Prussian Debt Commission on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prussia (; ;

 In 1211, King
In 1211, King
 On 18 January 1701, Frederick William's son, Elector Frederick III, elevated Prussia from a duchy to a kingdom and crowned himself King
On 18 January 1701, Frederick William's son, Elector Frederick III, elevated Prussia from a duchy to a kingdom and crowned himself King  Frederick William I died in 1740 and was succeeded by his son, Frederick II, whose accomplishments led to his reputation as "Frederick the Great". As crown prince, Frederick had focused, primarily, on philosophy and the arts. He was an accomplished flute player and composer. In 1740, Prussian troops crossed over the undefended border of
Frederick William I died in 1740 and was succeeded by his son, Frederick II, whose accomplishments led to his reputation as "Frederick the Great". As crown prince, Frederick had focused, primarily, on philosophy and the arts. He was an accomplished flute player and composer. In 1740, Prussian troops crossed over the undefended border of
 During the reign of King Frederick William II (1786–1797), Prussia annexed additional Polish territory through the
During the reign of King Frederick William II (1786–1797), Prussia annexed additional Polish territory through the
 Bismarck realised that the dual administration of Schleswig and Holstein was only a temporary solution, and tensions rose between Prussia and Austria. The struggle for supremacy in Germany then led to the Austro-Prussian War (1866), triggered by the dispute over Schleswig and Holstein, with Bismarck using proposed injustices as the Casus belli, reason for war.
On the Austrian side stood the south German states (including Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Kingdom of Württemberg, Württemberg), some central German states (including Kingdom of Saxony, Saxony), and Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover in the north. On the side of Prussia were Kingdom of Italy, Italy, most north German states, and some smaller central German states. Eventually, the better-armed Prussian troops won the crucial victory at the Battle of Königgrätz under Helmuth von Moltke the Elder. The century-long struggle between Berlin and Vienna for the dominance of Germany was now over. As a sideshow in this war, Prussia defeated Hanover in the Battle of Langensalza (1866). While Hanover hoped in vain for help from Britain (as they had previously been in personal union), Britain stayed out of a confrontation with a continental great power and Prussia satisfied its desire for merging the once separate territories and gaining strong economic and strategic power, particularly from the full access to the resources of the Ruhr.
Bismarck desired Austria as an ally in the future, and so he declined to annex any Austrian territory. But in the Peace of Prague (1866), Peace of Prague in 1866, Prussia annexed four of Austria's allies in northern and central GermanyHanover, Electorate of Hesse, Hesse-Kassel, Duchy of Nassau, Nassau and Free City of Frankfurt, Frankfurt. Prussia also won full control of Schleswig-Holstein. As a result of these territorial gains, Prussia now stretched uninterrupted across the northern two-thirds of Germany and contained two-thirds of Germany's population. The German Confederation was dissolved, and Prussia impelled the 21 states north of the Main (river), Main river into forming the
Bismarck realised that the dual administration of Schleswig and Holstein was only a temporary solution, and tensions rose between Prussia and Austria. The struggle for supremacy in Germany then led to the Austro-Prussian War (1866), triggered by the dispute over Schleswig and Holstein, with Bismarck using proposed injustices as the Casus belli, reason for war.
On the Austrian side stood the south German states (including Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Kingdom of Württemberg, Württemberg), some central German states (including Kingdom of Saxony, Saxony), and Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover in the north. On the side of Prussia were Kingdom of Italy, Italy, most north German states, and some smaller central German states. Eventually, the better-armed Prussian troops won the crucial victory at the Battle of Königgrätz under Helmuth von Moltke the Elder. The century-long struggle between Berlin and Vienna for the dominance of Germany was now over. As a sideshow in this war, Prussia defeated Hanover in the Battle of Langensalza (1866). While Hanover hoped in vain for help from Britain (as they had previously been in personal union), Britain stayed out of a confrontation with a continental great power and Prussia satisfied its desire for merging the once separate territories and gaining strong economic and strategic power, particularly from the full access to the resources of the Ruhr.
Bismarck desired Austria as an ally in the future, and so he declined to annex any Austrian territory. But in the Peace of Prague (1866), Peace of Prague in 1866, Prussia annexed four of Austria's allies in northern and central GermanyHanover, Electorate of Hesse, Hesse-Kassel, Duchy of Nassau, Nassau and Free City of Frankfurt, Frankfurt. Prussia also won full control of Schleswig-Holstein. As a result of these territorial gains, Prussia now stretched uninterrupted across the northern two-thirds of Germany and contained two-thirds of Germany's population. The German Confederation was dissolved, and Prussia impelled the 21 states north of the Main (river), Main river into forming the
 The controversy with the Second French Empire over the candidacy of Leopold, Prince of Hohenzollern to the Spanish throne was escalated both by France and Bismarck. With his Ems Dispatch, Bismarck took advantage of an incident in which the French ambassador had approached William. The government of Napoleon III, expecting another civil war among the German states, declared war against Prussia, continuing Franco-German enmity. However, honouring their treaties, the German states joined forces and quickly defeated France in the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. Following victory under Bismarck's and Prussia's leadership, Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden, Württemberg and Bavaria, which had remained outside the North German Confederation, accepted incorporation into a united
The controversy with the Second French Empire over the candidacy of Leopold, Prince of Hohenzollern to the Spanish throne was escalated both by France and Bismarck. With his Ems Dispatch, Bismarck took advantage of an incident in which the French ambassador had approached William. The government of Napoleon III, expecting another civil war among the German states, declared war against Prussia, continuing Franco-German enmity. However, honouring their treaties, the German states joined forces and quickly defeated France in the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. Following victory under Bismarck's and Prussia's leadership, Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden, Württemberg and Bavaria, which had remained outside the North German Confederation, accepted incorporation into a united
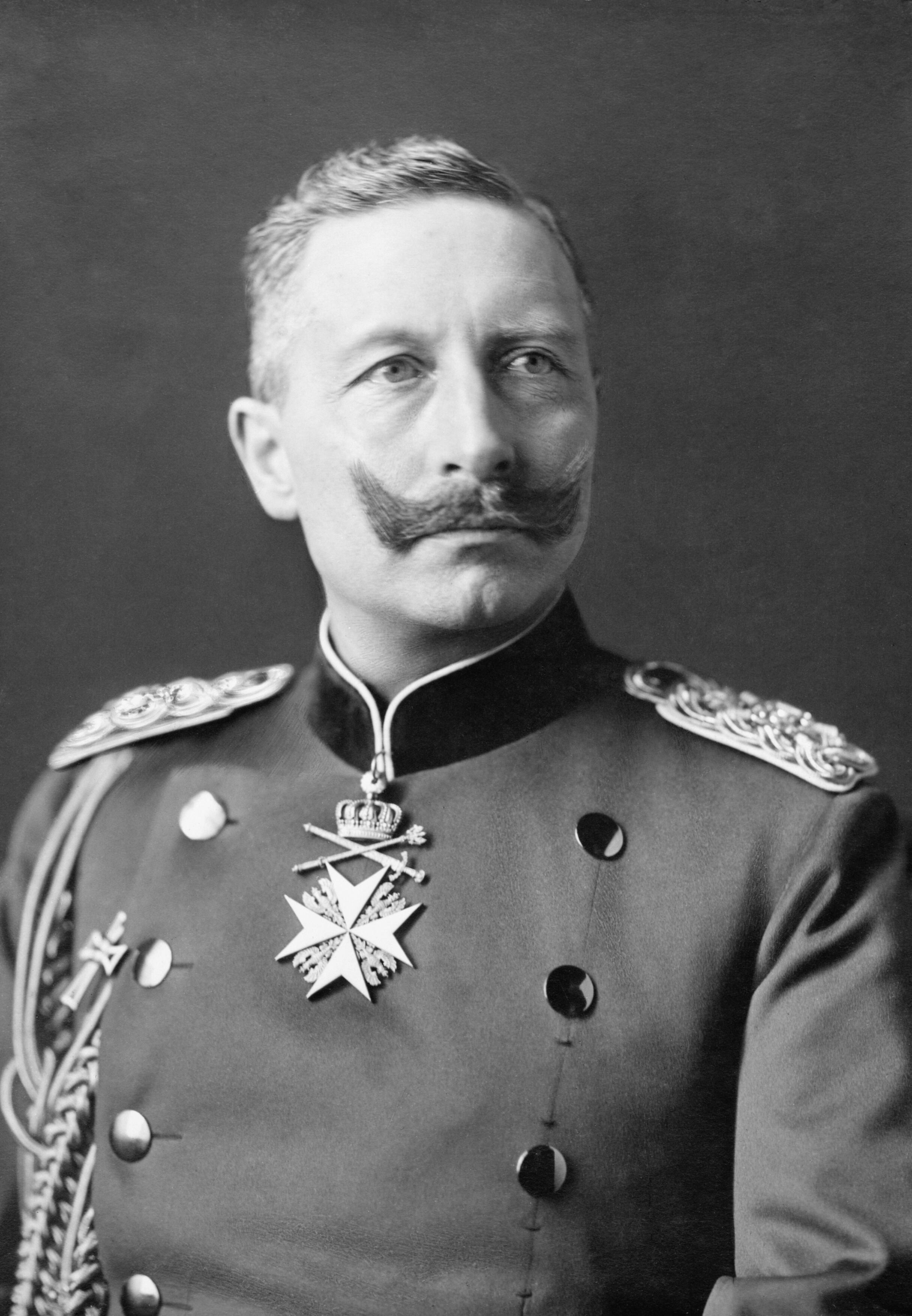 At age 29, Wilhelm became Kaiser Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II after a difficult youth and conflicts with his British mother Victoria, Princess Royal. He turned out to be a man of limited experience, narrow and reactionary views, poor judgment, and occasional bad temper, which alienated former friends and allies.
At age 29, Wilhelm became Kaiser Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II after a difficult youth and conflicts with his British mother Victoria, Princess Royal. He turned out to be a man of limited experience, narrow and reactionary views, poor judgment, and occasional bad temper, which alienated former friends and allies.
 The German government seriously considered breaking up Prussia into smaller states, but eventually traditionalist sentiment prevailed and Prussia became by far the largest state of the Weimar Republic, comprising 60% of its territory. With the abolition of the older Prussian franchise, it became a stronghold of the left. Its incorporation of "Red Berlin" and the industrialised Ruhr Area, both with working-class majorities, ensured left-wing dominance.
From 1919 to 1932, Prussia was governed by a coalition of the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democrats, Centre Party (Germany), Catholic Centre and German Democratic Party, German Democrats; from 1921 to 1925, coalition governments included the German People's Party. Unlike in other states of the German Reich, majority rule by democratic parties in Prussia was never endangered. Nevertheless, in East Prussia and some rural areas, the National Socialist German Workers Party, Nazi Party of Adolf Hitler gained more and more influence and popular support, especially from the lower middle class starting in 1930. Except for Catholic
The German government seriously considered breaking up Prussia into smaller states, but eventually traditionalist sentiment prevailed and Prussia became by far the largest state of the Weimar Republic, comprising 60% of its territory. With the abolition of the older Prussian franchise, it became a stronghold of the left. Its incorporation of "Red Berlin" and the industrialised Ruhr Area, both with working-class majorities, ensured left-wing dominance.
From 1919 to 1932, Prussia was governed by a coalition of the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democrats, Centre Party (Germany), Catholic Centre and German Democratic Party, German Democrats; from 1921 to 1925, coalition governments included the German People's Party. Unlike in other states of the German Reich, majority rule by democratic parties in Prussia was never endangered. Nevertheless, in East Prussia and some rural areas, the National Socialist German Workers Party, Nazi Party of Adolf Hitler gained more and more influence and popular support, especially from the lower middle class starting in 1930. Except for Catholic

 After the appointment of Hitler as the new chancellor, the Nazis used the absence of Franz von Papen as an opportunity to appoint
After the appointment of Hitler as the new chancellor, the Nazis used the absence of Franz von Papen as an opportunity to appoint
 The areas east of the Oder–Neisse line, mainly Eastern Prussia, Western Prussia, Pomerania and
The areas east of the Oder–Neisse line, mainly Eastern Prussia, Western Prussia, Pomerania and
 Under the rule of Frederick I of Prussia, Frederick III (I) (reign: 1688–1713), the Brandenburg Prussian territories were ''de facto'' reduced to provinces of the monarchy. Frederick William's testament would have divided Brandenburg-Prussia among his sons, but his firstborn son Frederick III (I), with the Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, emperor's backing, succeeded in becoming the sole ruler based on the House Treaty of Gera of 1599, which forbade a division of Hohenzollern territories.Kotulla (2008), p. 269 In 1689, a new central chamber for all Brandenburg-Prussian territories was established, called ''Geheime Hofkammer'' (from 1713: ''Generalfinanzdirektorium''). This chamber functioned as a superior agency of the territories' ''Amtskammer'' chambers.Kotulla (2008), p. 270 The General War Commissariat (''Generalkriegskommissariat'') emerged as a second central agency, superior to the local ''Kriegskommissariat'' agencies initially concerned with the administration of the army, but before 1712 transformed into an agency also concerned with general tax and police tasks.
