Prostate specific antigen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The prostate is an
File:Illu prostate lobes.jpg, Lobes of prostate
File:Prostate zones.png, Zones of prostate
Inside of the prostate, adjacent and parallel to the prostatic urethra, there are two longitudinal muscle systems. On the front side ( ventrally) runs the urethral
PDF
File:Internal_iliac_branches.PNG, Imaging showing the inferior vesical, inferior pudendal and middle rectal arteries arising from the
 The prostate consists of glandular and
The prostate consists of glandular and
File:Prostatehistology.jpg, Microscopic glands of the prostate
File:Prostate gland microanatomy.png, Microanatomy of a prostatic gland, showing both luminal cells and surrounding basal cells. H&E stain.
File:Histology of normal prostate.jpg, Histology of normal prostate, H&E stain, with benign features: Glands are rounded to irregularly branching, with an inner layer of epithelial cells surrounded by an outer layer of basal cells. They are surrounded by ample stroma.
File:Histology of prostate atrophy.jpg, Histology of prostate with gradually increasing simple atrophy from left to right, H&E stain. Crowding and angulation may mimic that of adenocarcinoma, but there is nuclear basophilia rather than atypia, and occasional basal cells can still be seen.
 Prostatitis is
Prostatitis is
accessory gland
This glossary of entomology describes terms used in the formal study of insect species by entomologists.
A–C
A synthetic chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticide
Insecticides are pestic ...
of the male reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvic cavity, pelvis.
The main male sex organs are the hu ...
and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in Placentalia, placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, v ...
and ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
, with the urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy
Gross anatomy is the study of anatomy at the visible or macroscopic level. The counterpart to gross anatomy is the field of histology, which studies microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy of the human body or other animals seeks to understand the ...
as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visi ...
by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
.
The prostate produces and contains fluid that forms part of semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
, the substance emitted during ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
as part of the male sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the first part of ejaculate, together with most of the sperm, because of the action of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
tissue within the prostate. In comparison with the few spermatozoa expelled together with mainly seminal vesicular fluid, those in prostatic fluid have better motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently using metabolism, metabolic energy. This biological concept encompasses movement at various levels, from whole organisms to cells and subcellular components.
Motility is observed in ...
, longer survival, and better protection of genetic material.
Disorders of the prostate include enlargement, inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. The word ''prostate'' is derived from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(), meaning "one who stands before", "protector", "guardian", with the term originally used to describe the seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands or seminal glands) are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that largely composes the semen.
The vesicles are 5 ...
.
Structure
The prostate is aexocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of ...
of the male reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvic cavity, pelvis.
The main male sex organs are the hu ...
. In adults, it is about the size of a walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''. They are accessory fruit because the outer covering of the fruit is technically an i ...
, and has an average weight of about , usually ranging between . The prostate is located in the pelvis. It sits below the urinary bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the ...
and surrounds the urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
. The part of the urethra passing through it is called the prostatic urethra
The prostatic urethra, the widest and most dilatable part of the urethra canal, is about 3 cm long.
It runs almost vertically through the prostate from its base to its apex, lying nearer its anterior than its posterior surface; the form of ...
, which joins with the two ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the Excretory duct of seminal gland, duct of the seminal vesicle. They pa ...
s. The prostate is covered in a surface called the ''prostatic capsule'' or ''prostatic fascia''.
The internal structure of the prostate has been described using both lobes and zones. Because of the variation in descriptions and definitions of lobes, the zone classification is used more predominantly.
The prostate has been described as consisting of three or four zones. Zones are more typically able to be seen on histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
, or in medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
, such as ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
.
The "lobe" classification describes lobes that, while originally defined in the fetus, are also visible in gross anatomy, including dissection and when viewed endoscopically. The five lobes are the anterior lobe or isthmus, the posterior lobe, the right and left lateral lobes, and the middle or median lobe.
dilator
Dilator or dilatator is a medical term with a number of uses, including:
*A surgical instrument or medical implement used to induce dilation, that is, to expand an opening or passage such as the cervix (see cervical dilator), urethra, esophagus, ...
(''musculus dilatator urethrae''), on the backside (dorsally
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
) runs the muscle switching the urethra into the ejaculatory state (''musculus ejaculatorius'').Michael Schünke, Erik Schulte, Udo Schumacher: ''PROMETHEUS Innere Organe. LernAtlas Anatomie'', vol 2: ''Innere Organe'', Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart/Germany 2012, , p. 298Blood and lymphatic vessels
The prostate receives blood through theinferior vesical artery
The inferior vesical artery (or inferior vesical artery) is an artery of the pelvis which arises from the internal iliac artery and supplies parts of the urinary bladder as well as other structures of the urinary system and structures of the male ...
