Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Respiratory epithelium, or airway epithelium, is
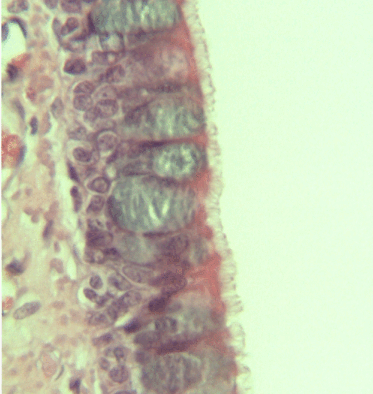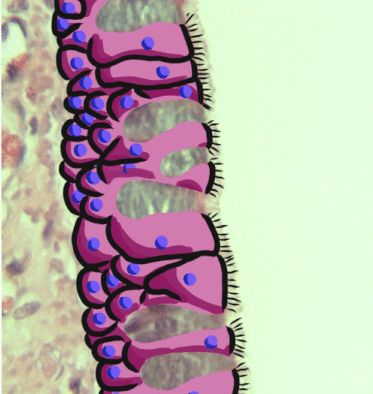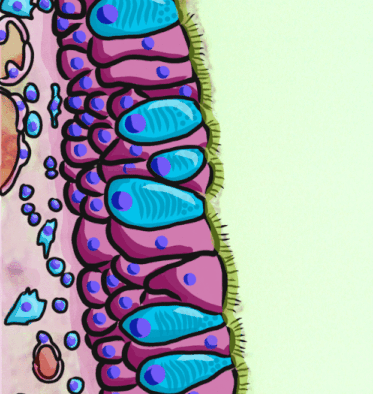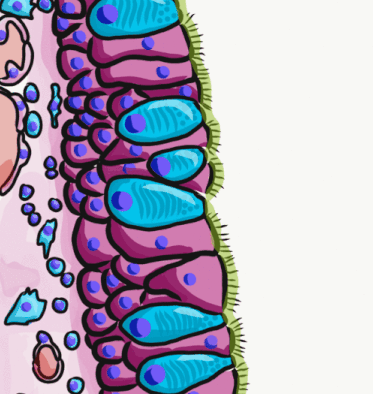
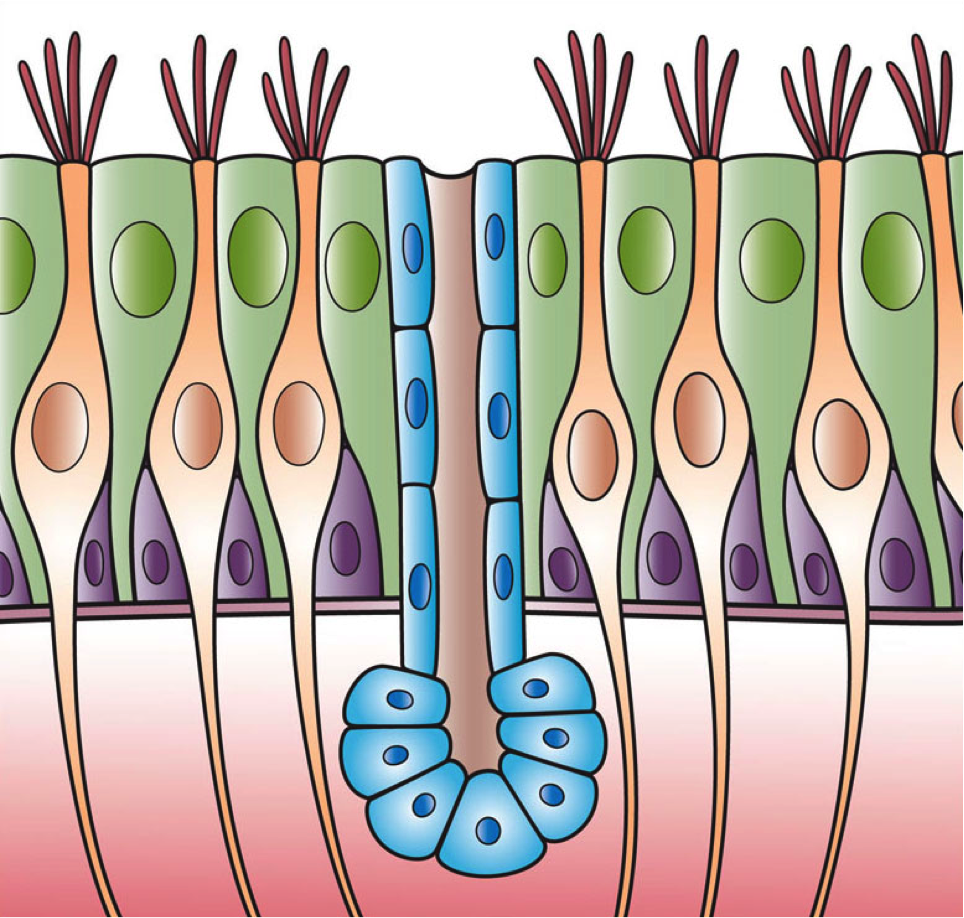 The respiratory epithelium lining the upper respiratory airways is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This designation is due to the arrangement of the multiple cell types composing the respiratory epithelium. While all cells make contact with the
The respiratory epithelium lining the upper respiratory airways is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This designation is due to the arrangement of the multiple cell types composing the respiratory epithelium. While all cells make contact with the
PMC 4491388
/ref>U.S. EPA. Integrated Science Assessment for Oxides of Nitrogen – Health Criteria (2016 Final Report). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-15/068, 2016
Federal Register Notice Jan 28, 2016
Free download available a
Report page at EPA website
The
2304 Pseudostratified Epithelium.jpg, Cross-section of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
2308 The Trachea-b.jpg, Second cross-section
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a type of epithelium that, though comprising only a single layer of cells, has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified columnar epithelium. A stratified epithelium rarely occurs as ...
a type of columnar epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many ...
found lining most of the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
as respiratory mucosa, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It is not present in the vocal cords
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
of the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
, or the oropharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
and laryngopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
, where instead the epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
is stratified squamous
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural ...
. It also functions as a barrier to potential pathogens and foreign particles, preventing infection and tissue injury by the secretion of mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
and the action of mucociliary clearance
Mucociliary clearance (MCC), mucociliary transport, or the mucociliary escalator describes the self-clearing mechanism of the respiratory tract, airways in the respiratory system. It is one of the two protective processes for the lungs in removi ...
.
Structure

 The respiratory epithelium lining the upper respiratory airways is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This designation is due to the arrangement of the multiple cell types composing the respiratory epithelium. While all cells make contact with the
The respiratory epithelium lining the upper respiratory airways is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This designation is due to the arrangement of the multiple cell types composing the respiratory epithelium. While all cells make contact with the basement membrane