The Kingdom of Prussia functioned as an absolute monarchy until the German revolutions of 1848–1849, after which Prussia became a constitutional monarchy and King Frederick William IV appointed Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg Prussia's first Prime Minister of Prussia, prime minister (''Ministerpräsident''). Constitution of Prussia (1848), Prussia's first constitution dated from 1848, but was only briefly in effect as it had been forced on the king. The Constitution of Prussia (1850), 1850 Prussian Constitution established a Bicameralism, two-chamber parliament. The lower house, the Prussian House of Representatives represented all taxpayers, who were Prussian three-class franchise, divided into three classes according to the amount of taxes paid. This assured dominance by the more well-to-do elements of the population. The upper house (First Chamber or ''Erste Kammer''), later renamed the Prussian House of Lords (''Herrenhaus''), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. The Prussian Secret Police, formed in response to the German revolutions of 1848–1849, aided the conservative government.
Under the rule of Frederick I of Prussia, Frederick III (I) (reign: 1688–1713), the Brandenburg Prussian territories were ''de facto'' reduced to provinces of the monarchy. Frederick William's testament would have divided Brandenburg-Prussia among his sons, but his firstborn son Frederick III (I), with the Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, emperor's backing, succeeded in becoming the sole ruler based on the House Treaty of Gera of 1599, which forbade a division of Hohenzollern territories.Kotulla (2008), p. 269 In 1689, a new central chamber for all Brandenburg-Prussian territories was established, called ''Geheime Hofkammer'' (from 1713: ''Generalfinanzdirektorium''). This chamber functioned as a superior agency of the territories' ''Amtskammer'' chambers.Kotulla (2008), p. 270 The General War Commissariat (''Generalkriegskommissariat'') emerged as a second central agency, superior to the local ''Kriegskommissariat'' agencies initially concerned with the administration of the army, but before 1712 transformed into an agency also concerned with general tax and police tasks.
The Kingdom of Prussia functioned as an absolute monarchy until the German revolutions of 1848–1849, after which Prussia became a constitutional monarchy and King Frederick William IV appointed Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg Prussia's first Prime Minister of Prussia, prime minister (''Ministerpräsident''). Constitution of Prussia (1848), Prussia's first constitution dated from 1848, but was only briefly in effect as it had been forced on the king. The Constitution of Prussia (1850), 1850 Prussian Constitution established a Bicameralism, two-chamber parliament. The lower house, the Prussian House of Representatives represented all taxpayers, who were Prussian three-class franchise, divided into three classes according to the amount of taxes paid. This assured dominance by the more well-to-do elements of the population. The upper house (First Chamber or ''Erste Kammer''), later renamed the Prussian House of Lords (''Herrenhaus''), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. The Prussian Secret Police, formed in response to the German revolutions of 1848–1849, aided the conservative government.

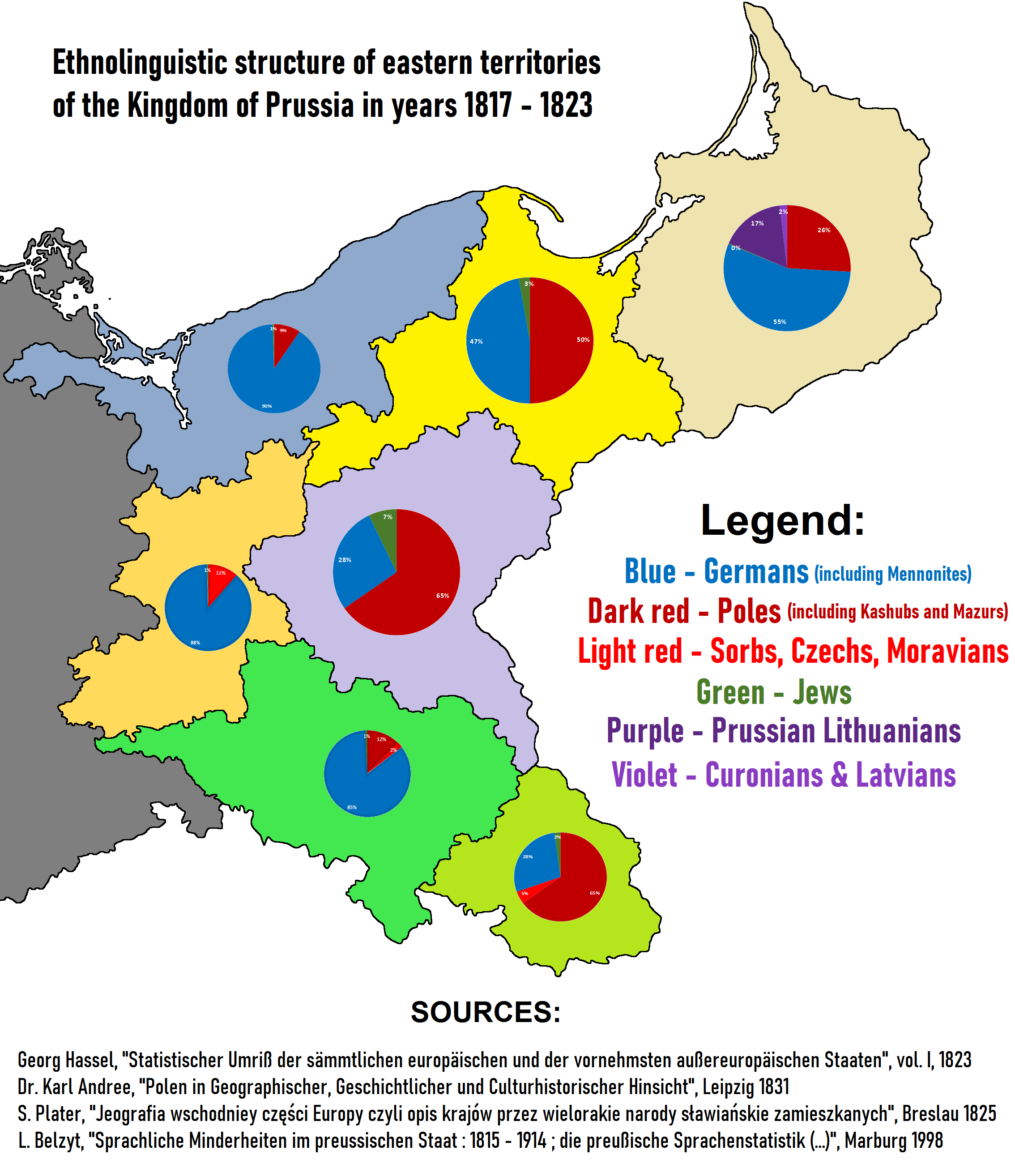 In 1871, Prussia's population numbered 24.69 million, accounting for 60% of the
In 1871, Prussia's population numbered 24.69 million, accounting for 60% of the
 In 1871, approximately 2.4 million Poles lived in Prussia, constituting the largest minority. Other minorities were Jews, Danes, Frisians, Dutch people, Dutchmen, Kashubians (72,500 in 1905), Masurians (248,000 in 1905),
In 1871, approximately 2.4 million Poles lived in Prussia, constituting the largest minority. Other minorities were Jews, Danes, Frisians, Dutch people, Dutchmen, Kashubians (72,500 in 1905), Masurians (248,000 in 1905),
File:CretiusEmpfang.jpg, King Frederick William I of Prussia welcoming the expelled Salzburg Protestants
File:Dom, Berlin 1900.png, The Berlin Cathedral
File:Prussian deportations.PNG, Prussian deportations (''Polenausweisungen'') were the mass expulsions of ethnic
online
maintains its Prussian history and remembrance culture in the form of the Prussian Museums in Wesel and Minden.
 * Alte Nationalgalerie, Berlin
* Altes Museum, Berlin
* Bode Museum, Berlin
* East Prussian Regional Museum
* List of museums and galleries in Berlin
* List of museums in Germany
* Alte Nationalgalerie, Berlin
* Altes Museum, Berlin
* Bode Museum, Berlin
* East Prussian Regional Museum
* List of museums and galleries in Berlin
* List of museums in Germany
online
862pp. * Christopher Clark, Clark, Christopher. ''Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600–1947'' (2009), a standard scholarly history * Craig, Gordon. ''The politics of the Prussian Army 1640–1945'' (1955)
online
* Fay, Sidney Bradshaw. ''The Rise of Brandenburg-Prussia To 1786'' (1937
online
*
online review
* Friedrich, Karin. ''Brandenburg-Prussia, 1466–1806: The Rise of a Composite State'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2011); 157pp. Emphasis on historiography. * Glees, Anthony. "Albert C. Grzesinski and the politics of Prussia, 1926–1930." ''English Historical Review'' 89.353 (1974): 814–834
online
* * Hamerow, Theodore S. ''Restoration, Revolution, Reaction: Economics and Politics in Germany, 1815–1871'' (1958
online
* Hamerow, Theodore S. ''The social foundations of German unification, 1858–1871'' (1969
online
* Henderson, William O. ''The state and the industrial revolution in Prussia, 1740–1870'' (1958
online
* * Horn, David Bayne. ''Great Britain and Europe in the eighteenth century'' (1967) covers 1603–1702; pp. 144–177 for Prussia; pp. 178–200 for other Germany; pp. 111–143 for Austria * Hornung, Erik. "Immigration and the diffusion of technology: The Huguenot diaspora in Prussia." ''American Economic Review'' 104.1 (2014): 84–122
online
* Koch, H. W. ''History of Prussia'' (1987
online
* Kotulla, Michael
''Deutsche Verfassungsgeschichte: vom Alten Reich bis Weimar (1495–1934)'' (Springer, 2008)
* * Muncy, Lysbeth W. "The Junkers and the Prussian Administration from 1918 to 1939." ''Review of Politics'' 9.4 (1947): 482–501
online
* Nipperdey, Thomas. ''Germany from Napoleon to Bismarck: 1800–1866'' (1996)
excerpt
* Orlow, Dietrich. ''Weimar Prussia, 1918–1925: The Unlikely Rock of Democracy'' (1986
online
* Orlow, Dietrich. ''Weimar Prussia, 1925–1933: The Illusion of Strength'' (1991)
online
* , stress on cultural topics * Sagarra, Eda. ''A Social History of Germany, 1648–1914'' (1977
online
* Schulze, Hagen, and Philip G. Dwyer. "Democratic Prussia in Weimar Germany, 1919–33." in ''Modern Prussian History 1830–1947'' (Routledge, 2014) pp. 211–229. * * Taylor, A. J. P. ''The Course of German History: A Survey of the Development of German History since 1815'' (1945
online
* Taylor, A. J. P. ''Bismarck'' (1955)
online
* Treasure, Geoffrey. ''The Making of Modern Europe, 1648–1780'' (3rd ed. 2003). pp. 427–462. *
chronology and summaries
Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation website
Stiftung Preußischer Kulturbesitz
(picture archive).
Foundation for Prussian Palaces and Gardens Berlin-Brandenburg
{{Authority control Prussia, States and territories established in 1525 States and territories disestablished in 1947 Former countries in Europe History of Brandenburg 1525 establishments in Prussia 1947 disestablishments in Prussia Historical regions
Old Prussian
Old Prussian is an extinct West Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European languages, which was once spoken by the Old Prussians, the Baltic peoples of the Prussian region. The language is called Old Prussian to av ...
: ''Prūsija'') was a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
state centred on the North European Plain
The North European Plain ( – North German Plain; ; – Central European Plain; and ; French: ''Plaine d'Europe du Nord'') is a geomorphological region in Europe that covers all or parts of Belgium, the Netherlands (i.e. the Low Countries), ...
that originated from the 1525 secularization
In sociology, secularization () is a multilayered concept that generally denotes "a transition from a religious to a more worldly level." There are many types of secularization and most do not lead to atheism or irreligion, nor are they automatica ...
of the Prussian
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzoll ...
part of the State of the Teutonic Order
The State of the Teutonic Order () was a theocratic state located along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Europe. It was formed by the knights of the Teutonic Order during the early 13th century Northern Crusades in the region ...
. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, Prince-elector, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern Castle, Hohenzollern, Margraviate of Bran ...
ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in 1701, Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
, decisively shaped the history of Germany
The concept of Germany as a distinct region in Central Europe can be traced to Julius Caesar, who referred to the unconquered area east of the Rhine as ''Germania'', thus distinguishing it from Gaul. The victory of the Cherusci, Germanic tribes ...