, internal pudendal artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.
Structure
The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk ...
, and middle rectal arteries. These vessels enter the prostate on its outer surface where it meets the bladder, and travel forward to the apex of the prostate. Both the inferior vesical and the middle rectal arteries often arise together directly from the internal iliac arteries
The internal iliac artery (formerly known as the hypogastric artery) is the main artery of the pelvis.
Structure
The internal iliac artery supplies the walls and viscera of the pelvis, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compart ...
. On entering the bladder, the inferior vesical artery splits into a urethral branch, supplying the urethral prostate; and a capsular branch, which travels around the capsule and has smaller branches, which perforate into the prostate.
The veins of the prostate form a network – the prostatic venous plexus
The prostatic veins form a well-marked prostatic plexus which lies partly in the fascial sheath of the prostate and partly between the sheath and the prostatic capsule. It collects blood from the prostate, and (via the v. dorsalis profunda clitor ...
, primarily around its front and outer surface. This network also receives blood from the deep dorsal vein of the penis
Deep or The Deep may refer to:
Places United States
* Deep Creek (Appomattox River tributary), Virginia
* Deep Creek (Great Salt Lake), Idaho and Utah
* Deep Creek (Mahantango Creek tributary), Pennsylvania
* Deep Creek (Mojave River tributary ...
, and is connected via branches to the vesical plexus and internal pudendal veins
The internal pudendal veins (internal pudic veins) are a set of veins in the pelvis. They are the venae comitantes of the internal pudendal artery. Internal pudendal veins are enclosed by pudendal canal, with internal pudendal artery and pudenda ...
. Veins drain into the vesical and then internal iliac vein
The internal iliac vein (hypogastric vein) begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to for ...
s.
The lymphatic drainage of the prostate depends on the positioning of the area. Vessels surrounding the vas deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididyma ...
, some of the vessels in the seminal vesicle, and a vessel from the posterior surface of the prostate drain into the external iliac lymph nodes
The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels.
They are arranged in three groups, one on the lateral, another on the medial, and a third on the anterior aspect of the vessel ...
. Some of the seminal vesicle vessels, prostatic vessels, and vessels from the anterior prostate drain into internal iliac lymph nodes. Vessels of the prostate itself also drain into the obturator and sacral lymph nodes.
internal iliac arteries
The internal iliac artery (formerly known as the hypogastric artery) is the main artery of the pelvis.
Structure
The internal iliac artery supplies the walls and viscera of the pelvis, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compart ...
.
File:Gray611.png, Image showing the external iliac lymph nodes
The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels.
They are arranged in three groups, one on the lateral, another on the medial, and a third on the anterior aspect of the vessel ...
and their positions around the external iliac artery and vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
Microanatomy
 The prostate consists of glandular and
The prostate consists of glandular and connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
. Tall column-shaped cells form the lining (the epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
) of the glands. These form one layer or may be pseudostratified. The epithelium is highly variable and areas of low cuboidal
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many ...
or flat cells can also be present, with transitional epithelium in the outer regions of the longer ducts. Basal cell
A basal cell is a general cell type that is present in many forms of epithelial tissue throughout the body. Basal cells are located between the basement membrane and the remainder of the epithelium, effectively functioning as an anchor for the epi ...
s surround the luminal epithelial cells in benign glands. The glands are formed as many follicles, which drain into canals and subsequently 12–20 main ducts, These in turn drain into the urethra as it passes through the prostate. There are also a small amount of flat cells, which sit next to the basement membranes of glands, and act as stem cells.
The connective tissue of the prostate is made up of fibrous tissue and smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
. The fibrous tissue separates the gland into lobules. It also sits between the glands and is composed of randomly orientated smooth-muscle bundles that are continuous with the bladder.