The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tis ...
and are, therefore, a single layer of cells, their nuclei are not aligned in the same plane. Hence, it appears as though several layers of cells are present and the epithelium is called '' pseudostratified'' (falsely layered). The respiratory mucosa transitions to simple ciliated cuboidal epithelium and finally to simple squamous epithelium
A simple squamous epithelium, also known as pavement epithelium and tessellated epithelium, is a single layer of flattened, polygonal cells in contact with the basal lamina (one of the two layers of the basement membrane) of the epithelium. This ...
in the alveolar duct
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air bar ...
s and alveoli
Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
.
Cells
The cells in the respiratory epithelium are of five main types: a) ciliated cells, b)goblet cells
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 2 in the lower gastrointestinal tract, and mucin 5AC in the respiratory tract. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting ...
, c) brush cells, d) airway basal cell Airway basal cells are found deep in the respiratory epithelium, attached to, and lining the basement membrane.
Basal cells are the stem cells or progenitors of the airway epithelium and can cellular differentiation, differentiate to replenish all ...
s, and e) small granule cells (NDES) Goblet cells become increasingly fewer further down the respiratory tree until they are absent in the terminal bronchioles; club cells take over their role to some extent here. Another important cell type is the pulmonary neuroendocrine cell
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this way they bri ...
. These are innervated cells that only make up around 0.5% of the respiratory epithelial cells. The ciliated cells are columnar epithelial cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many ...
s with specialized ciliary modifications. The ciliated cells make up between 50 and 80 per cent of the epithelium.
Between the ciliated cells are numerous microvilli
Microvilli (: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, cellula ...
, attached as tufts to brush cells sometimes referred to as pulmonary brush cells; these are also known as the tuft cell
Tuft cells are chemosensory cells in the epithelial lining of the intestines. Similar tufted cells are found in the respiratory epithelium where they are known as brush cells. The name "tuft" refers to the brush-like microvilli projecting from ...
s of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
, or intestinal tuft cells, although there is a difference between the two types: the brush cells lack the terminal web
The terminal web is a structure found at the apical surface of epithelial cells that possess microvilli. It is composed primarily of actin filaments stabilized by spectrin, which also anchors the terminal web to the apical cell membrane. The pr ...
that lies under the microvilli of the tuft cells. Although their function is not yet fully understood, it has been suggested that they exhibit a virulence associated clearance role, activating mucociliary clearance by releasing acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
.