. Prussia formed the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
when it united the German states in 1871. It was '' de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor
The chancellor of Germany, officially the federal chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany, is the head of the federal government of Germany. The chancellor is the chief executive of the Federal Cabinet and heads the executive branch. Th ...
Franz von Papen
Franz Joseph Hermann Michael Maria von Papen, (; 29 October 18792 May 1969) was a German politician, diplomat, Prussian nobleman and army officer. A national conservative, he served as Chancellor of Germany in 1932, and then as Vice-Chancell ...
in 1932 and ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' (; ; ) describes practices that are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. The phrase is often used in contrast with '' de facto'' ('from fa ...
'' by an Allied decree in 1947.
The name ''Prussia'' derives from the Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon ...
who were conquered by the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
an organized Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
medieval military order of German crusaders in the 13th century. In 1308, the Teutonic Knights conquered the region of Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
with Danzig. Their monastic state was mostly Germanised
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In l ...
through immigration from central and western Germany, and, in the south, it was Polonised by settlers from Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
. The imposed Second Peace of Thorn (1466)
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń (; ), was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 between the Polish king Casimir IV Jagiellon and the Teutonic K ...
split Prussia into the western Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia (; or , ) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) became a province of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, which was annexed follow ...
, a province of Poland, and the eastern Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
, a feudal fief of the Crown of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (; ) was a political and legal concept formed in the 14th century in the Kingdom of Poland, assuming unity, indivisibility and continuity of the state. Under this idea, the state was no longer seen as the pa ...
until 1657. After 1525, the Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Sa ...
relocated their headquarters to Mergentheim
Bad Mergentheim (; Mergentheim until 1926; East Franconian: ''Märchedol'') is a town in the Main-Tauber-Kreis district in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It has a population of around 23,000. An officially recognized spa town since 1926, ...
, but managed to keep land in Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
until 1561. The union of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 led to the proclamation of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in 1701.
Prussia entered the ranks of the great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
s shortly after becoming a kingdom. It became increasingly large and powerful in the 18th and 19th centuries. It had a major voice in European affairs under the reign of Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
(1740–1786). At the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
(1814–15), which redrew the map of Europe following Napoleon's defeat, Prussia acquired rich new territories, including the coal-rich Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
. The country then grew rapidly in influence economically and politically, and became the core of the North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
in 1867, and then of the German Empire in 1871. The Kingdom of Prussia was now so large and so dominant in the new Germany that and other Prussian élites identified more and more as Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
and less as Prussians.
The Kingdom ended in 1918 along with other German monarchies that were terminated by the German Revolution
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
. In the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
, the Free State of Prussia
The Free State of Prussia (, ) was one of the States of the Weimar Republic, constituent states of Weimar Republic, Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it cont ...
lost nearly all of its legal and political importance following the 1932 coup led by Franz von Papen. Subsequently, it was effectively dismantled into Nazi German '' Gaue'' in 1935. Nevertheless, some Prussian ministries were kept and Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician, aviator, military leader, and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which gov ...
remained in his role as Minister President of Prussia
The Minister-President (), or Prime Minister, of Prussia was the head of government of the Prussian state. The office existed from 1848, when it was formed by Frederick William IV of Prussia, King Frederick William IV during the German revolutio ...
until the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
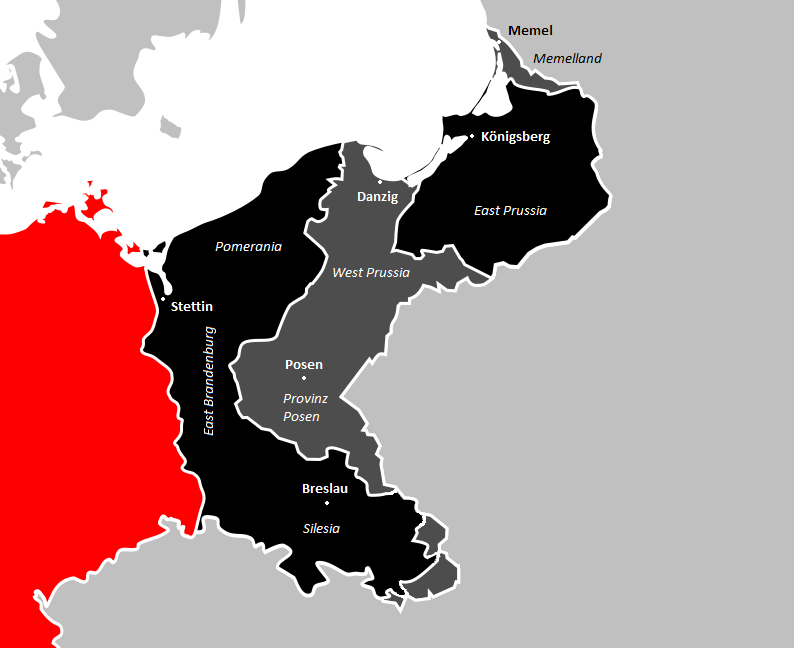
. Former eastern territories of Germany
In present-day Germany, the former eastern territories of Germany () refer to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e. the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed b ...
that made up a significant part of Prussia lost the majority of their German population after 1945 as the Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. ...
and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
both absorbed these territories and had most of its German inhabitants expelled by 1950. Prussia, deemed "a bearer of militarism and reaction" by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
, was officially abolished by an Allied declaration in 1947. The international status of the former eastern territories of the Kingdom of Prussia was disputed until the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany
The Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany (),
more commonly referred to as the Two Plus Four Agreement (),
is an international agreement that allowed the reunification of Germany in October 1990. It was negotiated in 1990 betwee ...
in 1990, but its return to Germany remains a cause among far-right
Far-right politics, often termed right-wing extremism, encompasses a range of ideologies that are marked by ultraconservatism, authoritarianism, ultranationalism, and nativism. This political spectrum situates itself on the far end of the ...
politicians, the Federation of Expellees
The Federation of Expellees (; BdV) is a non-profit organization formed in West Germany on 27 October 1957 to represent the interests of German nationals of all ethnicities and foreign ethnic Germans and their families (usually naturalised as Ge ...
and various political revanchists
Revanchism (, from ''revanche'', "revenge") is the political manifestation of the will to reverse the territorial losses which are incurred by a country, frequently after a war or after a social movement. As a term, ''revanchism'' originated i ...
and irredentists.
The terms "Prussian" and "Prussianism
Prussianism comprises the practices and doctrines of the Prussians, specifically the militarism and the severe discipline traditionally associated with the Prussian ruling class.
History
Prussianism had its origins with the rise to the thron ...
" have often been used, especially outside Germany, to denote the militarism, military professionalism, aggressiveness, and conservatism of the class of landed aristocrats in the East who dominated first Prussia and then the German Empire.
Symbols
The maincoat of arms of Prussia
The state of Prussia developed from the State of the Teutonic Order. The original flag of the Teutonic Knights had been a black cross on a white flag. Emperor Frederick II in 1229 granted them the right to use the black Eagle of the Holy Roman E ...
, as well as the flag of Prussia
The state of Prussia had its origins in the separate lands of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and of the Duchy of Prussia. The Margraviate of Brandenburg developed from the medieval Northern March of the Holy Roman Empire, passing to the House of H ...
, depicted a black eagle
The black eagle (''Ictinaetus malaiensis'') is a bird of prey. Like all eagles, it is in the family Accipitridae, and is the only member of the genus ''Ictinaetus''. They soar over forests in the hilly regions of tropical and subtropical South a ...
on a white background.
The black and white national colours
National colours are frequently part of a country's set of national symbols. Many states and nations have formally adopted a set of colours as their official "national colours" while others have '' de facto'' national colours that have become well ...
were already used by the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
and by the Hohenzollern dynasty
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
. The Teutonic Order wore a white coat embroidered
Embroidery is the art of decorating Textile, fabric or other materials using a Sewing needle, needle to stitch Yarn, thread or yarn. It is one of the oldest forms of Textile arts, textile art, with origins dating back thousands of years across ...
with a black cross with gold insert and black imperial eagle. The combination of the black and white colours with the white and red Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
colours of the free cities Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
, Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
and Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
, as well as of Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, resulted in the black-white-red commercial flag of the North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
, which became the flag of the German Empire in 1871.
('to each, his own'), the motto of the Order of the Black Eagle
The Order of the Black Eagle () was the highest order of chivalry in the Kingdom of Prussia. The order was founded on 17 January 1701 by Elector Friedrich III of Brandenburg (who became Friedrich I of Prussia, Friedrich I, King in Prussia, the ...
created by King Frederick I Frederick I or Friedrich I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I ...
in 1701, was often associated with the whole of Prussia. The Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
, a military decoration created by King Frederick William III
Frederick William III (; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, when the empire was dissolved. ...
in 1813, was also commonly associated with the country. The region, originally populated by Baltic Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon ...
who were Christianised, became a favoured location for immigration by (later mainly Protestant) Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
(''see ''), as well as Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
and Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
along the border regions.
Territory
Before its abolition, the territory of theFree State of Prussia
The Free State of Prussia (, ) was one of the States of the Weimar Republic, constituent states of Weimar Republic, Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it cont ...
included the provinces of East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
; Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
; Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
(including much of the present-day state of Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt ( ; ) is a States of Germany, state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the List of German states ...
and parts of the state of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
in Germany); Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
; Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
; Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ...
; Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
(without Austrian Silesia
Austrian Silesia, officially the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia, was an autonomous region of the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Habsburg monarchy (from 1804 the Austrian Empire, and from 1867 the Cisleithanian portion of Austria-Hungary). It is la ...
); Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
; Hanover
Hanover ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Lower Saxony. Its population of 535,932 (2021) makes it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-l ...
; Hesse-Nassau
The Province of Hesse-Nassau () was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868 to 1918, then a province of the Free State of Prussia until 1944.
Hesse-Nassau was created as a consequence of the Austro-Prussian War of ...
; and a small detached area in the south called Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
, the ancestral home of the Prussian ruling family. The land that the Teutonic Knights occupied was flat and covered with fertile soil. The area was perfectly suited to the large-scale raising of wheat. The rise of early Prussia was based on the raising and selling of wheat. Teutonic Prussia became known as the "bread basket of Western Europe" (in German, ''Kornkammer'', or granary). The port cities which rose on the back of this wheat production included: Stettin in Pomerania (now Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
, Poland); Danzig in Prussia (now Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
, Poland); Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
in Livonia (now Riga, Latvia); Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
in Prussia (now Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
, Russia); and Memel in Prussia (now Klaipėda
Klaipėda ( ; ) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the List of cities in Lithuania, third-largest city in Lithuania, the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, fifth-largest city in the Baltic States, and the capi ...
, Lithuania). Wheat production and trade brought Prussia into a close relationship with the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
during the period of time from 1356 (official founding of the Hanseatic League) until the decline of the League in about 1500.
The expansion of Prussia based on its connection with the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
cut both Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
off from the coast of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
and trade abroad. This meant that Poland and Lithuania would be traditional enemies of Prussia, which was still called the Teutonic Knights.
History
Teutonic Order

 In 1211, King
In 1211, King Andrew II of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and ...
granted Burzenland in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
as a fiefdom
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
to the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
, a German military order of crusading
The crusading movement encompasses the framework of ideologies and institutions that described, regulated, and promoted the Crusades. The crusades were religious wars that the Latin Church initiated, supported, and sometimes directed during th ...
knights, headquartered in the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
at Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
. In 1225, he expelled them, and they transferred their operations to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
area. Konrad I, the Polish Duke of Masovia, had unsuccessfully attempted to conquer pagan Prussia in crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
in 1219 and 1222. In 1226, Duke Konrad invited the Teutonic Knights to conquer the Baltic Prussian tribes on his borders.
During 60 years of struggles against the Old Prussians, the Order established an independent state that came to control Prūsa. After the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword (; ) was a Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (monastic society), military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert of Riga, Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theode ...
joined the Teutonic Order in 1237, the Order also controlled Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
(now Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
and Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
). Around 1252 they finished the conquest of the northernmost Prussian tribe of the Skalvians
The Scalovians (; ), also known as the Skalvians, ''Schalwen'' and ''Schalmen'', were a Baltic tribe related to the Prussians. According to the '' Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' of Peter of Dusburg, the now extinct Scalovians inhabited the land of ...
as well as of the western Baltic Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. ...
, and erected Memel Castle
Memel, a name derived from the Couronian-Latvian ''memelis, mimelis, mēms'' for "mute, silent", may refer to:
*Memel, East Prussia, Germany, now , Lithuania
**, ( Klaipėda Castle), the in Memel, a castle built in 1252 by Teutonic Knights which ...
, which developed into the major port city of Memel. The Treaty of Melno
The Treaty of Melno (; ) or Treaty of Lake Melno () was a peace treaty ending the Gollub War. It was signed on 27 September 1422, between the State_of_the_Teutonic_Order, Teutonic Knights and an alliance of the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kin ...
defined the final border between Prussia and the adjoining Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
in 1422.
The Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
officially formed in northern Europe in 1356 as a group of trading cities. This League came to hold a monopoly on all trade leaving the interior of Europe and Scandinavia and on all sailing trade in the Baltic Sea for foreign countries.
In the course of the (German eastward expansion) process, settlers were invited by German-speaking episcopal and secular authorities, bringing changes in the ethnic composition as well as in language, culture, and law of the eastern borders of the German lands. As a majority of these settlers were Germans, Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" ...
became the dominant language.
The Knights of the Teutonic Order were subordinate to the papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
and to the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
. Their initially close relationship with the Polish Crown deteriorated after they conquered Polish-controlled Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
and Danzig in 1308. Eventually, Poland and Lithuania, allied through the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; ; ) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made at Kreva Castle on 14 August 1385 by Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, in regard to his prospectiv ...
(1385), defeated the Knights in the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
(Tannenberg) in 1410.
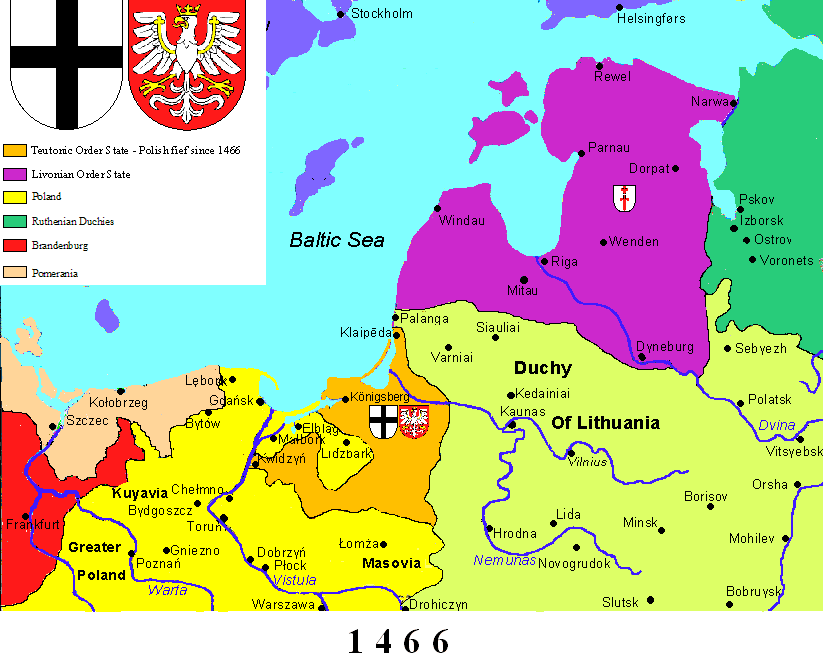
The Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) began when the Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (, ) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Marienwerder (present-day Kwidzyn) by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based o ...
, a coalition of Hanseatic cities of western Prussia, rebelled against the Order and requested help from the Polish king, Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (Casimir Andrew Jagiellon; ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447 until his death in 1492. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers; under ...
. The Teutonic Knights were forced to acknowledge the sovereignty of, and to pay tribute to Casimir IV in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466)
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń (; ), was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 between the Polish king Casimir IV Jagiellon and the Teutonic K ...
, losing western Prussia (Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia (; or , ) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) became a province of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, which was annexed follow ...
) to Poland in the process. Pursuant to the Second Peace of Thorn, two Prussian states were established.
During the period of the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights, mercenaries from the Holy Roman Empire were granted lands by the Order and gradually formed a new landed Prussian nobility, from which the Junkers
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English language, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft manufacturer, aircraft and aircraft engine manufactu ...
would evolve to take a major role in the militarization of Prussia and, later, Germany.
Duchy of Prussia
On 10 April 1525, after signing of theTreaty of Kraków
The Treaty of Kraków was signed on 8 April 1525 between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. It officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War (1519-1521)John Freely Celestial Revolutionary: Copernicus, the Man and H ...
, which officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War (1519–21), in the main square of the Polish capital Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, Albert I Albert I may refer to:
People Born before 1300
* Albert I, Count of Vermandois (917–987)
* Albert I, Count of Namur ()
* Albert I of Moha
*Albert I of Brandenburg (), first margrave of Brandenburg
* Albert I, Margrave of Meissen (1158–1195)
*Al ...
resigned his position as Grand Master of the Teutonic Order
The grand master of the Teutonic Order (; ) is the supreme head of the Teutonic Order. It is equivalent to the Grand master (order), grand master of other Military order (religious society), military orders and the superior general in non-milit ...
and received the title "Duke of Prussia" from King Zygmunt I the Old
Sigismund I the Old (, ; 1 January 1467 – 1 April 1548) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until his death in 1548. Sigismund I was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty, the son of Casimir IV and younger brother of Kings ...
of Poland. As a symbol of vassalage, Albert received a standard with the Prussian coat of arms from the Polish king. The black Prussian eagle on the flag was augmented with a letter "S" (for Sigismundus) and had a crown placed around its neck as a symbol of submission to Poland. Albert I, a member of a cadet branch of the House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, Prince-elector, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern Castle, Hohenzollern, Margraviate of Bran ...
became a Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
Protestant and secularized the Order's Prussian territories. This was the area east of the mouth of the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
river, later sometimes called "Prussia proper". For the first time, these lands came into the hands of a branch of the Hohenzollern family, who already ruled the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg () was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that, having electoral status although being quite poor, grew rapidly in importance after inheriting the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 and then came ...
, since the 15th century. Furthermore, with his renunciation of the Order, Albert could now marry and produce legitimate heirs.
Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg and Prussia united two generations later. In 1594Duchess Anna of Prussia
Duchess Anna of Prussia and Jülich-Cleves-Berg (3 July 1576 – 30 August 1625) was Electress consort of Brandenburg and Duchess consort of Prussia by marriage to John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg. She was the daughter of Albert Frederic ...
, granddaughter of Albert I and daughter of Albert Frederick, Duke of Prussia
Albert Frederick (; ; 7 May 1553 – 27 August 1618) was the Duke of Prussia, from 1568 until his death. He was a son of Albert of Prussia and Anna Marie of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He was the second and last Prussian duke of the Ansbach bran ...
(reigned 1568–1618), married her cousin Elector
Elector may refer to:
* Prince-elector or elector, a member of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Holy Roman Emperors
* Elector, a member of an electoral college
** Confederate elector, a member of t ...
John Sigismund of Brandenburg. When Albert Frederick died in 1618 without male heirs, John Sigismund was granted the right of succession to the Duchy of Prussia, then still a Polish fief. From this time the Duchy of Prussia was in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with the Margraviate of Brandenburg. The resulting state, known as Brandenburg-Prussia, consisted of geographically disconnected territories in Prussia, Brandenburg, and the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
lands of Cleves
Kleve (; traditional ; ; ; ; ; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century onwards, Cleves was capital of a county and later a duchy ...
and Mark
Mark may refer to:
In the Bible
* Mark the Evangelist (5–68), traditionally ascribed author of the Gospel of Mark
* Gospel of Mark, one of the four canonical gospels and one of the three synoptic gospels
Currencies
* Mark (currency), a currenc ...
.
During the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648), various armies repeatedly marched across the disconnected Hohenzollern lands, especially the occupying Swedes
Swedes (), or Swedish people, are an ethnic group native to Sweden, who share a common ancestry, Culture of Sweden, culture, History of Sweden, history, and Swedish language, language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, ...
. The ineffective and militarily weak Elector George William (1619–1640) fled from Berlin to Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
, the historic capital of the Duchy of Prussia, in 1637. His successor, Frederick William I (1640–1688), reformed the army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
to defend the lands.
Frederick William I went to Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
in 1641 to render homage to King Władysław IV Vasa
Władysław IV Vasa or Ladislaus IV (9 June 1595 – 20 May 1648) was King of Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania and claimant of the thrones of Monarchy of Sweden, Sweden and List of Russian monarchs, Russia. Born into the House of Vasa as a prince ...
of Poland for the Duchy of Prussia, which was still held in fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
from the Polish crown. In January 1656, during the first phase of the Second Northern War
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of ...
(1654–1660), he received the duchy as a fief from the Swedish king who later granted him full sovereignty in the Treaty of Labiau
The Treaty of Labiau was a treaty signed between Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg and Charles X Gustav of Sweden on 10 November ( O.S.) / 20 November ( N.S.) 1656 in Labiau (now Polessk). With several concessions, the most important b ...
(November 1656). In 1657 the Polish king renewed this grant in the treaties of Wehlau
Znamensk (; ; ; ) is a rural locality (a settlement) in Gvardeysky District of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Pregolya River at its confluence with the Lava River east of Kaliningrad. Population figures:
Histo ...
and Bromberg
Bydgoszcz is a city in northern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Kuyavia. Straddling the confluence of the Vistula River and its left-bank tributary, the Brda, the strategic location of Bydgoszcz has made it an inland ...
. With Prussia, the Brandenburg Hohenzollern dynasty
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
now held a territory free of any feudal obligations, which constituted the basis for their later elevation to kings.
Frederick William I succeeded in organizing the electorate by establishing an absolute monarchy in Brandenburg-Prussia, an achievement for which he became known as the "Great Elector". Above all, he emphasised the importance of a powerful military to protect the state's disconnected territories, while the Edict of Potsdam
The Edict of Potsdam () was a proclamation issued by Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, in Potsdam on 29 October 1685, as a response to the revocation of the Edict of Nantes by the Edict of Fontainebleau. It encouraged ...
(1685) opened Brandenburg-Prussia for the immigration of Protestant refugees (especially Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
s), and he established a bureaucracy to carry out state administration efficiently.
Kingdom of Prussia
 On 18 January 1701, Frederick William's son, Elector Frederick III, elevated Prussia from a duchy to a kingdom and crowned himself King
On 18 January 1701, Frederick William's son, Elector Frederick III, elevated Prussia from a duchy to a kingdom and crowned himself King Frederick I Frederick I or Friedrich I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I ...
. In the Crown Treaty {{Short description, 1700 treaty between Brandenburg and Emperor Leopold I
In the Crown Treaty (also called Treaty of the Crown, ''Krontraktat'' in German) signed on 16 November 1700, Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, had ...
of 16 November 1700, Leopold I, emperor of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, allowed Frederick only to title himself "King in Prussia
King ''in'' Prussia (German language, German: ''König in Preußen'') was a title used by the Prussian kings (also in personal union Elector of Brandenburg, Electors of Brandenburg) from 1701 to 1772. Subsequently, they used the title King ''of' ...
", not "King of Prussia
The monarchs of Prussia were members of the House of Hohenzollern who were the hereditary rulers of the former German state of Prussia from its founding in 1525 as the Duchy of Prussia. The Duchy had evolved out of the Teutonic Order, a Roman C ...
". The state of Brandenburg-Prussia became commonly known as "Prussia", although most of its territory, in Brandenburg, Pomerania, and western Germany, lay outside Prussia proper. The Prussian state grew in splendour during the reign of Frederick I, who sponsored the arts at the expense of the treasury.
Frederick I was succeeded by his son, Frederick William I (1713–1740), the austere "Soldier King", who did not care for the arts but was thrifty and practical. He was the main creator of the vaunted Prussian bureaucracy and the professionalised standing army, which he developed into one of the most powerful in Europe. His troops only briefly saw action during the Great Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the ant ...
. In view of the size of the army in relation to the total population, Mirabeau
Mirabeau may refer to:
People
* Victor de Riqueti, marquis de Mirabeau (1715–1789), French physiocrat
* Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau (1749–1791), renowned orator, a figure in the French Revolution and son of Victor
* André Bon ...
said later: "Prussia, is not a state with an army, but an army with a state." Frederick William also settled more than 20,000 Protestant refugees from Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
in thinly populated East Prussia, which was eventually extended to the west bank of the Neman
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms Lithuania–Russia border, the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its s ...
river, and other regions. In the Treaty of Stockholm (1720), he acquired half of Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania (; ) was a dominions of Sweden, dominion under the Sweden, Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815 on what is now the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish-Swedish War, Polish War and the Thirty Years' War ...
.