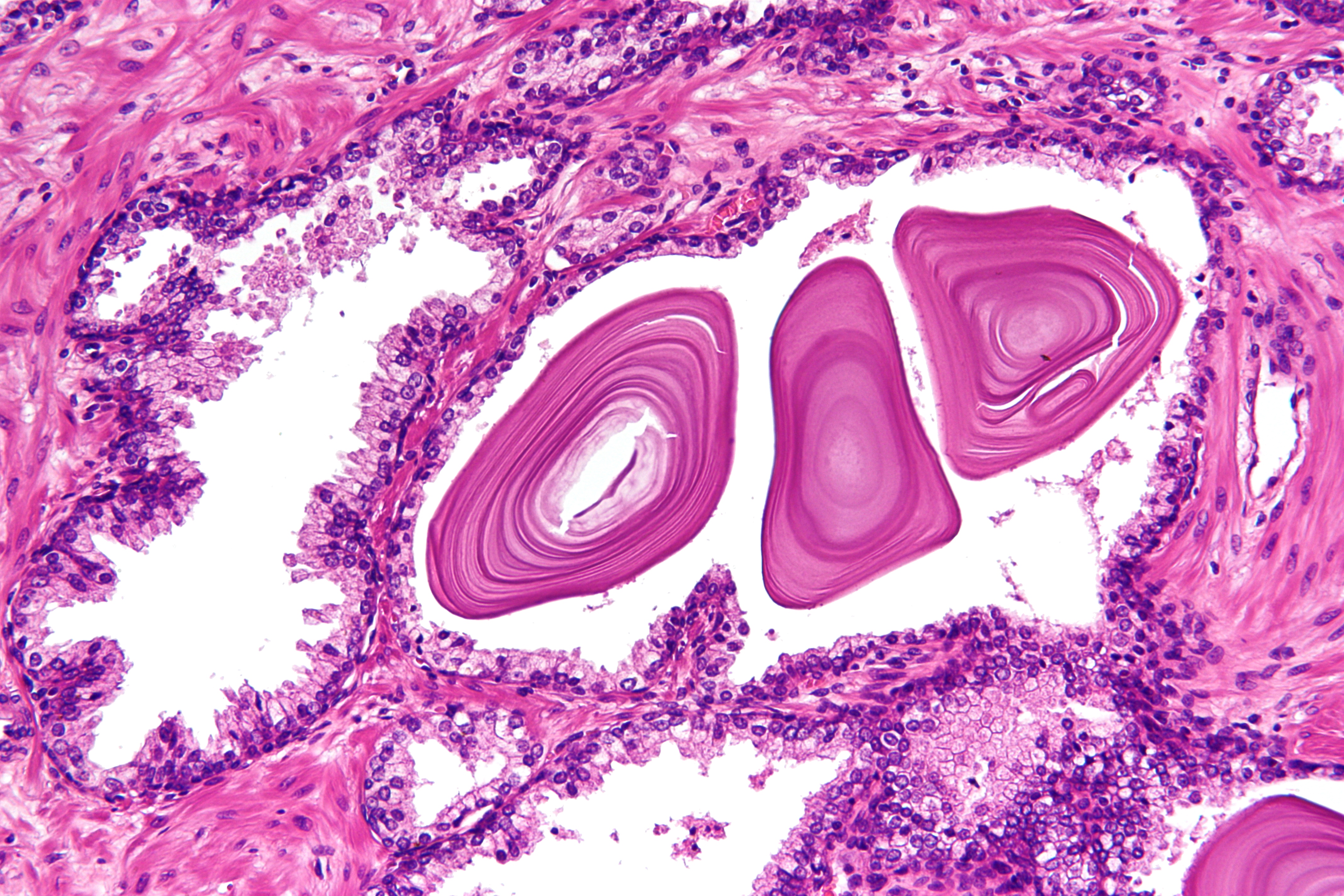
Over time, thickened secretions called corpora amylacea accumulate in the gland.
Gene and protein expression
About 20,000protein-coding genes
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated s ...
are expressed in human cells and almost 75% of these genes are expressed in the normal prostate. About 150 of these genes are more specifically expressed in the prostate, with about 20 genes being highly prostate specific. The corresponding specific proteins are expressed in the glandular and secretory cells of the prostatic gland and have functions that are important for the characteristics of semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
, including prostate-specific protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, such as the prostate specific antigen (PSA), and the prostatic acid phosphatase
Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP), also prostatic specific acid phosphatase (PSAP), is an enzyme produced by the prostate. It may be found in increased amounts in men who have prostate cancer or other diseases.
The highest levels of acid phosphata ...
.
Development
In the developingembryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
, at the hind end lies an inpouching called the cloaca
A cloaca ( ), : cloacae ( or ), or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, cartilagin ...
. This, over the fourth to the seventh week, divides into a urogenital sinus
The urogenital sinus is a body part of a human or other Placentalia, placental only present in the development of the urinary system, development of the urinary and development of the reproductive organs, reproductive organs. It is the ventral p ...
and the beginnings of the anal canal
The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional s ...
, with a wall forming between these two inpouchings called the urorectal septum
The urorectal septum is an invagination of the cloaca. It divides it into a dorsal part (the hindgut) and a ventral part (the urogenital sinus). It invaginates from cranial to caudal, formed from the endodermal cloaca, and fuses with the cloa ...
. The urogenital sinus divides into three parts, with the middle part forming the urethra; the upper part is largest and becomes the urinary bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the ...
, and the lower part then changes depending on the biological sex of the embryo.
