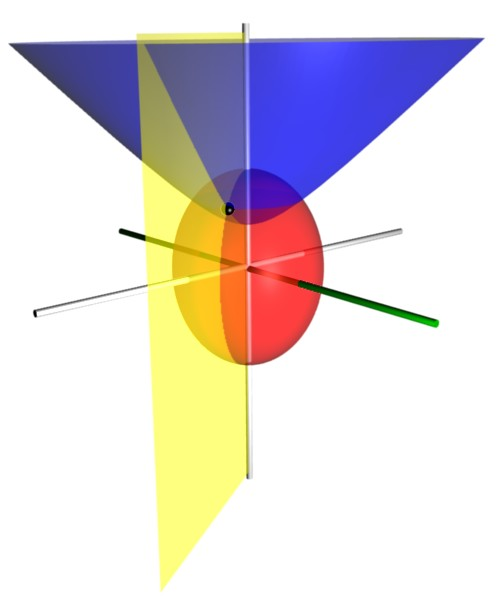
Prolate spheroidal coordinates are a three-dimensional
orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendic ...
coordinate system
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are ...
that results from rotating the two-dimensional
elliptic coordinate system about the focal axis of the ellipse, i.e., the symmetry axis on which the foci are located. Rotation about the other axis produces
oblate spheroidal coordinates. Prolate spheroidal coordinates can also be considered as a
limiting case of
ellipsoidal coordinates in which the two smallest
principal axes are equal in length.
Prolate spheroidal coordinates can be used to solve various
partial differential equation
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which involves a multivariable function and one or more of its partial derivatives.
The function is often thought of as an "unknown" that solves the equation, similar to ho ...
s in which the boundary conditions match its symmetry and shape, such as solving for a field produced by two centers, which are taken as the foci on the ''z''-axis. One example is solving for the
wavefunction
In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi (letter) ...
of an
electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
moving in the
electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
of two positively charged
nuclei, as in the
hydrogen molecular ion, H
2+. Another example is solving for the
electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
generated by two small
electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
tips. Other limiting cases include areas generated by a line segment (''μ'' = 0) or a line with a missing segment (ν=0). The electronic structure of general diatomic molecules with many electrons can also be solved to excellent precision in the prolate spheroidal coordinate system.
Definition

The most common definition of prolate spheroidal coordinates
is
:
:
:
where
is a nonnegative real number and
 Prolate spheroidal coordinates are a three-dimensional
Prolate spheroidal coordinates are a three-dimensional  The most common definition of prolate spheroidal coordinates is
:
:
:
where is a nonnegative real number and
The most common definition of prolate spheroidal coordinates is
:
:
:
where is a nonnegative real number and
 Prolate spheroidal coordinates are a three-dimensional
Prolate spheroidal coordinates are a three-dimensional  The most common definition of prolate spheroidal coordinates is
:
:
:
where is a nonnegative real number and
The most common definition of prolate spheroidal coordinates is
:
:
:
where is a nonnegative real number and