 Frederick William I died in 1740 and was succeeded by his son, Frederick II, whose accomplishments led to his reputation as "Frederick the Great". As crown prince, Frederick had focused, primarily, on philosophy and the arts. He was an accomplished flute player and composer. In 1740, Prussian troops crossed over the undefended border of
Frederick William I died in 1740 and was succeeded by his son, Frederick II, whose accomplishments led to his reputation as "Frederick the Great". As crown prince, Frederick had focused, primarily, on philosophy and the arts. He was an accomplished flute player and composer. In 1740, Prussian troops crossed over the undefended border of Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
and rapidly conquered the region. Silesia was the richest province of Habsburg Austria The term Habsburg Austria may refer to the lands ruled by the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs, or the historical Austria. Depending on the context, it may be defined as:
* The Duchy of Austria, after 1453 the Archduchy of Austria
* The '' Erblande ...
. It signalled the beginning of three Silesian Wars
The Silesian Wars () were three wars fought in the mid-18th century between Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia (under King Frederick the Great) and Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Austria (under Empress Maria Theresa) for control of the Central European ...
(1740–1763). The First Silesian War
The First Silesian War () was a war between Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Habsburg monarchy, Austria that lasted from 1740 to 1742 and resulted in Prussia's seizing most of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland) from Austria. The ...
(1740–1742) and the Second Silesian War
The Second Silesian War () was a war between Prussia and Austria that lasted from 1744 to 1745 and confirmed Prussia's control of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland). The war was fought mainly in Silesia, Bohemia, and Upper S ...
(1744–1745) have, historically, been grouped together with the general European war called the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
(1740–1748). Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
Charles VI had died on 20 October 1740. He was succeeded to the throne by his daughter, Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
.
By defeating the Austrian Army at the Battle of Mollwitz
The Battle of Mollwitz was fought by Prussia and Austria on 10 April 1741, during the First Silesian War (in the early stages of the War of the Austrian Succession). It was the first battle of the new Prussian King Frederick II, in which both si ...
on 10 April 1741, Frederick succeeded in conquering Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław.
The first ...
(the northwestern half of Silesia). In the next year, 1742, he conquered Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
(the southeastern half). Furthermore, in the Third Silesian War
The Third Silesian War () was a war between Prussia and Austria (together with its allies) that lasted from 1756 to 1763 and confirmed Prussia's control of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland). The war was fought mainly in Silesi ...
(part of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
) Frederick won a victory over Austria at the Battle of Lobositz
The Battle of Lobositz or Lovosice also Lowositz on 1 October 1756 was the opening land battle of the Third Silesian War and the wider Seven Years' War. Frederick the Great's 28,000 Prussians were prevented by 33,000 Austrians under Maximilian ...
on 1 October 1756. In spite of some victories afterward, his situation became far less comfortable the following years, as he failed in his attempts to knock Austria out of the war and was gradually reduced to a desperate defensive war. However, he never gave up and on 3 November 1760 the Prussian king won another battle, the hard-fought Battle of Torgau
In the Battle of Torgau on 3 November 1760, King Frederick the Great's Prussian army fought an Austrian army under the command of Field Marshal Leopold Josef Graf Daun. The Prussians won a costly victory in one of the bloodiest battles of the T ...
. Despite being several times on the verge of defeat Frederick, allied with Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
, Hanover
Hanover ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Lower Saxony. Its population of 535,932 (2021) makes it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-l ...
and Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, also known as the Hessian Palatinate (), was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. The state was created in 1567 when the Landgraviate of Hesse was divided upon t ...
, was finally able to hold the whole of Silesia against a coalition of Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, the Habsburg monarchy, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
, a close friend of the king, once described Frederick the Great's Prussia by saying "...it was Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
in the morning, Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
in the afternoon."
Silesia, full of rich soils and prosperous manufacturing towns, became a vital region to Prussia, greatly increasing the nation's area, population, and wealth. Success on the battleground against Austria and other powers proved Prussia's status as one of the great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
s of Europe. The Silesian Wars began more than a century of rivalry and conflict between Prussia and Austria as the two most powerful states operating within the Holy Roman Empire (although both had extensive territory outside the empire). In 1744, the County of East Frisia
The County of East Frisia (; Frisian: ''Greefskip Eastfryslân''; Dutch: ''Graafschap Oost-Friesland'') was a county (though ruled by a prince after 1662) in the region of East Frisia in the northwest of the present-day German state of Lower S ...
fell to Prussia following the extinction of its ruling Cirksena
The House of Cirksena was the ruling family of East Frisia (). They descended from a line of East Frisian chieftains from Greetsiel.
East Frisia
In 1439, in the wake of clashes between different lines of chieftains, the town of Emden was first ...
dynasty.
In the last 23 years of his reign until 1786, Frederick II, who understood himself as the "first servant of the state", promoted the development of Prussian areas such as the Oderbruch The Oderbruch () is a landscape located at the Oder river in eastern Germany on the Polish border, with a small part also in Poland. It extends from the towns Oderberg and Bad Freienwalde in the north to Lebus in the south, in the county of Märkisc ...
. At the same time he built up Prussia's military power and participated in the First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia an ...
with Austria and Russia in 1772, an act that geographically connected the Brandenburg territories with those of Prussia proper. The partition also added Polish Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia (; or , ) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) became a province of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, which was annexed follow ...
to the kingdom, allowing Frederick to re-style himself King ''of'' Prussia. During this period, he also opened Prussia's borders to immigrants fleeing from religious persecution in other parts of Europe, such as the Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
. Prussia became a safe haven in much the same way that the United States welcomed immigrants seeking freedom in the 19th century.Clark, ''Iron Kingdom'' ch 7
Frederick the Great (reigned 1740–1786) practised enlightened absolutism
Enlightened absolutism, also called enlightened despotism, refers to the conduct and policies of European absolute monarchs during the 18th and early 19th centuries who were influenced by the ideas of the Enlightenment, espousing them to enhanc ...
. He built the world's best army, and usually won his many wars. He introduced a general civil code, abolished torture and established the principle that the Crown would not interfere in matters of justice. He also promoted an advanced secondary education, the forerunner of today's German gymnasium (grammar school) system, which prepares the brightest pupils for university studies. The Prussian education system
The Prussian education system was established in Prussia as a result of educational reforms in the late 18th and early 19th century, and has had widespread influence since. The Prussian education system was introduced as a basic concept in the l ...
was emulated in various countries, including the United States.
Napoleonic Wars
 During the reign of King Frederick William II (1786–1797), Prussia annexed additional Polish territory through the
During the reign of King Frederick William II (1786–1797), Prussia annexed additional Polish territory through the Second Partition of Poland
The 1793 Second Partition of Poland was the second of partitions of Poland, three partitions (or partial annexations) that ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The second partition (politics), partition occurred i ...
in 1793 and the Third Partition of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polis ...
in 1795. His successor, Frederick William III
Frederick William III (; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, when the empire was dissolved. ...
(1797–1840), announced the union of the Prussian Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
and Reformed churches
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian ...
into one church.Clark, ''Iron Kingdom'' ch 12
Prussia took a leading part in the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
, but remained quiet for more than a decade because of the Peace of Basel
The Peace of Basel of 1795 consists of three peace treaties involving France during the French Revolution (represented by François de Barthélemy).
*The first was with Prussia (represented by Karl August von Hardenberg) on 5 April;
*The s ...
of 1795, only to go once more to war with France in 1806 as negotiations with that country over the allocation of the spheres of influence in Germany failed. Prussia suffered a devastating defeat against Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's troops in the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
, leading Frederick William III and his family to flee temporarily to Memel. Under the Treaties of Tilsit
The Treaties of Tilsit (), also collectively known as the Peace of Tilsit (; ), were two peace treaties signed by French Emperor Napoleon in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland, at the end of the War o ...
in 1807, the state lost about one-third of its area, including the areas gained from the second and third Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
, which now fell to the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw (; ; ), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a First French Empire, French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars. It initially comprised the ethnical ...
. Beyond that, the king was obliged to pay a large indemnity, to cap his army at 42,000 men, and to let the French garrison troops throughout Prussia, effectively making the kingdom a French satellite.Clark, ''Iron Kingdom'' ch 11
In response to this defeat, reformers such as Stein
Stein may refer to:
Places Austria
* Stein, a neighbourhood of Krems an der Donau, Lower Austria
* Stein, Styria, a municipality in the district of Fürstenfeld, Styria
* Stein (Lassing), a village in the district of Liezen, Styria
* Stein a ...
and Hardenberg
Hardenberg (; or '' 'n Arnbarg'') is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Overijssel, Eastern Netherlands. The municipality of ...
set about modernising the Prussian state. Among their reforms were the liberation of peasants from serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
, the Jewish Emancipation, Emancipation of Jews and making full citizens of them. The school system was rearranged, and in 1818 free trade was introduced. The process of army reform ended in 1813 with the introduction of compulsory military service for men. By 1813, Prussia could mobilize almost 300,000 soldiers, more than half of which were conscripts of the ''Landwehr'' of variable quality. The rest consisted of regular soldiers that were deemed excellent by most observers, and very determined to repair the humiliation of 1806.
After the Napoleon's invasion of Russia, defeat of Napoleon in Russia, Prussia quit its alliance with France and took part in the Sixth Coalition during the "Wars of Liberation" (''Befreiungskriege'') against the French occupation. Prussian troops under Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher contributed crucially (alongside the British and Dutch) to the final victory over Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo of June 1815. Prussia's reward in 1815 at the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
was the recovery of her lost territories, as well as the whole of the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, Westphalia, 40% of Kingdom of Saxony, Saxony and some other territories. These western lands were of vital importance because they included the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
region, the centre of Germany's fledgling industrialisation, especially in the arms industry. These territorial gains also meant the doubling of Prussia's population. In exchange, Prussia withdrew from areas of central Poland to allow the creation of Congress Poland under Russian sovereignty. In 1815 Prussia became part of the German Confederation.
Wars of liberation
The first half of the 19th century saw a prolonged struggle in Germany between liberals, who wanted a united, federal Germany under a democratic constitution, and Conservatism, conservatives, who wanted to maintain Germany as a patchwork of independent, monarchical states with Prussia and Austrian Empire, Austria competing for influence. One small movement that signalled a desire for German unification in this period was the Burschenschaft student movement, by students who encouraged the use of the black-red-gold flag, discussions of a unified German nation, and a progressive, liberal political system. Because of Prussia's size and economic importance, smaller states began to join its free trade area in the 1820s. Prussia benefited greatly from the creation in 1834 of the German Customs Union (Zollverein), which included most German states but excluded Austria. In 1848, the liberals saw an opportunity when Revolutions of 1848, revolutions broke out across Europe. Alarmed, King Frederick William IV of Prussia, Frederick William IV agreed to convene a Prussian National Assembly, National Assembly and grant a Constitution of Prussia (1848), constitution. When the Frankfurt Parliament offered Frederick William the crown of a united Germany, he refused on the grounds that he would not accept a crown from a revolutionary assembly without the sanction of Germany's other monarchs. The Frankfurt Parliament was forced to dissolve in 1849, and Frederick William issued a Constitution of Prussia (1850), constitution by his own authority in 1850. This conservative document provided for a two-house parliament, the Landtag of Prussia. The lower house, or ''Prussian House of Representatives'' was elected by all males over the age of 25. They were divided into Prussian three-class franchise, three classes whose votes were weighted according to the amount of taxes paid. In one typical election, the first class (with those who paid the most in taxes) included 4% of voters and the third class (with those who paid the least) had 82%, yet each group chose the same number of electors. The system but assured dominance by the more well-to-do men of the population. The upper house, the ''Prussian House of Lords'', was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority, and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. The constitution nevertheless contained a number of liberal elements such as the introduction of jury courts and a catalog of fundamental rights that included freedom of religion, speech and the press.Wars of unification
In 1862, King Wilhelm I, German Emperor, Wilhelm I appointed Otto von Bismarck asMinister President of Prussia
The Minister-President (), or Prime Minister, of Prussia was the head of government of the Prussian state. The office existed from 1848, when it was formed by Frederick William IV of Prussia, King Frederick William IV during the German revolutio ...
. Bismarck was determined to defeat both the liberals and conservatives and increase Prussian supremacy and influence among the German states. There has been much debate as to whether Bismarck actually planned to create a united Germany when he set out on this journey, or whether he simply took advantage of the circumstances that fell into place. Bismarck curried support from large sections of the people by promising to lead the fight for greater German unification. He successfully guided Prussia through three wars, which unified Germany and brought William the position of German Emperor.