The prostatic part of the urethra develops from the middle, pelvic, part of the urogenital sinus, which is of endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastr ...
al origin. Around the end of the third month of embryonic life, outgrowths arise from the prostatic part of the urethra and grow into the surrounding mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
. The cells lining this part of the urethra differentiate into the glandular epithelium of the prostate. The associated mesenchyme differentiates into the dense connective tissue and the smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
of the prostate.
Condensation of mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
, urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
, and Wolffian duct
The mesonephric duct, also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct, is a paired organ that develops in the early stages of embryonic development in humans and other mammals. It is an important structure that p ...
s gives rise to the adult prostate gland, a composite organ made up of several tightly fused glandular and non-glandular components. To function properly, the prostate needs male hormones
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
(androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s), which are responsible for male sex
Sex is the biological trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. During sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote, which develops into an offspring that inheri ...
characteristics. The main male hormone is testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
, which is produced mainly by the testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s. It is dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone primarily involved in the growth and repair of the prostate and the penis, as well as the production o ...
(DHT), a metabolite of testosterone, that predominantly regulates the prostate. The prostate gland enlarges over time, until the fourth decade of life.
Function
In ejaculation
The prostate secretes fluid, which becomes part of thesemen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
. Its secretion forms up to 30% of the semen. Semen is the fluid emitted ( ejaculated) through the male urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
during the sexual response. Sperm are emitted from the vas deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididyma ...
into the male urethra via the ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the Excretory duct of seminal gland, duct of the seminal vesicle. They pa ...
, which lies within the prostate gland. Semen is moved into the urethra following contractions of the smooth muscle of the vas deferens and seminal vesicles, following stimulation, primarily of the glans penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, (; from Latin ''glans'' meaning "acorn") is the bulbous structure at the Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, distal end of the human penis ...
. Stimulation sends nerve signals via the internal pudendal nerves to the upper lumbar spine
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
; the nerve signals causing contraction act via the hypogastric nerves. After traveling into the urethra, the seminal fluid is ejaculated by contraction of the bulbocavernosus muscle. The secretions of the prostate include proteolytic enzyme
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do t ...
s, prostatic acid phosphatase
Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP), also prostatic specific acid phosphatase (PSAP), is an enzyme produced by the prostate. It may be found in increased amounts in men who have prostate cancer or other diseases.
The highest levels of acid phosphata ...
, fibrinolysin, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, and prostate-specific antigen. Together with the secretions from the seminal vesicles, these form the major fluid part of semen. The prostate contains various metals, including zinc, and is known to be the primary source of most metals found in semen, which are released during ejaculation.
In urination
The prostate's changes of shape, which facilitate the mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation, are mainly driven by the two longitudinal muscle systems running along the prostatic urethra. These are the ''urethraldilator
Dilator or dilatator is a medical term with a number of uses, including:
*A surgical instrument or medical implement used to induce dilation, that is, to expand an opening or passage such as the cervix (see cervical dilator), urethra, esophagus, ...
'' (''musculus dilatator urethrae'') on the urethra's front side, which contracts during urination and thereby shortens and tilts the prostate in its vertical dimension thus widening the prostatic section of the urethral tube, and the muscle switching the urethra into the ejaculatory state (''musculus ejaculatorius'') on its backside.
In case of an operation, e.g. because of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), damaging or sparing of these two muscle systems varies considerably depending on the choice of operation type and details of the procedure of the chosen technique. The effects on postoperational urination and ejaculation vary correspondingly.
In stimulation
It is possible for some men to achieveorgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling"), sexual climax, or simply climax, is the sudden release of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, characterized by intense sexual pleasure resulting in rhythmic, involu ...
solely through stimulation of the prostate gland, such as via prostate massage
Prostate massage is the massage or stimulation of the male prostate gland for medicine, medical purposes or sexual stimulation.
The prostate takes part in the Human sexual response cycle, sexual response cycle and is essential for the productio ...
or anal intercourse
Anal sex or anal intercourse principally means the insertion and thrusting of the erect penis into a person's anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure.Sepages 270–271for anal sex information, anpage 118for information about the clitoris ...
. This has led to the area of the rectal wall adjacent to the prostate to be popularly referred to as the "male G-spot
The G-spot, also called the Gräfenberg spot (for German gynecologist Ernst Gräfenberg), is characterized as an erogenous area of the vagina that, when stimulated, may lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and potential female eja ...
".
Clinical significance
Inflammation
 Prostatitis is
Prostatitis is inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the prostate gland. It can be caused by infection with bacteria, or other noninfective causes. Inflammation of the prostate can cause painful urination or ejaculation, groin pain, difficulty passing urine, or constitutional symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
such as fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
or tiredness
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions ...
