Priority Encoder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A priority encoder is a circuit or
 Priority encoders can be easily connected in arrays to make larger encoders, such as one 16-to-4 encoder made from six 4-to-2 priority encoders – four 4-to-2 encoders having the signal source connected to their inputs, and the two remaining encoders take the output of the first four as input.
Priority encoders can be easily connected in arrays to make larger encoders, such as one 16-to-4 encoder made from six 4-to-2 priority encoders – four 4-to-2 encoders having the signal source connected to their inputs, and the two remaining encoders take the output of the first four as input.
 A behavioral description of priority encoder in Verilog is as follows. In this case, the LSB has the highest priority.
A behavioral description of priority encoder in Verilog is as follows. In this case, the LSB has the highest priority.
// behavioural description of priority enconder;
// https://github.com/AmeerAbdelhadi/Indirectly-Indexed-2D-Binary-Content-Addressable-Memory-BCAM
module pe_bhv
#( parameter OHW = 512 ) // encoder one-hot input width
( input clk , // clock for pipelined priority encoder
input rst , // registers reset for pipelined priority encoder
input OHW -1:0oht , // one-hot input / OHW -1:0 output reg log2(OHW)-1:0bin , // first '1' index/ log2(OHW)-1:0 output reg vld ); // binary is valid if one was found
// use while loop for non fixed loop length
// synthesizable well with Intel's QuartusII
always @(*) begin
bin = ;
vld = oht in ;
while ((!vld) && (bin!=(OHW-1))) begin
bin = bin + 1 ;
vld = oht in
end
end
endmodule
 A
A
algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
that compresses multiple binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical op ...
inputs into a smaller number of outputs, similar to a simple encoder
An encoder (or "simple encoder") in digital electronics is a one-hot to binary converter. That is, if there are 2''n'' input lines, and at most only one of them will ever be high, the binary code of this 'hot' line is produced on the ''n''-bit ou ...
. The output of a priority encoder is the binary representation of the index
Index (: indexes or indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on the Halo Array in the ...
of the most significant activated line. In contrast to the simple encoder, if two or more inputs to the priority encoder are active at the same time, the input having the highest priority will take precedence. It is an improvement on a simple encoder because it can handle all possible input combinations, but at the cost of extra logic.
Applications of priority encoders include their use in interrupt controllers (to allow some interrupt request
In a computer, an interrupt request (or IRQ) is a hardware signal sent to the processor that temporarily stops a running program and allows a special program, an interrupt handler, to run instead. Hardware interrupts are used to handle events s ...
s to have higher priority than others), decimal or binary encoding
A binary code represents text, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system. The two-symbol system used is often "0" and "1" from the binary number system. The binary code assigns a pattern of binary digits, also ...
, and analog-to-digital
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
/ digital to-analog conversion.
Implementation
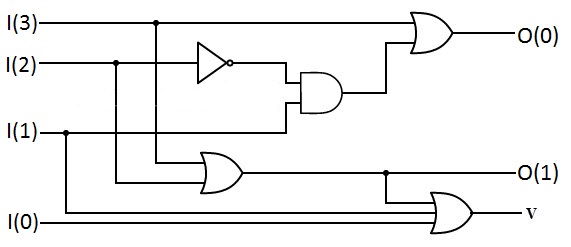
Atruth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
of a single bit 4-to-2 priority encoder is shown, where the inputs are shown in decreasing order of priority left-to-right, and "x" indicates a don't care term
In digital logic, a don't-care term (abbreviated DC, historically also known as ''redundancies'', ''irrelevancies'', ''optional entries'', ''invalid combinations'', ''vacuous combinations'', ''forbidden combinations'', ''unused states'' or ''l ...
- i.e. any input value there yields the same output since it is superseded by a higher-priority input. The (usually-included) "v" output indicates if the input is valid.
 Priority encoders can be easily connected in arrays to make larger encoders, such as one 16-to-4 encoder made from six 4-to-2 priority encoders – four 4-to-2 encoders having the signal source connected to their inputs, and the two remaining encoders take the output of the first four as input.
Priority encoders can be easily connected in arrays to make larger encoders, such as one 16-to-4 encoder made from six 4-to-2 priority encoders – four 4-to-2 encoders having the signal source connected to their inputs, and the two remaining encoders take the output of the first four as input.
Recursive construction of priority encoders
Sources: A priority-encoder, also called leading zero detector (LZD) or leading zero counter (LZC), receives an -bit input vector and detects the index of the first binary ‘1’ in the input vector. A valid signal indicates if any binary ‘1’ was detected in the input vector, hence the index is valid. Priority-encoders can be efficiently constructed by recursion. The input vector is split into equal fragments with bits. A priority encoder with a narrower width of 𝑛/𝑘 is applied for each fragment. The valid bit of each of the ‘s goes to a bit to detect the first valid fragment. The location of this fragment is the higher part of the overall index, and steers the exact location within the fragment itself to produce the lower part of the overall index. The depth of the proposed structure is , while the hardware area complexity is . If Altera's Stratix V or equivalent device is used, is recommended to achieve higher performance and area compression, since the mux can be implemented using 6-LUT, hence an entire ALM. An open-sourceVerilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits, with the highest level of abstraction being at the re ...
generator for the recursive priority-encoder is available online.Simple encoder
 A
A simple encoder
An encoder (or "simple encoder") in digital electronics is a one-hot to binary converter. That is, if there are 2''n'' input lines, and at most only one of them will ever be high, the binary code of this 'hot' line is produced on the ''n''-bit ou ...
circuit is a one-hot
In digital circuits and machine learning, a one-hot is a group of bits among which the legal combinations of values are only those with a single high (1) bit and all the others low (0). A similar implementation in which all bits are '1' except ...
to binary converter. That is, if there are 2''n'' input lines, and at most only one of them will ever be high, the binary code of this 'hot' line is produced on the ''n''-bit output lines.
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Priority Encoder Digital circuits