=Schleswig Wars
= The Kingdom of Denmark was at the time in personal union with the Duchies of Duchy of Schleswig, Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, Holstein, both of which had close ties with each other, although only Holstein was part of the German Confederation. When the Danish government tried to integrate Schleswig, but not Holstein, into the Danish state, Prussia led the German Confederation against Denmark in the First War of Schleswig (1848–1851). Because Russia supported Austria, Prussia also conceded predominance in the German Confederation to Austria in the Punctation of Olmütz in 1850, resulting in a return to the status quo. In 1863, Denmark introduced a shared constitution for Denmark and Schleswig. This led to conflict with the German Confederation, which authorised the occupation of Holstein by the Confederation, from which Danish forces withdrew. In 1864, Prussian and Austrian forces crossed the border between Holstein and Schleswig initiating the Second War of Schleswig. The Austro-Prussian forces defeated the Danes, who surrendered both territories. In the resulting Gastein Convention of 1865 Prussia took over the administration of Schleswig while Austria assumed that of Holstein.=Austro-Prussian War
= Bismarck realised that the dual administration of Schleswig and Holstein was only a temporary solution, and tensions rose between Prussia and Austria. The struggle for supremacy in Germany then led to the Austro-Prussian War (1866), triggered by the dispute over Schleswig and Holstein, with Bismarck using proposed injustices as the Casus belli, reason for war.
On the Austrian side stood the south German states (including Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Kingdom of Württemberg, Württemberg), some central German states (including Kingdom of Saxony, Saxony), and Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover in the north. On the side of Prussia were Kingdom of Italy, Italy, most north German states, and some smaller central German states. Eventually, the better-armed Prussian troops won the crucial victory at the Battle of Königgrätz under Helmuth von Moltke the Elder. The century-long struggle between Berlin and Vienna for the dominance of Germany was now over. As a sideshow in this war, Prussia defeated Hanover in the Battle of Langensalza (1866). While Hanover hoped in vain for help from Britain (as they had previously been in personal union), Britain stayed out of a confrontation with a continental great power and Prussia satisfied its desire for merging the once separate territories and gaining strong economic and strategic power, particularly from the full access to the resources of the Ruhr.
Bismarck desired Austria as an ally in the future, and so he declined to annex any Austrian territory. But in the Peace of Prague (1866), Peace of Prague in 1866, Prussia annexed four of Austria's allies in northern and central GermanyHanover, Electorate of Hesse, Hesse-Kassel, Duchy of Nassau, Nassau and Free City of Frankfurt, Frankfurt. Prussia also won full control of Schleswig-Holstein. As a result of these territorial gains, Prussia now stretched uninterrupted across the northern two-thirds of Germany and contained two-thirds of Germany's population. The German Confederation was dissolved, and Prussia impelled the 21 states north of the Main (river), Main river into forming the
Bismarck realised that the dual administration of Schleswig and Holstein was only a temporary solution, and tensions rose between Prussia and Austria. The struggle for supremacy in Germany then led to the Austro-Prussian War (1866), triggered by the dispute over Schleswig and Holstein, with Bismarck using proposed injustices as the Casus belli, reason for war.
On the Austrian side stood the south German states (including Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Kingdom of Württemberg, Württemberg), some central German states (including Kingdom of Saxony, Saxony), and Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover in the north. On the side of Prussia were Kingdom of Italy, Italy, most north German states, and some smaller central German states. Eventually, the better-armed Prussian troops won the crucial victory at the Battle of Königgrätz under Helmuth von Moltke the Elder. The century-long struggle between Berlin and Vienna for the dominance of Germany was now over. As a sideshow in this war, Prussia defeated Hanover in the Battle of Langensalza (1866). While Hanover hoped in vain for help from Britain (as they had previously been in personal union), Britain stayed out of a confrontation with a continental great power and Prussia satisfied its desire for merging the once separate territories and gaining strong economic and strategic power, particularly from the full access to the resources of the Ruhr.
Bismarck desired Austria as an ally in the future, and so he declined to annex any Austrian territory. But in the Peace of Prague (1866), Peace of Prague in 1866, Prussia annexed four of Austria's allies in northern and central GermanyHanover, Electorate of Hesse, Hesse-Kassel, Duchy of Nassau, Nassau and Free City of Frankfurt, Frankfurt. Prussia also won full control of Schleswig-Holstein. As a result of these territorial gains, Prussia now stretched uninterrupted across the northern two-thirds of Germany and contained two-thirds of Germany's population. The German Confederation was dissolved, and Prussia impelled the 21 states north of the Main (river), Main river into forming the North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
.
Prussia was the dominant state in the new confederation, as the kingdom comprised almost four-fifths of the new state's territory and population. Prussia's near-total control over the confederation was secured in the North German Constitution, constitution drafted for it by Bismarck in 1867. Executive power was held by a Bundespräsidium, president, assisted by a chancellor responsible only to him. The presidency was a hereditary office of the House of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern rulers of Prussia. There was also a two-house parliament. The lower house, or ''Reichstag (North German Confederation), Reichstag'' (Diet), was elected by universal male suffrage. The upper house, or ''Bundesrat (German Empire), Bundesrat'' (Federal Council) was appointed by the state governments. The Bundesrat was, in practice, the stronger chamber. Prussia had 17 of 43 votes, and could easily control proceedings through alliances with the other states.
As a result of the peace negotiations, the states south of the Main remained theoretically independent, but received the (compulsory) protection of Prussia. Additionally, mutual defence treaties were concluded. However, the existence of these treaties was kept secret until Bismarck made them public in 1867 when France tried to Luxembourg Crisis, acquire Luxembourg.
=Franco-Prussian War
=German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
.
The empire was a "Lesser German" solution (in German, "kleindeutsche Lösung") to the question of uniting all German-speaking peoples into one state, because it excluded Austria, which remained connected to Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary and whose territories included non-German populations. On 18 January 1871 (the 170th anniversary of the coronation of King Frederick I Frederick I or Friedrich I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I ...
), William was Proclamation of the German Empire, proclaimed "German Kaiser, Emperor" (not "Emperor of Germany") in the Hall of Mirrors at Palace of Versailles, Versailles outside Paris, while Siege of Paris (1870–1871), the French capital was still under siege.
German Empire
The two decades after the unification of Germany were the peak of Prussia's fortunes, but the seeds for potential strife were built into the Prusso-German political system. The Constitution of the German Empire was a version of the North German Confederation's constitution. Officially, the German Empire was a federal state. In practice, Prussia overshadowed the rest of the empire. Prussia included three-fifths of the German territory and two-thirds of its population. The Imperial German Army was, in practice, an enlarged Prussian army, although the other kingdoms (Bavarian Army, Bavaria, Royal Saxon Army, Saxony and Army of Württemberg, Württemberg) retained their own small armies, coming under Imperial control in wartime. The imperial crown was a hereditary office of the House of Hohenzollern, the royal house of Prussia. The Minister President of Prussia was, except for two brief periods (January–November 1873 and 1892–94), also Chancellor of Germany, imperial chancellor. But the empire itself had no right to collect taxes directly from its subjects; the only incomes fully under federal control were the customs duties, common excise duties, and the revenue from postal and telegraph services. While all men above age 25 were eligible to vote in imperial elections, Prussia retained its restrictive three-class voting system. This effectively required the king/emperor and prime minister/chancellor to seek majorities from legislatures elected by two different franchises. In both the kingdom and the empire, the original constituencies were never redrawn to reflect changes in population, meaning that rural areas were grossly overrepresented by the turn of the 20th century. As a result, Prussia and the German Empire were something of a paradox. Bismarck knew that his new German Empire was now a colossus and economically and militarily dominant in Europe; Britain was still dominant in finance, trade and at sea. He declared Germany a "satisfied" power, using his talents to preserve peace, for example at the Congress of Berlin. Bismarck did not set up his own party. He had mixed success in some of his domestic policies. His anti-Catholic ''Kulturkampf'' inside Prussia (and not the wider German state) was a failure. He ended his support for the anticlerical National Liberal Party (Germany), Liberals and worked instead with the Catholic Centre Party (Germany), Centre Party. He tried to destroy the socialist movement, with limited success. The large Polish population resisted Germanisation of Poles during Partitions, Germanisation. Frederick III, German Emperor, Frederick III became emperor in March 1888, after the death of his father, but he died of cancer only 99 days later. At age 29, Wilhelm became Kaiser Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II after a difficult youth and conflicts with his British mother Victoria, Princess Royal. He turned out to be a man of limited experience, narrow and reactionary views, poor judgment, and occasional bad temper, which alienated former friends and allies.
At age 29, Wilhelm became Kaiser Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II after a difficult youth and conflicts with his British mother Victoria, Princess Royal. He turned out to be a man of limited experience, narrow and reactionary views, poor judgment, and occasional bad temper, which alienated former friends and allies.
Railways
Prussia nationalised its railways in the 1880s in an effort both to lower rates on freight service and to equalise those rates among shippers. Instead of lowering rates as far as possible, the government ran the railways as a profit-making endeavour, and the railway profits became a major source of revenue for the state. The nationalisation of the railways slowed the economic development of Prussia because the state favoured the relatively backward agricultural areas in its railway building. Moreover, the railway surpluses substituted for the development of an adequate tax system.The Free State of Prussia in the Weimar Republic
Because of theGerman Revolution
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
of 1918, Wilhelm II abdicated as German Emperor and King of Prussia. Prussia was proclaimed a "Free State" (i.e. a republic, German: ''Freistaat'') within the new Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
and in 1920 received a democratic Constitution of Prussia (1920), constitution.
Almost all of Germany's territorial losses, specified in the Treaty of Versailles, were areas that had been part of Prussia: Eupen and Malmedy to Belgium; South Jutland County, North Schleswig to Denmark; the Klaipėda Region, Memel Territory to Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
; the Hlučínsko, Hultschin area to Czechoslovakia. Many of the areas Prussia annexed in the partitions of Poland, such as the provinces of Province of Posen, Posen and West Prussia, as well as eastern Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, went to the Second Polish Republic. Danzig became the Free City of Danzig under the administration of the League of Nations. Also, the Saargebiet was created mainly from formerly Prussian territories, except present Saarpfalz-Kreis, Saarpfalz district, which was part of the Kingdom of Bavaria. East Prussia became an exclave, only reachable by ship. (the Seedienst Ostpreußen, Sea Service East Prussia) or by a railway through the Polish corridor.
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, the Nazi Party in 1932 became the largest party in most parts of the Free State of Prussia. However, the democratic parties in coalition remained a majority, while Communist Party of Germany, Communists and Nazis were in the opposition.
The East Prussian Otto Braun, who was Prussian minister-president almost continuously from 1920 to 1932, is considered one of the most capable Social Democrats in history. He implemented several trend-setting reforms together with his minister of the interior, Carl Severing, which were also models for the later Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. For instance, a Prussian minister-president could be forced out of office only if there was a "positive majority" for a potential successor. This concept, known as the constructive vote of no confidence, was carried over into the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany. Most historians regard the Prussian government during this time as far more successful than that of Germany as a whole.
In contrast to its pre-war authoritarianism, Prussia was a pillar of democracy in the Weimar Republic. This system was destroyed by the ''Preußenschlag'' ("Prussian coup") of Reich Chancellor Franz von Papen
Franz Joseph Hermann Michael Maria von Papen, (; 29 October 18792 May 1969) was a German politician, diplomat, Prussian nobleman and army officer. A national conservative, he served as Chancellor of Germany in 1932, and then as Vice-Chancell ...
. In this coup d'état, the government of the Reich deposed the Prussian government on 20 July 1932, under the pretext that the latter had lost control of public order in Prussia (during the Altona Bloody Sunday, Bloody Sunday of Altona, Hamburg, which was still part of Prussia at that time) and by using fabricated evidence that the Social Democrats and the Communists were planning a joint "putsch". The Defence Minister General Kurt von Schleicher, who was the prime mover behind the coup, manufactured evidence that the Prussian police under Braun's orders were favouring the Communist ''Rotfrontkämpferbund'' in street clashes with the Sturmabteilung, SA as part of an alleged plan to foment a Marxist revolution, which he used to get an emergency decree from President Paul von Hindenburg imposing ''Reich'' control on Prussia. Papen appointed himself Reich commissioner for Prussia and took control of the government. The ''Preußenschlag'' made it easier, only half a year later, for Hitler to take power decisively in Germany, since he had the whole apparatus of the Prussian government, including the police, at his disposal.
Prussia and Nazi Germany

 After the appointment of Hitler as the new chancellor, the Nazis used the absence of Franz von Papen as an opportunity to appoint
After the appointment of Hitler as the new chancellor, the Nazis used the absence of Franz von Papen as an opportunity to appoint Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician, aviator, military leader, and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which gov ...
federal commissioner for the Prussian ministry of the interior. The March 1933 German federal election, Reichstag election of 5 March 1933 strengthened the position of the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP or "Nazi" Party), although they did not achieve an absolute majority.
The Reichstag building having been Reichstag fire, set on fire a few weeks earlier on 27 February, a new Reichstag (Weimar Republic), Reichstag was opened in the Garrison Church (Potsdam), Garrison Church of Potsdam on 21 March 1933 in the presence of President Paul von Hindenburg. In a propaganda-filled meeting between Hitler and the Nazi Party, the "marriage of old Prussia with young Germany" was celebrated, to win over the Prussian monarchists, conservatives and nationalists and induce them into supporting and subsequently voting in favor of the Enabling Act of 1933.