. When inflamed, the prostate becomes enlarged and is tender when touched during digital rectal examination
Digital rectal examination (DRE), also known as a prostate exam (), is an internal examination of the rectum performed by a healthcare provider.
Prior to a 2018 report from the United States Preventive Services Task Force, a digital exam was a c ...
. The bacteria responsible for the infection may be detected by a urine culture
Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. ''Escherichia coli'' is the ...
.
Acute prostatitis and chronic bacterial prostatitis are treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s. Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, or male chronic pelvic pain syndrome is treated by a large variety of modalities including the medications alpha blockers
Alpha blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as neutral antagonist, antagonists on Adrenergic receptor#.CE.B1 receptors, α-adrenergic receptors (Adrenergic receptor ...
, non-steroidal anti-inflammatories and amitriptyline
Amitriptyline, sold under the brand name Elavil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, and a variety of pain syndromes such as neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine and tension headac ...
, antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s, and other anxiolytic
An anxiolytic (; also antipanic or anti-anxiety agent) is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxie ...
s. Other treatments that are not medications may include physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
, psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of Psychology, psychological methods, particularly when based on regular Conversation, personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase hap ...
, nerve modulators, and surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
. More recently, a combination of trigger point
Myofascial trigger points (MTrPs), also known as trigger points, are described as hyperirritable spots in the skeletal muscle. They are associated with palpable nodules in taut bands of muscle fibers. They are a topic of ongoing controvers ...
and psychological therapy has proved effective for category III prostatitis as well.
Prostate enlargement
An enlarged prostate is called prostatomegaly, with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) being the most common cause. BPH refers to an enlargement of the prostate due to an increase in the number of cells that make up the prostate () from a cause that is not a malignancy. It is very common in older men. It is often diagnosed when the prostate has enlarged to the point where urination becomes difficult. Symptoms include needing to urinate often (urinary frequency
Frequent urination, or urinary frequency (sometimes called pollakiuria), is the need to urinate more often than usual. Diuretics are medications that increase urinary frequency. Nocturia is the need of frequent urination at night. The most common ...
) or taking a while to get started ( urinary hesitancy). If the prostate grows too large, it may constrict the urethra and impede the flow of urine, making urination painful and difficult, or in extreme cases completely impossible, causing urinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
. Over time, chronic retention may cause the bladder to become larger and cause a backflow of urine into the kidneys (hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and Renal calyx, calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dila ...
).
BPH can be treated with medication, a minimally invasive procedure
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definiti ...
or, in extreme cases, surgery that removes the prostate. In general, treatment often begins with an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor
alpha-1 (α1) adrenergic are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) associated with the Gq alpha subunit, Gq heterotrimeric G protein. α1-adrenergic receptors are subdivided into three highly homologous subtypes, i.e., α1A-adrenergic, α1A-, α1B ...
antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.tamsulosin, which reduces the tone of the
smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
found in the urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
that passes through the prostate, making it easier for urine to pass through. For people with persistent symptoms, procedures may be considered. The surgery most often used in such cases is transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection of the prostate (commonly known as a TURP, plural TURPs, and rarely as a transurethral prostatic resection, TUPR) is a urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, ...
, in which an instrument is inserted through the urethra to remove prostate tissue that is pressing against the upper part of the urethra and restricting the flow of urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
. Minimally invasive procedures include transurethral needle ablation of the prostate and transurethral microwave thermotherapy
Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) is one of a number of effective and safe procedures used in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is an alternative treatment to pharmacotherapy such ...
. These outpatient procedures may be followed by the insertion of a temporary stent
In medicine, a stent is a tube usually constructed of a metallic alloy or a polymer. It is inserted into the Lumen (anatomy), lumen (hollow space) of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open.
Stenting refers to the placement of ...
, to allow normal voluntary urination, without exacerbating irritative symptoms.
Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most commoncancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s affecting older men in the UK, US, Northern Europe and Australia, and a significant cause of death
In law, medicine, and statistics, cause of death is an official determination of the conditions resulting in a human's death, which may be recorded on a death certificate. A cause of death is determined by a medical examiner. In rare cases, an ...
for elderly men worldwide. Often, a person does not have symptoms; when they do occur, symptoms may include urinary frequency, urgency, hesitation and other symptoms associated with BPH. Uncommonly, such cancers may cause weight loss, retention of urine, or symptoms such as back pain
Back pain (Latin: ''dorsalgia'') is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area ...
due to lesions that have spread outside of the prostate.
A digital rectal examination
Digital rectal examination (DRE), also known as a prostate exam (), is an internal examination of the rectum performed by a healthcare provider.
