replacement policies (also known as cache replacement algorithms or cache algorithms) are optimizing instructions or algorithms which a computer program or hardware-maintained structure can utilize to manage a cache of infor ...
which improve on the performance of the Least Recently Used
In computing, cache replacement policies (also known as cache replacement algorithms or cache algorithms) are Program optimization, optimizing instructions or algorithms which a computer program or hardware-maintained structure can utilize to ma ...
(LRU) algorithm by replacing values using approximate measures of age rather than maintaining the exact age of every value in the cache.
PLRU usually refers to two cache replacement algorithms: tree-PLRU and bit-PLRU.
Tree-PLRU
Tree-PLRU is an efficientalgorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
to select an item that most likely has not been accessed very recently, given a set of items and a sequence of access events to the items.
This technique is used in the CPU cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, whi ...
of the Intel 486
The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor introduced in 1989. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of ...
and in many processors in the PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., App ...
family, such as Freescale's PowerPC G4
PowerPC G4 is a designation formerly used by Apple Inc., Apple to describe a ''fourth generation'' of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various (though closely related) processor models from Freescale Semiconductor, Fr ...
used by Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Co ...
.
The algorithm works as follows: consider a binary search tree
In computer science, a binary search tree (BST), also called an ordered or sorted binary tree, is a Rooted tree, rooted binary tree data structure with the key of each internal node being greater than all the keys in the respective node's left ...
for the items in question. Each node of the tree has a one-bit flag denoting "go left to insert a pseudo-LRU element" or "go right to insert a pseudo-LRU element". To find a pseudo-LRU element, traverse the tree according to the values of the flags. To update the tree with an access to an item N, traverse the tree to find N and, during the traversal, set the node flags to denote the direction that is opposite to the direction taken.
 This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction, B would be chosen instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction, B would be chosen instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
Bit-PLRU
Bit-PLRU stores one status bit for each cache line. These bits are called MRU-bits. Every access to a line sets its MRU-bit to 1, indicating that the line was recently used. Whenever the last remaining 0 bit of a set's status bits is set to 1, all other bits are reset to 0. At cache misses, the leftmost line whose MRU-bit is 0 is replaced./ref>
See also
*Cache algorithms
In computing, cache replacement policies (also known as cache replacement algorithms or cache algorithms) are optimizing instructions or algorithms which a computer program or hardware-maintained structure can utilize to manage a cache of infor ...
References
* https://people.cs.clemson.edu/~mark/464/p_lru.txt * http://www.ipdps.org/ipdps2010/ipdps2010-slides/session-22/2010IPDPS.pdf * http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.217.3594&rep=rep1&type=pdf