In the centralised state created by the Nazis in the "Law on the Reconstruction of the Reich" ("Gesetz über den Neuaufbau des Reichs", 30 January 1934) and the "Reichsstatthalter#Reich Governors Law (1935), Law on Reich Governors" ("Reichsstatthaltergesetz", 30 January 1935) the states were dissolved, in fact if not in law. The state ''landtage'' were abolished and the state governments were now controlled by ''Reichsstatthaltern'' (Reich Governors) who were appointed by the chancellor. Parallel to that, the organisation of the party into districts (''Gau (German), Gaue'') gained increasing importance, as the official in charge of a ''Gau'' (the head of which was called a ''Gauleiter'') was again appointed by the chancellor who was at the same time chief of the Nazi Party.
This centralising policy went even further in Prussia. From 1934 to 1945, almost all ministries were merged and only a few departments were able to maintain their independence. Adolf Hitler, Hitler himself became formally the governor of Prussia. However, his functions were exercised by Hermann Göring as Prussian prime minister.
As provided for in the "Greater Hamburg Act" ("Groß-Hamburg-Gesetz"), certain exchanges of territory took place. Prussia was extended on 1 April 1937, for instance, by the incorporation of the Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck.
The Prussian lands transferred to Poland after the Treaty of Versailles were re-annexed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. However, most of this territory was not reintegrated back into Prussia but assigned to separate ''Gaue'' of Danzig-West Prussia and Wartheland during much of the duration of the war.
The end of Prussia
 The areas east of the Oder–Neisse line, mainly Eastern Prussia, Western Prussia, Pomerania and
The areas east of the Oder–Neisse line, mainly Eastern Prussia, Western Prussia, Pomerania and Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, were annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union in 1945 owing to the Treaty of Potsdam between three of the Allies: the United States, United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union. This included important Prussian cities like Danzig, Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
, Breslau, and Stettin. The Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–50), population fled, mostly to the Western zones, or was driven out.
As part of their wartime goals, the Western allies sought the abolition of Prussia. Joseph Stalin, Stalin was initially content to retain the name, Russians having a different historical view of their neighbour and sometime former ally. Nonetheless, by Law No. 46, which was accepted and implemented by the Allied Control Council on 25 February 1947, Prussia was officially proclaimed to be dissolved.
In the Soviet occupation zone, which became East Germany (officially, the German Democratic Republic) in 1949, the former Prussian territories were reorganised into the states of Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
and Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt ( ; ) is a States of Germany, state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the List of German states ...
, with the remaining parts of the Province of Pomerania (1815–1945), Province of Pomerania going to Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. These states were ''de facto'' abolished in 1952 in favour of ''Administrative divisions of East Germany#Division into Bezirke, Bezirke'' (districts), but were Administrative divisions of East Germany#Restoration of the Länder, recreated shortly before German reunification in 1990.
In the Allied-occupied Germany, Western Zones of occupation, which became West Germany (officially, the Federal Republic of Germany) in 1949, the former Prussian territories were divided up among North Rhine-Westphalia, Lower Saxony, Hesse, Rhineland-Palatinate and Schleswig-Holstein. Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern were later merged with Baden to create the state of Baden-Württemberg. The Saar region, which had been administered by the French as Saar Protectorate, a protectorate separate from the rest of Western Germany, was admitted to the Federal Republic of Germany as Saarland, a separate state following the 1955 Saar Statute referendum.
One year later, in 1957, the Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation was established and implemented by federal statutes in West Germany in response to a ruling from the Federal Constitutional Court, Federal Constitutional Court of Germany. The fundamental goal of this institution is protecting the cultural legacy of Prussia. As of 2021, it continues to operate from its headquarters in Berlin.
Administrative and constitutional frameworks
In the mid-16th century, the List of rulers of Brandenburg, margraves of Brandenburg had become highly dependent on the estates (representing counts, lords, knights, and towns, but not prelates, owing to the Protestant Reformation in 1538).Kotulla (2008), p. 262 The margraviate's liabilities and tax income as well as the margrave's finances were in the hands of the ''Kreditwerk'', an institution not controlled by the elector, and of the ''Großer Ausschuß'' (Great Committee) of the estates.Kotulla (2008), p. 263 This was because of concessions made by Joachim II, Elector of Brandenburg, Elector Joachim II in 1541 in return for financial aid by the estates; however, the ''Kreditwerk'' went bankrupt between 1618 and 1625. The margraves further had to yield to the veto of the estates in all issues concerning the "better or worse of the country", in all legal commitments, and in all issues concerning pawn or sale of the elector's real property. To reduce the influence of the estates, in 1604, Joachim Frederick, Elector of Brandenburg, Joachim Frederick created a council called ''Geheimer Rat für die Kurmark'' (Privy Council for the Electorate), which instead of the estates would function as the supreme advisory council for the elector. While the council was permanently established in 1613, it failed to gain any influence until 1651, owing to theThirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648)
Until after the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, the various territories of Brandenburg-Prussia remained politically independent from each other, connected only by the common feudal superior.Kotulla (2008), p. 265 Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg, Frederick William (ruled 1640–1688), who envisioned the transformation of the personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
into a real union, started to centralise the Brandenburg-Prussian government with an attempt to establish the ''Geheimer Rat'' as a central authority for all territories in 1651, but this project proved unfeasible. Instead, the elector continued to appoint a governor (''Kurfürstlicher Rat'') for each territory, who in most cases was a member of the ''Geheimer Rat''. The most powerful institution in the territories remained the governments of the estates (''Landständische Regierung'', named ''Oberratsstube'' in Prussia and ''Geheime Landesregierung'' in Mark and Cleves), which were the highest government agencies regarding jurisdiction, finances and administration. The elector attempted to balance the estates' governments by creating ''Amtskammer'' chambers to administer and coordinate the elector's domains, tax income and privileges. Such chambers were introduced in Brandenburg in 1652, in Cleves and Mark in 1653, in Pomerania in 1654, in Prussia in 1661 and in Magdeburg in 1680.Kotulla (2008), p. 267 Also in 1680, the ''Kreditwerk'' came under the aegis of the elector.Kotulla (2008), p. 266
Frederick William I's excise tax (''Akzise''), which from 1667 replaced the property tax raised in Brandenburg for Brandenburg-Prussia's standing army with the estates' consent, was raised by the elector without consultation with the estates. The conclusion of the Second Northern War
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of ...
of 1655–1660 had strengthened the elector politically, enabling him to reform the constitution of Cleves and Mark in 1660 and 1661 to introduce officials loyal to him and independent of the local estates. In the Duchy of Prussia he confirmed the traditional privileges of the Prussian estates in 1663, but the latter accepted the caveat that these privileges were not to be used to interfere with the exertion of the elector's sovereignty. As in Brandenburg, Frederick William ignored the privilege of the Prussian estates to confirm or veto taxes raised by the elector: while in 1656, an ''Akzise'' was raised with the estates' consent, the elector by force collected taxes not approved by the Prussian estates for the first time in 1674. From 1704 the Prussian estates ''de facto'' relinquished their right to approve the elector's taxes while formally still entitled to do so. In 1682 the elector introduced an ''Akzise'' to Pomerania and in 1688 to Magdeburg, while in Cleves and Mark an ''Akzise'' was introduced only between 1716 and 1720. Owing to Frederick William I's reforms, the state income increased threefold during his reign, and the tax burden per subject reached a level twice as high as in France.
 Under the rule of Frederick I of Prussia, Frederick III (I) (reign: 1688–1713), the Brandenburg Prussian territories were ''de facto'' reduced to provinces of the monarchy. Frederick William's testament would have divided Brandenburg-Prussia among his sons, but his firstborn son Frederick III (I), with the Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, emperor's backing, succeeded in becoming the sole ruler based on the House Treaty of Gera of 1599, which forbade a division of Hohenzollern territories.Kotulla (2008), p. 269 In 1689, a new central chamber for all Brandenburg-Prussian territories was established, called ''Geheime Hofkammer'' (from 1713: ''Generalfinanzdirektorium''). This chamber functioned as a superior agency of the territories' ''Amtskammer'' chambers.Kotulla (2008), p. 270 The General War Commissariat (''Generalkriegskommissariat'') emerged as a second central agency, superior to the local ''Kriegskommissariat'' agencies initially concerned with the administration of the army, but before 1712 transformed into an agency also concerned with general tax and police tasks.
The Kingdom of Prussia functioned as an absolute monarchy until the German revolutions of 1848–1849, after which Prussia became a constitutional monarchy and King Frederick William IV appointed Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg Prussia's first Prime Minister of Prussia, prime minister (''Ministerpräsident''). Constitution of Prussia (1848), Prussia's first constitution dated from 1848, but was only briefly in effect as it had been forced on the king. The Constitution of Prussia (1850), 1850 Prussian Constitution established a Bicameralism, two-chamber parliament. The lower house, the Prussian House of Representatives represented all taxpayers, who were Prussian three-class franchise, divided into three classes according to the amount of taxes paid. This assured dominance by the more well-to-do elements of the population. The upper house (First Chamber or ''Erste Kammer''), later renamed the Prussian House of Lords (''Herrenhaus''), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. The Prussian Secret Police, formed in response to the German revolutions of 1848–1849, aided the conservative government.
Under the rule of Frederick I of Prussia, Frederick III (I) (reign: 1688–1713), the Brandenburg Prussian territories were ''de facto'' reduced to provinces of the monarchy. Frederick William's testament would have divided Brandenburg-Prussia among his sons, but his firstborn son Frederick III (I), with the Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, emperor's backing, succeeded in becoming the sole ruler based on the House Treaty of Gera of 1599, which forbade a division of Hohenzollern territories.Kotulla (2008), p. 269 In 1689, a new central chamber for all Brandenburg-Prussian territories was established, called ''Geheime Hofkammer'' (from 1713: ''Generalfinanzdirektorium''). This chamber functioned as a superior agency of the territories' ''Amtskammer'' chambers.Kotulla (2008), p. 270 The General War Commissariat (''Generalkriegskommissariat'') emerged as a second central agency, superior to the local ''Kriegskommissariat'' agencies initially concerned with the administration of the army, but before 1712 transformed into an agency also concerned with general tax and police tasks.
The Kingdom of Prussia functioned as an absolute monarchy until the German revolutions of 1848–1849, after which Prussia became a constitutional monarchy and King Frederick William IV appointed Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg Prussia's first Prime Minister of Prussia, prime minister (''Ministerpräsident''). Constitution of Prussia (1848), Prussia's first constitution dated from 1848, but was only briefly in effect as it had been forced on the king. The Constitution of Prussia (1850), 1850 Prussian Constitution established a Bicameralism, two-chamber parliament. The lower house, the Prussian House of Representatives represented all taxpayers, who were Prussian three-class franchise, divided into three classes according to the amount of taxes paid. This assured dominance by the more well-to-do elements of the population. The upper house (First Chamber or ''Erste Kammer''), later renamed the Prussian House of Lords (''Herrenhaus''), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. The Prussian Secret Police, formed in response to the German revolutions of 1848–1849, aided the conservative government.
Prussia inside Weimar Republic
Unlike its authoritarian pre-1918 predecessor, Prussia from 1918 to 1932 was a promising democracy within Germany. The abolition of the political power of the aristocracy transformed Prussia into a region strongly dominated by the left wing of the political spectrum, with "Red Berlin" and the industrial centre of the Ruhr Area exerting major influence. During this period a coalition of centre-left parties ruled, predominantly under the leadership (1920–1932) of East Prussian Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democrat Otto Braun. While in office Braun implemented several reforms (together with his Minister of the Interior, Carl Severing) that became models for the later Federal Republic of Germany. For instance, a Prussian prime minister could only be forced out of office if there was a "positive majority" for a potential successor. This concept, known as the constructive vote of no confidence, became part of the Basic Law of the Federal Republic of Germany. Historians regard the Prussian government during the 1920s as far more successful than that of Germany as a whole. Similar to other German states both States of Germany, now and Weimar Republic#Constituent states, at the time, executive power remained vested in a Minister-President, Minister-President of Prussia and in laws established by a Landtag elected by the people.