Prior to a 2018 report from the United States Preventive Services Task Force, a digital exam was a c ...
and the measurement of a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level are usually the first investigations done to check for prostate cancer. PSA values are difficult to interpret, because a high value might be present in a person without cancer, and a low value can be present in someone with cancer. The next form of testing is often the taking of a prostate biopsy to assess for tumour activity and invasiveness. Because of the significant risk of overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of disease that will never cause symptoms or death during a patient's ordinarily expected lifetime and thus presents no practical threat regardless of being pathologic. Overdiagnosis is a side effect of screening ...
with widespread screening in the general population, prostate cancer screening
Prostate cancer screening is the screening process used to detect undiagnosed prostate cancer in men without signs or symptoms. When abnormal prostate tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat and cure, but it is unclear if earl ...
is controversial. If a tumour is confirmed, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
such as an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
or bone scan
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique used to help diagnose and assess different bone diseases. These include cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be vis ...
may be done to check for the presence of tumour in other parts of the body.
Prostate cancer that is only present in the prostate is often treated with either surgical removal of the prostate or with radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
or by the insertion of small radioactive particles of iodine-125
Iodine-125 (125I) is a radioisotope of iodine which has uses in biological assays, nuclear medicine imaging and in radiation therapy as brachytherapy to treat a number of conditions, including prostate cancer, uveal melanomas, and brain tumor ...
or palladium-103, called brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation, radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. The word "brachytherapy" comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word , meaning "short-distance" or "s ...
. Cancer that has spread to other parts of the body is usually treated also with hormone therapy, to deprive a tumour of sex hormones (androgens) that stimulate proliferation. This is often done through the use of GnRH analogues or agents (such as bicalutamide
Bicalutamide, sold under the brand name Casodex among others, is an antiandrogen medication that is primarily used to treat prostate cancer. It is typically used together with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogue or surgical remo ...
) that block the receptors that androgens act on; occasionally, surgical removal of the testes may be done instead. Cancer that does not respond to hormonal treatment, or that progresses after treatment, might be treated with chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
such as docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cel ...
. Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
may also be used to help with pain associated with bony lesions.
Sometimes, the decision may be made not to treat prostate cancer. If a cancer is small and localised, the decision may be made to monitor for cancer activity at intervals ("active surveillance") and defer treatment. If a person, because of frailty or other medical conditions or reasons, has a life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
less than ten years, then the impacts of treatment may outweigh any perceived benefits.
Surgery
Surgery to remove the prostate is called prostatectomy, and is usually done as a treatment for cancer limited to the prostate, or prostatic enlargement. When it is done, it may be done asopen surgery
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definitio ...
or as laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery. These are done under general anaesthetic
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awaren ...
. Usually the procedure for cancer is a radical prostatectomy
Prostatectomy (from the Greek , "prostate" and , "excision") is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This operation is done for benign conditions that cause urinary retention, as well as for prostate cancer and for other ...
, which means that the seminal vesicles are removed and the vasa deferentia are also tied off. Part of the prostate can also be removed from within the urethra, called transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection of the prostate (commonly known as a TURP, plural TURPs, and rarely as a transurethral prostatic resection, TUPR) is a urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, ...
(TURP). Open surgery may involve a cut that is made in the perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
, or via an approach that involves a cut down the midline from the belly button to the pubic bone
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
. Open surgery may be preferred if there is a suspicion that lymph nodes are involved and they need to be removed or biopsied during a procedure. A perineal approach will not involve lymph node removal and may result in less pain and a faster recovery following an operation. A TURP procedure uses a tube inserted into the urethra via the penis and some form of heat, electricity or laser to remove prostate tissue.
The whole prostate can be removed. Complications that might develop because of surgery include urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women ...
and erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
because of damage to nerves during the operation, particularly if a cancer is very close to nerves. Ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
of semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
will not occur during orgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling"), sexual climax, or simply climax, is the sudden release of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, characterized by intense sexual pleasure resulting in rhythmic, involu ...
if the vasa deferentia are tied off and seminal vesicles removed, such as during a radical prosatectomy. This will mean a man becomes infertile
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's sta ...
. Sometimes, orgasm may not be able to occur or may be painful. The penis length may shorten slightly if the part of the urethra within the prostate is also removed. General complications due to surgery can also develop, such as infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s, bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethr ...
, inadvertent damage to nearby organs or within the abdomen, and the formation of blood clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
s.