Function
The respiratory epithelium functions to moisten and protect the airways. It acts as a physical barrier to pathogens, as well as their removal in the mechanism ofmucociliary clearance
Mucociliary clearance (MCC), mucociliary transport, or the mucociliary escalator describes the self-clearing mechanism of the respiratory tract, airways in the respiratory system. It is one of the two protective processes for the lungs in removi ...
.
The ciliated cells are the primary components in the mucociliary clearance mechanism. Each epithelial cell has around 200 cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
that beat constantly at a rate of between 10 and 20 times per second. The direction of their beat is targeted towards the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, either upwards from the lower respiratory tract or downwards from the nasal structures.
Goblet cells
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 2 in the lower gastrointestinal tract, and mucin 5AC in the respiratory tract. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting ...
, so named because they are shaped like a wine goblet, are columnar epithelial cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many ...
s that contain membrane-bound mucous granules and secrete mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
as part of the airway surface liquid (ASL), also known as the ''epithelial lining fluid'', the composition of which is tightly regulated; the mucus helps maintain epithelial moisture and traps particulate material and pathogens moving through the airway. and determines how well mucociliary clearance works.Stanke F The Contribution of the Airway Epithelial Cell to Host Defense. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:463016.PMC 4491388
/ref>U.S. EPA. Integrated Science Assessment for Oxides of Nitrogen – Health Criteria (2016 Final Report). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-15/068, 2016
Federal Register Notice Jan 28, 2016
Free download available a
Report page at EPA website
The
basal cells
The stratum basale (basal layer, sometimes referred to as ''stratum germinativum'') is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the external covering of skin in mammals.
The stratum basale is a single layer of columnar or cuboida ...
are small, nearly cuboidal
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many ...
that differentiate into the other cell types found within the epithelium. Basal cells respond to injury of the airway epithelium, migrating to cover a site denuded of differentiated epithelial cells, and subsequently differentiating to restore a healthy epithelial cell layer. The differentiated epithelial cells can also dedifferentiate into stem cells and contribute to the repairing of the barrier.
Club cell
Club cells, also known as bronchiolar exocrine cells, are low columnar/cuboidal cells with short microvilli, found in the small airways (bronchioles) of the lungs. They were formerly known as ''Clara cells''.
Club cells are found in the ciliated ...
s carry out similar functions in the more distal airways.
Certain parts of the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
, such as the oropharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
, are also subject to the abrasive swallowing of food. To prevent the destruction of the epithelium in these areas, it changes to stratified squamous epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural ...
, which is better suited to the constant sloughing
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is a process by which an animal casts off parts of its body to serve some beneficial purpose, either at ...
and abrasion. The squamous layer of the oropharynx is continuous with the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
.
The respiratory epithelium has a further role of immunity for the lungs - that of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
. The glucose concentration in the airway surface liquid is held at a level of around 12 times lower than that of the blood sugar concentration. The tight junctions act as a barrier that restricts the passage of glucose across the epithelium into the airway lumen. Some glucose passes through, where it diffuses into the airway surface liquid to be kept at its reduced level by pulmonary glucose transport, and metabolism. However, airway inflammation decreases the effectiveness of the tight junctions making the barrier more permeable to glucose. Higher levels of glucose promote the proliferation of bacteria by providing glucose as a source for carbon for them. Increased levels of glucose in the airway surface liquid is associated with respiratory diseases, and hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition where unusually high amount of glucose is present in blood. It is defined as blood glucose level exceeding 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL) after fasting for 8 hours or 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) 2 hours after eating.
Blood gluc ...
.
Clinical significance
Long-term irritation of the epithelial cells can cause the overproduction of mucus, known asmucus hypersecretion
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
. Mucus hypersecretion results in the productive cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ...
of chronic bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
.
Pulmonary neuroendocrine cell
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this way they bri ...
s have been associated with a range of chronic lung disorders. They are also the originating cells of small-cell lung cancer
Small-cell carcinoma, also known as oat cell carcinoma, is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tr ...
.
References
Additional images
External links
{{Authority control Respiratory system Epithelium