Social history
Population
 In 1871, Prussia's population numbered 24.69 million, accounting for 60% of the
In 1871, Prussia's population numbered 24.69 million, accounting for 60% of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
's population. The population grew rapidly from 45 million in 1880 to 56 million in 1900, thanks to declining mortality, even as birth rates declined. About 6 million Germans, primarily young families, migrated to the United States, especially the mid-western farming regions. Their place in agriculture was often taken by young Polish farm workers. In addition, large numbers of Polish miners moved to Upper Silesia and many Germans and Poles moved to industrial jobs in the fast-growing cities especially in the Rhineland and Westphalia. In 1910, the population had increased to 40.17 million (62% of the Empire's population). In 1914, Prussia had an area of 354,490 km2. In May 1939, Prussia had an area of 297,007 km2 and a population of 41,915,040 inhabitants.
Ethnicity
Apart from ethnic Germans the country was inhabited also by Ethnolinguistic group, ethnolinguistic minorities such asPoles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
(including Kashubians, Kashubs in West Prussia and Masurians, Mazurs in East Prussia), Prussian Lithuanians (in East Prussia), Sorbs (in Lusatia), Czechs and Moravians (in Silesia), Danes (in Schleswig), Jews, Frisians, Dutch people, Dutch, Walloons, Russians (in Wojnowo, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Wojnowo), French people, French, Italians, Hungarians and others.
Religion
TheDuchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
was the first state to State religion, officially adopt Lutheranism in 1525. In the wake of the Reformation, Prussia was dominated by two major Protestant confessions: Lutheranism and Calvinism. The majority of the Prussian population was Lutheran, although there were dispersed Calvinist minorities in central and western parts of the state especially Province of Brandenburg, Brandenburg, Rhine Province, Rhineland, Province of Westphalia, Westphalia and Province of Hesse-Nassau, Hesse-Nassau. In 1613, John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg, John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg and Grand Duke of Prussia declared himself for the Calvinist creed and transferred the Berlin Cathedral from the Lutheran to the Calvinist church. Lutherans and Calvinist congregations all over the kingdom were merged in 1817 by the Prussian Union of churches, which came under tight royal control. In Protestant regions, writes Nipperdey:
Prussia received significant Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
population after the issuing of the Edict of Fontainebleau by Louis XIV of France and the following dragonnades. Prussian monarchs, beginning with Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg opened the country to the fleeing French Calvinist refugees. In Berlin, they built and worshipped at their own church called the French Cathedral, Berlin, French Cathedral on Gendarmenmarkt. Time passed by, and the French Reformed assimilated into the wider Protestant community in Prussia. East Prussia's southern region of Masuria was mostly made up of Germanised
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In l ...
Lutheran Masurians.
After 1814, Prussia contained millions of Catholics in the west and in the east. There were substantial populations in the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, parts of Westphalia, eastern parts of Province of Silesia, Silesia, West Prussia, Ermland and the Province of Posen. Communities in Poland were often ethnically Polish people, Polish, although this is not the case of eastern Silesia as the majority of Catholics there were German. During the 19th-century Kulturkampf, Prussian Catholics were forbidden from fulfilling any official functions for the state and were largely distrusted.
Prussia contained a relatively large Jewish community, which was mostly concentrated in large urban areas. According to the 1880 census, it was the biggest one in Germany with 363,790 individuals.
In 1925, 64.9% of the Prussian population was Protestant, 31.3% was Catholic, 1.1% was Jewish, 2.7% was placed in other religious categories.
Non-German population
 In 1871, approximately 2.4 million Poles lived in Prussia, constituting the largest minority. Other minorities were Jews, Danes, Frisians, Dutch people, Dutchmen, Kashubians (72,500 in 1905), Masurians (248,000 in 1905),
In 1871, approximately 2.4 million Poles lived in Prussia, constituting the largest minority. Other minorities were Jews, Danes, Frisians, Dutch people, Dutchmen, Kashubians (72,500 in 1905), Masurians (248,000 in 1905), Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
(101,500 in 1905), Walloons, Czechs, Kursenieki, and Sorbs.
The area of Greater Poland, where the Polish nation had originated, became the Province of Posen after the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
. Poles in this Polish-majority province (62% Polish, 38% German) resisted German rule. Also, the southeast portion of Silesia (Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
) had a Polish majority. But Catholics and Jews did not have equal status with Protestants.
As a result of the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, the Second Polish Republic was granted not only these two areas, but also areas with a German majority in the province of West Prussia. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, East Prussia, most of Pomerania and Silesia, and the eastern part of Brandenburg were either annexed by the Soviet Union or given to Poland, and the German language, German-speaking populations Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland during and after World War II, forcibly expelled.
Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
between 1885 and 1890.
Education
The German states in the 19th century were world leaders in prestigious education and Prussia set the pace. For boys free public education was widely available, and the gymnasium system for elite students was highly professionalized. The modern university system emerged from the 19th century German universities, especially Friedrich Wilhelm University (now named Humboldt University of Berlin). It pioneered the model of the research university with well-defined career tracks for professors. The United States, for example, paid close attention to German models. Families focused on educating their sons. The traditional schooling for girls was generally provided by mothers and governesses. Elite families increasingly favoured Catholic convent boarding schools for their daughters. Prussia's Kulturkampf laws in the 1870s limited Catholic schools thus providing an opening for a large number of new private schools for girls.Continuation of Prussian traditions
The States of Germany, German states on the former territory of the Free State of Prussia are successor states to Prussia in legal terms, particularly in terms of constitutional and international law. For example, the state of North Rhine-Westphalia is bound to the concordat that the Free State of Prussia concluded with the Holy See. Despite its dissolution in 1947, many aspects of Prussia have been preserved to this day in everyday life, in culture, in sport and even in names.Federal government
* In the federal government according to the prevailing view, the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany as a subject of international law is identical to the federal state initiated and dominated by Prussia, which was founded in 1867 under the name of theNorth German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
and expanded into the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871.
* Prussia's capital Berlin also became the capital of the newly founded empire in 1871. The capital city resolution of 1991, which designated Berlin as the federal capital of the reunified Germany, the "Berlin Republic", stands in this tradition. Several federal institutions use buildings from former Prussian institutions, for example the Federal Council (Germany), Bundesrat uses the Prussian House of Lords building. The Federal President has his first official residence in Bellevue Palace, the first classical building in Prussia. As the central shield of the Reich coat of arms, the Prussian state coat of arms is depicted in the gable above the main entrance to the Reichstag building.
* The constructive vote of no confidence anchored in the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, Basic Law of the Federal Republic of Germany, which only allows the head of government to be voted out if a new successor is simultaneously elected, is directly based on a constitutional regulation of the Free State of Prussia.
* The Prussian war award of the Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
is, in a modified form, the symbol of the Bundeswehr.
* In the tradition of the 1st Guards Regiment on Foot, which was introduced in 1806 as the personal regiment of the King of Prussia, the guard battalion at the Federal Ministry of Defense has followed.
* As part of state visits, the presentation march of Friedrich Wilhelm III is a regular part of the federal diplomatic protocol at the reception with military honors and the marching down the front of the Wachbataillon, guard battalion's honor formation at the Federal Ministry of Defence (Germany), Federal Ministry of Defense is played.
* The Bundeswehr's Great Tattoo, played particularly when bidding farewell to President of Germany, Federal Presidents, Chancellor of Germany, Chancellors, Federal Defense Ministers and senior military officers, is largely composed of traditional elements of Prussian military music.
* The police star, the emblem of the Federal Police (Germany), Federal Police and the Feldjäger of the Bundeswehr, is derived from the Prussian Guard Star, which went back to the eight-pointed breast star of the Order of the Black Eagle, Black Eagle Order. The guard star can also be found on the bell trees of the Bundeswehr music corps.
* In 2002, the then Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
Social Minister Alwin Ziel suggested naming the planned new federal state of Berlin-Brandenburg "Prussia".
Within Germany
* The state coat of arms ofSaxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt ( ; ) is a States of Germany, state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the List of German states ...
shows, among other things the Prussian eagle.
* The large coat of arms of Baden-Württemberg contains the house coat of arms of the House of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollerns.
*The Prussian government and administration model was decisive for a large number of political institutions at the state level and is still expressed today in terms such as Minister-president, Regierungsbezirk and Landrat. Today's North Rhine-Westphalia regional associations go back to the Prussian provincial associations.
* The Rhineland Regional Association in North Rhine-Westphalia - in continuation of the tradition of the Rhine Province and its provincial association - also has the Prussian eagle in the upper part of its association coat of arms.
* The states on the former territory of the Free State of Prussia are successor states to Prussia in legal terms, particularly in terms of constitutional and international law. North Rhine-Westphalia, the largest successor state to Prussia,Markus Reiners: ''Verwaltungsstrukturreformen in den deutschen Bundesländern. Radikale Reformen auf der Ebene der staatlichen Mittelinstanz''. VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften, Wiesbaden 2008, ISBN 978-3-531-15774-0, S. 162online
maintains its Prussian history and remembrance culture in the form of the Prussian Museums in Wesel and Minden.
In churches
* The Union of Protestant Churches in the EKD, Union of Evangelical Churches emerged from the Evangelical Church of the Union, a church association of the Old Prussian Protestant regional churches, i.e. H. of the churches whose area already belonged to Prussia before 1866 * The Prussian state coat of arms is depicted in the niche above the main (west) door within Berlin Cathedral, relating to the link between church and state.See also
 * Alte Nationalgalerie, Berlin
* Altes Museum, Berlin
* Bode Museum, Berlin
* East Prussian Regional Museum
* List of museums and galleries in Berlin
* List of museums in Germany
* Alte Nationalgalerie, Berlin
* Altes Museum, Berlin
* Bode Museum, Berlin
* East Prussian Regional Museum
* List of museums and galleries in Berlin
* List of museums in Germany
References
Notes CitationsFurther reading
* * , covers medieval period * Carroll, E. Malcolm. ''Germany and the great powers, 1866–1914: A study in public opinion and foreign policy'' (1938online
862pp. * Christopher Clark, Clark, Christopher. ''Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600–1947'' (2009), a standard scholarly history * Craig, Gordon. ''The politics of the Prussian Army 1640–1945'' (1955)
online
* Fay, Sidney Bradshaw. ''The Rise of Brandenburg-Prussia To 1786'' (1937
online
*
online review
* Friedrich, Karin. ''Brandenburg-Prussia, 1466–1806: The Rise of a Composite State'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2011); 157pp. Emphasis on historiography. * Glees, Anthony. "Albert C. Grzesinski and the politics of Prussia, 1926–1930." ''English Historical Review'' 89.353 (1974): 814–834
online
* * Hamerow, Theodore S. ''Restoration, Revolution, Reaction: Economics and Politics in Germany, 1815–1871'' (1958
online
* Hamerow, Theodore S. ''The social foundations of German unification, 1858–1871'' (1969
online
* Henderson, William O. ''The state and the industrial revolution in Prussia, 1740–1870'' (1958
online
* * Horn, David Bayne. ''Great Britain and Europe in the eighteenth century'' (1967) covers 1603–1702; pp. 144–177 for Prussia; pp. 178–200 for other Germany; pp. 111–143 for Austria * Hornung, Erik. "Immigration and the diffusion of technology: The Huguenot diaspora in Prussia." ''American Economic Review'' 104.1 (2014): 84–122
online
* Koch, H. W. ''History of Prussia'' (1987
online
* Kotulla, Michael
''Deutsche Verfassungsgeschichte: vom Alten Reich bis Weimar (1495–1934)'' (Springer, 2008)
* * Muncy, Lysbeth W. "The Junkers and the Prussian Administration from 1918 to 1939." ''Review of Politics'' 9.4 (1947): 482–501
online
* Nipperdey, Thomas. ''Germany from Napoleon to Bismarck: 1800–1866'' (1996)
excerpt
* Orlow, Dietrich. ''Weimar Prussia, 1918–1925: The Unlikely Rock of Democracy'' (1986
online
* Orlow, Dietrich. ''Weimar Prussia, 1925–1933: The Illusion of Strength'' (1991)
online
* , stress on cultural topics * Sagarra, Eda. ''A Social History of Germany, 1648–1914'' (1977
online
* Schulze, Hagen, and Philip G. Dwyer. "Democratic Prussia in Weimar Germany, 1919–33." in ''Modern Prussian History 1830–1947'' (Routledge, 2014) pp. 211–229. * * Taylor, A. J. P. ''The Course of German History: A Survey of the Development of German History since 1815'' (1945
online
* Taylor, A. J. P. ''Bismarck'' (1955)
online
* Treasure, Geoffrey. ''The Making of Modern Europe, 1648–1780'' (3rd ed. 2003). pp. 427–462. *
External links
chronology and summaries
Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation website
Stiftung Preußischer Kulturbesitz
(picture archive).
Foundation for Prussian Palaces and Gardens Berlin-Brandenburg
{{Authority control Prussia, States and territories established in 1525 States and territories disestablished in 1947 Former countries in Europe History of Brandenburg 1525 establishments in Prussia 1947 disestablishments in Prussia Historical regions