History
The prostate was first formally identified by Venetian anatomist Niccolò Massa in ''Anatomiae libri introductorius'' (Introduction to Anatomy) in 1536 and illustrated byFlemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
anatomist Andreas Vesalius
Andries van Wezel (31 December 1514 – 15 October 1564), latinized as Andreas Vesalius (), was an anatomist and physician who wrote '' De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ''in seven books''), which is ...
in ''Tabulae anatomicae sex'' (six anatomical tables) in 1538. Massa described it as a "glandular flesh upon which rests the neck of the bladder," and Vesalius as a "glandular body". The first time a word similar to ''prostate'' was used to describe the gland is credited to André du Laurens in 1600, who described it as a term already in use by anatomists at the time. The term was however used at least as early as 1549 by French surgeon Ambroise Pare.
At the time, Du Laurens was describing what was considered to be a pair of organs (not the single two-lobed organ), and the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
term ''prostatae'' that was used was a mistranslation of the term for the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
word used to describe the seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands or seminal glands) are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that largely composes the semen.
The vesicles are 5 ...
, ''parastatai''; although it has been argued that surgeons in Ancient Greece and Rome must have at least seen the prostate as an anatomical entity. The term ''prostatae'' was taken rather than the grammatically correct ''prostator'' (singular) and ''prostatores'' (plural) because the gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
of the Ancient Greek term was taken as female, when it was in fact male.
The fact that the prostate was one and not two organs was an idea popularised throughout the early 18th century, as was the English language term used to describe the organ, ''prostate'', attributed to William Cheselden
William Cheselden (; 19 October 168810 April 1752) was an English surgeon and teacher of anatomy and surgery, who was influential in establishing surgery as a scientific medical profession. Via the medical missionary Benjamin Hobson, his wor ...
. A monograph
A monograph is generally a long-form work on one (usually scholarly) subject, or one aspect of a subject, typically created by a single author or artist (or, sometimes, by two or more authors). Traditionally it is in written form and published a ...
, "Practical observations on the treatment of the diseases of the prostate gland" by Everard Home in 1811, was important in the history of the prostate by describing and naming anatomical parts of the prostate, including the median lobe. The idea of the five lobes of the prostate was popularized following anatomical studies conducted by American urologist Oswald Lowsley in 1912. John E. McNeal first proposed the idea of "zones" in 1968; McNeal found that the relatively homogeneous cut surface of an adult prostate in no way resembled "lobes" and thus led to the description of "zones".
Prostate cancer was first described in a speech to the Medical and Chiurgical Society of London in 1853 by surgeon John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
and increasingly described by the late 19th century. Prostate cancer was initially considered a rare disease, probably because of shorter life expectancies and poorer detection methods in the 19th century. The first treatments of prostate cancer were surgeries to relieve urinary obstruction. Samuel David Gross has been credited with the first mention of a prostatectomy, as "too absurd to be seriously entertained" The first removal for prostate cancer (radical perineal prostatectomy
Prostatectomy (from the Ancient Greek language, Greek , "prostate" and , "excision") is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This operation is done for benignity, benign conditions that cause urinary retention, as well as ...
) was first performed in 1904 by Hugh H. Young at Johns Hopkins Hospital
Johns Hopkins Hospital (JHH) is the teaching hospital and biomedical research facility of Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1889, Johns Hopkins Hospital and its school of medicine are considered to be the foundin ...
; partial removal of the gland was conducted by Theodore Billroth
Christian Albert Theodor Billroth (26 April 18296 February 1894) was a German surgeon and amateur musician.
As a surgeon, he is generally regarded as the founding father of modern abdominal surgery. As a musician, he was a close friend and conf ...
in 1867.
Transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection of the prostate (commonly known as a TURP, plural TURPs, and rarely as a transurethral prostatic resection, TUPR) is a urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, ...
(TURP) replaced radical prostatectomy for symptomatic relief of obstruction in the middle of the 20th century because it could better preserve penile erectile function. Radical retropubic prostatectomy was developed in 1983 by Patrick Walsh. In 1941, Charles B. Huggins published studies in which he used estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
to oppose testosterone production in men with metastatic prostate cancer. This discovery of "chemical castration
Castration is any action, surgery, surgical, chemical substance, chemical, or otherwise, by which a male loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical cas ...
" won Huggins the 1966 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
.
The role of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and rele ...
(GnRH) in reproduction was determined by Andrzej W. Schally and Roger Guillemin
Roger Charles Louis Guillemin (; January 11, 1924 – February 21, 2024) was a French-American neuroscientist. He received the National Medal of Science in 1976, and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prize for Medicine in 1977 for ...
, who both won the 1977 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this work. GnRH receptor agonists, such as leuprorelin
Leuprorelin, also known as leuprolide, is a manufactured version of a hormone used to treat prostate cancer, breast cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, for early puberty, as part of transgender hormone therapy, or to perform chemical ca ...
and goserelin
Goserelin, sold under the brand name Zoladex among others, is a medication which is used to suppress production of the sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen), particularly in the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is an injectab ...
, were subsequently developed and used to treat prostate cancer. Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
for prostate cancer was first developed in the early 20th century and initially consisted of intraprostatic radium
Radium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in alkaline earth metal, group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, ...
implants. External beam radiotherapy
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is a form of radiotherapy that utilizes a high-energy collimated beam of ionizing radiation, from a source outside the body, to target and kill cancer cells. The radiotherapy beam is composed of particl ...
became more popular as stronger X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
radiation sources became available in the middle of the 20th century. Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation, radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. The word "brachytherapy" comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word , meaning "short-distance" or "s ...
with implanted seeds (for prostate cancer) was first described in 1983. Systemic chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
for prostate cancer was first studied in the 1970s. The initial regimen of cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
and 5-fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU, 5-fluorouracil), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stoma ...
was quickly joined by multiple regimens using a host of other systemic chemotherapy drugs.
Other animals
The prostate is found only in mammals. The prostate glands of malemarsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s are proportionally larger than those of placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished ...
mammals. The presence of a functional prostate in monotreme
Monotremes () are mammals of the order Monotremata. They are the only group of living mammals that lay eggs, rather than bearing live young. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and the four species of echidnas. Monotremes are typified ...
s is controversial, and if monotremes do possess functional prostates, they may not make the same contribution to semen as in other mammals.
The structure of the prostate varies, ranging from tubuloalveolar (as in humans) to branched tubular. The gland is particularly well developed in carnivora
Carnivora ( ) is an order of placental mammals specialized primarily in eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the sixth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species. Carnivor ...
ns and boars, though in other mammals, such as bulls, it can be small and inconspicuous. In other animals, such as marsupials and small ruminants
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principa ...
, the prostate is disseminate, meaning not specifically localisable as a distinct tissue, but present throughout the relevant part of the urethra; in other animals, such as red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
and American elk
The elk (: ''elk'' or ''elks''; ''Cervus canadensis'') or wapiti, is the second largest species within the deer family, Cervidae, and one of the largest terrestrial mammals in its native range of North America and Central and East Asia. ...
, it may be present as a specific organ and in a disseminate form. In some marsupial species, the size of the prostate gland changes seasonally. The prostate is the only accessory gland that occurs in male dogs. Dogs can produce in one hour as much prostatic fluid as a human can in a day. They excrete this fluid along with their urine to mark their territory. Additionally, dogs are the only species apart from humans seen to have a significant incidence of prostate cancer. The prostate is the only male accessory gland that occurs in cetaceans
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
, consisting of diffuse urethral glands surrounded by a very powerful compressor muscle.
The prostate gland originates with tissues in the urethral wall. This means the urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
, a compressible tube used for urination, runs through the middle of the prostate; enlargement of the prostate can constrict the urethra so that urinating becomes slow and painful.
Prostatic secretions vary among species. They are generally composed of simple sugars and are often slightly alkaline. In eutheria
Eutheria (from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ), also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of Placentalia, placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.
Eutherians ...
n mammals, these secretions usually contain fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
. The prostatic secretions of marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s usually contain N-Acetylglucosamine or glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
instead of fructose.
Skene's gland
Because theSkene's gland
In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands ( , also known as the lesser vestibular glands or paraurethral glands) are two glands located towards the lower end of the urethra. The glands are surrounded by tissue that swells with ...
and the male prostate act similarly by secreting prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which is an ejaculate
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural concepti ...
protein produced in males, and of prostate-specific acid phosphatase
Acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2, systematic name ''phosphate-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum)'') is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion. It can be further classified as a phosphoric monoeste ...
, the Skene's gland is sometimes referred to as the "female prostate". Although homologous to the male prostate (developed from the same embryological
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos an ...
tissues), various aspects of its development in relation to the male prostate are widely unknown and a matter of research.
See also
*Ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the Excretory duct of seminal gland, duct of the seminal vesicle. They pa ...
* List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
The list of human cell types provides an enumeration and description of the various specialized cells found within the human body, highlighting their distinct functions, characteristics, and contributions to overall physiological processes. Cell ...
* Prostate evolution in monotreme mammals
* Seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands or seminal glands) are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that largely composes the semen.
The vesicles are 5 ...
References
Citations
Sources
*Attribution
* Portions of the text of this article originate from NIH Publication No. 02-4806, a public domain resource.External links
* * {{Authority control Exocrine system Glands Human male reproductive system Mammal male reproductive system Sex organs Sexual anatomy